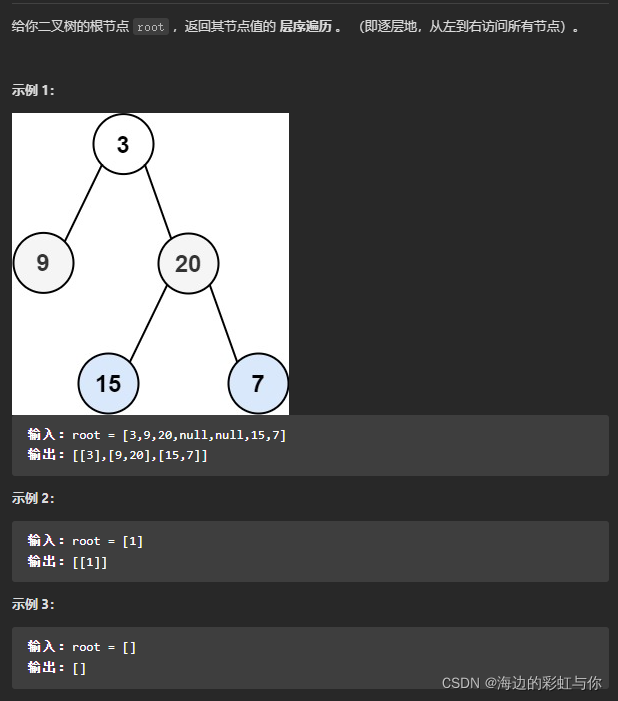
1.
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> levelOrder(TreeNode root) {
List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();
if(root == null)
return res;
Queue<TreeNode> q = new LinkedList<>();
q.offer(root);
while(!q.isEmpty()) {
List<Integer> a = new ArrayList<>();
int len = q.size();
for(int i = 0;i < len;i++) {
TreeNode r = q.poll();
a.add(r.val);
if(r.left != null) {
q.offer(r.left);
}
if(r.right != null) {
q.offer(r.right);
}
}
res.add(a);
}
return res;
}
}
2.
给定一个 完美二叉树 ,其所有叶子节点都在同一层,每个父节点都有两个子节点。二叉树定义如下:
struct Node {
int val;
Node *left;
Node *right;
Node *next;
}
填充它的每个 next 指针,让这个指针指向其下一个右侧节点。如果找不到下一个右侧节点,则将 next 指针设置为 NULL。
初始状态下,所有 next 指针都被设置为 NULL。
1.BFS
/*
// Definition for a Node.
class Node {
public int val;
public Node left;
public Node right;
public Node next;
public Node() {}
public Node(int _val) {
val = _val;
}
public Node(int _val, Node _left, Node _right, Node _next) {
val = _val;
left = _left;
right = _right;
next = _next;
}
};
*/
class Solution {
public Node connect(Node root) {
if(root == null)
return root;
Queue<Node> q = new LinkedList<>();
q.offer(root);
while(!q.isEmpty()) {
int len = q.size();
for(int i = 0;i < len;i++) {
Node n = q.poll();
if(i < len - 1) {
n.next = q.peek();
}
if(n.left != null) {
q.offer(n.left);
}
if(n.right != null) {
q.offer(n.right);
}
}
}
return root;
}
}
2.递归
/*
// Definition for a Node.
class Node {
public int val;
public Node left;
public Node right;
public Node next;
public Node() {}
public Node(int _val) {
val = _val;
}
public Node(int _val, Node _left, Node _right, Node _next) {
val = _val;
left = _left;
right = _right;
next = _next;
}
};
*/
/*
*/
class Solution {
public Node connect(Node root) {
if(root == null)
return root;
if(root.left != null) {
root.left.next = root.right;
root.right.next = (root.next != null) ? root.next.left : null;
connect(root.left);
connect(root.right);
}
return root;
}
}
3.
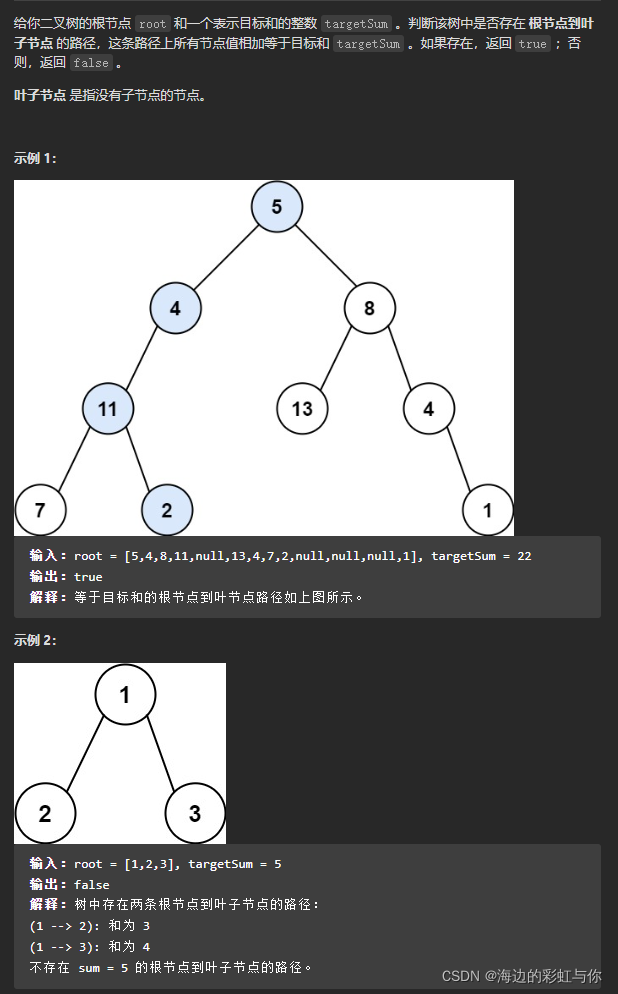
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public boolean is = false;
public boolean hasPathSum(TreeNode root, int targetSum) {
if(root == null)
return false;
dfs(root,root.val,targetSum);
return is;
}
public void dfs(TreeNode root,int sum,int goal) {
if(root.left == null && root.right == null) {
if(sum == goal)
is = true;
return;
}
if(root.left != null)
dfs(root.left,sum + root.left.val,goal);
if(root.right != null)
dfs(root.right,sum + root.right.val,goal);
}
}
4.
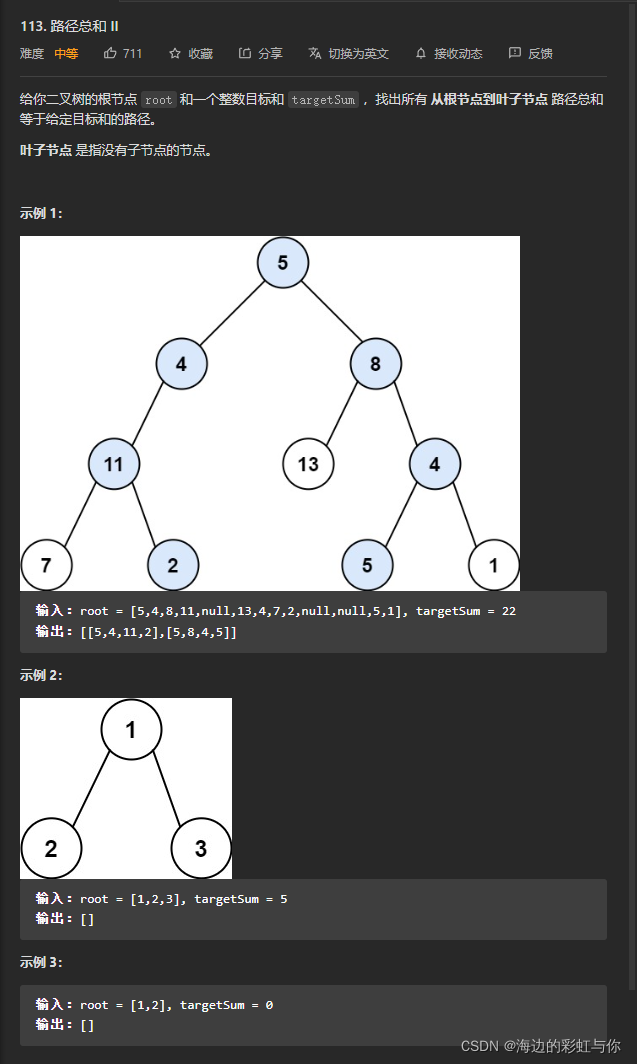
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();
int targetSum;
List<Integer> l = new ArrayList<>();
public List<List<Integer>> pathSum(TreeNode root, int targetSum) {
this.targetSum = targetSum;
dfs(0,root);
return res;
}
public void dfs(int sum,TreeNode root) {
if(root == null)
return;
sum += root.val;
l.add(root.val);
if(root.left == null && root.right == null && sum == targetSum) {
res.add(new ArrayList(l));
}
dfs(sum,root.left);
dfs(sum,root.right);
l.remove(l.size() - 1);
}
}
























 2722
2722

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










