0.1.1. 读取图像形式的MNIST
#划分为train/test
#对数据进行归一化,即0-1之间,数据要变成float类型
#把数据顺序打乱
#注:若训练慢,可以减少训练图像数量
### 题目1:定义并训练一个由3层线性分类器组成的神经网络
#定义网络
#L2损失函数
#中间层激活函数sigmoid
#使用0-1之间的数随机初始化网络
#使用L2正则化项
import os
from PIL import Image
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
'''
绘图
'''
def drawing(x,y,title):
plt.plot(x,y)
plt.title(title)
plt.show()
'''
根据名称整出来训练集、测试集和对应的标签
'''
def load_images_and_split(folder):
train_images = []
test_images = []
test_labels = []
train_labels = []
for filename in os.listdir(folder):
if filename.endswith('.jpg'):
img_path = os.path.join(folder, filename)
try:
img = Image.open(img_path)
img_array = np.array(img)
label = filename[-5]
if 'test' in filename:
test_images.append(img_array)
try:
# 尝试将标签转换为整数
test_labels.append(int(label))
except ValueError:
print(f"Invalid label in {filename}: {label}. Skipping this image.")
elif 'training' in filename:
train_images.append(img_array)
try:
train_labels.append(int(label))
except ValueError:
print(f"Invalid label in {filename}: {label}. Skipping this image.")
except Exception as e:
print(f"Error loading {img_path}: {e}")
train_images = np.array(train_images)
test_images = np.array(test_images)
train_labels = np.array(train_labels)
test_labels = np.array(test_labels)
return train_images, train_labels, test_images, test_labels
'''
数据预处理
'''
def preprocess_data(train_images, test_images):
# 展平图片数据
train_images_flat = train_images.reshape(train_images.shape[0], -1)
test_images_flat = test_images.reshape(test_images.shape[0], -1)
# 归一化处理
train_images_normalized = train_images_flat / 255.0
test_images_normalized = test_images_flat / 255.0
return train_images_normalized, test_images_normalized
folder_path = "E:/Strudy/Data/nearestk/mnist_jpg/mnist_jpg"
train_images, train_labels, test_images, test_labels = load_images_and_split(folder_path)
train_images_normalized, test_images_normalized = preprocess_data(train_images, test_images)
num_classes = len(np.unique(train_labels))
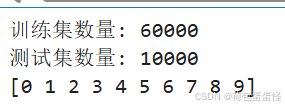
print(f"训练集数量: {len(train_images)}")
print(f"测试集数量: {len(test_images)}")
print(np.unique(test_labels))
#定义参数矩阵w1\w2的梯度计算方法
print('running')
'''
onehot编码方便交叉熵损失计算
'''
def one_hot_encode(labels, num_classes):
one_hot = np.zeros((labels.shape[0], num_classes))
one_hot[np.arange(labels.shape[0]), labels] = 1
return one_hot
'''
两层模型评估
'''
# test_images_normalized, test_labels, best_weights1, best_bias1,best_weights2,best_bias2, x_row)
def two_evaluate_model(test_images, test_labels, weights1, bias1,weights2,bias2,weights3,bias3,x_row):
#隐藏
# 前向传播
# 第一层y1=W1x+b
h1 = 1 / (1 + np.exp(-np.dot(test_images, weights1) + bias1))
#第二层y2=W2y1+b
h2 = 1/ ( 1 + np.exp(-np.dot(h1, weights2) + bias2))
#第三层y_pred
y_pred = np.dot(h2,weights3)+bias3
predicted_labels = np.argmax(y_pred, axis=1)
accuracy = np.mean(predicted_labels == test_labels)
print(f'Accuracy on the test set: {accuracy * 100}%')
return accuracy
'''
SGD
'''
def SGD(test_images_normalized, test_labels, train_images, train_labels, num_classes, num_trials=1000, batch_size=32):
input_size = train_images.shape[1]
x_row = []
y_loss_row = []
y_rate_row = []
# 初始化第一层
weights1 = np.random.randn(input_size, num_classes)
bias1 = np.zeros((1, num_classes))
# 初始化第二层
weights2 = np.random.randn(num_classes, num_classes)
bias2 = np.zeros((1, num_classes))
#初始化第三层
weights3 = np.random.randn(num_classes, num_classes)
bias3 = np.zeros((1, num_classes))
num_samples = train_images.shape[0]
for trial in range(num_trials):
# 随机打乱样本顺序
permutation = np.random.permutation(num_samples)
shuffled_images = train_images[permutation]
shuffled_labels = train_labels[permutation]
for i in range(0, num_samples, batch_size):
# 取出一个小批量样本
batch_images = shuffled_images[i:i + batch_size]
batch_labels = shuffled_labels[i:i + batch_size]
# 前向传播
# 第一层y1=W1x+b
h1 = 1 / (1 + np.exp(-np.dot(batch_images, weights1) + bias1))
#第二层y2=W2y1+b
h2 = 1/ ( 1 + np.exp(-np.dot(h1, weights2) + bias2))
#第三层y_pred
y_pred = np.dot(h2,weights3)+bias3
# 计算损失
y_true = one_hot_encode(batch_labels, num_classes)
loss = np.square((y_pred - y_true)**2).sum()
#L2
lambda_reg=0.01
l2_reg = lambda_reg * (np.sum(np.square(weights1)) + np.sum(np.square(weights2)) + np.sum(np.square(weights3)))
# 更新参数
grad_y_pred = 2 * (y_pred - y_true)
grad_w3 = np.dot(h2.T, grad_y_pred)+ lambda_reg*weights3/batch_size
grad_b3 = np.sum(grad_y_pred, axis=0, keepdims=True)
grad_h2 = np.dot(grad_y_pred, weights3.T) * h2 * (1 - h2)
grad_w2 = np.dot(h1.T, grad_h2)+ lambda_reg*weights2/batch_size
grad_b2 = np.sum(grad_h2, axis=0, keepdims=True)
grad_h1 = np.dot(grad_h2, weights2.T) * h1 * (1 - h1)
grad_w1 = np.dot(batch_images.T, grad_h1)+ lambda_reg*weights1/batch_size
grad_b1 = np.sum(grad_h1, axis=0, keepdims=True)
weights1 -= 1e-4 * grad_w1
weights2 -= 1e-4 * grad_w2
weights3-=1e-4 * grad_w3
bias1 -= 1e-4 * grad_b1
bias2 -= 1e-4 * grad_b2
bias3 -= 1e-4 * grad_b3
x_row.append(trial)
# 计算当前批次的平均损失
y_loss_row.append(loss)
acc = two_evaluate_model(test_images_normalized, test_labels, weights1, bias1, weights2, bias2,weights3,bias3,x_row)
y_rate_row.append(acc)
print(f'Trial {trial + 1}, Loss: {loss}')
drawing(x_row, y_loss_row, 'Loss')
drawing(x_row, y_rate_row, 'Accuracy')
SGD(test_images_normalized, test_labels,train_images_normalized, train_labels, num_classes)
Accuracy on the test set: 82.53% Trial 1000, Loss: 3.421813822563138
损失:
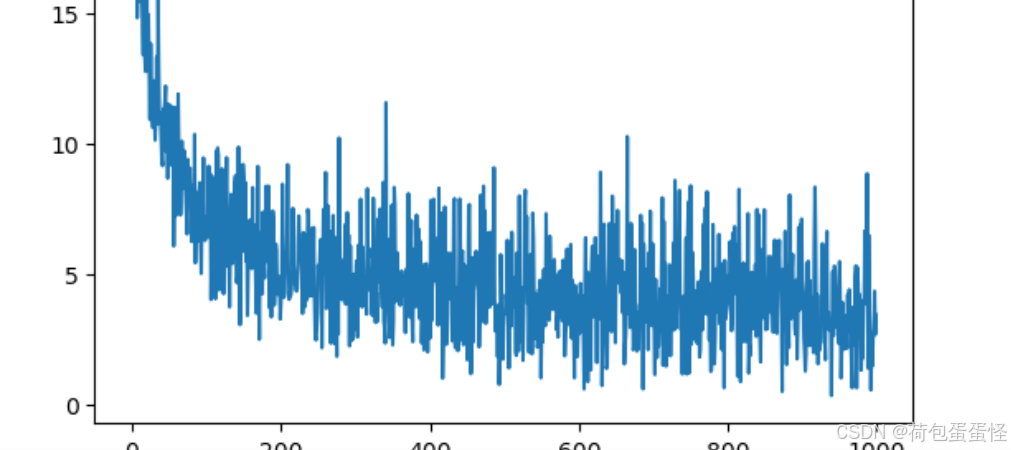
准确率:
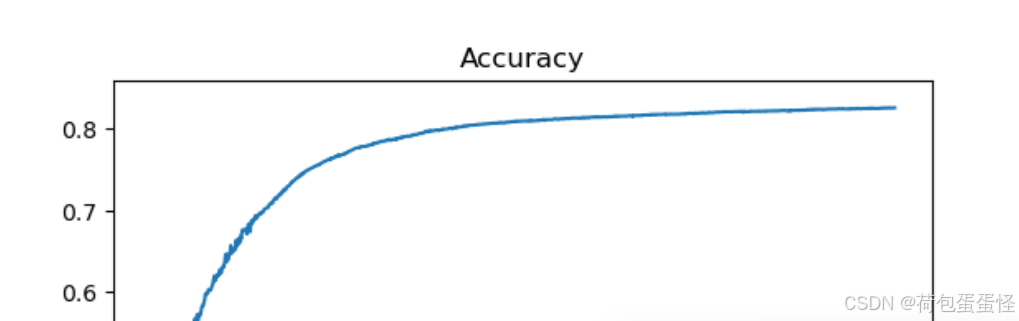
实验结果分析:
1、3层的网络精度远高于两层的神经网络,并且模型复杂,因此需要添加正则化
2、正则化系数越大,收敛速度越慢
3、总体上损失不断下降,推测继续加深迭代次数精度还会继续上升
4、200次以后迭代速度变慢,并且发现损失跳变成都越来越大,推测和学习率有关,如果随着迭代降低学习速率应该可以加快迭代速度。
0.1.3. 题目2:参考PPT,添加dropout,再次训练、测试,对比分析dropout的作用
'''
dropout evaluate注意,这个评估函数要变化
'''
def dropout_evaluate(test_images, test_labels, weights1, bias1,weights2,bias2,weights3,bias3,x_row):
#隐藏
# 前向传播
# 第一层y1=W1x+b
p=0.5
h1 = 1 / (1 + np.exp(-np.dot(test_images, weights1) + bias1))*p
#第二层y2=W2y1+b
h2 = 1/ ( 1 + np.exp(-np.dot(h1, weights2) + bias2))*p
#第三层y_pred
y_pred = np.dot(h2,weights3)+bias3
predicted_labels = np.argmax(y_pred, axis=1)
accuracy = np.mean(predicted_labels == test_labels)
print(f'Accuracy on the test set: {accuracy * 100}%')
return accuracy
'''
dropout
'''
def dropout(test_images_normalized, test_labels, train_images, train_labels, num_classes, num_trials=1000, batch_size=32):
input_size = train_images.shape[1]
x_row = []
y_loss_row = []
y_rate_row = []
# 初始化第一层
weights1 = np.random.randn(input_size, num_classes)
bias1 = np.zeros((1, num_classes))
# 初始化第二层
weights2 = np.random.randn(num_classes, num_classes)
bias2 = np.zeros((1, num_classes))
#初始化第三层
weights3 = np.random.randn(num_classes, num_classes)
bias3 = np.zeros((1, num_classes))
num_samples = train_images.shape[0]
for trial in range(num_trials):
# 随机打乱样本顺序
permutation = np.random.permutation(num_samples)
shuffled_images = train_images[permutation]
shuffled_labels = train_labels[permutation]
for i in range(0, num_samples, batch_size):
# 取出一个小批量样本
batch_images = shuffled_images[i:i + batch_size]
batch_labels = shuffled_labels[i:i + batch_size]
# 前向传播
#dropout
p=0.5
# 第一层y1=W1x+b
h1 = 1 / (1 + np.exp(-np.dot(batch_images, weights1) + bias1))
u1=np.random.rand(*h1.shape) <p
h1*=u1
#第二层y2=W2y1+b
h2 = 1/ ( 1 + np.exp(-np.dot(h1, weights2) + bias2))
u2=np.random.rand(*h2.shape) <p
h2*=u2
#第三层y_pred
y_pred = np.dot(h2,weights3)+bias3
# 计算损失
y_true = one_hot_encode(batch_labels, num_classes)
loss = np.square((y_pred - y_true)**2).sum()
# 更新参数
grad_y_pred = 2 * (y_pred - y_true)
grad_w3 = np.dot(h2.T, grad_y_pred)
grad_b3 = np.sum(grad_y_pred, axis=0, keepdims=True)
grad_h2 = np.dot(grad_y_pred, weights3.T) * h2 * (1 - h2)
grad_w2 = np.dot(h1.T, grad_h2)
grad_b2 = np.sum(grad_h2, axis=0, keepdims=True)
grad_h1 = np.dot(grad_h2, weights2.T) * h1 * (1 - h1)
grad_w1 = np.dot(batch_images.T, grad_h1)
grad_b1 = np.sum(grad_h1, axis=0, keepdims=True)
weights1 -= 1e-4 * grad_w1
weights2 -= 1e-4 * grad_w2
weights3-=1e-4 * grad_w3
bias1 -= 1e-4 * grad_b1
bias2 -= 1e-4 * grad_b2
bias3 -= 1e-4 * grad_b3
x_row.append(trial)
# 计算当前批次的平均损失
y_loss_row.append(loss)
acc = dropout_evaluate(test_images_normalized, test_labels, weights1, bias1, weights2, bias2,weights3,bias3,x_row)
y_rate_row.append(acc)
print(f'Trial {trial + 1}, Loss: {loss}')
drawing(x_row, y_loss_row, 'Loss')
drawing(x_row, y_rate_row, 'Accuracy')
dropout(test_images_normalized, test_labels,train_images_normalized, train_labels, num_classes)
准确率:
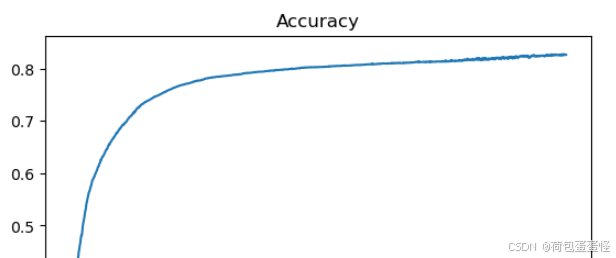
损失:
实验结果分析:
1、p=0.5的时候很难收敛,原因是空白的值太多,所以本人悄咪咪改成了0.8
2、从收敛速度上来看,dropout的收敛速度非常慢,并且受到超参数p的影响非常大。p越小越容易不收敛或者收敛速度慢
0.1.4. 题目3:参考PPT进行数据增强,再次训练、测试,对比分析数据增强的作用
#水平翻转
#旋转
本人使用的办法是使用numpy直接对矩阵进行操作。
注意,数据增强是在原有数据集上增加新的数据,所以在增强后数据量是原来的三倍。
'''
数据增强函数
'''
def augment_data(images, labels):
augmented_images = []
augmented_labels = []
for img, label in zip(images, labels):
# 原始图像
augmented_images.append(img)
augmented_labels.append(label)
# 水平翻转
img_flipped = np.fliplr(img)
augmented_images.append(img_flipped)
augmented_labels.append(label)
# 旋转 90 度
img_rotated_90 = np.rot90(img)
augmented_images.append(img_rotated_90)
augmented_labels.append(label)
augmented_images = np.array(augmented_images)
augmented_labels = np.array(augmented_labels)
return augmented_images, augmented_labels
folder = "E:/Strudy/Data/nearestk/mnist_jpg/mnist_jpg"
train_images, train_labels, test_images, test_labels = load_images_and_split(folder)
train_images_augmented, train_labels_augmented = augment_data(train_images, train_labels)
train_images_normalized, test_images_normalized = preprocess_data(train_images_augmented, test_images)
SGD(test_images_normalized, test_labels,train_images_normalized, train_labels_augmented, num_classes)
#这里传入的SGD的tiranlabel是要进行修改的,因为trainlabel变化了。
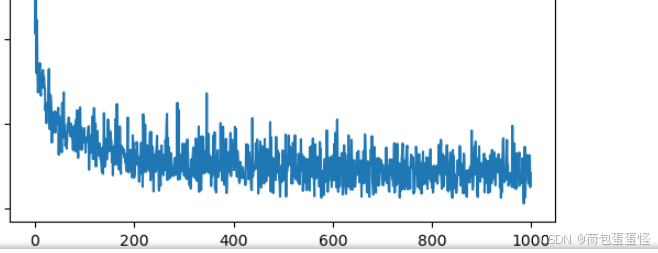
损失:
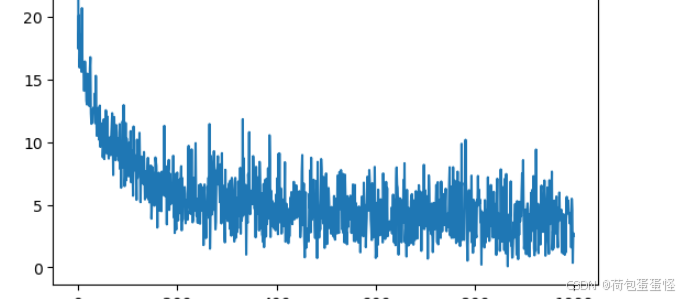
准确率:
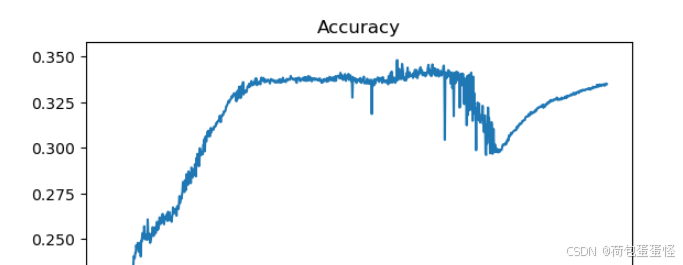
实验结果分析:
数据在增强后,变成了原有数据集的三倍。按照常理而言数据量扩大并且增强,容易得到更为精确的结果。然而本次增强使用的翻转和旋转,可能导致数据样式变化,反而降低准确率。比如数字6翻转后辩证了数字9。
本次实验结果精度大约为30%,也就是三份数据中的一份的准确率。
'''
数据增强函数,由于老师说翻转不行,所以改成平移
'''
def translation_augment_data(images, labels):
augmented_images = []
augmented_labels = []
for img, label in zip(images, labels):
# 原始图像
augmented_images.append(img)
augmented_labels.append(label)
# 水平向右平移
shift_right = 3
img_shifted_right = np.roll(img, shift_right, axis=1)
img_shifted_right[:, :shift_right] = 0 # 填充空白部分为 0
augmented_images.append(img_shifted_right)
augmented_labels.append(label)
# 水平向左平移
shift_left = 3
img_shifted_left = np.roll(img, -shift_left, axis=1)
img_shifted_left[:, -shift_left:] = 0
augmented_images.append(img_shifted_left)
augmented_labels.append(label)
# 垂直向上平移
shift_up = 3
img_shifted_up = np.roll(img, -shift_up, axis=0)
img_shifted_up[-shift_up:, :] = 0
augmented_images.append(img_shifted_up)
augmented_labels.append(label)
# 垂直向下平移
shift_down = 3
img_shifted_down = np.roll(img, shift_down, axis=0)
img_shifted_down[:shift_down, :] = 0
augmented_images.append(img_shifted_down)
augmented_labels.append(label)
augmented_images = np.array(augmented_images)
augmented_labels = np.array(augmented_labels)
return augmented_images, augmented_labels
folder = "E:/Strudy/Data/nearestk/mnist_jpg/mnist_jpg"
train_images, train_labels, test_images, test_labels = load_images_and_split(folder)
train_images_augmented, train_labels_augmented = translation_augment_data(train_images, train_labels)
train_images_normalized, test_images_normalized = preprocess_data(train_images_augmented, test_images)
SGD(test_images_normalized, test_labels,train_images_normalized, train_labels_augmented, num_classes)
ctnnd,这个代码训练的真的慢……




















 9418
9418

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








