本文来源公众号“戎易大数据”,仅用于学术分享,侵权删,干货满满。
原文链接:https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/VyQwShDWd8lO35CQ-cL2zA
https://blog.youkuaiyun.com/csdn_xmj/article/details/151566419
篇幅略长,后续内容请看上一篇!
产品间供应链关系探索
6.1 特征工程
# 特征工程:产品是否接近过期(假设存活时间小于1年为接近过期)data['Near_Expiry'] = np.where(data['life_cycle'] < 365, 1, 0)# 特征工程:产品价格区间data['Price_Range'] = pd.cut(data['Price'], bins=[0, 100, 200, 300, 400, 500, np.inf],labels=['0-100', '100-200', '200-300', '300-400', '400-500', '500+'])# 特征工程:库存状态(高、中、低)data['Stock_Status'] = pd.qcut(data['Stock Quantity'], q=3, labels=['Low', 'Medium', 'High'])# 特征工程:产品类别编码category_mapping = {category: idx for idx, category in enumerate(data['Product Name'].unique())}data['Category_Code'] = data['Product Name'].map(category_mapping)
6.2 产品间关系分析
plt.figure(figsize=(25, 6))plt.subplot(1, 3, 1)# 类别分布分析category_distribution = data['Product Name'].value_counts().reset_index()category_distribution.columns = ['Product Name', 'Count']sns.barplot(x='Product Name', y='Count', data=category_distribution, palette='spring')plt.title('商品分布', fontsize=16)plt.xlabel('商品名称', fontsize=12)plt.ylabel('数量', fontsize=12)for p in plt.gca().patches:plt.gca().annotate(format(p.get_height(), '.0f'), (p.get_x() + p.get_width() / 2., p.get_height()), ha = 'center', va = 'center', xytext = (0, 5), textcoords = 'offset points')# 类别间价格比较plt.subplot(1, 3, 2)sns.boxplot(x='Product Name', y='Price', data=data, palette='summer')plt.title('不同商品价格分布', fontsize=16)plt.xlabel('商品名称', fontsize=12)plt.ylabel('价格', fontsize=12)# 类别间库存状态分析plt.subplot(1, 3, 3)sns.countplot(x='Product Name', hue='Stock_Status', data=data, palette='autumn')plt.title('不同商品库存状态分布', fontsize=16)plt.xlabel('商品名称', fontsize=12)plt.ylabel('数量', fontsize=12)for p in plt.gca().patches:plt.gca().annotate(format(p.get_height(), '.0f'), (p.get_x() + p.get_width() / 2., p.get_height()), ha = 'center', va = 'center', xytext = (0, 5), textcoords = 'offset points')plt.show()
输出:
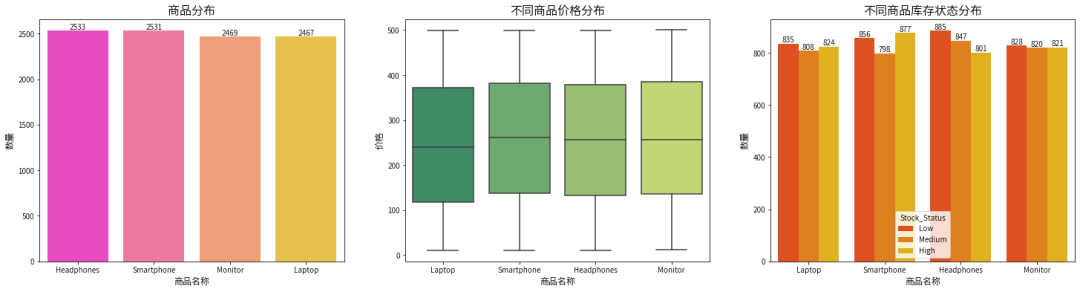
在低水平库存数量组别下,耳机以显著的库存优势位居首位。
中等水平库存数量组别中,耳机依然维持其领先地位。
高水平库存数量组别里,智能手机取代耳机成为排名第一的商品。
6.3 产品供应链时间维度分析
import matplotlib.dates as mdatesplt.figure(figsize=(20, 6))# 制造日期分布plt.subplot(1, 3, 1)plt.hist(data['Manufacturing Date'], bins=30, edgecolor='black')plt.title('生产日期分布', fontsize=16)plt.xlabel('生产日期', fontsize=12)plt.ylabel('数量', fontsize=12)plt.gca().xaxis.set_major_formatter(mdates.DateFormatter('%Y-%m')) # 设置日期显示格式# 过期日期分布plt.subplot(1, 3, 2)plt.hist(data['Expiration Date'], bins=30, edgecolor='black')plt.title('过期日期分布', fontsize=16)plt.xlabel('过期日期', fontsize=12)plt.ylabel('数量', fontsize=12)plt.gca().xaxis.set_major_formatter(mdates.DateFormatter('%Y-%m')) # 设置日期显示格式# 有效期分布plt.subplot(1, 3, 3)sns.distplot(data['life_cycle'], bins=30, kde=True)plt.title('商品有效期分布', fontsize=16)plt.xlabel('有效期(天)', fontsize=12)plt.ylabel('数量', fontsize=12)plt.tight_layout()plt.show()
输出:

生产日期最早的是2023年1月,最晚的是2023年8月
过期日期最早的是2024年1月,最晚的是2026年1月
# 过期产品分析near_expiry_products = data[data['Near_Expiry'] == 1]print(f"Number of products near expiry: {len(near_expiry_products)}")print(near_expiry_products[['Product Name', 'Product Category', 'Expiration Date', 'life_cycle']])
输出:
Number of products near expiry: 2183Product Name Product Category Expiration Date life_cycle10 Monitor Audio 2024-01-01 15511 Headphones Audio 2024-01-01 29215 Smartphone Mobile 2024-01-01 15522 Headphones Audio 2024-01-01 15523 Laptop Computer 2024-01-01 15525 Smartphone Mobile 2024-01-01 15526 Monitor Audio 2024-01-01 29228 Monitor Audio 2024-01-01 29232 Smartphone Mobile 2024-01-01 15533 Monitor Audio 2024-01-01 15534 Laptop Computer 2024-01-01 29237 Monitor Audio 2024-01-01 15542 Laptop Computer 2024-01-01 15544 Laptop Computer 2024-01-01 29249 Headphones Audio 2024-01-01 29257 Smartphone Mobile 2024-01-01 15559 Smartphone Mobile 2024-01-01 15565 Laptop Computer 2024-01-01 29275 Headphones Audio 2024-01-01 15576 Smartphone Mobile 2024-01-01 29277 Laptop Computer 2024-01-01 29279 Headphones Audio 2024-01-01 15589 Monitor Audio 2024-01-01 29295 Headphones Audio 2024-01-01 155100 Headphones Audio 2024-01-01 155101 Laptop Computer 2024-01-01 292103 Smartphone Mobile 2024-01-01 292104 Headphones Audio 2024-01-01 292107 Smartphone Mobile 2024-01-01 155110 Smartphone Mobile 2024-01-01 155... ... ... ... ...9854 Smartphone Mobile 2024-01-01 1559860 Smartphone Mobile 2024-01-01 1559862 Monitor Audio 2024-01-01 1559864 Monitor Audio 2024-01-01 1559865 Monitor Audio 2024-01-01 1559867 Headphones Audio 2024-01-01 1559874 Monitor Audio 2024-01-01 2929879 Smartphone Mobile 2024-01-01 1559883 Laptop Computer 2024-01-01 2929885 Headphones Audio 2024-01-01 1559887 Smartphone Mobile 2024-01-01 2929892 Smartphone Mobile 2024-01-01 1559893 Smartphone Mobile 2024-01-01 2929899 Monitor Audio 2024-01-01 1559900 Headphones Audio 2024-01-01 2929904 Monitor Audio 2024-01-01 2929905 Smartphone Mobile 2024-01-01 1559907 Laptop Computer 2024-01-01 2929908 Monitor Audio 2024-01-01 1559910 Monitor Audio 2024-01-01 1559915 Smartphone Mobile 2024-01-01 1559926 Headphones Audio 2024-01-01 1559930 Laptop Computer 2024-01-01 1559933 Smartphone Mobile 2024-01-01 1559940 Smartphone Mobile 2024-01-01 1559945 Monitor Audio 2024-01-01 2929947 Laptop Computer 2024-01-01 1559974 Laptop Computer 2024-01-01 1559988 Headphones Audio 2024-01-01 1559993 Smartphone Mobile 2024-01-01 292[2183 rows x 4 columns]
6.4 产品价格与库存关系分析
# 价格与库存散点图plt.figure(figsize=(20, 8))scatter_plot = sns.scatterplot(x='Price', y='Stock Quantity', hue='Product Name', data=data, alpha=0.6, palette='hsv')plt.title('价格与库存散点图', fontsize=16)plt.xlabel('价格', fontsize=12)plt.ylabel('库存数量', fontsize=12)plt.legend(bbox_to_anchor=(1.05, 1), loc='upper left', title='产品名称')plt.show()
输出:
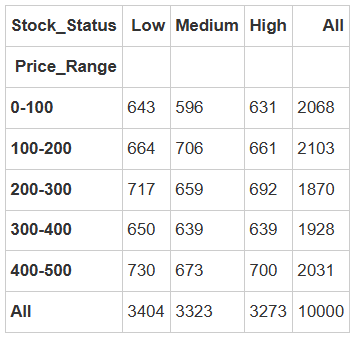
price_stock_table = pd.crosstab(data['Price_Range'], data['Stock_Status'], margins=True)price_stock_table
输出:
price_stock_table = price_stock_table.iloc[:-1] # 去掉总计行price_stock_table.plot(kind='bar', stacked=True, figsize=(20, 6), cmap='tab10')plt.title('价格区间与库存状态交叉分析', fontsize=16)plt.xlabel('价格区间', fontsize=12)plt.ylabel('库存状态数量', fontsize=12)plt.xticks(rotation=0)plt.tight_layout()plt.show()
输出:
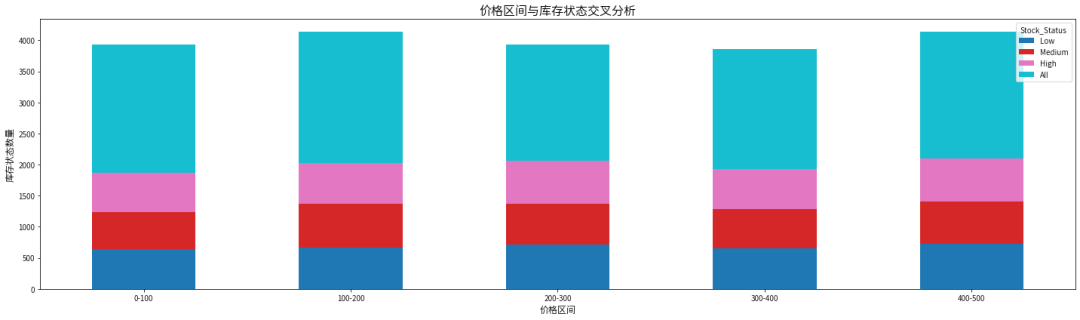
低库存状态
低库存状态下,商品总数为 3404 件,占总商品数(10000 件)的 34.04%。这表明有较大比例的商品处于库存紧张状态,需重点关注此类商品的供应链补货效率和市场需求响应速度。
价格区间分布差异:在价格区间 400 - 500 内,低库存商品数量最多,达 730 件。
中等库存状态
中等库存状态下,商品总数为 3323 件,占比 33.23%。这一库存水平的商品处于相对较为理想的状态,既能满足日常市场需求,又避免了过高库存带来的成本压力。
价格区间分布特征 :价格区间 100 - 200 内中等库存商品数量最多,达 706 件。
高库存状态
高库存状态下,商品总数为 3273 件,占比 32.73%。这类商品占比较高,可能面临库存积压风险,增加了企业的仓储成本和资金占用压力,需要深入分析其滞销原因并制定针对性的促销或库存处理策略。
价格区间分布差异 :价格区间 400 - 500 内高库存商品数量相对较多,达 700 件。
6.5 产品评分与供应链关系分析
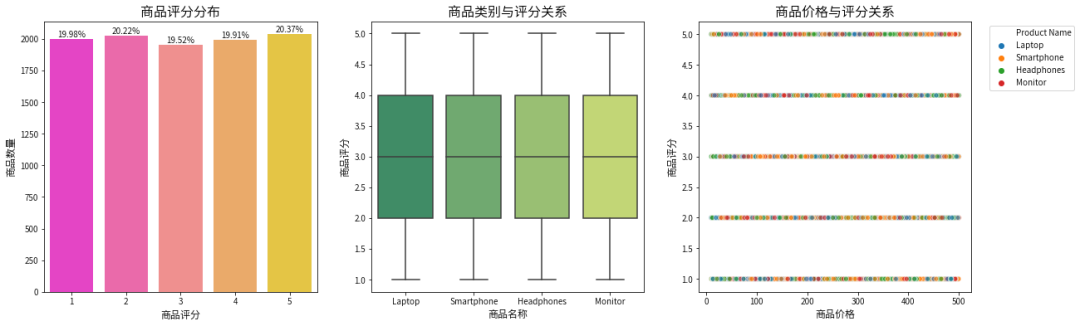
plt.figure(figsize=(20, 6))# 产品评分分布plt.subplot(1, 3, 1)sns.countplot(x='Product Ratings', data=data,palette='spring')plt.title('商品评分分布', fontsize=16)plt.xlabel('商品评分', fontsize=12)plt.ylabel('商品数量', fontsize=12)for p in plt.gca().patches:height = p.get_height()plt.text(p.get_x() + p.get_width() / 2, height + 5, '{:1.2f}%'.format(height / len(data) * 100), ha='center', va='bottom')# 评分与类别关系plt.subplot(1, 3, 2)sns.boxplot(x='Product Name', y='Product Ratings', data=data,palette='summer')plt.title('商品类别与评分关系', fontsize=16)plt.xlabel('商品名称', fontsize=12)plt.ylabel('商品评分', fontsize=12)# 评分与价格关系plt.subplot(1, 3, 3)sns.scatterplot(x='Price', y='Product Ratings', hue='Product Name', data=data, alpha=0.6)plt.title('商品价格与评分关系', fontsize=16)plt.xlabel('商品价格', fontsize=12)plt.ylabel('商品评分', fontsize=12)plt.legend(bbox_to_anchor=(1.05, 1), loc='upper left')plt.show()
输出:
6.6 产品属性关联分析
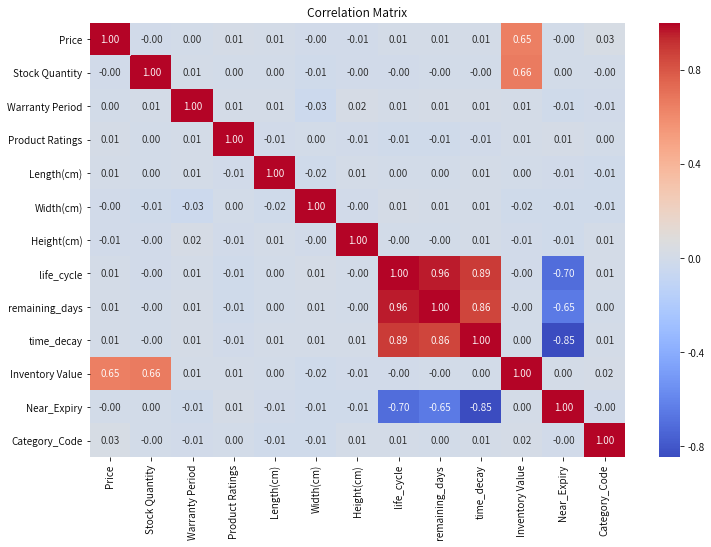
# 相关性矩阵features = data.select_dtypes(include=['int64', 'float64']).columnscorrelation_matrix = data[features].corr()plt.figure(figsize=(12, 8))sns.heatmap(correlation_matrix, annot=True, cmap='coolwarm', fmt='.2f')plt.title('Correlation Matrix')plt.show()
输出:
from mlxtend.preprocessing import TransactionEncoderfrom mlxtend.frequent_patterns import apriori, association_rules# 创建事务数据集(示例:将产品属性组合成事务)product_attributes = data[['Product Name', 'Price_Range', 'Stock_Status', 'Near_Expiry']].copy()# 将分类变量转换为哑变量product_attributes = pd.get_dummies(product_attributes, columns=['Product Name', 'Price_Range', 'Stock_Status'])# 将数据转换为事务格式transactions = product_attributes.values.tolist()# 应用Apriori算法te = TransactionEncoder()te_ary = te.fit(transactions).transform(transactions)df_transactions = pd.DataFrame(te_ary, columns=te.columns_)frequent_itemsets = apriori(df_transactions, min_support=0.01, use_colnames=True)# 修复关联规则生成部分rules = association_rules(frequent_itemsets, metric='lift', min_threshold=1)print(rules[['antecedents', 'consequents', 'support', 'confidence', 'lift']].head(20))
输出:
antecedents consequents support confidence lift0 (0) (1) 1.0 1.0 1.01 (1) (0) 1.0 1.0 1.0
结果表明,在这个数据集中,0 和 1 是完全相关的,每个事务同时包含这两个属性。这可能是因为数据中存在冗余或者重复的属性,或者是数据集结构过于简单,导致所有事务都包含相同的属性组合。
简易智能库存管理系统构建
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegressionimport datetime# 数据层 - 加载产品数据class ProductDatabase:def __init__(self, file_path):self.data = pd.read_csv(file_path)def get_product_by_id(self, product_id):return self.data[self.data['Product ID'] == product_id].iloc[0]def update_stock(self, product_id, new_stock):self.data.loc[self.data['Product ID'] == product_id, 'Stock Quantity'] = new_stockdef save_to_file(self, file_path):self.data.to_csv(file_path, index=False)# 业务逻辑层 - 库存管理class InventoryManager:def __init__(self, product_db):self.product_db = product_dbdef update_stock(self, product_id, quantity_change):product = self.product_db.get_product_by_id(product_id)new_stock = product['Stock Quantity'] + quantity_changeself.product_db.update_stock(product_id, new_stock)return new_stockdef predict_demand(self, product_id, days=30):# 简单的线性回归预测示例# 实际应用中需要更复杂的时间序列模型product = self.product_db.get_product_by_id(product_id)# 假设销售记录存储在另一个数据结构中sales_data = pd.DataFrame({'date': pd.date_range(end=datetime.datetime.now(), periods=30),'sales': [product['Stock Quantity'] - i*2 for i in range(30)] # 示例数据})sales_data['day'] = sales_data['date'].dt.dayofyearX = sales_data[['day']]y = sales_data['sales']model = LinearRegression()model.fit(X, y)future_days = pd.date_range(start=datetime.datetime.now(), periods=days)future_df = pd.DataFrame({'day': future_days.dayofyear})predictions = model.predict(future_df)return predictionsdef reorder_suggestion(self, product_id):product = self.product_db.get_product_by_id(product_id)# 简单的补货逻辑if product['Stock Quantity'] < product['Stock Quantity'] * 0.2:return f"Suggest reorder {product['Product Name']}, current stock: {product['Stock Quantity']}"else:return f"No reorder needed for {product['Product Name']}, current stock: {product['Stock Quantity']}"# 应用层 - 用户界面class InventoryApp:def __init__(self):self.product_db = ProductDatabase('/home/mw/input/kucun8458/products.csv')self.inventory_manager = InventoryManager(self.product_db)def run(self):while True:print("\nInventory Management System")print("1. Update Stock")print("2. Predict Demand")print("3. Reorder Suggestion")print("4. Exit")choice = input("Enter your choice: ")if choice == '1':product_id = input("Enter Product ID: ")quantity = int(input("Enter quantity change: "))new_stock = self.inventory_manager.update_stock(product_id, quantity)print(f"Updated stock to {new_stock}")elif choice == '2':product_id = input("Enter Product ID: ")days = int(input("Enter days to predict: "))predictions = self.inventory_manager.predict_demand(product_id, days)print(f"Predicted demand for next {days} days: {predictions}")elif choice == '3':product_id = input("Enter Product ID: ")suggestion = self.inventory_manager.reorder_suggestion(product_id)print(suggestion)elif choice == '4':self.product_db.save_to_file('/home/mw/input/kucun8458/products.csv')print("Exiting...")breakif __name__ == "__main__":app = InventoryApp()app.run()
输出:
Inventory Management System1. Update Stock2. Predict Demand3. Reorder Suggestion4. ExitUpdated stock to 303Inventory Management System1. Update Stock2. Predict Demand3. Reorder Suggestion4. ExitPredicted demand for next 7 days: [245. 243. 241. 239. 237. 235. 233.]Inventory Management System1. Update Stock2. Predict Demand3. Reorder Suggestion4. ExitExiting...
案例来源:
https://www.heywhale.com/mw/project/6809940c7129c4c8a5f1492c
THE END !
文章结束,感谢阅读。您的点赞,收藏,评论是我继续更新的动力。大家有推荐的公众号可以评论区留言,共同学习,一起进步。























 2004
2004

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








