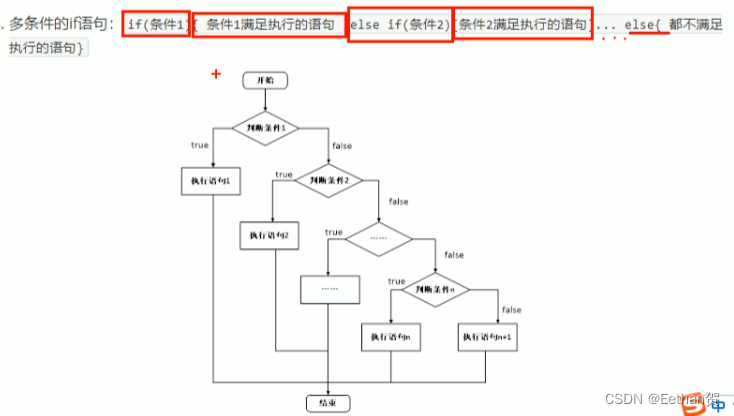
程序结构:
CPP支持的三种程序结构:顺序结构,选择结构,循环结构。

1. 顺序结构:
顺序结构已经学过了,不在赘述。
2. 选择结构:
(1)if 语句:

a. 单行 if 语句:
就一行 if 代码,基础的条件满足就执行,不满足就结束。
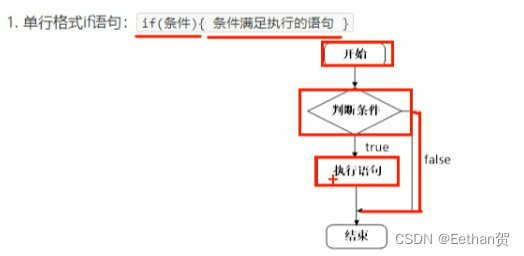
如下例子所示:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#include <string>//CPP风格字符串要包含这个头文件
int main()
{
//1. 用户输入高考分数
int score = 0;
cin >> score;
//打印用户输入的分数
cout <<"输入的分数为:"<<score << endl;
//判断是否过了600分,过了上985大学
if(score>600)
{
cout << "恭喜考上985" << endl;
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}
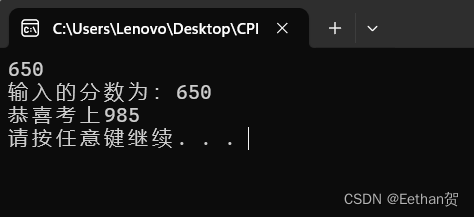
结果如下:
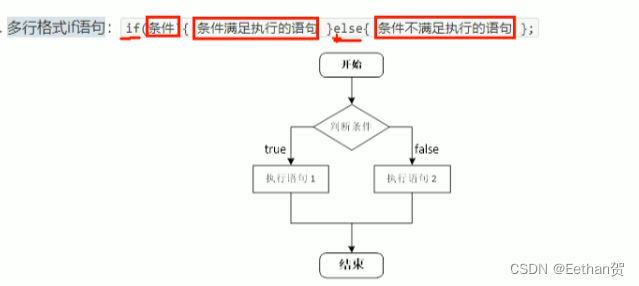
b. 多行 if 语句:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#include <string>//CPP风格字符串要包含这个头文件
int main()
{
//1. 用户输入高考分数
int score = 0;
cin >> score;
//打印用户输入的分数
cout <<"输入的分数为:"<<score << endl;
//判断是否过了600分,过了上985大学,未过就是考不上985
if(score>600)
{
cout << "恭喜考上985" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "未考上985" << endl;
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}
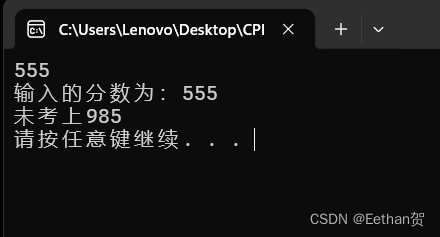
结果如下:
c. 多条件 if 语句:
#include <string>//CPP风格字符串要包含这个头文件
int main()
{
//1. 用户输入高考分数
int score = 0;
cin >> score;
//打印用户输入的分数
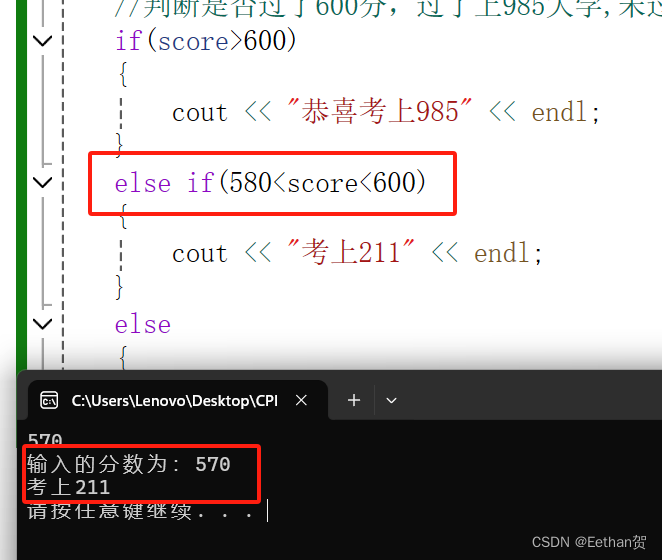
cout <<"输入的分数为:"<<score << endl;
//判断是否过了600分,过了上985大学,未过就是考不上985
if(score>600)
{
cout << "恭喜考上985" << endl;
}
else if(score>580)
{
cout << "考上211" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "未考上985211" << endl;
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}
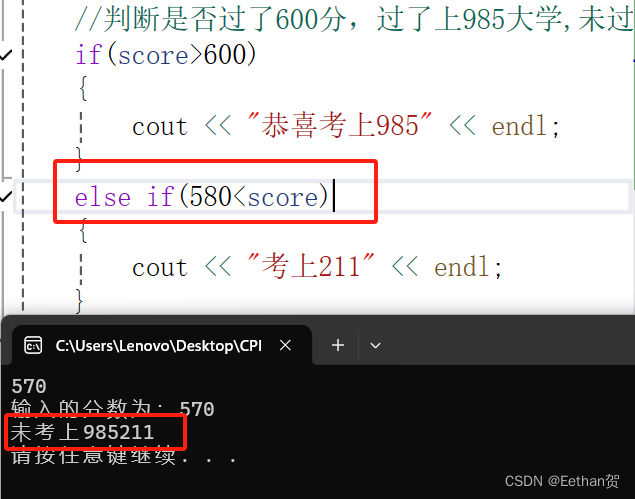
这里有一个需要注意的点:
else if (score>580) 这里,原本我写的是else if ( 600>score>580) ,得出的结果相同。
但是如果改成( 580<score<600 ),对应的结果则会出错,但是如果只写成(580<score)时候则正常。
因此,得出结论,else if这里不要多写!!!
d. 嵌套 if 语句:

#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#include <string>//CPP风格字符串要包含这个头文件
int main()
{
//1. 用户输入高考分数
int score = 0;
cin >> score;
//打印用户输入的分数
cout <<"输入的分数为:"<<score << endl;
//判断是否过了600分,过了上985大学,未过就是考不上985
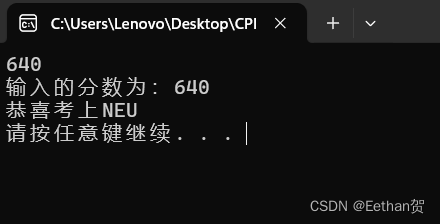
if(score>600)
{
if (score > 690)
{
cout << "恭喜考上TNU" << endl;
}
else if (score>630)
{
cout << "恭喜考上NEU" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "考上985" << endl;
}
}
else if(580<score)
{
cout << "考上211" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "未考上985211" << endl;
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}
(2)三目运算符:

#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#include <string>//CPP风格字符串要包含这个头文件
int main()
{
//三目运算符,将a和b进行比较,大的赋值给c
int a = 10;
int b = 20;
int c = 0;
c = (a > b ? a : b);
cout <<c<< endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
结果如下:

注意:在CPP中,三目运算符返回的是变量,可以继续赋值。
(a>b?a:b)=100;
(3)switch语句:

switch缺点:无法判断一个区间,只能判断是整型或字符型。
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#include <string>//CPP风格字符串要包含这个头文件
int main()
{
//给电影打分 5分经典,4分很好,3分一般,3以下烂片
int score = 0;
cin >> score;
switch (score)
{
case 5:
cout << "经典电影" << endl;
break;
case 4:
cout << "很好电影" << endl;
break;
case 3:
cout << "一般电影" << endl;
break;
default:
cout << "烂片" << endl;
break;
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}
结果如下:
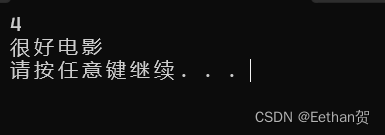
注意:每个case 都要加入break,如果不加,就会把其下面的case 都执行一遍。
3.循环结构:
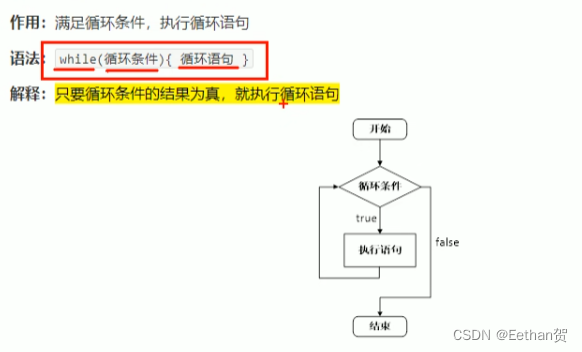
(1)while循环语句:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#include <string>//CPP风格字符串要包含这个头文件
int main()
{
//在屏幕中打印0-9这十个数
int num = 0;
while (num < 10)
{
cout << num << endl;//先输出一个0
num++;
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}
结果如下:

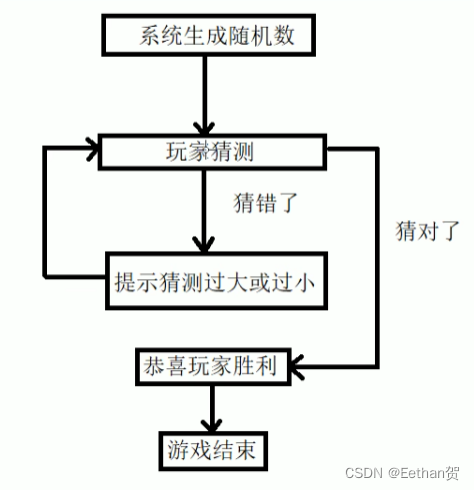
练习:猜数字





















 1380
1380

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








