课程安排
- MongoDB快速入门
- Spring Data MongoDB入门
- 分析作业范围功能需求
- 实现机构与快递员的作业范围
1、背景说明
生成快递员的取派件任务
需要设定每个快递员或机构的作业范围,而范围是一组经纬度数据
如果存储到mysql中,并不能很好通过范围查询。所以使用MongoDB存储作业范围数据。
2、MongoDB快速入门
基于分布式文件存储的数据库,由C++语言编写
介于关系数据库和非关系数据库之间的产品,是非关系数据库当中功能最丰富,最像关系数据库的


不支持ACID事务

数据模型即表的字段(MongoDB中1数据a,b字段。新插入2数据 a,b,c 字段也行)
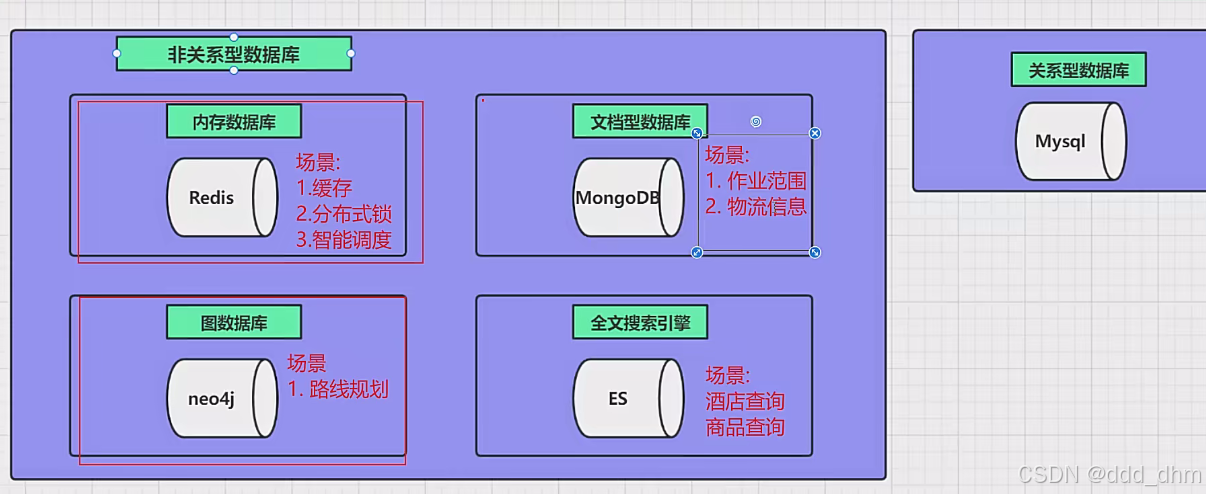
2.1、项目中一些数据库的使用场景
2.2、部署安装
docker run -d \
--name mongodb \
-p 27017:27017 \
--restart=always \
-v mongodb:/data/db \
-e MONGO_INITDB_ROOT_USERNAME=sl \
-e MONGO_INITDB_ROOT_PASSWORD=123321 \
mongo:4.4
#进入容器进行设置
docker exec -it mongodb /bin/bash
#进行认证
mongo -u "sl" -p "123321" --authenticationDatabase "admin"
#测试命令,查看已有数据库
> show dbs
admin 0.000GB
config 0.000GB
local 0.000GBctrl+c退出
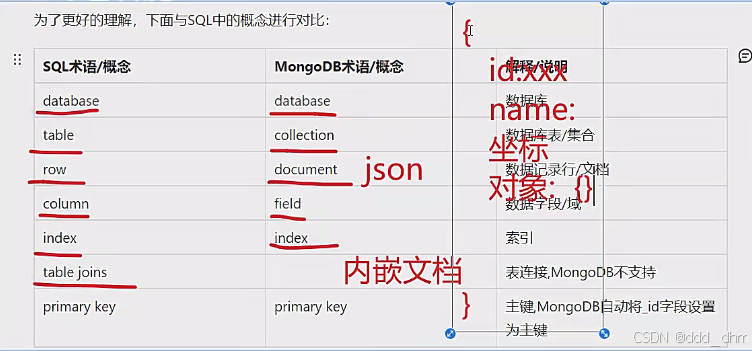
2.3、基本概念
与SQL中的概念进行对比:
MongoDB:database,collection,field,document(json)
| SQL术语/概念 | MongoDB术语/概念 | 解释/说明 |
| database | database | 数据库 |
| table | collection | 数据库表/集合 |
| row | document | 数据记录行/文档 |
| column | field | 数据字段/域 |
| index | index | 索引 |
| table joins | 表连接,MongoDB不支持 | |
| primary key | primary key | 主键,MongoDB自动将_id字段设置为主键 |
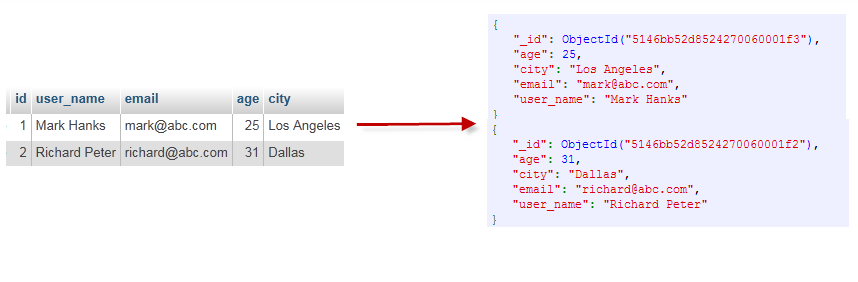
MongoDB可以内嵌文档的方式进行表连接json{ id,name,json{} }
2.4、MongoDB基本操作
在MongoDB中,存储的文档结构是一种类似于json的结构,称之为bson(全称为:Binary JSON)。
2.4.1、数据库以及表的操作
#查看所有的数据库
> show dbs
admin 0.000GB
config 0.000GB
local 0.000GB
#通过use关键字切换数据库
> use admin
switched to db admin
#创建数据库
#说明:在MongoDB中,数据库是自动创建的,通过use切换到新数据库中,进行插入数据即可自动创建数据库
> use testdb
switched to db testdb
> show dbs #并没有创建数据库
admin 0.000GB
config 0.000GB
local 0.000GB
> db.user.insert({id:1,name:'zhangsan'}) #插入数据
WriteResult({ "nInserted" : 1 })
> show dbs
admin 0.000GB
config 0.000GB
local 0.000GB
testdb 0.000GB #数据库自动创建
#查看表
> show tables
user
> show collections
user
>
#删除集合(表)
> db.user.drop()
true #如果成功删除选定集合,则 drop() 方法返回 true,否则返回 false。
#删除数据库
> use testdb #先切换到要删除的数据库中
switched to db testdb
> db.dropDatabase() #删除数据库
{ "dropped" : "testdb", "ok" : 1 }
> show dbs
admin 0.000GB
config 0.000GB
local 0.000GB2.4.2、新增数据insert()
先指定使用哪个数据库
语法:db。表。操作({json数据})
json数据格式 属性:值
注:使用insert插入已有数据(根据ObjectId判断)会报错,使用save会替换并保存
#插入数据
#语法:db.COLLECTION_NAME.insert(document)
> db.user.insert({id:1,username:'zhangsan',age:20})
WriteResult({ "nInserted" : 1 })
> db.user.save({id:2,username:'lisi',age:25})
WriteResult({ "nInserted" : 1 })
> db.user.find() #查询数据
{ "_id" : ObjectId("5c08c0024b318926e0c1f6dc"), "id" : 1, "username" : "zhangsan", "age" : 20 }
{ "_id" : ObjectId("5c08c0134b318926e0c1f6dd"), "id" : 2, "username" : "lisi", "age" : 25 }- id 是集合中文档的主键,用于区分文档(记录),id自动编入索引。
- 默认情况下,id 字段的类型为 ObjectID(自动生成),是 MongoDB 的 BSON 类型之一,如果需要,用户还可以将 id 覆盖为 ObjectID 以外的其他内容。
- ObjectID 长度为 12 字节,由几个 2-4 字节的链组成。每个链代表并指定文档身份的具体内容。以下的值构成了完整的 12 字节组合:
-
- 一个 4 字节的值,表示自 Unix 纪元以来的秒数
- 一个 3 字节的机器标识符
- 一个 2 字节的进程 ID
- 一个 3字节的计数器,以随机值开始
2.4.3、更新数据update()
update() 方法用于更新已存在的文档。语法格式如下:
db.collection.update(
<query>,
<update>,
[
upsert: <boolean>,
multi: <boolean>,
writeConcern: <document>
]
)参数说明:
- query : update的查询条件,类似sql update查询内where后面的。
- update : update的对象和一些更新的操作符(如,inc...)等,也可以理解为sql update查询内set后面的
- upsert : 可选,第一个参数,这个参数的意思是,如果不存在update的记录,是否插入objNew,true为插入,默认是false,不插入。
- multi : 可选,第二个参数,mongodb 默认是false,只更新找到的第一条记录,如果这个参数为true,就把按条件查出来多条记录全部更新。
- writeConcern :可选,抛出异常的级别。
db.user.update({id:1},{$set:{age:22}}) #更新数据需要对字段加$,否则会替换字段。
插入的数据不存在时,可在最后添加true添加该数据。db.user.update({id:3},{$set:{sex:1}},true)
> db.user.find()
{ "_id" : ObjectId("5c08c0024b318926e0c1f6dc"), "id" : 1, "username" : "zhangsan", "age" : 20 }
{ "_id" : ObjectId("5c08c0134b318926e0c1f6dd"), "id" : 2, "username" : "lisi", "age" : 25 }
> db.user.update({id:1},{$set:{age:22}}) #更新数据
WriteResult({ "nMatched" : 1, "nUpserted" : 0, "nModified" : 1 })
> db.user.find()
{ "_id" : ObjectId("5c08c0024b318926e0c1f6dc"), "id" : 1, "username" : "zhangsan", "age" : 22 }
{ "_id" : ObjectId("5c08c0134b318926e0c1f6dd"), "id" : 2, "username" : "lisi", "age" : 25 }
#注意:如果这样写,会删除掉其他的字段
> db.user.update({id:1},{age:25})
WriteResult({ "nMatched" : 1, "nUpserted" : 0, "nModified" : 1 })
> db.user.find()
{ "_id" : ObjectId("5c08c0024b318926e0c1f6dc"), "age" : 25 }
{ "_id" : ObjectId("5c08c0134b318926e0c1f6dd"), "id" : 2, "username" : "lisi", "age" : 25 }
#更新不存在的字段,会新增字段
> db.user.update({id:2},{$set:{sex:1}}) #更新数据
> db.user.find()
{ "_id" : ObjectId("5c08c0024b318926e0c1f6dc"), "age" : 25 }
{ "_id" : ObjectId("5c08c0134b318926e0c1f6dd"), "id" : 2, "username" : "lisi", "age" : 25, "sex" : 1 }
#更新不存在的数据,默认不会新增数据
> db.user.update({id:3},{$set:{sex:1}})
WriteResult({ "nMatched" : 0, "nUpserted" : 0, "nModified" : 0 })
> db.user.find()
{ "_id" : ObjectId("5c08c0024b318926e0c1f6dc"), "age" : 25 }
{ "_id" : ObjectId("5c08c0134b318926e0c1f6dd"), "id" : 2, "username" : "lisi", "age" : 25, "sex" : 1 }
#如果设置第一个参数为true,就是新增数据
> db.user.update({id:3},{$set:{sex:1}},true)
WriteResult({
"nMatched" : 0,
"nUpserted" : 1,
"nModified" : 0,
"_id" : ObjectId("5c08cb281418d073246bc642")
})
> db.user.find()
{ "_id" : ObjectId("5c08c0024b318926e0c1f6dc"), "age" : 25 }
{ "_id" : ObjectId("5c08c0134b318926e0c1f6dd"), "id" : 2, "username" : "lisi", "age" : 25, "sex" : 1 }
{ "_id" : ObjectId("5c08cb281418d073246bc642"), "id" : 3, "sex" : 1 }2.4.4、删除数据remove()
通过remove()方法进行删除数据,语法如下:
db.collection.remove(
<query>,
{
justOne: <boolean>,
writeConcern: <document>
}
)参数说明:
- query :(可选)删除的文档的条件。
- justOne : (可选)如果设为 true 或 1,则只删除一个文档,如果不设置该参数,或使用默认值 false,则删除所有匹配条件的文档。
- writeConcern :(可选)抛出异常的级别。
#删除所有数据
> db.user.remove({})
#说明:为了简化操作,官方推荐使用deleteOne()与deleteMany()进行删除数据操作。
db.user.deleteOne({id:1})
db.user.deleteMany({}) #删除所有数据
> db.user.remove({age:25})
WriteResult({ "nRemoved" : 2 }) #删除了2条数据
#插入4条测试数据
db.user.insert({id:1,username:'zhangsan',age:20})
db.user.insert({id:2,username:'lisi',age:21})
db.user.insert({id:3,username:'wangwu',age:22})
db.user.insert({id:4,username:'zhaoliu',age:22})
> db.user.remove({age:22},true)
WriteResult({ "nRemoved" : 1 }) #删除了1条数据
#删除所有数据
> db.user.remove({})
#说明:为了简化操作,官方推荐使用deleteOne()与deleteMany()进行删除数据操作。
db.user.deleteOne({id:1})
db.user.deleteMany({}) #删除所有数据2.4.5、查询数据find()
MongoDB 查询数据的语法格式为:db.user.find([query],[fields])
- query :可选,使用查询操作符指定查询条件
- fields :可选,使用投影操作符指定返回的键。查询时返回文档中所有键值, 只需省略该参数即可(默认省略)。
如果你需要以json方式来读取数据,可以使用 pretty() 方法,语法格式为:db.col.find().pretty()
条件查询:
| 操作 | 格式 | 范例 | RDBMS中的类似语句 |
| 等于 | {:} | db.col.find({"by":"黑马程序员"}).pretty() | where by = '黑马程序员' |
| 小于 | {:{$lt:}} | db.col.find({"likes":{$lt:50}}).pretty() | where likes < 50 |
| 小于或等于 | {:{$lte:}} | db.col.find({"likes":{$lte:50}}).pretty() | where likes <= 50 |
| 大于 | {:{$gt:}} | db.col.find({"likes":{$gt:50}}).pretty() | where likes > 50 |
| 大于或等于 | {:{$gte:}} | db.col.find({"likes":{$gte:50}}).pretty() | where likes >= 50 |
| 不等于 | {:{$ne:}} | db.col.find({"likes":{$ne:50}}).pretty() | where likes != 50 |
db.user.insert({id:1,username:'zhangsan',age:20})
db.user.insert({id:2,username:'lisi',age:21})
db.user.insert({id:3,username:'wangwu',age:22})
db.user.insert({id:4,username:'zhaoliu',age:22})
db.user.find() #查询全部数据
db.user.find({},{id:1,username:1}) #只查询id与username字段
db.user.find().count() #查询数据条数
db.user.find({id:1}) #查询id为1的数据
db.user.find({age:{$lte:21}}) #查询小于等于21的数据
db.user.find({age:{$lte:21}, id:{$gte:2}}) #and查询,age小于等于21并且id大于等于2
db.user.find({$or:[{id:1},{id:2}]}) #查询id=1 or id=2 逗号为and条件
#分页查询:Skip()跳过几条,limit()查询条数
db.user.find().limit(2).skip(1) #跳过1条数据,查询2条数据
db.user.find().sort({id:-1}) #按照age倒序排序,-1为倒序,1为正序
2.5、索引
索引通常能够极大的提高查询的效率,如果没有索引,MongoDB在读取数据时必须扫描集合中的每个文件并选取那些符合查询条件的记录。
MongoDB支持的索引类型有:
- 单字段索引(Single Field)
-
- 支持所有数据类型中的单个字段索引
- 复合索引(Compound Index)
-
- 基于多个字段的索引,创建复合索引时要注意字段顺序与索引方向
- 多键索引(Multikey indexes)
-
- 针对属性包含数组数据的情况,MongoDB支持针对数组中每一个element创建索引。
- 全文索引(Text Index)
-
- 支持任意属性值为string或string数组元素的索引查询。
- 注意:一个集合仅支持最多一个Text Index,中文分词不理想,推荐Elasticsearch。
- 地理空间索引(Geospatial Index)
-
- 2dsphere索引,用于存储和查找球面上的点
- 2d索引,用于存储和查找平面上的点
- 哈希索引(Hashed Index)
-
- 针对属性的哈希值进行索引查询,当要使用Hashed index时,MongoDB能够自动的计算hash值,无需程序计算hash值。
- hash index仅支持等于查询,不支持范围查询。
我们重点需要掌握的是【单字段索引】、【2dsphere索引】。
#单字段索引,1表示升序创建索引,-1表示降序创建索引
db.集合名.createIndex({"字段名":排序方式})
#2dsphere索引
db.集合名.createIndex({"字段名":"2dsphere"})
#示例,创建user集合,其中username和loc字段设置索引
db.user.createIndex({"username":1})
db.user.createIndex({"loc":"2dsphere"})
db.user.insert({id:1,username:'zhangsan',age:20,loc:{type:"Point",coordinates:[116.343847,40.060539]}})
db.user.insert({id:2,username:'lisi',age:22,loc:{type:"Point",coordinates:[121.612112,31.034633]}})
#查看索引
db.user.getIndexes()
#查看索引大小,单位:字节
db.user.totalIndexSize()
#删除索引
db.user.dropIndex("loc_2dsphere")
#或者,删除除了_id之外的索引
db.user.dropIndexes()
地理空间索引的type可以是下列的类型:
- Point(坐标点),coordinates必须是单个位置
- MultiPoint(多个点),coordinates必须是位置数组
- LineString(线形),coordinates必须是两个或多个位置的数组
- MultiLineString(多行线形),coordinates必须是LineString坐标数组的数组
- Polygon(多边形),coordinates成员必须是 LinearRing 坐标数组的数组,必须是闭环,也就是第一个和最后一个坐标点要相同。
- MultiPolygon(多个多边形),coordinates成员必须是 Polygon 坐标数组的数组。
- GeometryCollection(几何集合),geometries是任何一个对象的集合。
2.6、UI客户端工具
可以通过可视化工具操作MongoDB,在这里推荐使用Studio 3T。
官网:The Ultimate Client, IDE and GUI for MongoDB | Studio 3T
新建链接数据库,输入链接字符串:mongodb://sl:123321@192.168.150.101:27017/admin
3、Spring Data MongoDB
spring-data对MongoDB做了支持,使用spring-data-mongodb可以简化MongoDB的操作。
new一个maven工程,作为demo演示
3.1、创建工程
创建sl-express-mongodb工程对Spring Data MongoDB的使用做基本的学习。导入依赖:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<parent>
<groupId>com.sl-express</groupId>
<artifactId>sl-express-parent</artifactId>
<version>1.3</version>
</parent>
<groupId>com.sl-express.mongodb</groupId>
<artifactId>sl-express-mongodb</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<properties>
<maven.compiler.source>11</maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>11</maven.compiler.target>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-mongodb</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</project>3.2、配置
spring:
application:
name: sl-express-mongodb
data:
mongodb:
host: 192.168.150.101
port: 27017
database: sl
authentication-database: admin #认证数据库
username: sl
password: "123321"
auto-index-creation: true #自动创建索引3.3、Entity
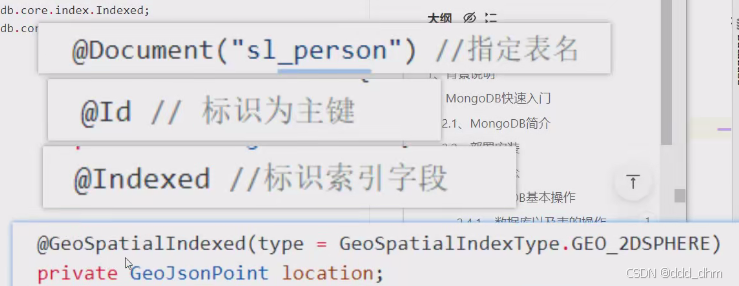
@Document("sl_person") //指定表名
对person.class的操作即为对表sl_person的操作
package com.sl.mongo.entity;
import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Builder;
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.NoArgsConstructor;
import org.bson.types.ObjectId;
import org.springframework.data.annotation.Id;
import org.springframework.data.mongodb.core.geo.GeoJsonPoint;
import org.springframework.data.mongodb.core.index.GeoSpatialIndexType;
import org.springframework.data.mongodb.core.index.GeoSpatialIndexed;
import org.springframework.data.mongodb.core.index.Indexed;
import org.springframework.data.mongodb.core.mapping.Document;
@Data
@Builder
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
@Document("sl_person") //指定表名
public class Person {
@Id // 标识为主键
private ObjectId id;
@Indexed //标识索引字段
private String name;
private int age;
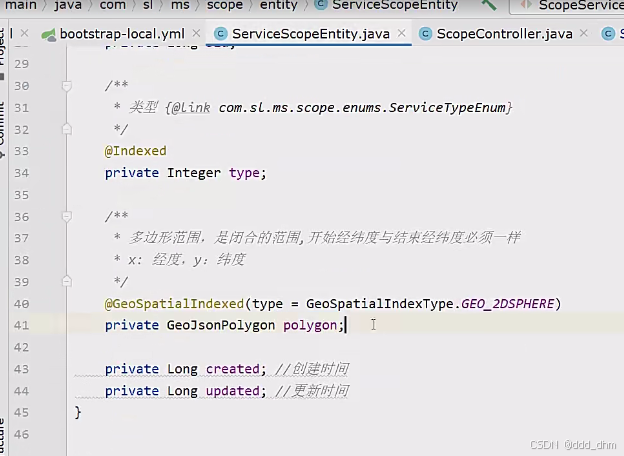
/**
* 用户位置
* x: 经度,y:纬度
*/
@GeoSpatialIndexed(type = GeoSpatialIndexType.GEO_2DSPHERE)
private GeoJsonPoint location;
//存储嵌套对象数据
private Address address;
}package com.sl.mongo.entity;
import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Builder;
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.NoArgsConstructor;
import org.springframework.data.mongodb.core.mapping.Document;
@Data
@Builder
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
@Document("sl_address") //指定表名
public class Address {
private String street;
private String city;
private String zip;
}使用方法与redis类似,用MongoTemplate
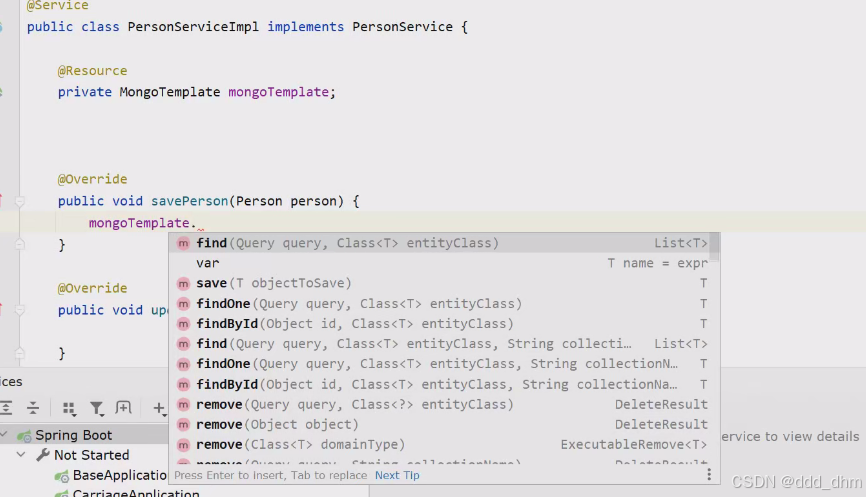
3.5、启动类
package com.sl.mongo;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
@SpringBootApplication
public class MongoApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(MongoApplication.class, args);
}
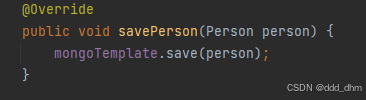
}3.6、测试
保存
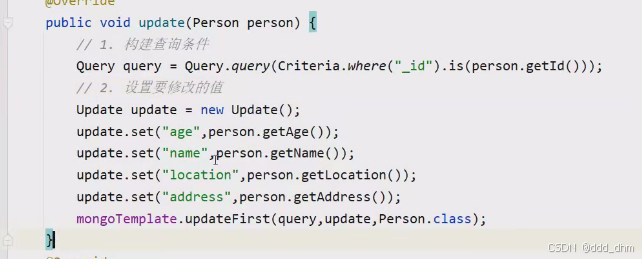
更新
Query.query(Criteria.where("_id").is(person.getId()));
其中"_id"字段前加_ 也可以省略
this.mongoTemplate.updateFirst(query, update, Person.class);
注意参数query, update, Person.class
查询
模糊查询为regex
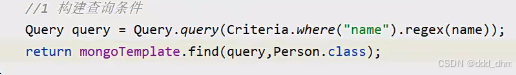
继续添加其他条件
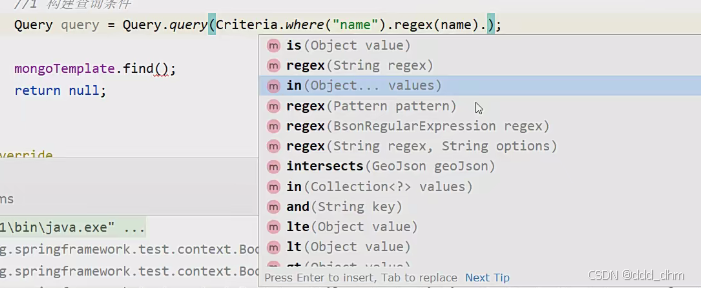
分页查询
从0开始,故page-1
PageRequest.of(page - 1, pageSize)
4、作业范围
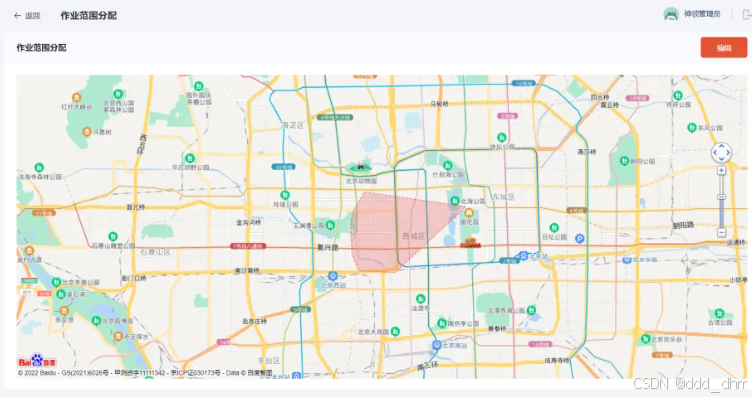
在项目中,会有两个作业范围,分别是机构作业范围和快递员作业范围,这两个作业范围的逻辑是一致的,就是在地图中进行画出范围,就是其作业范围。
逻辑:根据传入的坐标点进行查询,看属于哪一个多边形负责的区域。从而划分作业范围
![]()
机构作业范围
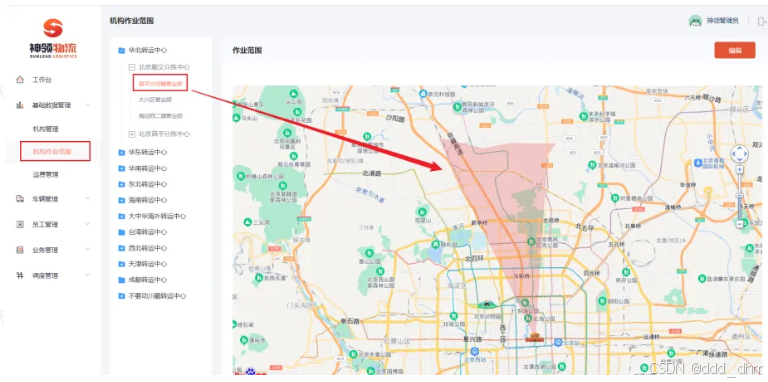
快递员作业范围

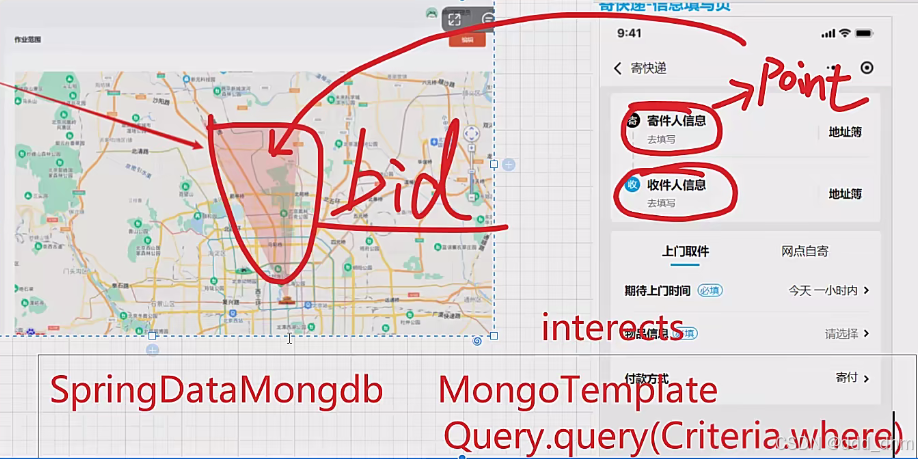
4.1、实现接口

Query query = Query.query(Criteria.where("bid").is
package com.sl.ms.scope.service.ScopeServiceImpl;
import cn.hutool.core.collection.CollUtil;
import cn.hutool.core.util.ObjectUtil;
import com.itheima.em.sdk.EagleMapTemplate;
import com.itheima.em.sdk.enums.ProviderEnum;
import com.itheima.em.sdk.vo.Coordinate;
import com.itheima.em.sdk.vo.GeoResult;
import com.sl.ms.scope.entity.ServiceScopeEntity;
import com.sl.ms.scope.enums.ServiceTypeEnum;
import com.sl.ms.scope.service.ScopeService;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.bson.types.ObjectId;
import org.springframework.data.geo.Point;
import org.springframework.data.mongodb.core.MongoTemplate;
import org.springframework.data.mongodb.core.geo.GeoJsonPoint;
import org.springframework.data.mongodb.core.geo.GeoJsonPolygon;
import org.springframework.data.mongodb.core.query.Criteria;
import org.springframework.data.mongodb.core.query.Query;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
import java.util.List;
@Slf4j
@Service
public class ScopeServiceImpl implements ScopeService {
@Resource
private MongoTemplate mongoTemplate;
@Resource
private EagleMapTemplate eagleMapTemplate;
@Override
public Boolean saveOrUpdate(Long bid, ServiceTypeEnum type, GeoJsonPolygon polygon) {
Query query = Query.query(Criteria.where("bid").is(bid).and("type").is(type.getCode()));
ServiceScopeEntity serviceScopeEntity = mongoTemplate.findOne(query, ServiceScopeEntity.class);
if(ObjectUtil.isEmpty(serviceScopeEntity)){
//新增
serviceScopeEntity = new ServiceScopeEntity();
serviceScopeEntity.setBid(bid);
serviceScopeEntity.setType(type.getCode());
serviceScopeEntity.setPolygon(polygon);
serviceScopeEntity.setCreated(System.currentTimeMillis());
serviceScopeEntity.setUpdated(serviceScopeEntity.getCreated());
}
else{
//更新
serviceScopeEntity.setPolygon(polygon);
serviceScopeEntity.setUpdated(System.currentTimeMillis());
}
try {
this.mongoTemplate.save(serviceScopeEntity);
return true;
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("新增/更新服务范围数据失败! bid = {}, type = {}, points = {}", bid, type, polygon.getPoints(), e);
}
return false;
}
@Override
public Boolean delete(String id) {
Query query = Query.query(Criteria.where("id").is(new ObjectId(id))); //构造查询条件
return this.mongoTemplate.remove(query, ServiceScopeEntity.class).getDeletedCount() > 0;
}
@Override
public Boolean delete(Long bid, ServiceTypeEnum type) {
Query query = Query.query(Criteria.where("bid").is(bid).and("type").is(type.getCode())); //构造查询条件
return this.mongoTemplate.remove(query, ServiceScopeEntity.class).getDeletedCount() > 0;
}
@Override
public ServiceScopeEntity queryById(String id) {
return this.mongoTemplate.findById(new ObjectId(id), ServiceScopeEntity.class);
}
@Override
public ServiceScopeEntity queryByBidAndType(Long bid, ServiceTypeEnum type) {
Query query = Query.query(Criteria.where("bid").is(bid).and("type").is(type.getCode())); //构造查询条件
return this.mongoTemplate.findOne(query, ServiceScopeEntity.class);
}
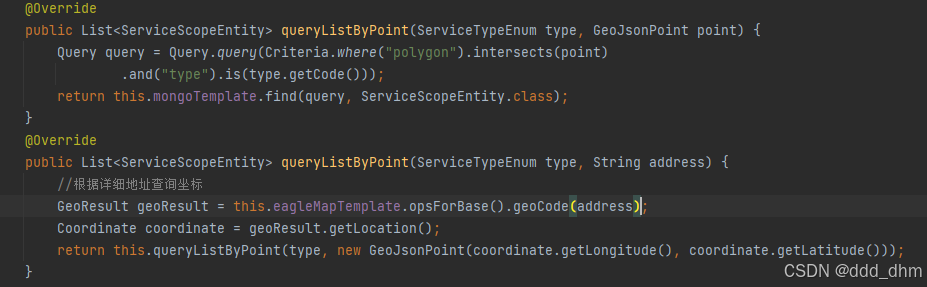
@Override
public List<ServiceScopeEntity> queryListByPoint(ServiceTypeEnum type, GeoJsonPoint point) {
Query query = Query.query(Criteria.where("polygon").intersects(point)
.and("type").is(type.getCode()));
return this.mongoTemplate.find(query, ServiceScopeEntity.class);
}
@Override
public List<ServiceScopeEntity> queryListByPoint(ServiceTypeEnum type, String address) {
//根据详细地址查询坐标
GeoResult geoResult = this.eagleMapTemplate.opsForBase().geoCode(address);
Coordinate coordinate = geoResult.getLocation();
return this.queryListByPoint(type, new GeoJsonPoint(coordinate.getLongitude(), coordinate.getLatitude()));
}
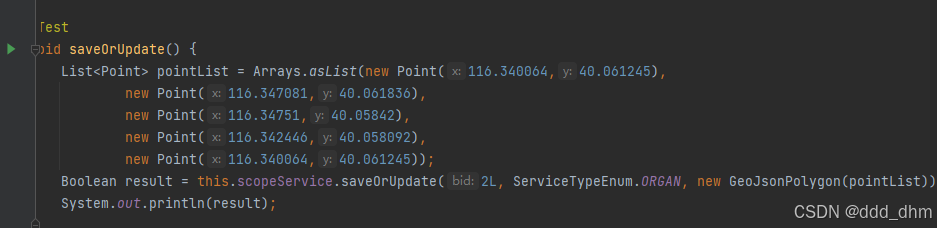
}测试
第一个坐标和最后一个要一样
构成pointList后传入GeoJsonPolygon中构成多边形范围
2L, ServiceTypeEnum.ORGAN代表为机构的营业范围,id为2
面试点
1介绍解决了什么问题(作业范围)
2介绍使用的技术(MongoDB)
3介绍实体类(重点介绍多边形范围)
每个营业网点可以在地图上画一个多边形范围(多个坐标点组成,首尾坐标点相同),存储到MongoDB数据库中,使用MongoDB提供的方法intersects(),只需将参数坐标点传入。就可以查出与坐标点有交集的机构网点id。

第二个方法是使用eagleMap根据地址查询出结果,从结果中得到坐标点经纬度,传给第一个方法。从而实现使用地址查找营业网点id。
5.1、练习1
难度系数:★★☆☆☆
描述:阅读后台系统中对于作业范围的管理相关代码。
5.2、练习2
难度系数:★★★☆☆
描述:阅读订单微服务中的下单时定位起点、终点机构的逻辑。
6、面试连环问
面试官问:
- MongoDB存储的数据结构与MySQL存储的数据结构有什么区别?
MySQL存储的是以行列维护的关系型数据库。
MongoDB是Bjson,以二进制存储的json。存的每一张表称为一个document
- 为什么会使用到MongoDB?MongoDB中如何存储坐标位置数据?如何实现附近的人查询?
作业范围的需求。多边形范围由多个坐标点构成。
MongoDB可以查询给定坐标点与多边形范围是否有交集,从而确定对应的管理机构id
实现附近的人查询:2、以当前用户位置绘制原点3、绘制半径
5、构建查询对象 NearQuery.near(point).maxDistance(distance)
/**
* 查询附近的人的所有用户id
*
* @param userId 用户id,中心点用户
* @param metre 距离,单位:米
* @return 附近的人
*/
@Override
public List<Long> queryNearUser(Long userId, Double metre) {
//1、根据用户id,查询用户的位置信息
Query query = Query.query(Criteria.where("userId").is(userId));
UserLocation location = mongoTemplate.findOne(query, UserLocation.class);
if (location == null) {
return null;
}
//2、以当前用户位置绘制原点
GeoJsonPoint point = location.getLocation();
//3、绘制半径
Distance distance = new Distance(metre / 1000, Metrics.KILOMETERS);
//5、构建查询对象
NearQuery nearQuery = NearQuery.near(point).maxDistance(distance);
//6、执行查询,由近到远排序
GeoResults<UserLocation> geoResults = mongoTemplate.geoNear(nearQuery, UserLocation.class);
//7、获取结果对象,其中userLocationGeoResult.getDistance()可以获取目标点与中心点的位置
return geoResults.getContent().stream()
.map(userLocationGeoResult -> userLocationGeoResult.getContent().getUserId())
.collect(Collectors.toList());
}- 用户下单后如何确定为其服务的快递员?
后台输入用户位置的坐标点,根据MongoDB进行多边形范围与坐标点交集的查询。从而匹配到对应的多边形范围的快递员id。
后台服务中,可以规划每个快递员或机构的多边形范围,存储入MongoDB数据库中。
- 作业范围如果不使用MongoDB,还可以使用其他技术实现吗?





















 520
520

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








