本文利用matlab进行了直线阵列天线的低副瓣方向图综合仿真实验。主要利用到了Matlab工具箱里面的遗传算法以及粒子群算法。为了比较方向图结果,也用到了泰勒综合法以及切比雪夫综合法进行方向图综合
主要物理参数及变量说明
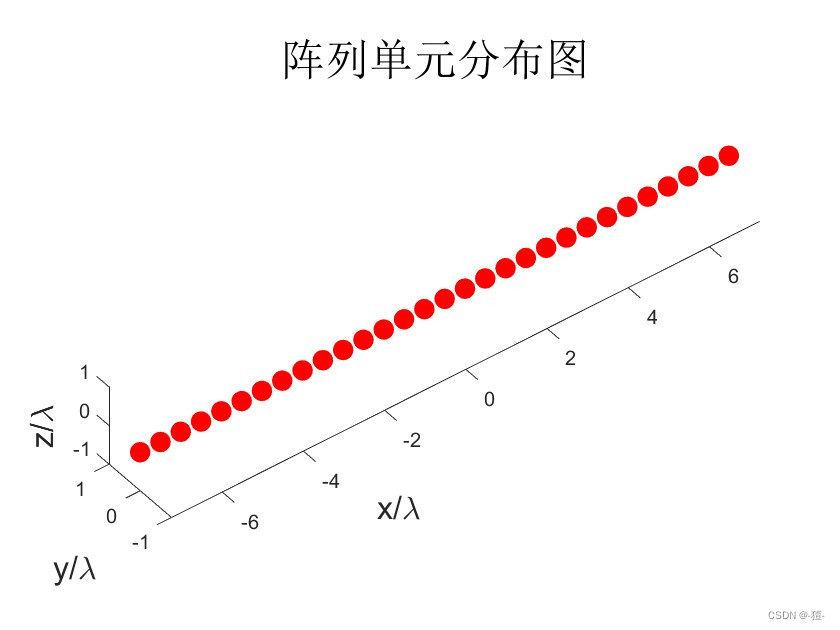
单元数量及排布: 30个全向单元(Nantenna值可以修改),沿着x轴方向分布,单元间距0.5倍波长
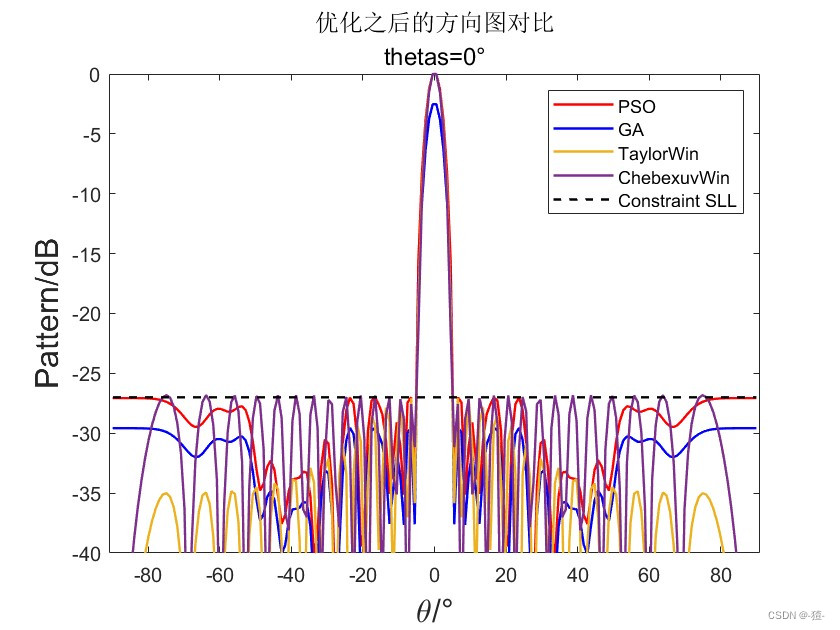
副瓣电平约束: SLL dB=-30dB(可以修改)
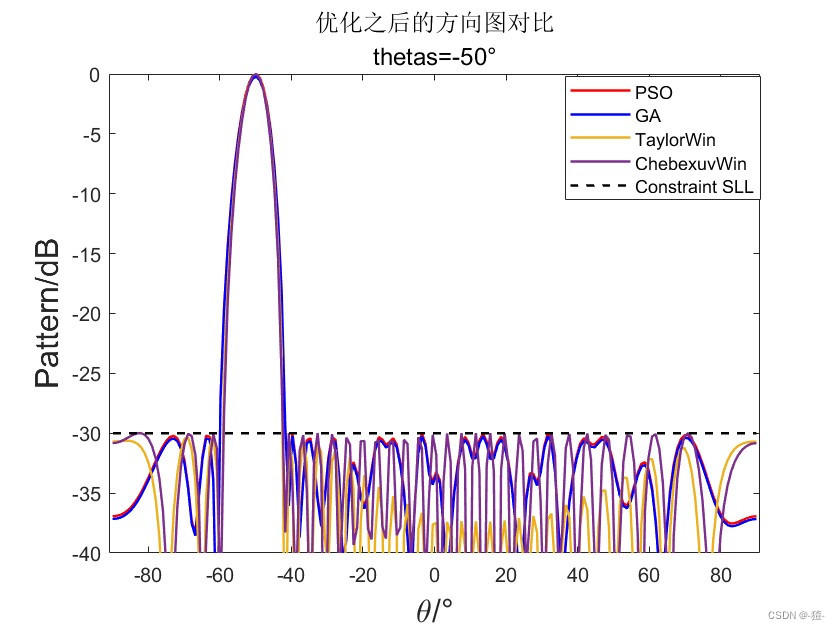
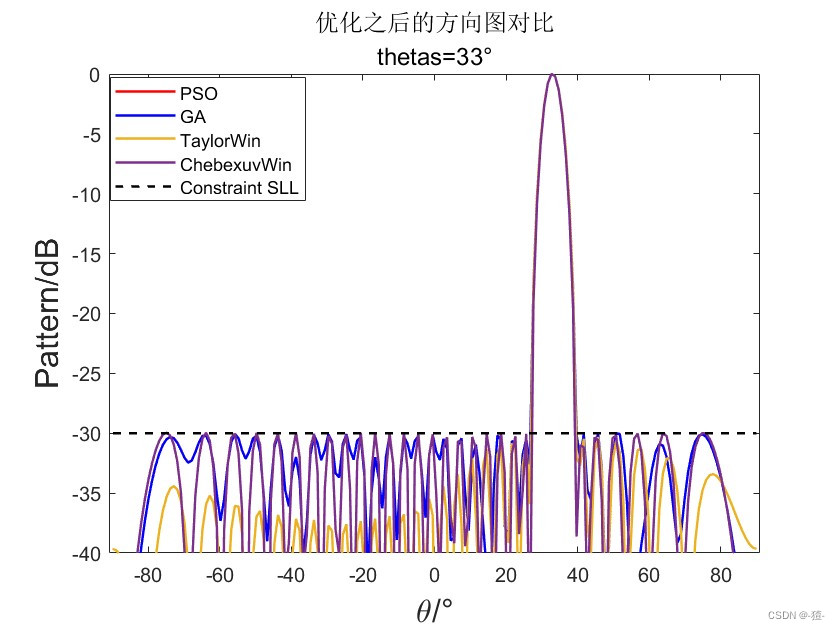
扫描角度: thetas可以取值-50°-50°(不起波束恶化)
算法参数: 种群规模,迭代次数,变异概率等等可以酌情修改(依托于Matlab自带工具箱)
仿真结果
主程序代码:
%程序功能:遗传算法和粒子群算法直线阵低副瓣方向图综合
%AUthor>> xtang225@foxmail.com
clc ;clear all;close all;
global SLL_dB SLL;
global AF;
global expphase0;
global widtheta theta side_flag scan_index;;
%%
lambda=1;
k=2*pi/lambda;
dx=0.5*lambda;
Np=180;%方向图采点数
theta=deg2rad(linspace(-90,90,Np));
thetas=deg2rad(0);%scannin angle
widtheta=deg2rad(6);%主瓣宽度,可以调整
SLL_dB=-27;%可以修改
SLL=10^(SLL_dB/20);
%% 生成阵列
Nantenna=30;
xx=linspace(-0.5*(Nantenna-1)*dx,0.5*(Nantenna-1)*dx,Nantenna);
zz=zeros(Nantenna,1);
yy=zeros(Nantenna,1);
plot3(xx/lambda,yy/lambda,zz/lambda,'.','MarkerSize',35,'Color','red');
xlabel('x/\lambda','FontSize',16);
ylabel('y/\lambda','FontSize',16);
zlabel('z/\lambda','FontSize',16);
title('阵列单元分布图','FontSize',22)
axis equal;
%% 计算阵列因子
AF=zeros(Np,Nantenna);%每一列存储一个天线的导向矢量
for n=1:Nantenna
xn=xx(n);yn=yy(n);zn=zz(n);
AF(:,n)=exp(1j*k*xn*sin(theta));
end
%% 确定主瓣副瓣区域
side_flag=zeros(Np,1);
[~,scan_index]=min(abs(theta-thetas));%扫描方向对应的索引值
for ind=1:Np
if(abs(theta(ind)-thetas)>widtheta)
side_flag(ind)=1;
end
end
%% 计算初始的移相值,根据波束扫描公式计算初始移相值
expphase0=zeros(Nantenna,1);
for n=1:Nantenna
xn=xx(n);yn=yy(n);zn=zz(n);
expphase0(n)=exp(-1j*k*xn*sin(thetas));
end
%
%% 利用遗传算法来进行低副瓣
choice=1;%选择优化算法
% rng(2024);% 设置种子以便复现结果
Nvars=Nantenna;%粒子群优化的变量个数,
down= -1*ones(1,Nvars);%变量下限都为-1
up=ones(1,Nvars);%变量上限都为1
X=rand(1,Nvars);
%粒子群算法
options1= optimoptions('particleswarm', ...
'PlotFcn','pswplotbestf', ...
'SwarmSize',100, ...
'HybridFcn', @fmincon, ...
'MaxStallIterations',20);
x_pso=particleswarm(@Linearfitness,Nvars,down,up,options1) ;
%遗传算法
options2 = optimoptions('ga', ...
'MaxGenerations', 600, ... % 最大迭代次数
'PopulationSize', 100, ... % 种群大小
'MutationFcn', {@mutationadaptfeasible, 0.05}, ... % 变异函数
'CrossoverFraction', 0.8, ... % 交叉概率
'SelectionFcn', @selectionroulette, ... % 选择函数
'PlotFcn', {@gaplotbestf, @gaplotstopping}); % 绘图函数
x_ga=ga(@Linearfitness,Nantenna, [], [], [], [], down, up, [], options2);
%% 优化之后的结果可视化
% 利用泰勒分布和切比雪夫分布
Amp_taylor=taylorwin(Nantenna,6,SLL_dB);
Pha_taylor=angle(expphase0);
Amp_cheb=chebwin(Nantenna,-SLL_dB);%转置?
Pha_cheb=angle(expphase0);
Amp_pso=(x_pso./max(abs(x_pso)))';%对优化之后的幅度进行归一化处理
Pha_pso=angle(expphase0);
S_pso_abs=abs(AF*(Amp_pso.*exp(1j*Pha_pso)));
S_max=max(S_pso_abs);
S_pso_norm=S_pso_abs/S_max;
S_pso_dB=20*log10(S_pso_norm);
Amp_ga=(x_ga./max(abs(x_ga)))';
Pha_ga=angle(expphase0);
S_ga_abs=abs(AF*(Amp_ga.*exp(1j*Pha_ga)));
S_max=max(S_ga_abs);
S_ga_norm=S_pso_abs/S_max;
S_ga_dB=20*log10(S_ga_norm);
S_taylor_abs=abs(AF*(Amp_taylor.*exp(1j*Pha_taylor)));
S_max=max(S_taylor_abs);
S_taylor_norm=S_taylor_abs/S_max;
S_taylor_dB=20*log10(S_taylor_norm);
S_cheb_abs=abs(AF*(Amp_cheb.*exp(1j*Pha_cheb)));
S_max=max(S_cheb_abs);
S_cheb_norm=S_cheb_abs/S_max;
S_cheb_dB=20*log10(S_cheb_norm);
figure()
plot(rad2deg(theta),S_pso_dB,'LineWidth',1.2,'color','red');hold on
plot(rad2deg(theta),S_ga_dB,'LineWidth',1.2,'color','blue');hold on
plot(rad2deg(theta),S_taylor_dB,'LineWidth',1.2);hold on
plot(rad2deg(theta),S_cheb_dB,'LineWidth',1.2);hold on
plot(rad2deg(theta),SLL_dB*ones(1,Np),'--','LineWidth',1.2,'Color','black');hold on
xlabel('\theta/°','FontSize',16);ylabel('Pattern/dB','FontSize',16);
title({['优化之后的方向图对比']},{['thetas=',num2str(rad2deg(thetas)),'°']},'FontSize',12);
legend('PSO','GA','TaylorWin','ChebexuvWin','Constraint SLL')
xlim([-91,91]);
ylim([-40,0])
%%
disp('程序运行结束!')
适应度函数代码
选则副瓣电平的最大值与设定的电平值之间的误差值作为目标函数,整个优化过程对目标函数进行极小化,即让峰值副瓣电平值被压到和设定的电平值最接近
function value=Linearfitness(X)
%程序功能:计算线阵低副瓣的适应读函数
%%
global SLL_dB SLL;
global AF;
global expphase0;
global widtheta theta side_flag scan_index;
%
w0=X';%转成列向量
w=w0.*expphase0;%复数权值
%%
S_abs=abs(AF*w);
S_max=max(S_abs);
S_norm=S_abs./S_max;
S_dB=20*log10(S_norm);
temp1=1-S_norm(scan_index);%控制主瓣在扫描的方向
%找到副瓣的电平峰值
side_index=find(side_flag==1);%将副瓣的索引提取出来
side_pattern=S_norm(side_index,1);
%利用对数值来计算
temp1=0-S_dB(scan_index);%控制主瓣在扫描的方向
%找到副瓣的电平峰值
side_index=find(side_flag==1);%将副瓣的索引提取出来
side_pattern_dB=S_dB(side_index,1);
[mSLL_dB,~]=max(side_pattern_dB);%最大的副瓣电平
maxSLL=mSLL_dB(1);%防止有多个最大值
value=abs(mSLL_dB-SLL_dB);
%%
end
本文程序仅作为公众号的读者学习参考,不宜用于其他途径!





















 238
238

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








