Why functional programming?
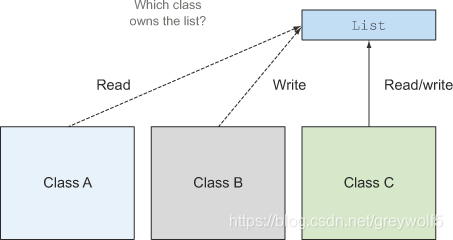
多个函数对同一个对象进行修改,会造成线程不安全
Transaction mostExpensive = transactions.get(0);
if(mostExpensive == null)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Empty list of transactions");
for(Transaction t: transactions.subList(1, transactions.size())){
if(t.getValue() > mostExpensive.getValue()){
mostExpensive = t;
}
}
Optional<Transaction> mostExpensive
= transactions.stream().max(comparing(Transaction::getValue));
相对于传统编程,declarative programming 简单,直接。
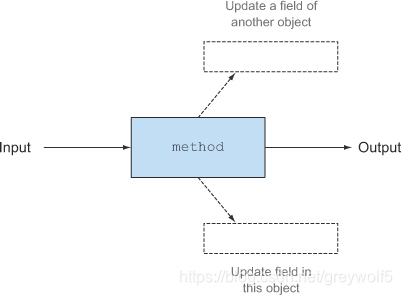
function with side-effect

pure function with no effect
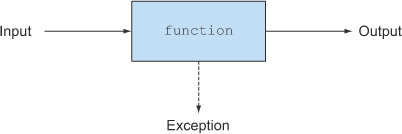
函数式的编程,一般不抛出异常


获取一个数列的所有子集数列。采用函数式编程(没有修改状态)。
static List<List<Integer>> concat(List<List<Integer>> a,
List<List<Integer>> b) {
a.addAll(b);
return a;
}
static List<List<Integer>> concat(List<List<Integer>> a,
List<List<Integer>> b) {
List<List<Integer>> r = new ArrayList<>(a);
r.addAll(b);
return r;
}
Recursion VS Iteration(递归 VS 迭代)
static int factorialIterative(int n) {
int r = 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
r *= i;
}
return r;
}
迭代的方式计算阶乘
static long factorialRecursive(long n) {
return n == 1 ? 1 : n * factorialRecursive(n-1);
}
递归的方式计算阶乘
static long factorialStreams(long n){
return LongStream.rangeClosed(1, n)
.reduce(1, (long a, long b) -> a * b);
}
Stream的方式计算阶乘
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.StackOverflowError
递归太深的可能导致Overflow
static long factorialTailRecursive(long n) {
return factorialHelper(1, n);
}
static long factorialHelper(long acc, long n) {
return n == 1 ? acc : factorialHelper(acc * n, n-1);
}
Tail-Recursive 可以引起虚拟机优化(JAVA JVM暂时不支持这个优化)
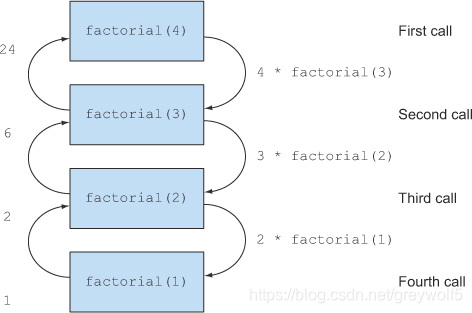
占用多个栈(Stack)的一半递归
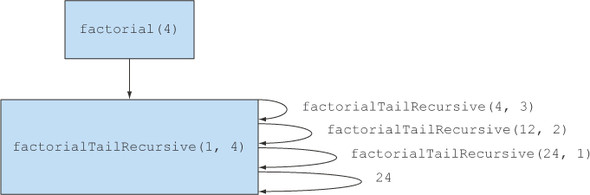
占用单个栈的tail-recursive





 本文探讨了函数式编程为何成为现代软件开发中备受青睐的选择。通过对比传统的命令式编程,文章阐述了函数式编程如何简化代码,提高线程安全性,并通过实例展示了纯函数、递归、Stream API等关键概念的应用。
本文探讨了函数式编程为何成为现代软件开发中备受青睐的选择。通过对比传统的命令式编程,文章阐述了函数式编程如何简化代码,提高线程安全性,并通过实例展示了纯函数、递归、Stream API等关键概念的应用。
















 518
518

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








