Floating-Point Format Conversion
题目描述
The Gould internal floating-point format has 1 sign bit, S, a 7-bit off set (base 16) exponent field,E, and a 24-bit (6 hex digits) hexadecimal mantissa. (Note that this means that up to 3 high bits of the mantissa may be zero.)
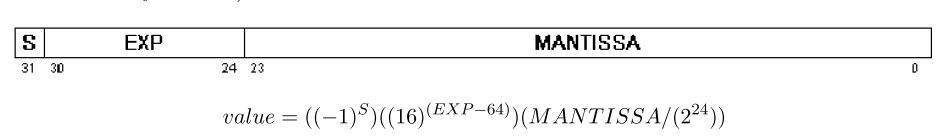
Floating-point zero is represented by 32 bits of 0.
The IEEE format has 1 sign bit, S, an 8-bit off set (base 2) exponent field, E, and a 24-bit mantissa,for which the high bit is (in normalized numbers) always 1 and not part of the 23 bits in the format.

If the exponent is not 255 and not 0, the value is a normalized floating point number,
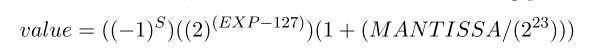
If the exponent is 255 and the mantissa is 0, the value is plus or minus infinity (depending on the sign bit). If the exponent is 255 and the mantissa is not 0, it indicates special values that will not be used in this problem.
If the exponent is 0 and the mantissa is zero, the value is plus or minus zero (depending on the sign bit).
If the exponent is 0 and the mantissa is not zero, the value is a de-normalized floating-point number with:
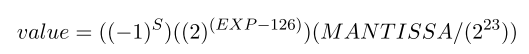
Write a program that takes as input a floating-point value in Gould format and outputs the value in IEEE format as follows:
• If the value is zero return (plus) zero.
• If the value is too large to be represented as a normalized floating-point value, return plus or minus infinity depending on the sign.
• If the value is too small to be represented as a normalized floating-point value:
– If it may be represented as a de-normalized value, return the de-normalized value.
– OthenNise, return plus or minus zero, depending on the sign.
• In all other cases, return the normalized value.
If there are less significant bits than required for IEEE floating-point, extend with 0 bits.
If there are more significant bits than required for IEEE floating-point, truncate the extra bits.
输入
Each data set consists of a single line of input. It contains the data set number, K, followed by 8 hex digits (0-9 ,A-F) of the Gould floating-point value.
输出
样例输入
复制样例数据
4
1 41200000
2 E0FFFFFE
3 E11FFFFF
4 88888888
样例输出
1 40000000
2 FF7FFFFE
3 FF800000
4 80000000
题意:就是转化一下格式,给你的不是IEEE格式,叫你转化为IEEE,计算机里本来就是IEEE格式,输入进去转化就行,不过,借鉴了源代码有点不懂。
#include <cstdio>
using namespace std;
typedef unsigned long ll;
ll solve(ll Gould)
{
ll s,exp,man;
ll ans;
int expp;
s=Gould&0x80000000;
exp=(Gould&0x7f000000)>>24;
expp=exp-64;
man=Gould&0xffffff;
if(man==0) return 0;
expp*=4;
while( (man&0x800000)==0 ){
expp--;
man<<=1;
}
expp--;
if(expp>127) ans=s|0x7f800000;
else if(expp<-149) ans=s;
else if(expp>=-126) {
exp=expp+127;
exp<<=23;
ans= s|exp|(man&0x7fffff);
}
else {
while (expp<-126) {
expp++;
man>>=1;
}
exp=0;
ans= s|exp|(man&0x7fffff);
}
return ans;
}
int main()
{
int qwq;
scanf ("%d",&qwq);
for(int i=1;i<=qwq;i++) {
int id;
ll g;
scanf ("%d %lx",&id,&g);
ll res=solve(g);
printf ("%d %08lX\n",i,res);
}
return 0;
}
借鉴源代码:
/*
* B - Floating Point Conversion
* ICPC 2013 Greater NY Regional
* Solution by Fred Pickel
* Problem by Fred Pickel
*/
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <math.h>
#include <ctype.h>
#include <string.h>
typedef unsigned long DWORD;
/*
Conversion process (FOR normalized numbers) (with example 0x22222222)
extract sign = GouldFP & 0x80000000 sign = 0
Gould offset exponent = (GouldFP & 0x7f000000) >> 24 off exp = 0x22 = 34
actual exponent = offset exponent - 64 (actual exponent = 34 - 64 = -30
mantissa = GouldFP & 0xffffff; mantissa = 0x222222
value = ((16)^-30)*(0x222222/2^24)
convert exponent to base 2 value = ((2)^-120)*(0x222222/2^24)
IF mantissa == 0, return 0
multiply mantissa by 2 and decrement exponent value = ((2)^-121)*(0x444444/2^24)
until MSB of matissa is 1 value = ((2)^-122)*(0x888888/2^24)
change mantissae divisor to 2^23
and decrement exponent value = ((2)^-123)*(0x888888/2^23)
pull out MSB of mantissa (now = 1)
mantissa &= 0x7fffff value = ((2)^-123)*(1 + (0x088888/2^23))
read off ieee FP terms
sign = Gould sign sign = 0 exp = -123 + 127 = 4 mantissa = 0x088888
exp = base 2 exp + 127
mantissa &= 0x7fffff
IEEE FP = Gould sing | (exp << 23) |mantissa 0x02088888
*/
DWORD FormatConvert(DWORD GouldFP)
{
DWORD sign, expon, mantissa, res;
int expv;
// extract Gould terms
sign = GouldFP & 0x80000000;
expon = (GouldFP & 0x7f000000) >> 24;
expv = expon - 64; // actual exponent
mantissa = GouldFP & 0xffffff;
if(mantissa == 0) {
return 0;
}
expv *= 4; // convert exponent to base 2
while((mantissa & 0x800000) == 0){ // multiply mantissa by 2 and decrement exponent
mantissa <<= 1; // until MSB of matissa is 1
expv--;
}
expv--; //change mantissae divisor to 2^23 and decrement exponent
if(expv > 127) { // +- infinity
res = sign | 0x7f800000;
} else if(expv < -149) {
res = sign; // +- 0
} else if(expv >= -126) {
expon = expv + 127; // normal number
expon <<= 23;
res = sign | expon | (mantissa & 0x7fffff);
} else { // denormal number
while(expv < -126) { // divide mantissa by 2 and increment exponent
expv++; // until exponent is -126
mantissa >>= 1;
}
expon = 0; // signal denormalized
res = sign | expon | (mantissa & 0x7fffff);
}
return res;
}
int main()
{
int nprob, curprob, index;
DWORD inval, res;
if(scanf("%d", &nprob) != 1)
{
fprintf(stderr, "Scan failed on problem count\n");
return -2;
}
for(curprob = 1; curprob <= nprob ; curprob++)
{
// get prob num and sequence index
if(scanf("%d %lx", &index, &inval) != 2)
{
fprintf(stderr, "scan failed on problem data problem index %d\n",
curprob);
return -6;
}
res = FormatConvert(inval);
printf("%d %08lX\n", curprob, res);
}
return 0;
}







 本文介绍了一种将Gould格式的浮点数转换为IEEE标准浮点数的方法。Gould格式使用16进制基数,包含1位符号位、7位偏移指数和24位十六进制尾数。而IEEE格式则采用1位符号位、8位二进制指数和24位尾数。文章详细描述了转换过程,包括特殊值如无穷大和零的处理,以及如何将非规范化值转换为规范化值。
本文介绍了一种将Gould格式的浮点数转换为IEEE标准浮点数的方法。Gould格式使用16进制基数,包含1位符号位、7位偏移指数和24位十六进制尾数。而IEEE格式则采用1位符号位、8位二进制指数和24位尾数。文章详细描述了转换过程,包括特殊值如无穷大和零的处理,以及如何将非规范化值转换为规范化值。
















 1422
1422

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








