结构:
建立一个结构声明:
struct book {
char title[MAXTITL];
char author[MAXAUTL];
float value;
};
声明一个结构变量:
struct book library;
编译器执行这行代码便创建了一个结构变量library。编译器使用book模板为该变量分配空间:一个内含MAXTITL个元素的char数组、一个内含MAXAUTL个元素的char数组和一个float类型的变量。这些存储空间都与一个名称library结合在一起。
我们看一下名为stuff的结构,内存分配如下图:
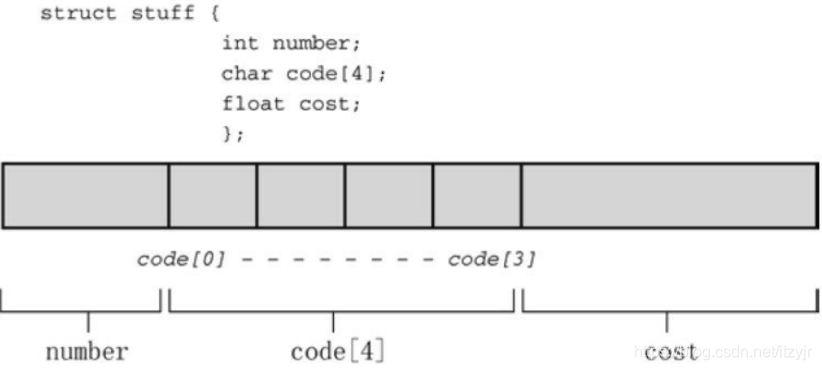
验证一下分配空间的连续性:
#include <stdio.h>
struct book {
int number;
char code[4];
float cost;
};
int main(void) {
struct book library;
printf("%p,%p,%p", &library.number, &library.code, &library.cost);
return 0;
}
012FFA44,012FFA48,012FFA4C ←此结果证明了分配的空间是连续的
初始化结构:
struct book library = {
"The Pious Pirate and the Devious Damsel",
"Renee Vivotte",
1.95
};
使用结构成员运算符——点(.)访问结构中的成员。例如,library.value即访问library的value部分。可以像使用任何float类型变量那样使用library.value。
可以只初始化单个结构成员:
struct book surprise = { .value = 10.99};
可以声明一个结构数组:
struct book library[MAXBKS]; /* book 类型结构的数组 */
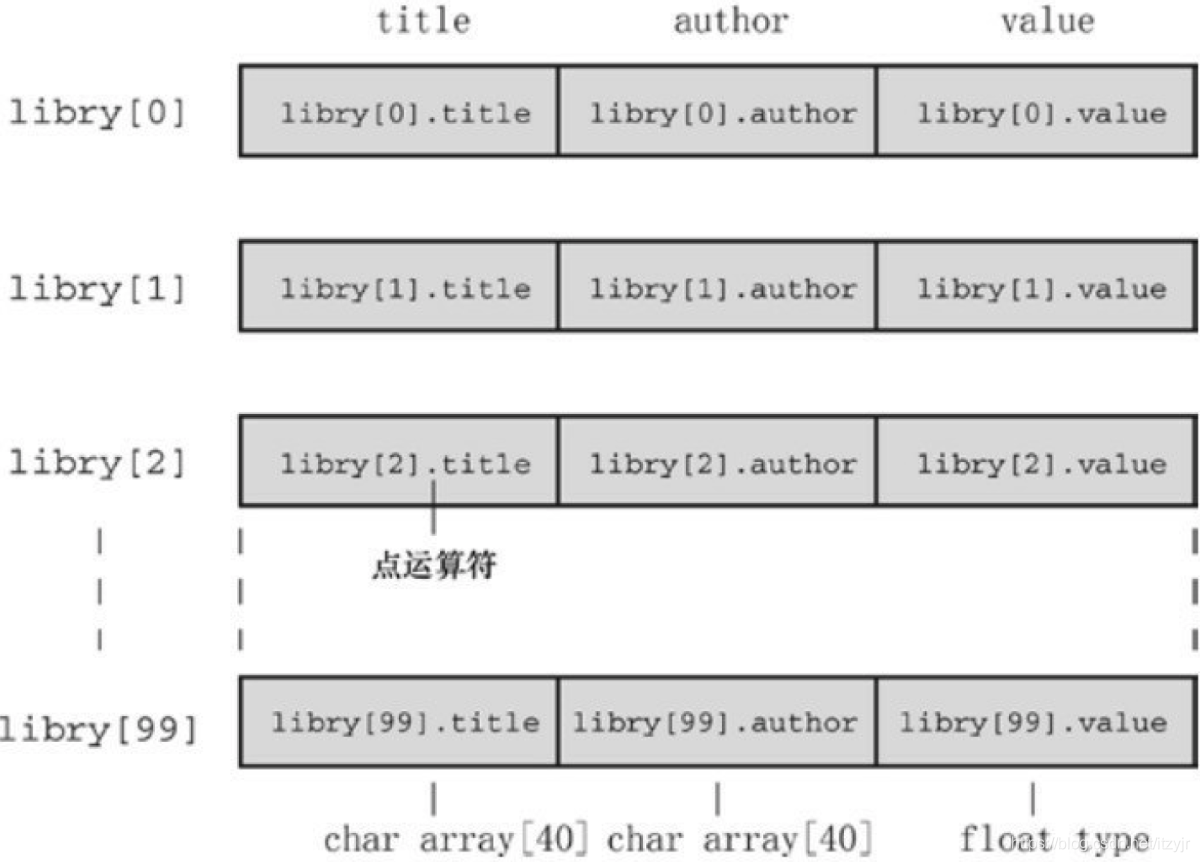
数组的用法都是那样,没什么区别。
也可以嵌套结构:
struct names { // 第1个结构
char first[LEN];
char last[LEN];
};
struct guy { // 第2个结构
struct names handle; // 嵌套结构
char favfood[LEN];
char job[LEN];
float income;
};
可以这样初始化之:
struct guy fellow = { // 初始化一个结构变量
{ "Ewen", "Villard" },
"grilled salmon",
"personality coach",
68112.00
};
结构指针:
至少有 4 个理由可以解释为何要使用指向结构的指针。
第一,就像指向数组的指针比数组本身更容易操控(如,排序问题)一样,指向结构的指针通常比结构本身更容易操控。
第二,在一些早期的C实现中,结构不能作为参数传递给函数,但是可以传递指向结构的指针。
第三,即使能传递一个结构,传递指针通常更有效率。
第四,一些用于表示数据的结构中包含指向其他结构的指针。
下面看一个实例:
#include <stdio.h>
#define LEN 20
struct names {
char first[LEN];
char last[LEN];
};
struct guy {
struct names handle;
char favfood[LEN];
char job[LEN];
float income;
};
int main(void) {
struct guy fellow[2] = {
{ { "Ewen", "Villard" }, "grilled salmon", "personality coach", 68112.00 },
{ { "Rodney", "Swillbelly" }, "tripe", "tabloid editor", 432400.00 }
};
struct guy *him; /* 这是一个指向结构的指针 */
printf("address #1: %p #2: %p\n", &fellow[0], &fellow[1]);
him = &fellow[0]; /* 告诉编译器该指针指向何处 */
printf("pointer #1: %p #2: %p\n", him, him + 1);
printf("him->income is $%.2f: (*him).income is $%.2f\n", him->income, (*him).income);
him++; /* 指向下一个结构 */
printf("him->favfood is %s: him->handle.last is %s\n", him->favfood, him->handle.last);
return 0;
}
address #1: 0x7fff5fbff820 #2: 0x7fff5fbff874
pointer #1: 0x7fff5fbff820 #2: 0x7fff5fbff874
him->income is $68112.00: (*him).income is $68112.00
him->favfood is tripe: him->handle.last is Swillbelly
通过以上实例,我们就知道了,如何声明一个结构指针变量,以及如何用指针访问结构成员。
结构指针作为函数参数也和其他指针作为参数没什么两样:
double sum(const struct funds *money) {
return (money->bankfund + money->savefund);
}
直接传递结构也是一样:
double sum(struct funds moolah) {
return (moolah.bankfund + moolah.savefund);
}
现在的C允许把一个结构赋值给另一个结构,但是数组不能这样做。也就是说,如果n_data和o_data都是相同类型的结构,可以这样做:
struct names right_field = {"Ruthie", "George"};
struct names captain = right_field; // 把一个结构初始化为另一个结构
结构当然也可以作为函数返回值:
struct namect makeinfo(struct namect info) {
info.letters = strlen(info.fname) + strlen(info.lname);
return info;
}
伸缩型数组成员(C99):
声明一个伸缩型数组成员有如下规则:
➀伸缩型数组成员必须是结构的最后一个成员;
➁结构中必须至少有一个成员;
➂伸缩数组的声明类似于普通数组,只是它的方括号中是空的。
struct flex {
int count;
double average;
double scores[]; // 伸缩型数组成员
}
struct flex * pf; // 声明一个指针
// 请求为一个结构和一个数组分配存储空间
pf = malloc(sizeof(struct flex) + 5 * sizeof(double));
用malloc()来分配足够的空间,以储存struct flex类型结构的常规内容和伸缩型数组成员所需的额外空间。现在有足够的存储空间储存count、average和一个内含5个double类型值的数组。可以用指针pf访问这些成员:
pf->count = 5; // 设置 count 成员
pf->scores[2] = 18.5; // 访问数组成员的一个元素
带伸缩型数组成员的结构确实有一些特殊的处理要求:
㊀不能用结构进行赋值或拷贝。
struct flex * pf1, *pf2; // *pf1 和*pf2 都是结构
...
*pf2 = *pf1; // 不要这样做
这样做只能拷贝除伸缩型数组成员以外的其他成员。确实要进行拷贝,应使用memcpy()函数。
㊁不要以按值方式把这种结构传递给结构。
原因相同,按值传递一个参数与赋值类似。要把结构的地址传递给函数。
㊂不要使用带伸缩型数组成员的结构作为数组成员或另一个结构的成员。
这种类似于在结构中最后一个成员是伸缩型数组的情况,称为struct hack。除了伸缩型数组成员在声明时用空的方括号外,struct hack特指大小为0的数组。然而,struct hack是针对特殊编译器(GCC)的,不属于C标准。这种伸缩型数组成员方法是标准认可的编程技巧。
最后看一个把结构保存在文件中的完整示例:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#define MAXTITL 40
#define MAXAUTL 40
#define MAXBKS 10 /* 最大书籍数量 */
char* s_gets(char *st, int n);
struct book { /* 建立 book 模板 */
char title[MAXTITL];
char author[MAXAUTL];
float value;
};
int main(void) {
struct book library[MAXBKS]; /* 结构数组 */
int count = 0;
int index, filecount;
FILE *pbooks;
int size = sizeof(struct book);
if ((pbooks = fopen("book.dat", "a+b")) == NULL) {
fputs("Can't open book.dat file\n", stderr);
exit(1);
}
rewind(pbooks); ← 定位到文件开始
while (count < MAXBKS && fread(&library[count], size, 1, pbooks) == 1) {
if (count == 0)
puts("Current contents of book.dat:");
printf("%s by %s: $%.2f\n", library[count].title, library[count].author, library[count].value);
count++;
}
filecount = count;
if (count == MAXBKS) {
fputs("The book.dat file is full.", stderr);
exit(2);
}
puts("Please add new book titles.");
puts("Press [enter] at the start of a line to stop.");
while (count < MAXBKS
&& s_gets(library[count].title, MAXTITL) != NULL
&& library[count].title[0] != '\0') {
puts("Now enter the author.");
s_gets(library[count].author, MAXAUTL);
puts("Now enter the value.");
scanf("%f", &library[count++].value);
while (getchar() != '\n')
continue; /* 清理输入行 */
if (count < MAXBKS)
puts("Enter the next title.");
}
if (count > 0) {
puts("Here is the list of your books:");
for (index = 0; index < count; index++)
printf("%s by %s: $%.2f\n", library[index].title, library[index].author, library[index].value);
fwrite(&library[filecount], size, count - filecount, pbooks);
} else
puts("No books? Too bad.\n");
puts("Bye.\n");
fclose(pbooks);
return 0;
}
char* s_gets(char *st, int n) {
char *ret_val;
char *find;
ret_val = fgets(st, n, stdin);
if (ret_val) {
find = strchr(st, '\n'); // 查找换行符
if (find) // 如果地址不是 NULL,
*find = '\0'; // 在此处放置一个空字符
else
while (getchar() != '\n')
continue; // 清理输入行
}
return ret_val;
}
Please add new book titles.
Press [enter] at the start of a line to stop.
|Metric Merriment
Now enter the author.
|Polly Poetica
Now enter the value.
|18.99
Enter the next title.
|Deadly Farce
Now enter the author.
|Dudley Forse
Now enter the value.
|15.99
Enter the next title.
|[enter]
Here is the list of your books:
Metric Merriment by Polly Poetica: $18.99
Deadly Farce by Dudley Forse: $15.99
Bye.
$ booksave
Current contents of book.dat:
Metric Merriment by Polly Poetica: $18.99
Deadly Farce by Dudley Forse: $15.99
Please add new book titles.
|The Third Jar
Now enter the author.
|Nellie Nostrum
Now enter the value.
|22.99
Enter the next title.
|[enter]
Here is the list of your books:
Metric Merriment by Polly Poetica: $18.99
Deadly Farce by Dudley Forse: $15.99
The Third Jar by Nellie Nostrum: $22.99
Bye.
注:写的时候fwrite()时写入结构地址&library[N],读的时候fread()对应读到结构地址&library[M]。
void rewind(FILE *stream) 设置文件位置为给定流 stream 的文件的开头。
size_t fread(void *ptr, size_t size, size_t nmemb, FILE *stream)
参数
ptr -- 这是指向带有最小尺寸 size*nmemb 字节的内存块的指针。
size -- 这是要读取的每个元素的大小,以字节为单位。
nmemb -- 这是元素的个数,每个元素的大小为 size 字节。
stream -- 这是指向 FILE 对象的指针,该 FILE 对象指定了一个输入流。
返回值
成功读取的元素总数会以 size_t 对象返回,size_t 对象是一个整型数据类型。如果总数与 nmemb 参数不同,则可能发生了一个错误或者到达了文件末尾。
size_t fwrite(const void *ptr, size_t size, size_t nmemb, FILE *stream)
参数
ptr -- 这是指向要被写入的元素数组的指针。
size -- 这是要被写入的每个元素的大小,以字节为单位。
nmemb -- 这是元素的个数,每个元素的大小为 size 字节。
stream -- 这是指向 FILE 对象的指针,该 FILE 对象指定了一个输出流。
返回值
如果成功,该函数返回一个 size_t 对象,表示元素的总数,该对象时一个整型数据类型。如果该数字与 nmemb 参数不同,则会显示一个错误。
fread(&library[count], sizeof(struct book), 1, pbooks);
将打开的pbooks文件流指针从文件中读取1个元素(结构)到地址&library[count]对应的内存中
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
fwrite(&library[filecount], sizeof(struct book), count - filecount, pbooks);
将连续的(count-filecount)个元素(结构)从首地址&library[filecount]开始追加写入到pbooks指向的文件中,
因为文件流指针pbooks打开方式是"a+b"
再次运行程序把这3本书作为当前的文件记录打印出来。
我们选择二进制模式是因为fread()和fwrite()函数要使用二进制文件。虽然结构中有些内容是文本,但是value成员不是文本。如果使用文本编辑器查看book.dat,该结构本文部分的内容显示正常,但是数值部分的内容不可读,甚至会导致文本编辑器出现乱码。
rewrite()函数确保文件指针位于文件开始处,为读文件做好准备。
联合:
联合(union) 是一种数据类型,它能在同一个内存空间中储存不同的数据类型(不是同时储存)。
union hold {
int digit;
double bigfl;
char letter;
};
根据以上形式声明的结构可以储存一个int类型、 一个double类型和char类型的值。 然而, 声明的联合只能储存一个int类型的或一个double类型的值或char类型的值。
fit.digit = 23; //把 23 储存在 fit, 占2字节
fit.bigfl = 2.0; // 清除23, 储存 2.0, 占8字节
fit.letter = 'h'; // 清除2.0, 储存h, 占1字节
初始化联合。需要注意的是,联合只能储存一个值,这与结构不同。有 3 种初始化的方法:1.把一个联合初始化为另一个同类型的联合;2.初始化联合的第1个元素;3.根据C99标准,使用指定初始化器:
union hold valA;
valA.letter = 'R';
union hold valB = valA; // 用另一个联合来初始化
union hold valC = {88}; // 初始化联合的digit 成员
union hold valD = {.bigfl = 118.2}; // 指定初始化器
联合指针:
和用指针访问结构使用->运算符一样, 用指针访问联合时也要使用间接成员运算符->:
pu = &fit;
x = pu->digit; // 相当于 x = fit.digit
 C语言结构体与联合详解
C语言结构体与联合详解






















 221
221

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










