从头到尾打印链表


/**
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next = null;
*
* ListNode(int val) {
* this.val = val;
* }
* }
*
*/
/*用栈的思路去解决*/
import java.util.Stack;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class Solution {
public ArrayList<Integer> printListFromTailToHead(ListNode listNode) { //返回一个list
if(listNode == null){ //头节点为空的情况
ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<Integer>();
return list;
}
Stack<Integer> stk = new Stack<Integer>();
while(listNode != null){ //入栈
stk.push(listNode.val);
listNode = listNode.next;
}
ArrayList<Integer> arr = new ArrayList<Integer>();
while(!stk.isEmpty()){
arr.add(stk.pop()); //出栈并记录
}
return arr;
}
}/*用递归的思路解决*/import java.util.ArrayList;
public class Solution {
public ArrayList<Integer> printListFromTailToHead(ListNode listNode) {
if(listNode == null){
ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<Integer>();
return list;
}
ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<Integer>();
if(listNode.next!=null){
list=this.printListFromTailToHead(listNode.next); //每次递归记录
}
list.add(listNode.val);
return list;
}
在O(1)时间删除链表节点


public static void deleteNode(Node head,Node delNode) {
if(head==null || delNode==null) {
return;
}
if(delNode.next!=null) { //删除节点下一节点不为空(正常情况)
delNode.data=delNode.next.data; //把有用信息拷贝过去
delNode.next=delNode.next.next; //删除含有delNode信息的节点
}else if(head==delNode) { //要删除的是只有一个元素的头节点
head=null;
}else { //删除节点是尾节点(顺序遍历)
Node cur=head;
while(cur.next!=delNode) { //找到删除节点的上一个节点
cur=cur.next;
}
cur.next=null; //删除尾节点
}
}
相关题目:
如何在不知道头节点的情况下删除节点
1.若节点是尾节点,则无法删除 ,无法使其上一节点next置为空
2 .若节点不是尾节点 则如上 换值删除即可
链表中倒数第K个节点

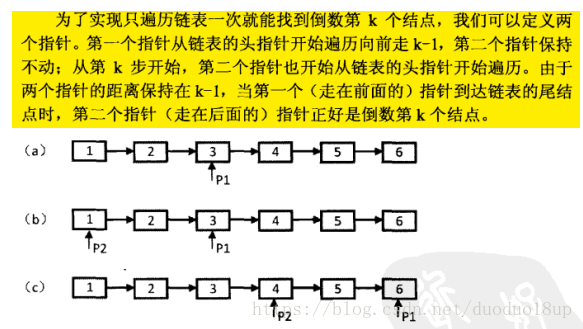
可能存在的问题和鲁棒性考虑:

public ListNode FindKthToTail(ListNode head,int k) {
if(head==null || k==0) //对于输入进行鲁棒性检测
return null;
ListNode p1=head;
ListNode p2=head;
for(int i=1;i<k;i++){
if(p1.next!=null)
p1=p1.next;
else
return null; //总长度<k
}
while(p1.next!=null){
p1=p1.next;
p2=p2.next;
}
return p2;
}
题目1:求中间节点(记住要考虑下一节点-->下下节点是否为空) 考虑奇数和偶数的情况
public Node searchMid(Node head) {
//定义两个指针 一个一步 一个两步
if(head==null)
return null;
Node p1=head;
Node p2=head;
//注意判断条件
while(p1.next!=null && p1.next.next!=null) {
p1=p1.next.next;
p2=p2.next;
}
return p2;
}public boolean searchMid(Node head) {
//定义两个指针 一个一步 一个两步
if(head==null)
return false;
Node p1=head;
Node p2=head;
//注意判断条件
while(p1!=null && p1.next!=null ) {
p1=p1.next.next;
p2=p2.next;
if(p1==p2)
return true;
}
return !(p1==null ||p1.next==null );
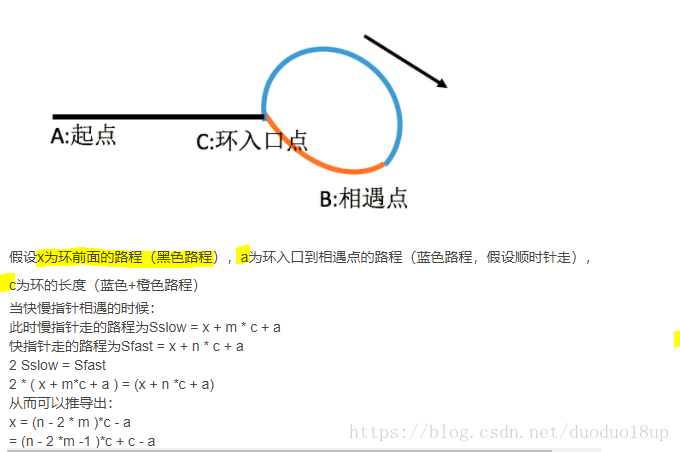
}环的入口:相遇时p2没有遍历完链表----p1已经循环了>1圈 相遇之后p1回到头节点,p2依然在相遇点-----两个均同步走一步----相遇第一点即为环入口点
public Node searchMid(Node head) {
//定义两个指针 一个一步 一个两步
if(head==null || head.next==null)
return null;
Node p1=head;
Node p2=head;
//注意判断条件
while(p1!=null && p1.next!=null ) {
p1=p1.next.next;
p2=p2.next;
if(p1==p2)
break;
}
if(p1==null ||p1.next==null)
return null; //无环
p1=head; //回到头节点
while(p1!=p2) { //找相遇点
p1=p1.next;
p2=p2.next;
}
return p2;
}推导环的入口:

反转链表


1. 递归的方法其实是非常巧的,它利用递归走到链表的末端,然后再更新每一个node的next 值 ,实现链表的反转。而newhead 的值没有发生改变,为该链表的最后一个结点,所以,反转后,我们可以得到新链表的head。
public ListNode ReverseList(ListNode head) {
if(head==null || head.next==null)
return head;
ListNode Phead=ReverseList(head.next); //递归的思想去解决该问题
head.next.next=head;
head.next=null;
return Phead;
}2. 常规 定义3个指针节点
if(head==null)
return null;
if(head.next==null){
return head;
}
//定义三个指针节点
ListNode Phead=null;
ListNode Ppre=null;
ListNode Pcur=head;
while(Pcur!=null){
ListNode Pnext=Pcur.next;
if(Pnext==null)
Phead=Pcur;
Pcur.next=Ppre;
Ppre=Pcur;
Pcur=Pnext;
}
return Phead;
合并两个排序的链表


1. 简单递归思路:
public ListNode Merge(ListNode list1,ListNode list2) {
//用递归的思路 每次选择两个链表中最小的节点 跟在新链表节点后面
if(list1==null)
return list2;
if(list2==null)
return list1;
if(list1==null && list2==null)
return null;
ListNode mergeHead=null;
if(list1.val < list2.val){
mergeHead=list1;
mergeHead.next=Merge(list1.next,list2);
}else{
mergeHead=list2;
mergeHead.next=Merge(list1,list2.next);
}
return mergeHead;
}2 正常思路:
public ListNode Merge(ListNode list1,ListNode list2) {
if(list1 == null){
return list2;
}
if(list2 == null){
return list1;
}
ListNode mergeHead = null; //合并链表头节点
ListNode current = null;
while(list1!=null && list2!=null){
if(list1.val <= list2.val){
if(mergeHead == null){ //若头节点为空
mergeHead = current = list1; //则此为第一个节点
}else{
current.next = list1; //正常节点则依次连接
current = current.next;
}
list1 = list1.next; //右移节点
}else{
if(mergeHead == null){
mergeHead = current = list2;
}else{
current.next = list2;
current = current.next;
}
list2 = list2.next;
}
}
if(list1 == null){ //若list1节点合并完毕 则将list2剩余节点依次合并
current.next = list2;
}else{
current.next = list1;
}
return mergeHead;
}复杂链表的复制

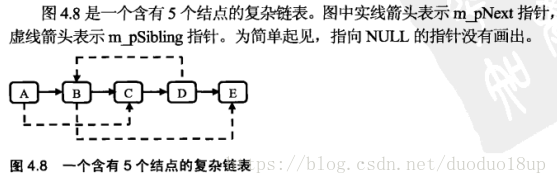
方法1 :先将正常的next进行链接,之后再找对应位置进行sibling的链接操作

方法2 :优化查找sibling操作

import java.util.HashMap;
public class Solution {
public RandomListNode Clone(RandomListNode pHead){
if(pHead == null)
return null;
HashMap<RandomListNode, RandomListNode> map = new HashMap<RandomListNode, RandomListNode>(); //建立哈希表
RandomListNode newHead = new RandomListNode(pHead.label); //新链表头节点
RandomListNode pre = pHead, newPre = newHead;
map.put(pre, newPre);
while(pre.next != null){
newPre.next = new RandomListNode(pre.next.label);
pre = pre.next;
newPre = newPre.next;
map.put(pre, newPre);
}
pre = pHead;
newPre = newHead;
while(newPre != null){
newPre.random = map.get(pre.random);
pre = pre.next;
newPre = newPre.next;
}
return newHead;
}
}方法3 : 分治法
第一步
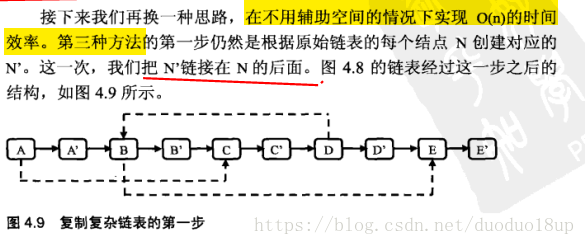
第二步
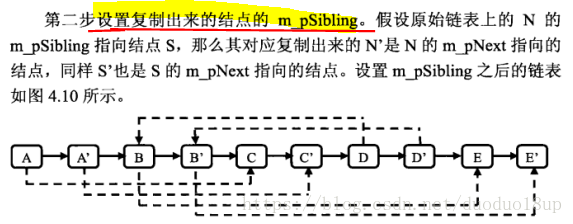
第三步
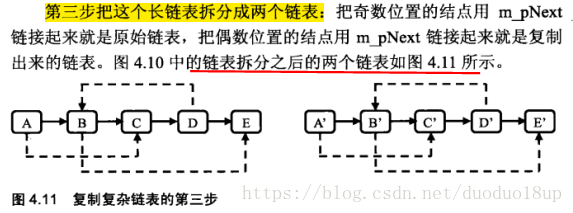
public class Solution {
public RandomListNode Clone(RandomListNode pHead){
if(pHead==null)
return null;
RandomListNode pCur = pHead;
//复制next 如原来是A->B->C 变成A->A'->B->B'->C->C'
while(pCur!=null){
RandomListNode node = new RandomListNode(pCur.label);
node.next = pCur.next;
pCur.next = node;
pCur = node.next;
}
pCur = pHead; //重新恢复指向
//复制random pCur是原来链表的结点 pCur.next是复制pCur的结点
while(pCur!=null){
if(pCur.random!=null)
pCur.next.random = pCur.random.next;
pCur = pCur.next.next;
}
//拆分链表
RandomListNode head = pHead.next; //复制链表头部 后期返回值
RandomListNode cur = head; //复制链表当前指向节点
pCur = pHead; //原链表当前指向节点
while(pCur!=null){ /注意此时的判断条件
pCur.next=pCur.next.next;
if(cur.next!=null){ //判断是否到达null 没有节点 容易出错!!!
cur.next=cur.next.next;
}
pCur=pCur.next;
cur=cur.next;
}
return head;
}
}
二叉搜索树与双向链表

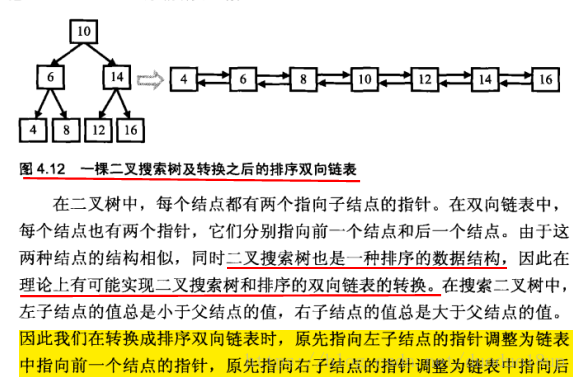
解法思路:
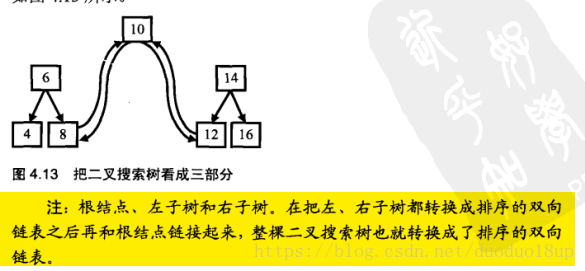
有3 种方法:
1 .非递归法(利用Stack实现)
中序遍历回顾:
import java.util.Stack;
public Node inOrderNotCur(Node root){
if(root==null)
return null;
Stack<Node> s=new Stack<Node>();
while(root!=null || !s.isEmpty()){ //当前节点不为空或者栈不为空时
if(root!=null){ //当前节点不为空时
s.push(root); //压入节点 并找寻左子节点 一直到达最左端节点 再开始出栈
root=root.left;
}else{ //当前节点没有左子节点 则开始出栈
root=s.pop();
System.out.println(root.data); //打印弹出节点数据
root=root.right; //压入当前节点的右子节点
}
}
}使用“中序遍历”原理:
import java.util.Stack;
public class Solution {
public TreeNode Convert(TreeNode root) {
if(root==null)
return null;
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<TreeNode>();
TreeNode p = root;
TreeNode pre = null; // 用于保存中序遍历序列的上一节点
boolean isFirst = true; //标识链表的头节点
while(p!=null || !stack.isEmpty()){
while(p!=null){
stack.push(p);
p = p.left;
}
p = stack.pop();
if(isFirst){ //看是否是第一个节点 即链表的头节点
root = p; // 将中序遍历序列中的第一个节点记为root
pre = root;
isFirst = false;
}else{ //不是链表的头节点
pre.right = p; //为每个弹出节点进行链表连接
p.left = pre;
pre = p;
}
p = p.right;
}
return root;
}
}2 .递归法
//方法二:递归版
// 解题思路:
//1. 将左子树构造成双链表,并返回链表头节点。
//2. 定位至左子树双链表最后一个节点。
//3. 如果左子树链表不为空的话,将当前root追加到左子树链表。
//4. 将右子树构造成双链表,并返回链表头节点。
//5. 如果右子树链表不为空的话,将该链表追加到root节点之后。
//6. 根据左子树链表是否为空确定返回的节点。
public TreeNode Convert(TreeNode root) {
if(root==null)
return null;
if(root.left==null&&root.right==null)
return root;
// 1.将左子树构造成双链表,并返回链表头节点
TreeNode left = Convert(root.left);
TreeNode p = left;
// 2.定位至左子树双链表最后一个节点
while(p!=null&&p.right!=null){
p = p.right;
}
// 3.如果左子树链表不为空的话,将当前root追加到左子树链表
if(left!=null){
p.right = root;
root.left = p;
}
// 4.将右子树构造成双链表,并返回链表头节点
TreeNode right = Convert(root.right);
// 5.如果右子树链表不为空的话,将该链表追加到root节点之后
if(right!=null){
right.left = root;
root.right = right;
}
return left!=null?left:root;
}// 最喜欢的思路: 用全局变量去一直记录最后一个节点(按照中序遍历也就是最右节点)
// 方法三:改进递归版
// 解题思路:
// 思路与方法二中的递归版一致,仅对第2点中的定位作了修改,新增一个全局变量记录左子树的最后一个节点。 // 记录子树链表的最后一个节点,终结点只可能为只含左子树的非叶节点与叶节点
protected TreeNode leftLast = null;
public TreeNode Convert(TreeNode root) {
if(root==null)
return null;
if(root.left==null&&root.right==null){
leftLast = root; // 最后的一个节点可能为最右侧的叶节点
return root;
}
// 1.将左子树构造成双链表,并返回链表头节点
TreeNode left = Convert(root.left);
// 3.如果左子树链表不为空的话,将当前root追加到左子树链表
if(left!=null){
leftLast.right = root;
root.left = leftLast;
}
leftLast = root; // 当根节点只含左子树时,则该根节点为最后一个节点
// 4.将右子树构造成双链表,并返回链表头节点
TreeNode right = Convert(root.right);
// 5.如果右子树链表不为空的话,将该链表追加到root节点之后
if(right!=null){
right.left = root;
root.right = right;
}
return left!=null?left:root;
}两个链表的第一个公共节点

解法1 :蛮力法 时间复杂度O(mn)
解法2: 用栈来处理 倒序 时间复杂度O(m+n) 空间复杂度O(m+n)

解法3: 遍历长度---长的先走--共同走--第一个相同点即为交点 时间复杂度O(m+n) 无额外空间

/*
public class ListNode {
int val;
ListNode next = null;
ListNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
}*/
public class Solution {
public ListNode FindFirstCommonNode(ListNode pHead1, ListNode pHead2) {
if(pHead1==null || pHead2==null)
return null;
int len1=getListLength(pHead1);
int len2=getListLength(pHead2);
int dif=0;
ListNode longNode=null;
ListNode shortNode=null;
if(len1>len2){
dif=len1-len2;
longNode=pHead1;
shortNode=pHead2;
}else{
dif=len2-len1;
longNode=pHead2;
shortNode=pHead1;
}
for(int i=0;i<dif;i++){
longNode=longNode.next; //较长端先走
}
//开始一起走
while(longNode!=null && shortNode!=null && longNode!=shortNode){
longNode=longNode.next;
shortNode=shortNode.next;
}
//走到相同点
return longNode;
}
//长度统计
public int getListLength(ListNode node){
int count=1;
while(node.next!=null){
count++;
node=node.next;
}
return count;
}
}

输入两个树节点 求他们的最低公共祖先

几个逐渐思考的过程:
1 这个树是否是二叉树? 二叉排序树?

2 此树只是普通的树,连二叉树可能都不是 ,则问? 是否每个节点有指向父节点的指针?
这样 则可以转化为两个链表的第一个公共节点问题----
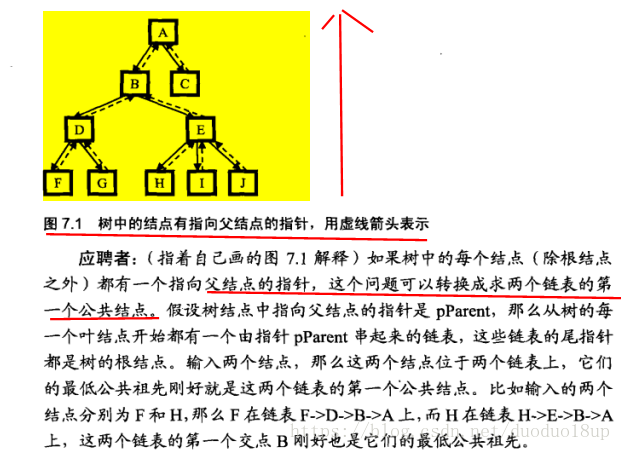
3 此树只是普通的树,连二叉树可能都不是 且每个节点没有指向父节点的指针

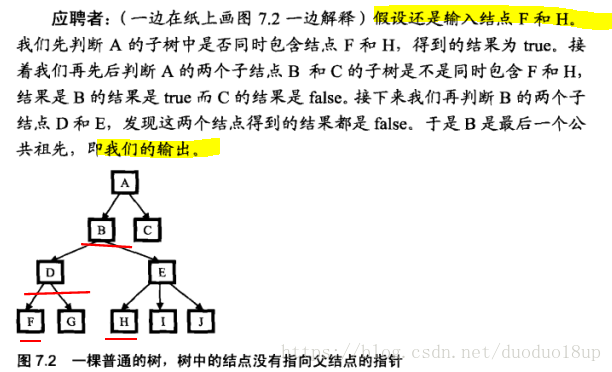
4 可能会有重复的计算 判断A的子节点---判断B的子节点



最终我简化问题:
在二叉树中找到两个节点的最近公共祖先
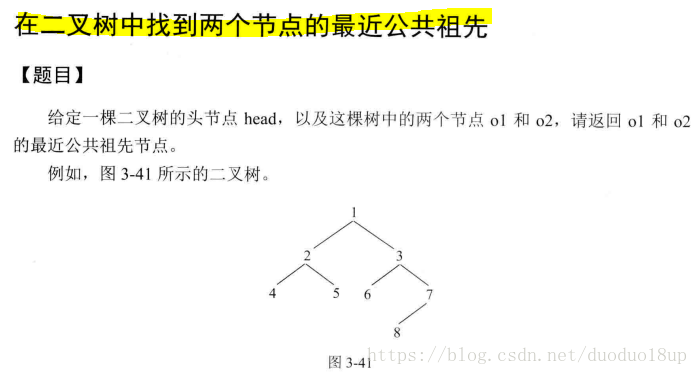

//在二叉树中找到两个节点的最近公共祖先
public class firstAncestor {
public Node firstAncestor (Node head, Node h1,Node h2) {
if(head==null || head==h1 ||head==h2 )
return head;
Node left=firstAncestor(head.left, h1,h2);
Node right=firstAncestor(head.right,h1,h2);
if(left!=null && right!=null) {
return head;
}
return left!=null ? left:right;
}
}
删除链表中重复的节点:
在一个排序的链表中,存在重复的结点,请删除该链表中重复的结点,重复的结点不保留,返回链表头指针。 例如,链表1->2->3->3->4->4->5 处理后为 1->2->5
方法1 :采用递归的方法(最简便) 时间0(n)
public class Solution {
public ListNode deleteDuplication(ListNode pHead) {
if (pHead == null || pHead.next == null) { // 只有0个或1个结点,则返回
return pHead;
}
if (pHead.val == pHead.next.val) { // 当前结点是重复结点
ListNode pNode = pHead.next;
while (pNode != null && pNode.val == pHead.val) {
// 跳过值与当前结点相同的全部结点,找到第一个与当前结点不同的结点
pNode = pNode.next;
}
return deleteDuplication(pNode); // 从第一个与当前结点不同的结点开始递归
} else { // 当前结点不是重复结点
pHead.next = deleteDuplication(pHead.next); // 保留当前结点,从下一个结点开始递归
return pHead;
}
}
}方法2 : 采用常规循环方法 对应3个指针进行移动
public class Solution {
public ListNode deleteDuplication(ListNode pHead){
ListNode first=new ListNode(Integer.MIN_VALUE); //创建一个新的头节点,主要是怕原头节点重复,需要删除
ListNode last=first; //定义一个当前节点的上一节点 以后期删除节点之后连接之后的节点
first.next=pHead;
while(pHead!=null && pHead.next!=null){ //考虑当前节点和下一节点均不为空 否则返回的是pHead
if(pHead.val==pHead.next.val){ //如果当前节点和下一节点的值相同
int temp=pHead.val;
while(pHead!=null && pHead.val==temp){ //则不断向后移动找到与当前节点值不同的节点
pHead=pHead.next;
}
last.next=pHead; //删除重复节点,与之前节点进行连接
}else{
last=pHead; //如果当前节点和下一节点并不相同
pHead=pHead.next; //则前一节点和当前节点均向后移动一位
}
}
return first.next; //最终返回新建头节点之后的节点即可
}
}




 本文深入讲解链表的各种操作,包括正向打印、反向打印、删除节点、查找倒数第K个节点、寻找中间节点、判断是否有环及环入口、链表反转、合并排序链表等,提供多种实现思路如递归、栈、双指针等。
本文深入讲解链表的各种操作,包括正向打印、反向打印、删除节点、查找倒数第K个节点、寻找中间节点、判断是否有环及环入口、链表反转、合并排序链表等,提供多种实现思路如递归、栈、双指针等。
















 321
321

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








