Java数据结构———顺序表
1. 认识线性表和顺序表
线性表(linear list)是n个具有相同特性的数据元素的有限序列。 线性表是一种在实际中广泛使用的数据结构,常见的线性表:顺序表、链表、栈、队列、字符串…
线性表在逻辑上是线性结构,也就说是连续的一条直线。但是在物理结构上并不一定是连续的,线性表在物理上存储时,通常以数组和链式结构的形式储存。
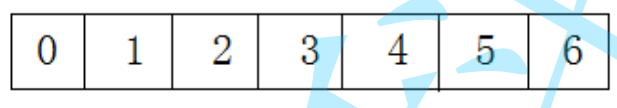
2. Java中的 List 和 ArrayList
Collection:元素集合
List: 线性表
ArrayList: 顺序表
// 为了便于理解,以下代码并不完全符合语法规则,
package java.util;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.ListIterator;
/**
* 线性结构
* 特点:
* 1. 元素和元素之间有前后关系
* 2. 元素会有在第几个位置的概念,位置通过下标(index)表示,从 0 开始
* 3. 插入可以根据位置的不同,分为:头插、尾插、按位置插入
* 4. 删除可以根据位置的不同,分为:头删、尾删、按位置删除
* 5. 遍历可以分为从前往后遍历和从后往前遍历
* 6. Java 中,List 是一个接口,并且是 Collection 的子接口
*/
public interface List extends Collection {
/**
* 将 e 尾插到线性表中
* @参数 e 待插入的元素
* @返回值 一定是 true,表示插入成功。线性表是不会出现插入不成功的情况的
*/
boolean add(元素类型 e);
/**
* 将 e 插入到线性表的 index 位置处;要求原来 index 及之后的元素全部向后移动
* index 的可选范围是 0 <= index <= size()
* @参数 index 插入位置(下标)
* @参数 待插入的元素
*/
void add(int index, 元素类型 e);
/**
* 删除 index 位置的元素,并返回该元素;要求 原来 index + 1 及之后元素全部向前移动
* index 的可选范围是 0 <= index < size()
* @参数 index 待删除位置(下标)
* @返回值 被删除掉的元素
*/
元素类型 remove(int index);
/**
* 删除从前往后遍历时,遇到的第一个相等的(equals)元素
* @参数 待删除元素
* @返回值 true:删除成功; false:没有找到相等的元素
*/
boolean remove(元素类型 e);
/**
* 返回 index 位置的元素
* index 的可选范围是 0 <= index < size()
* @参数 index 获取元素的位置(下标)
* @返回值 获取到的元素
*/
元素类型 get(int index);
/**
* 用新的元素 e 替换 index 位置的元素,并返回 index 位置的原来的元素
* index 的可选范围是 0 <= index < size()
* @参数 index 待替换元素的位置(下标)
* @参数 e 要替换的新元素
* @返回值 index 位置的老元素
*/
元素类型 set(int index, 元素类型 e);
/**
* 通过遍历的方式,判断与元素 e 相等(equals)的元素是否存在于线性表中
* @参数 e 待查找元素
* @返回 true:包含;false:不包含
*/
boolean contains(元素类型 e);
/**
* 按照从前往后遍历的方式,找到第一个与元素 e 相等(equals)的元素的下标
* @param e 待查找元素
* @return >= 0 表示找到并且返回下标;-1 代表没有找到
*/
int indexOf(元素类型 e);
/**
* 按照从后往前遍历的方式,找到第一个与元素 e 相等(equals)的元素的下标
* @param e 待查找元素
* @return >= 0 表示找到并且返回下标;-1 代表没有找到
*/
int lastIndexOf(元素类型 e);
/**
* 清空线性表,也就是,调用 clear() 后,线性表的 size() == 0;isEmpty() ==
true
*/
void clear();
/**
* 返回线性表中已有元素的个数
* @return 返回元数个数
*/
int size();
/**
* 返回线性表是不是一个空的容器
* @return true 为空容器
*/
boolean isEmpty();
///// 以下的使用频率略低
Iterator iterator();
void sort(Comparator 比较器);
List subList(int fromIndex, int toIndex);
}
2.1 迭代能力(Iterable) 和 迭代器(Iterator)
每种容器(Collection)都是具备迭代能力(Iterable)的。所以,每种容器都自带一个方法,返回一个合适的
迭代器(Iterator)以对容器进行无视实现差别的迭代。
3. 自己实现一个 ArrayList
自己实现一个MyArrayList, 并实现以下十二个基本方法
class MyArrayList {
private String[] array;
private int size;
boolean add(String e);
void add(int index, String e);
String remove(int index);
boolean remove(String e);
String get(int index);
String set(int index, String e);
boolean contains(String e);
int indexOf(String e);
int lastIndexOf(String e);
void clear();
int size();
boolean empty();
3.1 创建一个 MyArrayList
- 代码
//为了代码简单,就不写泛型版本的,直接认为 ArrayList 中存的是 String
public class MyArrayList {
//确定属性和方法
//属性
private String[] data = null;
private int size = 0;//表示当前数组内的有效数组元素的个数
private int capacity = 100;//表示当前顺序表最大容纳元素个数,如果 size 超过了 capacity, 就需要扩容
//方法,增删改查
//因为 data = null, 所以不能直接引用,这里写一个构造方法.也可以称为实例化
public MyArrayList(){
data = new String[capacity];
}
//实现扩容
private void realloc(){
//先把 capacity 变大(具体变大的公式自己随便定,根据实际要求进行确定)
capacity = 2 * capacity;
String[] newData = new String[capacity];
//把旧的数据组中的数据拷贝到新数组中
for (int i = 0; i < data.length; i++) {
newData[i] = data[i];
}
//把新的大的数组赋值给原有 的属性 data ,同时会释放掉旧的数组(GC)
data = newData;
}
//alt + insert 选择 toString 方法。
// 注意 toString 和 println 不要混为一谈,toSting 只是把对象转化为一个 String 而已
//具体转化为 toString 之后是保存,是赋值,还是打印,还是写文件等等 都可以。
@Override
public String toString() {
StringBuilder stringBuilder = new StringBuilder();
stringBuilder.append("[");
for (int i = 0; i <size; i++) {
stringBuilder.append(data[i]);
if (i <size-1) {
stringBuilder.append(",");
}
}
stringBuilder.append("]");
return stringBuilder.toString();
}
3.2 十二个基本方法实现
3.2.1 元素尾插到顺序表末尾
- 代码
//1、元素尾插到顺序表末尾
// O(1)的时间复杂度
public void add(String elem) {
if (size >= capacity) {
//需要先扩容
}
//就直接把新的元素放到下标为 size 的位置上即可
data[size] = elem;
size++;
}
3.2.2 把元素插入到任意中间位置
- 代码
//2、把元素插入到任意中间位置
//O(n)的复杂度
public void add(int index, String elem) {
//如果 Index == size ,相当于把新元素插入到末尾~
if (index <= 0 || index > size){
return;
}
if (size >= capacity) {
realloc();
}
//把 elem 放到 index 位置上, 不能覆盖掉已经有的元素
// 需要把 index 位置的元素,依次往后搬运。给 index 位置腾出一个空闲空间,来放置 elem
for (int i = size-1; i >= index; i--) {
data[i+1] = data[i];
}
//搬运完毕,把新的元素放到 index 位置上
data[index] = elem;
size++;
}
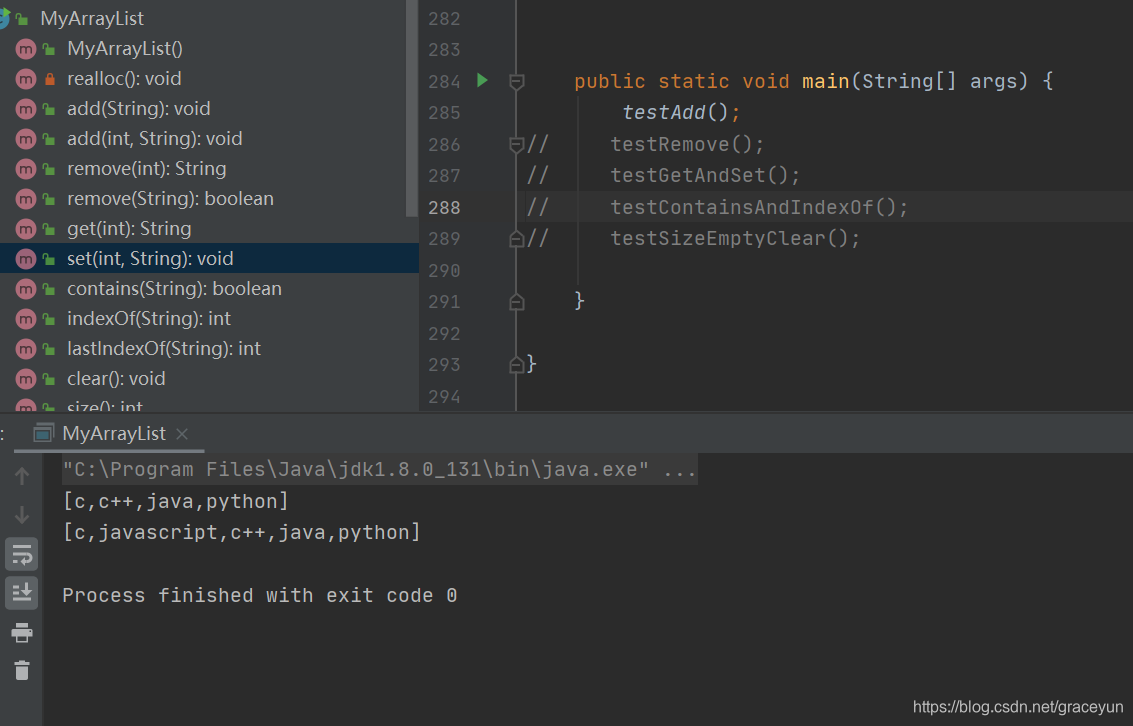
结果验证: 写代码一定要测试,每次写一些逻辑,都尽快的进行验证。!!通过一些简单的测试代码,来测试另外一些代码的功能,这种测试我们称为“单元测试”。“单元测试”是开发写的,是一种思想方法的体现,意识。
- 代码
private static void testAdd() {
MyArrayList myArrayList = new MyArrayList();
//写代码一定要测试,每次写一些逻辑,都尽快的进行验证。!!
//通过一些简单的测试代码,来测试另外一些代码的功能,这种测试我们称为“单元测试”。
//“单元测试”是开发写的,是一种思想方法的体现,意识。
//1. 验证尾插
myArrayList.add("c");
myArrayList.add("c++");
myArrayList.add("java");
myArrayList.add("python");
System.out.println(myArrayList);
//2,验证中间位置插入
myArrayList.add(1,"javascript");
System.out.println(myArrayList);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
testAdd();
}
代码运行结果:
3.2.3 按照下标位置删除元素(这个方法的返回结果就是被删除元素)
- 代码
//3. 按照下标位置删除元素,这个方法的返回结果就是被删除元素
//O(n)的复杂度
public String remove(int index) {
//仍然是需要进行搬运,把 index 位置的元素覆盖掉即可
if (index < 0 || index > size) {
return null;
}
String result = data[index];
for (int i = index; i < size-1; i++) {
data[i] = data[i+1];
}
//别忘记 size 要更新
size--;
return result;
}
3.3.4 按照元素的值来删除元素(这个方法返回成功/失败)
- 代码
//4. 按照元素的值来删除元素,这个方法返回成功/失败
//O(n)的复杂度
public boolean remove(String elem) {
//先找到元素所在的位置
int index = 0;
for(; index < size; index++) {
if (data[index].equals(elem)) {
break;
}
}
if (index >= size ) {
//没找到匹配的元素,删除时不黑
return false;
}
//找到匹配的元素了, 从 index 位置开始搬运
for (int i = index; i < size-1 ; i++) {
data[i] = data[i+1];
}
size--;
return true;
}
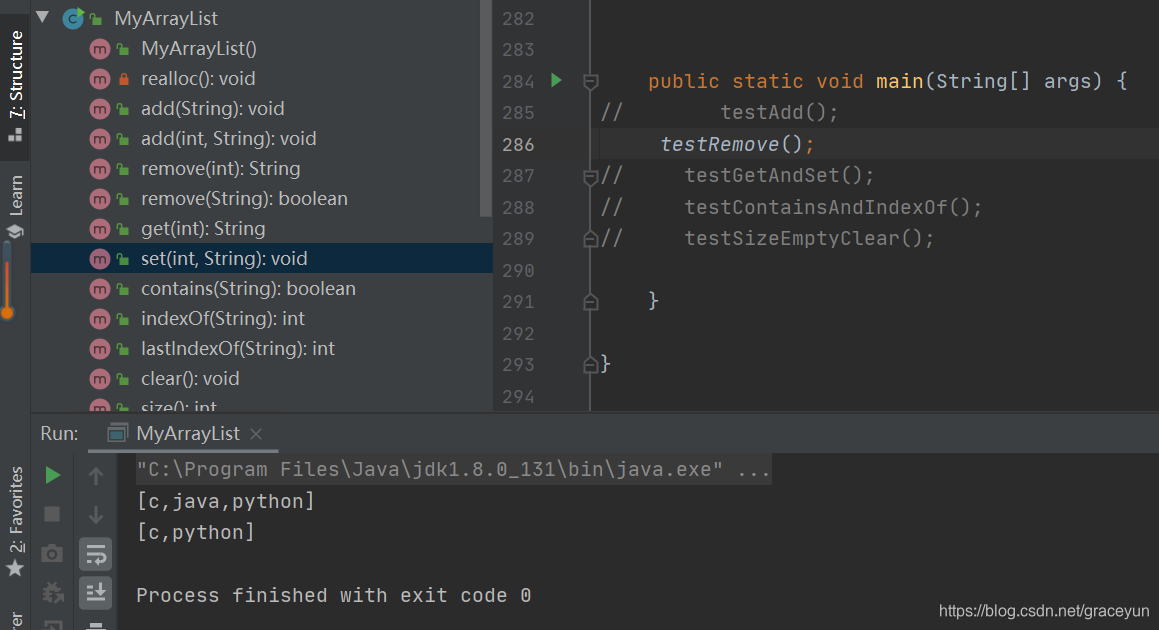
结果验证
- 代码
private static void testRemove(){
MyArrayList myArrayList = new MyArrayList();
myArrayList.add("c");
myArrayList.add("c++");
myArrayList.add("java");
myArrayList.add("python");
myArrayList.remove(1);
System.out.println(myArrayList);
myArrayList.remove("java");
System.out.println(myArrayList);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
testRemove();
}
运行结果
3.2.5 根据下标获取元素
- 代码
//5. 根据下标获取元素
// O(1)的时间复杂度
public String get(int index) {
if (index < 0 || index > size){
//此处可以返回一个 null; 也可以抛出一个异常
// return null;
throw new MyArrayListIndexOutOfRangException("下标越界了!index:" + index);
}
return data[index];
}
3.2.6 根据下标获取元素
- 代码
//6.按照下标修改元素
// O(1)的时间复杂度
public void set(int index, String elem) {
if (index < 0 || index > size){
//此处可以返回一个 null; 也可以抛出一个异常
// return null;
throw new MyArrayListIndexOutOfRangException("下标越界了!index:" + index);
}
data[index] = elem;
}
注意:这里抛出了一个异常,在最上面要引入 RuntimeException
代码
class MyArrayListIndexOutOfRangException extends RuntimeException{
public MyArrayListIndexOutOfRangException(String message) {
super(message);
}
}
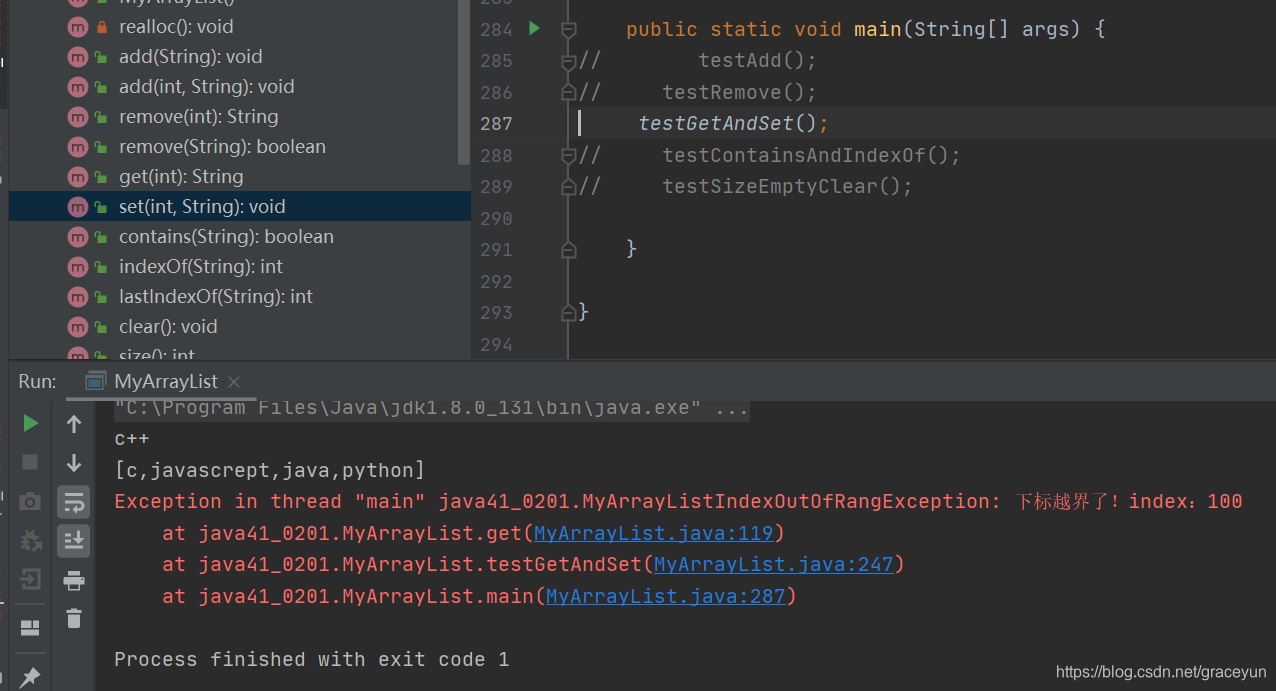
结果验证
- 代码
private static void testGetAndSet() {
MyArrayList myArrayList = new MyArrayList();
myArrayList.add("c");
myArrayList.add("c++");
myArrayList.add("java");
myArrayList.add("python");
System.out.println(myArrayList.get(1));
myArrayList.set(1,"javascrept");
System.out.println(myArrayList);
myArrayList.get(100);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
testGetAndSet();
}
运行结果
3.2.7 判断元素是否存在
- 代码
//7.判断元素是否存在
//O(n)
public boolean contains(String elem) {
//此处不太方便用 for each
//for each 遍历了整个 data 的所有元素
//实际上只需要遍历前 size 个元素即可
for (int i = 0; i < size;i++) {
if (data[i].equals(elem)){
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
3.2.8 查找元素位置
- 代码
//8. 查找元素位置
//O(n)
public int indexOf(String elem) {
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
if(data[i].equals(elem)){
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
3.2.9 查找元素位置
- 代码
//9. 查找元素位置(从后往前找)
//O(n)
public int lastIndexOf(String elem) {
for (int i = size-1 ; i >=0 ; i--){
if (data[i].equals(elem)) {
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
结果验证
- 代码
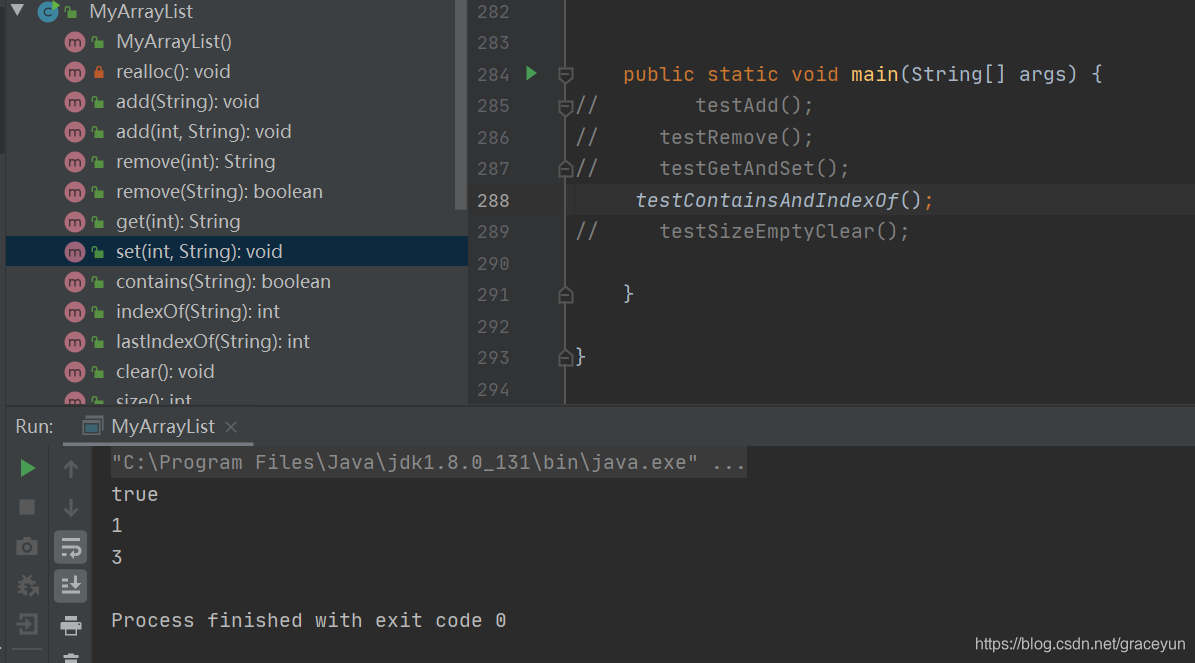
private static void testContainsAndIndexOf(){
MyArrayList myArrayList = new MyArrayList();
myArrayList.add("c");
myArrayList.add("c++");
myArrayList.add("java");
myArrayList.add("c++");
myArrayList.add("python");
System.out.println(myArrayList.contains("c++"));
System.out.println(myArrayList.indexOf("c++"));
System.out.println(myArrayList.lastIndexOf("c++"));
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
testContainsAndIndexOf();
}
运行结果
3.2.10 三个方法(SizeEmptyClear)实现
- 代码
public void clear() { //O(1)
size = 0;
}
public int size() { //O(1)
return size ;
}
public boolean isEmpty() { //O(1)
return size == 0;
}
代码验证
- 代码
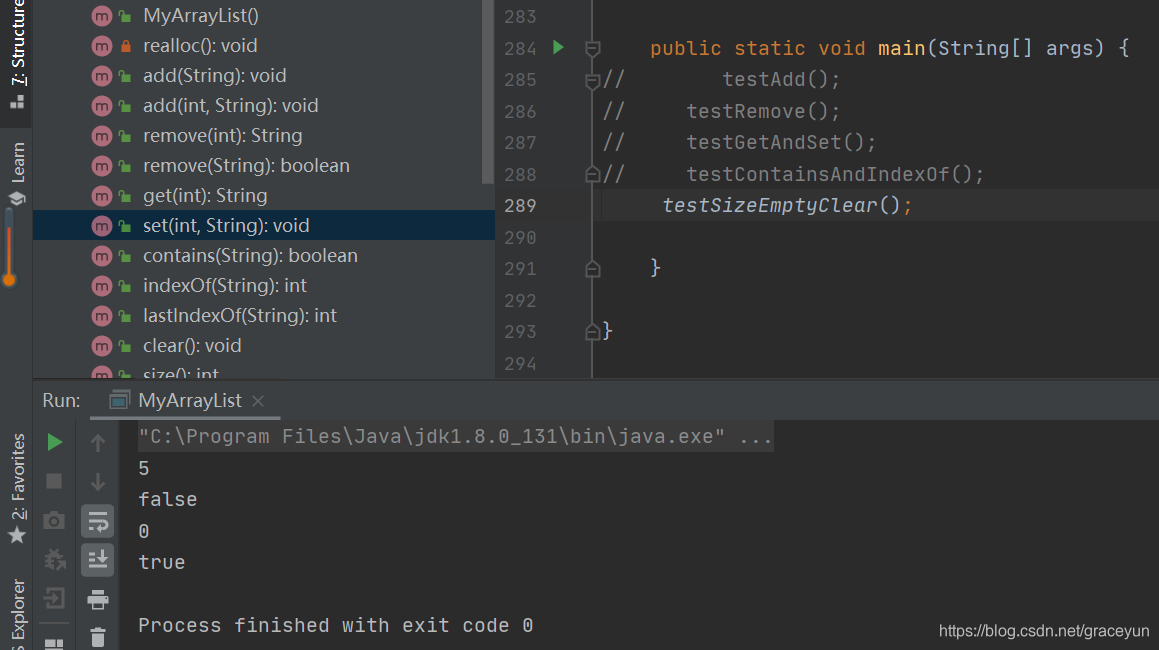
private static void testSizeEmptyClear() {
MyArrayList myArrayList = new MyArrayList();
myArrayList.add("c");
myArrayList.add("c++");
myArrayList.add("java");
myArrayList.add("c++");
myArrayList.add("python");
System.out.println(myArrayList.size());
System.out.println(myArrayList.isEmpty());
myArrayList.clear();
System.out.println(myArrayList.size());
System.out.println(myArrayList.isEmpty());
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
testSizeEmptyClear();
}
运行结果
完整代码 自己实现一个 ArrayList
package java41_0201;
import java.sql.Struct;
import java.util.Arrays;
class MyArrayListIndexOutOfRangException extends RuntimeException{
public MyArrayListIndexOutOfRangException(String message) {
super(message);
}
}
//为了代码简单,就不写泛型版本的,直接认为 ArrayList 中存的是 String
public class MyArrayList {
//确定属性和方法
//属性
private String[] data = null;
private int size = 0;//表示当前数组内的有效数组元素的个数
private int capacity = 100;//表示当前顺序表最大容纳元素个数,如果 size 超过了 capacity, 就需要扩容
//方法,增删改查
//因为 data = null, 所以不能直接引用,这里写一个构造方法.也可以称为实例化
public MyArrayList(){
data = new String[capacity];
}
//实现扩容
private void realloc(){
//先把 capacity 变大(具体变大的公式自己随便定,根据实际要求进行确定)
capacity = 2 * capacity;
String[] newData = new String[capacity];
//把旧的数据组中的数据拷贝到新数组中
for (int i = 0; i < data.length; i++) {
newData[i] = data[i];
}
//把新的大的数组赋值给原有 的属性 data ,同时会释放掉旧的数组(GC)
data = newData;
}
//1、元素尾插到顺序表末尾
// O(1)的时间复杂度
public void add(String elem) {
if (size >= capacity) {
//需要先扩容
}
//就直接把新的元素放到下标为 size 的位置上即可
data[size] = elem;
size++;
}
//2、把元素插入到任意中间位置
//O(n)的复杂度
public void add(int index, String elem) {
//如果 Index == size ,相当于把新元素插入到末尾~
if (index <= 0 || index > size){
return;
}
if (size >= capacity) {
realloc();
}
//把 elem 放到 index 位置上, 不能覆盖掉已经有的元素
// 需要把 index 位置的元素,依次往后搬运。给 index 位置腾出一个空闲空间,来放置 elem
for (int i = size-1; i >= index; i--) {
data[i+1] = data[i];
}
//搬运完毕,把新的元素放到 index 位置上
data[index] = elem;
size++;
}
//3. 按照下标位置删除元素,这个方法的返回结果就是被删除元素
//O(n)的复杂度
public String remove(int index) {
//仍然是需要进行搬运,把 index 位置的元素覆盖掉即可
if (index < 0 || index > size) {
return null;
}
String result = data[index];
for (int i = index; i < size-1; i++) {
data[i] = data[i+1];
}
//别忘记 size 要更新
size--;
return result;
}
//4. 按照元素的值来删除元素,这个方法返回成功/失败
//O(n)的复杂度
public boolean remove(String elem) {
//先找到元素所在的位置
int index = 0;
for(; index < size; index++) {
if (data[index].equals(elem)) {
break;
}
}
if (index >= size ) {
//没找到匹配的元素,删除时不黑
return false;
}
//找到匹配的元素了, 从 index 位置开始搬运
for (int i = index; i < size-1 ; i++) {
data[i] = data[i+1];
}
size--;
return true;
}
//5. 根据下标获取元素
// O(1)的时间复杂度
public String get(int index) {
if (index < 0 || index > size){
//此处可以返回一个 null; 也可以抛出一个异常
// return null;
throw new MyArrayListIndexOutOfRangException("下标越界了!index:" + index);
}
return data[index];
}
//6.按照下标修改元素
// O(1)的时间复杂度
public void set(int index, String elem) {
if (index < 0 || index > size){
//此处可以返回一个 null; 也可以抛出一个异常
// return null;
throw new MyArrayListIndexOutOfRangException("下标越界了!index:" + index);
}
data[index] = elem;
}
//7.判断元素是否存在
//O(n)
public boolean contains(String elem) {
//此处不太方便用 for each
//for each 遍历了整个 data 的所有元素
//实际上只需要遍历前 size 个元素即可
for (int i = 0; i < size;i++) {
if (data[i].equals(elem)){
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
//8. 查找元素位置
//O(n)
public int indexOf(String elem) {
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
if(data[i].equals(elem)){
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
//9. 查找元素位置(从后往前找)
//O(n)
public int lastIndexOf(String elem) {
for (int i = size-1 ; i >=0 ; i--){
if (data[i].equals(elem)) {
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
public void clear() { //O(1)
size = 0;
}
public int size() { //O(1)
return size ;
}
public boolean isEmpty() { //O(1)
return size == 0;
}
//alt + insert 选择 toString 方法。
// 注意 toString 和 println 不要混为一谈,toSting 只是把对象转化为一个 String 而已
//具体转化为 toString 之后是保存,是赋值,还是打印,还是写文件等等 都可以。
@Override
public String toString() {
StringBuilder stringBuilder = new StringBuilder();
stringBuilder.append("[");
for (int i = 0; i <size; i++) {
stringBuilder.append(data[i]);
if (i <size-1) {
stringBuilder.append(",");
}
}
stringBuilder.append("]");
return stringBuilder.toString();
}
private static void testAdd() {
MyArrayList myArrayList = new MyArrayList();
//写代码一定要测试,每次写一些逻辑,都尽快的进行验证。!!
//通过一些简单的测试代码,来测试另外一些代码的功能,这种测试我们称为“单元测试”。
//“单元测试”是开发写的,是一种思想方法的体现,意识。
//1. 验证尾插
myArrayList.add("c");
myArrayList.add("c++");
myArrayList.add("java");
myArrayList.add("python");
System.out.println(myArrayList);
//2,验证中间位置插入
myArrayList.add(1,"javascript");
System.out.println(myArrayList);
}
private static void testRemove(){
MyArrayList myArrayList = new MyArrayList();
myArrayList.add("c");
myArrayList.add("c++");
myArrayList.add("java");
myArrayList.add("python");
myArrayList.remove(1);
System.out.println(myArrayList);
myArrayList.remove("java");
System.out.println(myArrayList);
}
private static void testGetAndSet() {
MyArrayList myArrayList = new MyArrayList();
myArrayList.add("c");
myArrayList.add("c++");
myArrayList.add("java");
myArrayList.add("python");
System.out.println(myArrayList.get(1));
myArrayList.set(1,"javascrept");
System.out.println(myArrayList);
myArrayList.get(100);
}
private static void testContainsAndIndexOf(){
MyArrayList myArrayList = new MyArrayList();
myArrayList.add("c");
myArrayList.add("c++");
myArrayList.add("java");
myArrayList.add("c++");
myArrayList.add("python");
System.out.println(myArrayList.contains("c++"));
System.out.println(myArrayList.indexOf("c++"));
System.out.println(myArrayList.lastIndexOf("c++"));
}
private static void testSizeEmptyClear() {
MyArrayList myArrayList = new MyArrayList();
myArrayList.add("c");
myArrayList.add("c++");
myArrayList.add("java");
myArrayList.add("c++");
myArrayList.add("python");
System.out.println(myArrayList.size());
System.out.println(myArrayList.isEmpty());
myArrayList.clear();
System.out.println(myArrayList.size());
System.out.println(myArrayList.isEmpty());
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// testAdd();
// testRemove();
// testGetAndSet();
// testContainsAndIndexOf();
testSizeEmptyClear();
}
}





















 946
946

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








