一、堆
堆和栈,会不会有人立刻想到这两个数据结构?会不会有人想到OS中的堆和栈?这里的堆,其实指的数据结构的堆并由此实现的堆排序。什么是堆?堆就是一种以序列式集合而形成的二叉树。堆根据实现的情况分为大根(顶)堆,小根(顶)堆,也就是说,根(或父)节点比其孩子节点值大的为大根堆,反之为小根堆。在STL中一般是使用大根堆。
二、STL堆操作
在STL库中,主要的操作有如下几个函数:
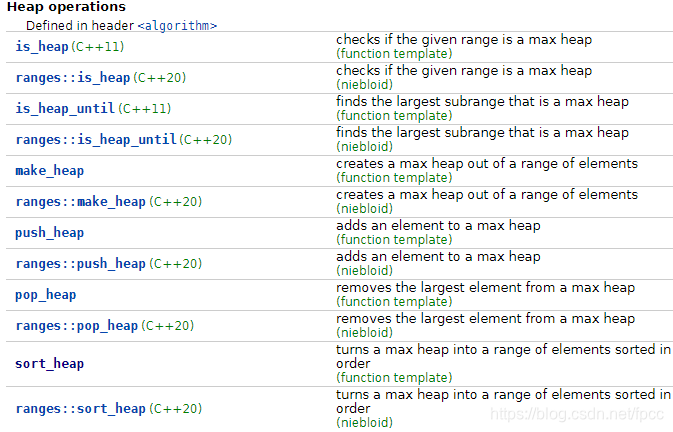
值得注意的是,很多的堆操作都放到c++11以后,也就是说,在c++11以前,堆基本是一个幕后英雄。
三、源码分析
这里对典型的几个堆操作源码进行一下分析:
template<class _RanIt,
class _Pr> inline
void _Make_heap_unchecked(_RanIt _First, _RanIt _Last, _Pr _Pred)
{ // make nontrivial [_First, _Last) into a heap, using _Pred
_Iter_diff_t<_RanIt> _Bottom = _Last - _First;//拿到根
//判断长度,小于2就不进行操作了,同时对根进行操作
for (_Iter_diff_t<_RanIt> _Hole = _Bottom >> 1; 0 < _Hole; ) // TRANSITION, VSO#433486
{ // reheap top half, bottom to top
--_Hole;
_Iter_value_t<_RanIt> _Val = _STD move(*(_First + _Hole));
_Pop_heap_hole_by_index(_First, _Hole, _Bottom, _STD move(_Val), _Pred);
}
}
template<class _RanIt,
class _Ty,
class _Pr> inline
void _Pop_heap_hole_by_index(_RanIt _First, _Iter_diff_t<_RanIt> _Hole, _Iter_diff_t<_RanIt> _Bottom,
_Ty&& _Val, _Pr _Pred)
{ // percolate _Hole to _Bottom, then push _Val, using _Pred
// precondition: _Bottom != 0
using _Diff = _Iter_diff_t<_RanIt>;
const _Diff _Top = _Hole;
_Diff _Idx = _Hole;
// Check whether _Idx can have a child before calculating that child's index, since
// calculating the child's index can trigger integer overflows
//检测防止溢出
const _Diff _Max_sequence_non_leaf = (_Bottom - 1) >> 1; // TRANSITION, VSO#433486
//迭代操作
while (_Idx < _Max_sequence_non_leaf)
{ // move _Hole down to larger child
_Idx = 2 * _Idx + 2;
if (_DEBUG_LT_PRED(_Pred, *(_First + _Idx), *(_First + (_Idx - 1))))
--_Idx;
*(_First + _Hole) = _STD move(*(_First + _Idx));
_Hole = _Idx;
}
if (_Idx == _Max_sequence_non_leaf && _Bottom % 2 == 0)
{ // only child at bottom, move _Hole down to it
*(_First + _Hole) = _STD move(*(_First + (_Bottom - 1)));
_Hole = _Bottom - 1;
}
_Push_heap_by_index(_First, _Hole, _Top, _STD move(_Val), _Pred);
}
再看一下push动作的源码:
template<class _RanIt,
class _Pr> inline
void push_heap(_RanIt _First, _RanIt _Last, _Pr _Pred)
{ // push *(_Last - 1) onto heap at [_First, _Last - 1), using _Pred
_Adl_verify_range(_First, _Last);
const auto _UFirst = _Get_unwrapped(_First);
auto _ULast = _Get_unwrapped(_Last);
using _Diff = _Iter_diff_t<_RanIt>;
_Diff _Count = _ULast - _UFirst;
if (2 <= _Count)
{
_Iter_value_t<_RanIt> _Val = _STD move(*--_ULast);
_Push_heap_by_index(_UFirst, --_Count, _Diff(0), _STD move(_Val), _Pass_fn(_Pred));
}
}
template<class _RanIt,
class _Ty,
class _Pr> inline
void _Push_heap_by_index(_RanIt _First, _Iter_diff_t<_RanIt> _Hole,
_Iter_diff_t<_RanIt> _Top, _Ty&& _Val, _Pr _Pred)
{ // percolate _Hole to _Top or where _Val belongs, using _Pred
for (_Iter_diff_t<_RanIt> _Idx = (_Hole - 1) >> 1; // TRANSITION, VSO#433486
_Top < _Hole && _DEBUG_LT_PRED(_Pred, *(_First + _Idx), _Val);
_Idx = (_Hole - 1) >> 1) // TRANSITION, VSO#433486
{ // move _Hole up to parent 此时新节点即洞值与父结点交换
*(_First + _Hole) = _STD move(*(_First + _Idx));
_Hole = _Idx;
}
*(_First + _Hole) = _STD move(_Val); // drop _Val into final hole
}
在Push过程中,需要一个上溯的过程,不断的把当前Key值和父结点比较,如果比它大,就进行交换,直到停止(不需要再交换或者到达了ROOT)。
VS的源码写得有点复杂,如果看侯捷先生的书会比较清晰,但原理基本都是一样的。
四、实例
看一下几个相关的实例(cppreference.com):
#include <algorithm>
#include <bit>
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
int main()
{
std::vector<int> v { 3, 1, 4, 1, 5, 9, 2, 6, 5, 3, 5, 8, 9, 7, 9 };
std::cout << "initially, v:\n";
for (auto i : v) std::cout << i << ' ';
std::cout << '\n';
if (!std::is_heap(v.begin(), v.end())) {
std::cout << "making heap...\n";
std::make_heap(v.begin(), v.end());
}
std::cout << "after make_heap, v:\n";
for (auto t{1U}; auto i : v)
std::cout << i << (std::has_single_bit(++t) ? " │ " : " ");
std::cout << '\n';
}
运行结果:
initially, v:
3 1 4 1 5 9 2 6 5 3 5 8 9 7 9
making heap...
after make_heap, v:
9 │ 6 9 │ 5 5 9 7 │ 1 1 3 5 8 3 4 2 │
再看一个c++20的新函数:
#include <algorithm>
#include <array>
#include <iostream>
void print(auto const& rem, auto const& v)
{
std::cout << rem;
for (const auto i : v)
std::cout << i << ' ';
std::cout << '\n';
}
int main()
{
std::array v {3, 1, 4, 1, 5, 9};
print("original array: ", v);
std::ranges::make_heap(v);
print("after make_heap: ", v);
std::ranges::sort_heap(v);
print("after sort_heap: ", v);
}
输出结果:
original array: 3 1 4 1 5 9
after make_heap: 9 5 4 1 1 3
after sort_heap: 1 1 3 4 5 9
如果对c++17以后的标准有想学习,可以移步到以前的相关文章。
五、总结
其实现在很多程序员对数据结构和算法都已经没感觉了,大量的底层库和框架,把这些数据结构和算法进行了层层的封装,你就是想看一些具体的算法也需要不断的向底层走,而有的人封装的水平有高有低,不要想当然的认为开源的大框架写得就一定好。其实相当多的开源的东西,只是有一个好的点子,实现的方式方法都有待商榷。
还是那句话,要善于学习,练就一双看透一切的眼睛!








 本文详细介绍了C++ STL中的堆数据结构及其操作,包括`make_heap`、`push_heap`等函数,并提供了源码分析和实例演示。通过实例展示了如何使用STL堆进行排序和元素插入。强调了理解数据结构和算法的重要性,即使在有大量库和框架的今天。
本文详细介绍了C++ STL中的堆数据结构及其操作,包括`make_heap`、`push_heap`等函数,并提供了源码分析和实例演示。通过实例展示了如何使用STL堆进行排序和元素插入。强调了理解数据结构和算法的重要性,即使在有大量库和框架的今天。
















 4848
4848










