4. Experiments(实验)

A. 段落分解和分析
逐句分析:
[句子1]
-
原文:We evaluate TimeSformer on four popular action recognition datasets: Kinetics-400 (Carreira & Zisserman, 2017), Kinetics-600 (Carreira et al., 2018), Something-SomethingV2 (Goyal et al., 2017b), and Diving-48 (Li et al., 2018).
-
翻译:我们在四个流行的动作识别数据集上评估TimeSformer:Kinetics-400(Carreira & Zisserman,2017)、Kinetics-600(Carreira等,2018)、Something-SomethingV2(Goyal等,2017b)和Diving-48(Li等,2018)。
-
解释:
- 句子结构:复合句,列举评估数据集
- 与上下文关系:说明实验设置的数据集选择
[句子2]
-
原文:We adopt the “Base” ViT architecture (Dosovitskiy et al., 2020) pretrained on ImageNet-1K or ImageNet-21K (Deng et al., 2009), as specified for each experiment.
-
翻译:根据每个实验的具体配置,我们采用了在ImageNet-1K/ImageNet-21K上预训练的"Base" ViT架构
-
解释:
- 句子结构:复合句,说明预训练设置
- 与上下文关系:说明使用的预训练模型
[句子3]
-
原文:Unless differently indicated, we use clips of size 8 × 224 × 224, with frames sampled at a rate of 1/32.
-
翻译:除非另有说明,我们使用大小为8 × 224 × 224的片段,帧采样率为1/32。
-
解释:
这里的8×224×224描述了视频处理的具体参数:在时序维度上,以1/32的采样率(即每32帧取1帧)采样8帧组成一个时序片段,每帧的空间尺寸为224×224像素。以30fps的视频为例,如果你的动作都是1s出头的,那么你采用和论文一样的采样率的话,基本你的一个视频就会变成一张图片了,就失去使用这种视频理解模型的意义了。这种采样方式对于Kinetics这样的长动作数据集较为适用,但对于Something-Something这类短动作数据集可能会错过关键动作信息,因此如果读者你的数据集是一个更短的任务,要注意你的帧采样率的选择。虽然我体验下来,更高的采样率,没有提升性能特别明显,但是太少了肯定是不行的,要结合你具体的任务来看。短动作数据集通常需要更密集的采样率(如1/4或1/8)来确保捕捉完整的动作细节。
[句子4]
-
原文:The patch size is 16 × 16 pixels.
-
翻译:patch大小为16 × 16像素。
-
解释:
- 重点词汇:patch size(patch大小)
- 这里遵循了ViT的设计理念:
- 将图像分割成固定大小的patch
- 每个224×224的帧被划分为14×14个patch(224/16=14)
- 每个patch大小为16×16像素
- 因此对于一个8帧的视频片段:
- 每帧会得到14×14=196个patch
- 8帧总共会得到8×196=1568个patch
- 这些patch会作为Transformer的输入序列
- 与上下文关系:补充模型的输入设置
- 难点解释:指定了基本处理单元的大小
[句子5]
-
原文:During inference, unless otherwise noted, we sample a single temporal clip in the middle of the video.
-
翻译:在推理过程中,除非另有说明,我们在视频中间采样单个时间片段。
-
解释:
- 重点词汇:inference(推理), temporal clip(时间片段)
- 句子结构:复合句,说明推理阶段的采样策略
- 与上下文关系:说明测试时的具体操作
- 难点解释:指明了测试时的视频采样方式
[句子6]
-
原文:We use 3 spatial crops (top-left, center, bottom-right) from the temporal clip and obtain the final prediction by averaging the scores for these 3 crops.
-
翻译:我们从时间片段中使用3个空间裁剪(左上、中心、右下),并通过对这3个裁剪的分数取平均值得到最终预测。
-
解释:
- 重点词汇:spatial crops(空间裁剪), final prediction(最终预测)
- 句子结构:复合句,说明空间采样和预测方式
- 与上下文关系:完整描述了测试阶段的处理流程
- 难点解释:详细说明了空间采样策略和最终预测方法
B. 段落整体理解
段落主旨:
详细说明了TimeSformer模型的实验设置和评估方法。
核心要点:
- 使用四个主要动作识别数据集
- 基于预训练的ViT架构
- 详细的视频处理参数设置
- 具体的推理阶段测试策略
实验设置细节:
- 视频尺寸:8 × 224 × 224
- 采样率:1/32
- Patch大小:16 × 16
- 空间裁剪:3个位置
C. 专业知识拓展
术语解释:
- TimeSformer:基于Transformer的视频处理模型
- ViT:Vision Transformer,用于视觉任务的Transformer模型
- ImageNet:大规模图像分类数据集
- Temporal clip:时间维度上的视频片段
- Spatial crops:空间维度上的图像裁剪
4.1. Analysis of Self-Attention Schemes 1段

A. 段落分解和分析
逐句分析:
[句子1]
-
原文:For this first set of experiments we start from a ViT pretrained on ImageNet-21K.
-
翻译:对于第一组实验,我们从在ImageNet-21K上预训练的ViT开始。
-
解释:
- 重点词汇:pretrained ViT(预训练的ViT)
- 句子结构:简单句,说明实验起点
- 与上下文关系:引入实验设置
- 难点解释:说明了模型的预训练基础
[句子2]
-
原文:In Table 1, we present the results obtained with TimeSformer for the five proposed space-time attention schemes on Kinetics-400 (K400) and Something-Something-V2 (SSv2).
-
翻译:在表1中,我们展示了TimeSformer在Kinetics-400(K400)和Something-Something-V2(SSv2)上使用五种提出的时空注意力方案获得的结果。
-
解释:
- 重点词汇:space-time attention schemes(时空注意力方案)
- 句子结构:复合句,介绍实验结果展示
- 与上下文关系:引出具体实验结果
- 难点解释:说明了实验的具体内容和范围
[句子3-4]
-
原文:First, we note that TimeSformer with space-only attention (S) performs well on K400. This is an interesting finding.
-
翻译:首先,我们注意到仅使用空间注意力(S)的TimeSformer在K400上表现良好。这是一个有趣的发现。
-
解释:
- 重点词汇:space-only attention(仅空间注意力)
- 句子结构:两个简单句,说明重要发现
- 与上下文关系:指出首个重要实验结果
- 难点解释:强调了一个意外的实验发现
[句子5]
-
原文:Indeed, prior work (Sevilla-Lara et al., 2021) has shown that on K400, spatial cues are more important than temporal information in order to achieve strong accuracy.
-
翻译:事实上,先前的工作(Sevilla-Lara等,2021)已经表明,在K400上,为了获得高准确率,空间线索比时间信息更重要。
-
解释:
- 重点词汇:spatial cues(空间线索), temporal information(时间信息)
- 句子结构:复合句,引用先前研究结果
- 与上下文关系:解释实验发现的原因
- 难点解释:说明了结果的理论基础
[句子6-7]
-
原文:Here, we show that it is possible to obtain solid accuracy on K400 without any temporal modeling. Note, however, that space-only attention performs poorly on SSv2.
-
翻译:在这里,我们证明了不使用任何时间建模也能在K400上获得可靠的准确率。然而需要注意的是,仅空间注意力在SSv2上表现不佳。
-
解释:
- 重点词汇:temporal modeling(时间建模)
- 句子结构:两个对比句,说明方法的优缺点
- 与上下文关系:总结实验发现的意义
- 难点解释:强调了方法在不同数据集上的表现差异
[最后一句]
-
原文:This stresses the importance of temporal modeling on this latter dataset.
-
翻译:这强调了时间建模在后一个数据集上(指SSv2)的重要性。
-
解释:
- 重点词汇:temporal modeling(时间建模)
- 句子结构:简单句,得出结论
- 与上下文关系:总结实验启示
- 难点解释:指出了实验的重要结论
B. 段落整体理解
段落主旨:
分析不同自注意力方案在不同数据集上的表现及其原因。
核心要点:
- 仅空间注意力在K400上表现良好
- 空间线索在K400上比时间信息更重要
- 仅空间注意力在SSv2上表现不佳
- 不同数据集对时间建模的需求不同
实验发现:
- K400可以只依靠空间信息达到好结果
- SSv2需要时间信息才能实现好的性能
- 数据集特性决定了模型设计策略
4.1. Analysis of Self-Attention Schemes 2-3段

A. 段落分解和分析
逐句分析:
[句子1-2]
-
原文:Furthermore, we observe that divided space-time attention achieves the best accuracy on both K400 and SSv2. This makes sense because compared to joint space-time attention, divided space-time attention has a larger learning capacity (see Table 1) as it contains distinct learning parameters for temporal attention and spatial attention.
-
翻译:此外,我们观察到分离的时空注意力在K400和SSv2两个数据集上都达到了最佳准确率。这是合理的,因为与联合时空注意力相比,分离的时空注意力具有更大的学习容量(见表1),因为它为时间注意力和空间注意力分别包含不同的学习参数。
-
解释:
- learning capacity(学习容量):指模型捕获和学习复杂模式的能力,与参数数量、模型复杂度和可表示的函数空间大小相关。在这里,分离的时空注意力通过使用独立的参数处理时间和空间信息,增加了模型的表达能力。
- distinct learning parameters(独立学习参数):时间注意力和空间注意力分别使用独立的参数集合,而不是共享参数,这使得模型可以分别优化空间和时间两个维度的特征学习。
- 句子结构:复合句,先说明实验结果(分离时空注意力效果最好),然后解释原因(更大的学习容量)
- 与上下文关系:在前文分析不同注意力机制性能的基础上,深入解释为什么分离式设计更有优势
[句子3]
-
原文:In Figure 3, we also compare the computational cost of joint space-time versus divided space-time attention when using higher spatial resolution (left) and longer (right) videos.
-
翻译:在图3中,我们还比较了在使用更高空间分辨率(左)和更长(右)视频时,联合时空注意力与分离时空注意力的计算成本。
-
解释:
- 重点词汇:computational cost(计算成本), spatial resolution(空间分辨率)
- 句子结构:复合句,引入新的比较维度
- 与上下文关系:转向效率分析
- 难点解释:说明了实验的新维度
[句子4]
-
原文:We note that the scheme of divided space-time scales gracefully under both of these settings.
-
翻译:我们注意到分离时空方案在这两种设置下都能很好地扩展。
-
解释:
- 重点词汇:scales gracefully(良好扩展)
- 句子结构:简单句,说明实验结果
- 与上下文关系:指出分离方案的优势
- 难点解释:强调了方法的可扩展性
[句子5-6]
-
原文:In contrast, the scheme of joint space-time attention leads to a dramatically higher cost when resolution or video length is increased. In practice, joint space-time attention causes a GPU memory overflow once the spatial frame resolution reaches 448 pixels, or once the number of frames is increased to 32 and thus it is effectively not applicable to large frames or long videos.
-
翻译:相比之下,当分辨率或视频长度增加时,联合时空注意力方案会导致显著更高的成本。实际上,一旦空间帧分辨率达到448像素,或帧数增加到32,联合时空注意力就会导致GPU内存溢出,因此它实际上不适用于大尺寸帧或长视频。
-
解释:
- 重点词汇:GPU memory overflow(GPU内存溢出)
- 句子结构:复合句,说明联合方案的局限性
- 与上下文关系:对比说明联合方案的问题
- 难点解释:指出了具体的限制条件
[最后两句]
-
原文:Thus, despite a larger number of parameters, divided space-time attention is more efficient than joint space-time attention when operating on higher spatial resolution, or longer videos. Thus, for all subsequent experiments we use a TimeSformer constructed with divided space-time self-attention blocks.
-
翻译:因此,尽管参数数量更多,但在处理更高空间分辨率或更长视频时,分离时空注意力比联合时空注意力更有效率。因此,对于所有后续实验,我们使用由分离时空自注意力模块构建的TimeSformer。
-
解释:
- 重点词汇:parameters(参数), efficient(有效率)
- 句子结构:两个总结性句子
- 与上下文关系:总结分析并引出后续实验设置
- 难点解释:说明了最终的方法选择
B. 段落整体理解
段落主旨:
比较分离时空注意力和联合时空注意力的性能和效率差异。
核心要点:
- 分离时空注意力具有更大的学习容量
- 分离方案在高分辨率和长视频上扩展性更好
- 联合方案在处理大规模输入时存在内存限制
- 选择分离方案进行后续实验
比较维度:
- 准确率表现
- 计算效率
- 内存消耗
- 可扩展性
4.2 Comparison to 3D CNNs 1-2段

A. 段落分解和分析
[段落1 - 引言]
总句数:3
[句子1]
- 原文:In this subsection we perform an empirical study aimed at understanding the distinguishing properties of TimeSformer compared to 3D convolutional architectures, which have been the prominent approach to video understanding in recent years.
- 翻译:在本小节中,我们进行实证研究,旨在理解TimeSformer与3D卷积架构相比的区别特性,后者是近年来视频理解的主要方法。
- 解释:
- 重点词汇:empirical study(实证研究), 3D convolutional architectures(3D卷积架构)
- 句子结构:复合句,说明研究目的
- 与上下文关系:引出比较研究的主题
- 难点解释:介绍了研究背景和动机
[句子2-3]
- 原文:We focus our comparison on two 3D CNN models: 1) SlowFast (Feichtenhofer et al., 2019b), which is the state-of-the-art in video classification, and 2) I3D (Carreira & Zisserman, 2017), which has been shown to benefit from image-based pretraining, similarly to our own model.
- 翻译:我们将比较重点放在两个3D CNN模型上:1) SlowFast(Feichtenhofer等,2019b),这是视频分类的最先进模型,以及2) I3D(Carreira & Zisserman,2017),该模型已被证明能从基于图像的预训练中受益,这一点与我们的模型类似。
- 解释:
- 重点词汇:SlowFast, I3D, image-based pretraining(基于图像的预训练)
- 句子结构:并列句,介绍两个比较对象
- 与上下文关系:详细说明比较研究的具体对象
- 难点解释:解释了选择这两个模型的原因
[段落2 - 模型容量分析]
总句数:2
[句子1-2]
- 原文:From Table 2, we first observe that although TimeSformer has a large learning capacity (the number of parameters is 121.4M), it has low inference cost (0.59 in TFLOPs). In contrast, SlowFast 8x8 R50 has a larger inference cost (1.97 TFLOPs) despite containing only 34.6M parameters. Similarly, I3D 8x8 R50 also has a larger inference cost (1.11 TFLOPs) despite containing fewer parameters (28.0M).
- 翻译:从表2中,我们首先观察到,尽管TimeSformer具有较大的学习容量(参数数量为121.4M),但它的推理成本较低(0.59 TFLOPs)。相比之下,SlowFast 8x8 R50尽管只有34.6M参数,但具有更大的推理成本(1.97 TFLOPs)。同样,I3D 8x8 R50尽管参数更少(28.0M),但也具有更大的推理成本(1.11 TFLOPs)
4.2 Comparison to 3D CNNs 3段

A. 段落分解和分析
[句子1-2]
- 原文:One significant advantage of ImageNet pretraining is that it enables very efficient training of TimeSformer on video data. Conversely, state-of-the-art 3D CNNs are much more expensive to train even if pretrained on image datasets.
- 翻译:ImageNet预训练的一个显著优势是它能够使TimeSformer在视频数据上进行非常高效的训练。相反,即使在图像数据集上预训练,最先进的3D CNNs训练成本也要高得多。
- 解释:
- 重点词汇:ImageNet pretraining(ImageNet预训练), efficient training(高效训练)
- 句子结构:对比句,说明不同模型在训练效率上的差异
- 难点解释:解释了预训练对训练效率的影响
[句子3-5]
- 原文:In Table 2, we compare the video training time on Kinetics-400 (in Tesla V100 GPU hours) of TimeSformer to that of SlowFast and I3D. Starting from a ResNet50 pretrained on ImageNet-1K, SlowFast 8×8 R50 requires 3,840 Tesla V100 GPU hours in order to reach an accuracy of 75.6% on Kinetics-400. Training I3D, under similar settings, requires 1,440 Tesla V100 GPU hours for a 73.4% accuracy.
- 翻译:在表2中,我们比较了TimeSformer与SlowFast和I3D在Kinetics-400上的视频训练时间(以Tesla V100 GPU小时计)。从ImageNet-1K预训练的ResNet50开始,SlowFast 8×8 R50需要3,840个Tesla V100 GPU小时才能在Kinetics-400上达到75.6%的准确率。在类似设置下训练I3D需要1,440个Tesla V100 GPU小时才能达到73.4%的准确率。
- 解释:
- 重点词汇:GPU hours(GPU小时), accuracy(准确率)
- 句子结构:包含具体数据的对比说明
- 难点解释:通过具体数据展示不同模型的训练成本差异
[句子6-7]
- 原文:In contrast, TimeSformer, also pretrained on ImageNet-1K, only requires 416 Tesla V100 GPU hours to achieve a higher 75.8% accuracy (see Table 2). Furthermore, if we constrain SlowFast to be trained under a somewhat similar computational budget as TimeSformer (i.e., 448 GPU hours), its accuracy drops to 70.0%.
- 翻译:相比之下,同样在ImageNet-1K上预训练的TimeSformer只需要416个Tesla V100 GPU小时就能达到更高的75.8%准确率(见表2)。此外,如果我们限制SlowFast在与TimeSformer相似的计算预算下训练(即448 GPU小时),其准确率会下降到70.0%。
- 解释:
- 重点词汇:computational budget(计算预算)
- 句子结构:对比说明,突出TimeSformer的优势
- 难点解释:说明了在相同计算资源下的性能差异
[句子8-9]
- 原文:This highlights the fact that some of the latest 3D CNNs require a very long optimization schedule to achieve good performance (even when using ImageNet pretraining). In contrast, TimeSformer provides a more efficient alternative to labs that do not have access to hundreds of GPUs.
- 翻译:这凸显了一个事实,即一些最新的3D CNNs需要很长的优化周期才能达到良好的性能(即使使用ImageNet预训练)。相比之下,TimeSformer为那些无法访问数百个GPU的实验室提供了一个更高效的选择。
- 解释:
- 重点词汇:optimization schedule(优化周期)
- 句子结构:总结性陈述,说明实际应用意义
- 难点解释:点明了研究的实际价值
B. 段落整体理解
- 段落主旨:比较TimeSformer与传统3D CNNs在训练效率上的差异
- 核心要点:
- TimeSformer训练效率显著高于传统模型
- 在相同计算资源下,TimeSformer性能更优
- 对计算资源受限的场景更友好
C. 专业知识拓展
- 术语解释:
- ImageNet预训练:使用ImageNet数据集进行模型初始化训练
- Tesla V100:NVIDIA的高性能GPU
- GPU小时:衡量计算资源消耗的单位
- Kinetics-400:标准视频分类数据集
4.2 Comparison to 3D CNNs 4-5段

A. 段落分解和分析
[段落1]
总句数:4
[句子1-2]
- 原文:Due to a large number of parameters, training our model from scratch is difficult. Thus, before training TimeSformer on video data, we initialize it with weights learned from ImageNet.
- 翻译:由于参数量很大,从头训练我们的模型很困难。因此,在对视频数据训练TimeSformer之前,我们用从ImageNet学习的权重进行初始化。
- 解释:
- 重点词汇:from scratch(从头训练), initialize(初始化)
- 句子结构:因果关系句
- 难点解释:说明了使用预训练的必要性
[句子3]
- 原文:In contrast, SlowFast can be learned on video data from scratch although at the expense of a very high training cost (see Table 2).
- 翻译:相比之下,SlowFast可以直接在视频数据上从头训练,但代价是非常高的训练成本(见表2)。
- 解释:
- 重点词汇:training cost(训练成本)
- 句子结构:对比说明句
- 难点解释:突出不同模型在训练策略上的差异
[句子4]
- 原文:We also attempted to train TimeSformer on Kinetics-400 directly, without any ImageNet pretraining. By using a longer training schedule and more data augmentations, we found it possible to train the model from scratch, albeit to a much lower video level accuracy of 64.8%.
- 翻译:我们还尝试直接在Kinetics-400上训练TimeSformer,不使用任何ImageNet预训练。通过使用更长的训练周期和更多的数据增强,我们发现可以从头训练模型,但视频级准确率只有64.8%,明显较低。
- 解释:
- 重点词汇:data augmentations(数据增强)
- 句子结构:实验说明句
- 难点解释:通过实验数据说明预训练的重要性
[段落2]
总句数:2
[句子1-2]
- 原文:In Table 3 we study the benefits of ImageNet-1K vs ImageNet-21K pretraining on K400 and SSv2. For these experiments, we use three variants of our model: (1) TimeSformer, which is the default version of our model operating on 8×224×224 video clips, (2) TimeSformer-HR, a high spatial resolution variant that operates on 16×448×448 video clips, and lastly (3) TimeSformer-L, a long-range configuration of our model that operates on 96×224×224 video clips with frames sampled at a rate of 1/4.
- 翻译:在表3中,我们研究了ImageNet-1K与ImageNet-21K预训练在K400和SSv2上的优势。对于这些实验,我们使用了三种模型变体:(1) TimeSformer,是我们模型的默认版本,处理8×224×224的视频片段;(2) TimeSformer-HR,高空间分辨率变体,处理16×448×448的视频片段;最后是(3) TimeSformer-L,我们模型的长程配置,处理96×224×224的视频片段,帧采样率为1/4。
- 解释:
- 重点词汇:spatial resolution(空间分辨率), frame sampling rate(帧采样率)
- 句子结构:实验设置说明句
- 难点解释:详细说明了不同模型变体的配置
B. 段落整体理解
- 段落主旨:说明预训练对TimeSformer的重要性及不同预训练策略的比较
- 核心要点:
- 预训练对大参数量模型很重要
- 从头训练虽然可能但效果差
- 提供了三种不同的模型变体配置
C. 专业知识拓展
- 术语解释:
- ImageNet-1K:包含1000个类别的图像分类数据集
- ImageNet-21K:包含21,000个类别的更大规模图像数据集
- Data augmentations:数据增强技术,用于增加训练数据的多样性
- Model variants:不同配置的模型变体,针对不同应用场景
4.2 Comparison to 3D CNNs 6段

A. 段落分解和分析
[句子1]
- 原文:Based on the results in Table 3, we observe that ImageNet-21K pretraining is beneficial for K400, where it leads to a consistently higher accuracy compared to ImageNet-1K pretraining.
- 翻译:基于表3的结果,我们观察到ImageNet-21K预训练对K400有益,与ImageNet-1K预训练相比,它能持续带来更高的准确率。
- 解释:
- 重点词汇:consistently higher accuracy(持续更高的准确率)
- 句子结构:观察结果陈述句
- 与上下文关系:引出主要发现
- 难点解释:说明更大规模预训练数据集的优势
[句子2]
- 原文:On the other hand, on SSv2, we observe that ImageNet-1K and ImageNet-21K pretrainings lead to similar accuracy.
- 翻译:另一方面,在SSv2上,我们观察到ImageNet-1K和ImageNet-21K预训练带来了相似的准确率。
- 解释:
- 重点词汇:similar accuracy(相似的准确率)
- 句子结构:对比说明句
- 与上下文关系:提供对比观察
- 难点解释:指出在不同数据集上的表现差异
[句子3]
- 原文:This makes sense as SSv2 requires complex spatiotemporal reasoning, whereas K400 is biased more towards spatial scene information, and thus, it benefits more from the features learned on the larger pretraining dataset.
- 翻译:这是合理的,因为SSv2需要复杂的时空推理,而K400更偏向于空间场景信息,因此它从更大的预训练数据集中学习到的特征中获益更多。
- 解释:
- 重点词汇:
- spatiotemporal reasoning(时空推理)
- spatial scene information(空间场景信息)
- 句子结构:因果解释句
- 与上下文关系:解释观察到的现象
- 难点解释:分析了不同数据集特性对预训练效果的影响
- 重点词汇:
B. 段落整体理解
- 段落主旨:分析不同规模ImageNet预训练在不同数据集上的效果差异
- 核心要点:
- ImageNet-21K预训练在K400上效果更好
- 在SSv2上两种预训练效果相似
- 数据集特性影响预训练效果
C. 专业知识拓展
-
术语解释:
- ImageNet-21K:包含21,000个类别的大规模图像数据集
- ImageNet-1K:包含1,000个类别的标准图像数据集
- K400 (Kinetics-400):侧重动作识别的视频数据集
- SSv2 (Something-Something-V2):侧重时空关系理解的视频数据集
- Spatiotemporal reasoning:时空推理能力,理解视频中动作和物体之间的时空关系
-
背景信息:
- 不同视频数据集关注不同的视觉理解任务
- 预训练数据集的规模和特性会影响模型性能
4.2 Comparison to 3D CNNs 7段

A. 段落分解和分析
[句子1]
- 原文:To understand the effects of video-data scale on performance, we trained TimeSformer on different subsets of K400 and SSv2: {25%, 50%, 75%, 100%} of the full datasets.
- 翻译:为了理解视频数据规模对性能的影响,我们在K400和SSv2的不同子集上训练TimeSformer:使用完整数据集的{25%、50%、75%、100%}。
- 解释:
- 重点词汇:video-data scale(视频数据规模), subsets(子集)
- 句子结构:实验设置说明句
- 难点解释:说明了实验的具体设置方法
[句子2]
- 原文:We show these results in Figure 4, where we also compare our method with SlowFast R50 (Feichtenhofer et al., 2019b), and I3D R50 (Carreira & Zisserman, 2017) trained on the same subsets and using the same pretraining.
- 翻译:我们在图4中展示了这些结果,其中我们还将我们的方法与在相同子集上训练且使用相同预训练的SlowFast R50和I3D R50进行了比较。
- 解释:
- 重点词汇:same pretraining(相同预训练)
- 句子结构:实验对比说明句
- 难点解释:指出了实验的对比基准
[段落2 - 结果分析]
总句数:2
[句子3-4]
- 原文:The results of Figure 4 show that, on K400, TimeSformer outperforms the other models for all training subsets. However, we observe a different trend on SSv2, where TimeSformer is the strongest model only when trained on 75% or 100% of the full data.
- 翻译:图4的结果显示,在K400上,TimeSformer在所有训练子集上都优于其他模型。但是,在SSv2上我们观察到不同的趋势,TimeSformer只有在使用75%或100%的完整数据训练时才是最强的模型。
- 解释:
- 重点词汇:outperforms(优于), different trend(不同趋势)
- 句子结构:对比说明句
- 难点解释:说明了不同数据集上的表现差异
[句子5]
- 原文:This may be explained by the fact that compared to K400, SSv2 requires learning more complex temporal patterns, and thus more examples are needed by TimeSformer to learn effectively those patterns.
- 翻译:这可能是因为与K400相比,SSv2需要学习更复杂的时序模式,因此TimeSformer需要更多的样本才能有效地学习这些模式。
- 解释:
- 重点词汇:temporal patterns(时序模式)
- 句子结构:解释说明句
- 难点解释:分析了性能差异的原因
B. 段落整体理解
- 段落主旨:研究数据规模对模型性能的影响
- 核心要点:
- 在不同数据规模下进行了对比实验
- K400和SSv2上表现出不同的趋势
- 数据集特性影响所需的训练数据量
C. 专业知识拓展
-
术语解释:
- K400:Kinetics-400数据集,主要用于动作识别
- SSv2:Something-Something-V2数据集,关注复杂时序关系
- Temporal patterns:时序模式,视频中的时间相关特征
- Data scale:数据规模,训练数据的数量
-
实验设计要点:
- 使用相同的预训练条件
- 统一的数据子集划分
- 多个基准模型对比
4.3. Varying the Number of Tokens

- 原文:The scalability of our model allows it to operate at higher spatial resolution and on longer videos compared to most 3D CNNs. We note that both of these aspects affect the length of the sequence of tokens fed to the Transformer.
- 翻译:与大多数3D CNNs相比,我们模型的可扩展性使其能够在更高的空间分辨率和更长的视频上运行。我们注意到,这两个方面都会影响输入到Transformer的令牌序列长度。
- 解释:
这里理解起来有点抽象,TimeSformer 模型的核心是将输入视频转换为 token 序列再输入 Transformer 处理。具体来说,视频中的每一帧都被划分为固定大小(如 16×16 像素)的 patches,每个 patch 经过线性投影后转换为一个 token。因此视频输入会生成 (H×W)/(P×P) × T + 1 个 token(其中 H,W 是帧的分辨率,P 是 patch 大小,T 是帧数,+1 是 CLS token)。
当空间分辨率提高时(比如从 224×224 变为 448×448),每一帧会产生更多的 patches,从而产生更多的 token;同样,当视频变长时(比如从 8 帧增加到 32 帧),需要处理的帧数增加,token 数量也会相应增加。这就解释了为什么这两个因素都会影响输入到 Transformer 的序列长度。
考虑到 Transformer 的计算复杂度是序列长度的平方级别 O(n²),序列长度的增加会显著影响计算开销。但 TimeSformer 通过其创新的注意力机制设计,使其能够高效处理这些更长的序列,从而实现了在更高分辨率和更长视频上的可扩展性。
[句子3-4]
- 原文:Specifically, increasing the spatial resolution results in a higher number of patches (N) per frame. The number of input tokens is also increased when using more frames.
- 翻译:具体来说,增加空间分辨率会导致每帧的图像块(N)数量增加。当使用更多帧时,输入令牌的数量也会增加。
- 解释:
- 重点词汇:patches(图像块), input tokens(输入令牌)
- 句子结构:细节说明句
- 难点解释:解释了两个维度对输入规模的影响
[句子5]
- 原文:To investigate the benefits, we conduct an empirical study where we separately increase the number of tokens along each of these two axes.
- 翻译:为了研究这些好处,我们进行了实证研究,分别沿着这两个轴增加令牌数量。
- 解释:
- 重点词汇:empirical study(实证研究)
- 句子结构:研究方法说明句
- 难点解释:说明研究设计
[句子6-7]
- 原文:We report the findings in Figure 5. We see that increasing the spatial resolution (up to a certain point) leads to a boost in performance.
- 翻译:我们在图5中报告了发现。我们看到增加空间分辨率(到某个程度)会导致性能提升。
- 解释:
- 重点词汇:boost in performance(性能提升)
- 句子结构:研究结果说明句
- 难点解释:指出空间分辨率的影响
[句子8-10]
- 原文:Similarly, we observe that increasing the length of the input clip leads to consistent accuracy gains. Due to GPU memory constraints, we are not able to test our model on clips longer than 96 frames. Still, we would like to point out that using clips of 96 frames is a significant departure from current convolutional models, which are typically limited to processing inputs of 8-32 frames.
- 翻译:同样,我们观察到增加输入片段的长度会带来持续的准确率提升。由于GPU内存限制,我们无法在超过96帧的片段上测试我们的模型。尽管如此,我们想指出,使用96帧的片段相比当前的卷积模型是一个重大突破,因为后者通常仅限于处理8-32帧的输入。
- 解释:
- 重点词汇:GPU memory constraints(GPU内存限制)
- 句子结构:限制和优势对比说明句
- 难点解释:说明了研究的局限性和重要性
B. 段落整体理解
- 段落主旨:分析模型在空间和时间维度上的可扩展性
- 核心要点:
- 可以处理更高分辨率和更长视频
- 两个维度的扩展都带来性能提升
- 96帧处理能力远超传统模型
C. 专业知识拓展
- 术语解释:
- Spatial resolution:空间分辨率,图像的细节程度
- Tokens:Transformer模型的输入单位
- Patches:图像被分割成的小块
- GPU memory constraints:GPU内存限制,硬件资源约束
- Input sequence length:输入序列长度,影响模型处理能力
4.4. The Importance of Positional Embeddings

A. 段落分解和分析
[句子1-2]
- 原文:To investigate the importance of our learned spatiotemporal positional embeddings, we also conduct experiments with a few variants of TimeSformer that use: (1) no positional embedding, (2) space-only positional embedding, and (3) space-time positional embedding.
- 翻译:为了研究学习到的时空位置嵌入的重要性,我们还对TimeSformer的几个变体进行了实验,这些变体分别使用:(1)无位置嵌入,(2)仅空间位置嵌入,(3)时空位置嵌入。
- 解释:
- 重点词汇:
- spatiotemporal positional embeddings(时空位置嵌入)
- variants(变体)
- 句子结构:实验设置说明句
- 难点解释:说明了不同的位置嵌入方式
- 重点词汇:
[句子3]
- 原文:We report these results in Table 4.
- 翻译:我们在表4中报告这些结果。
- 解释:
- 句子结构:过渡句
- 与上下文关系:引出结果分析
[句子4]
- 原文:Based on these results, we observe that the variant of our model that uses space-time positional embeddings produces the best accuracy on both Kinetics-400, and Something-Something-V2.
- 翻译:基于这些结果,我们观察到使用时空位置嵌入的模型变体在Kinetics-400和Something-Something-V2上都产生了最佳准确率。
- 解释:
- 重点词汇:best accuracy(最佳准确率)
- 句子结构:结果说明句
- 难点解释:指出最优模型配置
[句子5]
- 原文:Interestingly, we also observe that using space-only positional embeddings leads to solid results on Kinetics-400, but much worse results on Something-Something-V2.
- 翻译:有趣的是,我们还观察到仅使用空间位置嵌入在Kinetics-400上产生了不错的结果,但在Something-Something-V2上的结果却差得多。
- 解释:
- 重点词汇:solid results(不错的结果)
- 句子结构:对比说明句
- 难点解释:说明不同数据集上的表现差异
[句子6]
- 原文:This makes sense as Kinetics-400 is more spatially biased, whereas Something-Something-V2 requires complex temporal reasoning.
- 翻译:这是合理的,因为Kinetics-400更偏向于空间特征,而Something-Something-V2需要复杂的时序推理。
- 解释:
- 重点词汇:
- spatially biased(空间偏向)
- temporal reasoning(时序推理)
- 句子结构:解释说明句
- 难点解释:解释了性能差异的原因
- 重点词汇:
B. 段落整体理解
- 段落主旨:研究不同位置嵌入策略的效果
- 核心要点:
- 比较了三种位置嵌入方式
- 时空位置嵌入效果最好
- 数据集特性影响嵌入策略效果
C. 专业知识拓展
- 术语解释:
- Positional embeddings:位置嵌入,用于编码输入序列中元素位置信息的表示
- Space-only embedding:仅考虑空间维度的位置编码
- Space-time embedding:同时考虑空间和时间维度的位置编码
- Temporal reasoning:时序推理,理解视频中的时间关系
4.5. Comparison to the State-of-the-Art 1-2段


A. 段落分解和分析
[段落1 - K400验证集结果]
[句子1-2]
- 原文:In Table 5 we present our results on the validation set of K400. For these experiments, we use TimeSformer pretrained on ImageNet-21K.
- 翻译:我们在表5中展示了在K400验证集上的结果。这些实验中,我们使用了在ImageNet-21K上预训练的TimeSformer。
- 解释:
- 重点词汇:validation set(验证集)
- 句子结构:实验设置说明句
- 难点解释:说明了实验基础设置
[句子3-4]
- 原文:In addition to the accuracy metrics, we also include inference cost, given in TFLOPs. We note that whereas most previous methods use 10 temporal clips with 3 spatial crops (for a total of 30 space-time views) during inference, TimeSformer achieves solid accuracy with only 3 views (3 spatial crops), which reduces the inference cost.
- 翻译:除了准确率指标外,我们还包含了以TFLOPs为单位的推理成本。我们注意到,虽然大多数之前的方法在推理时使用10个时序片段和3个空间裁剪(总共30个时空视图),但TimeSformer仅使用3个视图(3个空间裁剪)就达到了不错的准确率,这降低了推理成本。
- 解释:
- 重点词汇:
- inference cost(推理成本)
- temporal clips(时序片段)
- spatial crops(空间裁剪)
- 句子结构:对比说明句
- 难点解释:突出了模型的效率优势
- 重点词汇:
[句子5-6]
- 原文:Our long-range variant, TimeSformer-L achieves a top-1 accuracy of 80.7%. Furthermore, our default TimeSformer has the lowest inference cost among recent state-of-the-art models. Yet, it still provides a solid accuracy of 78.0%, outperforming many more costly models.
- 翻译:我们的长程变体TimeSformer-L达到了80.7%的top-1准确率。此外,我们的默认TimeSformer在最近的最先进模型中具有最低的推理成本,但仍然提供了78.0%的不错准确率,优于许多成本更高的模型。
- 解释:
- 重点词汇:top-1 accuracy(top-1准确率), state-of-the-art(最先进的)
- 句子结构:性能对比说明句
- 难点解释:说明了性能和效率的平衡
[段落2 - 实际运行时间比较]
[句子7-8]
- 原文:We also measured the actual inference runtime on 20K validation videos of Kinetics-400 (using 8 Tesla V100 GPUs). Whereas SlowFast takes 14.88 hours to complete the inference, TimeSformer, TimeSformer-HR, and TimeSformer-L take 36 minutes, 1.06 hours and 2.6 hours, respectively.
- 翻译:我们还在Kinetics-400的20K验证视频上测量了实际推理运行时间(使用8个Tesla V100 GPU)。当SlowFast需要14.88小时完成推理时,TimeSformer、TimeSformer-HR和TimeSformer-L分别只需要36分钟、1.06小时和2.6小时。
- 解释:
- 重点词汇:inference runtime(推理运行时间)
- 句子结构:实验结果对比句
- 难点解释:通过具体数据说明效率优势
[句子9]
- 原文:Thus, even though SlowFast and TimeSformer-L have comparable cost in terms of TFLOPs, in practice the runtimes of all our versions of TimeSformer are much lower.
- 翻译:因此,尽管SlowFast和TimeSformer-L在TFLOPs方面成本相当,但实际上所有版本的TimeSformer的运行时间都要低得多。
- 解释:
- 重点词汇:comparable cost(相当的成本)
- 句子结构:结论句
- 难点解释:强调了理论计算量和实际效率的差异
B. 段落整体理解
- 段落主旨:展示TimeSformer在准确率和效率方面的优势
- 核心要点:
- 高准确率(80.7%)
- 低推理成本
- 显著更短的实际运行时间
C. 专业知识拓展
- 术语解释:
- TFLOPs:每秒万亿次浮点运算,计算复杂度度量
- Temporal clips:时序片段,视频的时间维度采样
- Spatial crops:空间裁剪,从帧中提取的空间区域
- Inference runtime:推理运行时间,实际处理数据所需时间
4.5. Comparison to the State-of-the-Art 3-4段

A. 段落分解和分析
[段落1 - Kinetics-600结果]
[句子1-2]
- 原文:In Table 6, we also present our results on Kinetics-600. Just like on Kinetics-400, we observe that TimeSformer performs well on this benchmark, outperforming all prior methods.
- 翻译:在表6中,我们还展示了在Kinetics-600上的结果。和在Kinetics-400上一样,我们观察到TimeSformer在这个基准测试上表现良好,优于所有先前的方法。
- 解释:
- 重点词汇:benchmark(基准测试)
- 句子结构:结果说明句
- 难点解释:说明模型在不同数据集上的一致性能
[段落2 - 多时序片段分析]
[句子3]
- 原文:Finally, in Figure 6, we study the effect of using multiple temporal clips during inference (each with a single spatial crop).
- 翻译:最后,在图6中,我们研究了在推理过程中使用多个时序片段(每个都有单个空间裁剪)的效果。
- 解释:
- 重点词汇:multiple temporal clips(多个时序片段)
- 句子结构:研究设置说明句
- 难点解释:介绍了新的实验设置
[句子4]
- 原文:We plot accuracy using K ∈ {1, 3, 5, 10} temporal clips for testing. We compare our model against X3D (Feichtenhofer, 2020), and SlowFast (Feichtenhofer et al., 2019b).
- 翻译:我们绘制了使用K ∈ {1, 3, 5, 10}个时序片段进行测试的准确率。我们将我们的模型与X3D和SlowFast进行了比较。
- 解释:
- 重点词汇:testing(测试)
- 句子结构:实验对比说明句
- 难点解释:说明具体的实验参数设置
[句子5-6]
- 原文:X3D and SlowFast require multiple (≥ 5) clips to approach their top accuracy. Conversely, our long-range variant, TimeSformer-L, does not require multiple clips to achieve its best performance, since it is able to span about 12 seconds of a Kinetics video with a single clip.
- 翻译:X3D和SlowFast需要多个(≥ 5)片段才能接近其最高准确率。相反,我们的长程变体TimeSformer-L不需要多个片段就能达到其最佳性能,因为它能够用单个片段跨越Kinetics视频约12秒的内容。
- 解释:
- 重点词汇:
- top accuracy(最高准确率)
- best performance(最佳性能)
- span(跨越)
- 句子结构:对比说明句
- 难点解释:强调了模型的效率优势
- 重点词汇:
B. 段落整体理解
- 段落主旨:分析模型在新数据集和多时序片段设置下的表现
- 核心要点:
- Kinetics-600上保持优势
- 时序片段数量对性能的影响
- TimeSformer-L的单片段优势
C. 专业知识拓展
- 术语解释:
- Temporal clips:时序片段,视频在时间维度上的采样
- Spatial crop:空间裁剪,从视频帧中提取的空间区域
- Inference:推理,模型应用于新数据的过程
- Long-range variant:长程变体,能处理更长时间范围的模型版本
4.5. Comparison to the State-of-the-Art 5-6段

A. 段落分解和分析
[段落1 - SSv2实验结果]
[句子1-3]
- 原文:In Table 7, we also validate our model on SSv2 and Diving-48. Since ImageNet-21K pretraining does not improve accuracy on SSv2 (see Table 3), in this case, we use TimeSformer pretrained on ImageNet-1K. This also allows us to apply the same pretraining to all other models in this comparison, using a ResNet pretrained on ImageNet-1K.
- 翻译:在表7中,我们还验证了模型在SSv2和Diving-48上的表现。由于ImageNet-21K预训练并不能提高在SSv2上的准确率(见表3),在这种情况下,我们使用了在ImageNet-1K上预训练的TimeSformer。这也使我们能够对比较中的所有其他模型应用相同的预训练,使用在ImageNet-1K上预训练的ResNet。
- 解释:
- 重点词汇:
- pretraining(预训练)
- validate(验证)
- 句子结构:实验设置说明句
- 难点解释:说明了预训练选择的原因
- 重点词汇:
[句子4-5]
- 原文:Our results suggest that TimeSformer achieves lower accuracy than the best models on this dataset. However, considering that our model uses a completely different design, we take these results as suggesting that TimesSformer is a promising approach even for challenging temporally-heavy datasets, such as SSv2.
- 翻译:我们的结果表明,TimeSformer在这个数据集上的准确率低于最佳模型。然而,考虑到我们的模型使用了完全不同的设计,我们认为这些结果表明TimeSformer即使对于具有挑战性的时序密集型数据集(如SSv2)也是一种有前途的方法。
- 解释:
- 重点词汇:
- promising approach(有前途的方法)
- temporally-heavy(时序密集型)
- 句子结构:结果分析句
- 难点解释:从积极角度解释了性能差异
- 重点词汇:
[段落2 - Diving-48结果]
[句子6-7]
- 原文:In Table 7, we also present our method on another “temporally-heavy” dataset, Diving-48. Due to a recently discovered issue with a previous version of Diving-48 labels, here, we only compare our method with a reproduced SlowFast 16×8 R101 model.
- 翻译:在表7中,我们还展示了我们的方法在另一个"时序密集型"数据集Diving-48上的表现。由于最近发现先前版本的Diving-48标签存在问题,在这里,我们只将我们的方法与重新实现的SlowFast 16×8 R101模型进行比较。
- 解释:
- 重点词汇:reproduced model(重新实现的模型)
- 句子结构:实验限制说明句
- 难点解释:说明了比较范围受限的原因
[句子8]
- 原文:Our results show that TimeSformer outperforms SlowFast by a substantial margin.
- 翻译:我们的结果显示,TimeSformer大幅优于SlowFast。
- 解释:
- 重点词汇:substantial margin(大幅优势)
- 句子结构:结果说明句
- 难点解释:强调了在特定数据集上的优势
B. 段落整体理解
- 段落主旨:分析模型在时序密集型数据集上的表现
- 核心要点:
- SSv2上表现相对较弱但有潜力
- Diving-48上表现出色
- 预训练策略的选择考虑
C. 专业知识拓展
-
术语解释:
- SSv2:Something-Something-V2,需要复杂时序理解的数据集
- Diving-48:跳水动作识别数据集
- Temporally-heavy:时序密集型,强调时序信息的重要性
- ImageNet-1K/21K:不同规模的预训练数据集
-
研究价值:
- 验证了模型在不同类型数据集上的适应性
- 展示了新架构在传统任务上的潜力
- 提供了预训练选择的参考依据
4.6. Long-Term Video Modeling 1-2段

A. 段落分解和分析
[段落1 - 数据集介绍]
[句子1-2]
- 原文:Lastly, we evaluate TimeSformer on the task of long-term video modeling using HowTo100M (Miech et al., 2019). HowTo100M is an instructional video dataset that contains around 1M instructional Web videos showing humans performing over 23K different tasks, such as cooking, repairing, making arts, etc.
- 翻译:最后,我们使用HowTo100M评估TimeSformer在长时视频建模任务上的表现。HowTo100M是一个教学视频数据集,包含约100万个网络教学视频,展示了人们执行超过23,000种不同任务的过程,如烹饪、维修、艺术创作等。
- 解释:
- 重点词汇:
- long-term video modeling(长时视频建模)
- instructional video(教学视频)
- 句子结构:任务和数据集介绍句
- 难点解释:说明了实验目的和数据来源
- 重点词汇:
[句子3-4]
- 原文:The average duration of these videos is around 7 minutes, which is orders of magnitude longer than the duration of videos in standard action recognition benchmarks. Each HowTo100M video has a label indicating the task demonstrated in the video (one out of the 23K classes), which can be used for supervised training.
- 翻译:这些视频的平均时长约为7分钟,比标准动作识别基准测试中的视频时长长很多个数量级。每个HowTo100M视频都有一个标签,指示视频中演示的任务(23,000个类别之一),可用于监督训练。
- 解释:
- 重点词汇:
- supervised training(监督训练)
- duration(时长)
- 句子结构:数据特征说明句
- 难点解释:强调了数据集的独特性
- 重点词汇:
[句子5]
- 原文:Thus, it is a good benchmark to assess the ability of a model to recognize activities exhibited over very long temporal extents.
- 翻译:因此,它是评估模型识别长时间跨度活动能力的良好基准。
- 解释:
- 重点词汇:temporal extents(时间跨度)
- 句子结构:结论句
- 难点解释:说明了数据集的用途
[段落2 - 实验设置]
[句子6-7]
- 原文:For this evaluation, we consider only categories that have at least 100 video examples. This gives a subset of HowTo100M corresponding to 120K videos spanning 1059 task categories.
- 翻译:对于这个评估,我们只考虑至少有100个视频样本的类别。这得到了一个HowTo100M子集,包含120,000个视频,跨越1,059个任务类别。
- 解释:
- 重点词汇:categories(类别)
- 句子结构:实验筛选说明句
- 难点解释:说明了数据筛选标准
[句子8]
- 原文:We randomly partition this collection into 85K training videos and 35K testing videos.
- 翻译:我们将这个集合随机分为85,000个训练视频和35,000个测试视频。
- 解释:
- 重点词汇:partition(分割)
- 句子结构:数据分割说明句
- 难点解释:说明了具体的数据划分方式
B. 段落整体理解
- 段落主旨:介绍长时视频识别实验设置
- 核心要点:
- 数据集规模和特点
- 视频时长特征
- 任务类别数量
- 数据筛选和划分方式
C. 专业知识拓展
-
术语解释:
- Long-term video modeling:长时视频建模,处理较长时间跨度视频的技术
- Instructional video:教学视频,展示具体任务执行过程的视频
- Temporal extents:时间跨度,视频持续的时间长度
- Supervised training:监督训练,使用带标签数据的训练方式
-
研究价值:
- 验证模型处理长视频的能力
- 提供实际应用场景的测试
- 扩展现有动作识别的范围
4.6. Long-Term Video Modeling 3-4段

A. 段落分解和分析
[句子1-2]
- 原文:We present our results in Table 8. As our baselines, we use four variants of SlowFast R101, all operating on video clips sampled at a frame rate of 1/32 but having varying number of frames: 8, 32, 64 and 96.
- 翻译:我们在表8中展示了结果。作为基准,我们使用了SlowFast R101的四种变体,它们都以1/32的帧率对视频片段进行采样,但帧数不同:8、32、64和96帧。
- 解释:
- 重点词汇:
- variants(变体)
- frame rate(帧率)
- 句子结构:实验设置说明句
- 难点解释:说明了基准模型的具体配置
- 重点词汇:
[句子3]
- 原文:We use the same four configurations for TimeSformer, starting from a ViT pretrained on ImageNet-21K. All models in this comparison are pretrained on Kinetics-400 before finetuning on HowTo100M.
- 翻译:我们对TimeSformer使用相同的四种配置,从在ImageNet-21K上预训练的ViT开始。在这个比较中的所有模型都在HowTo100M微调之前在Kinetics-400上进行了预训练。
- 解释:
- 重点词汇:
- configurations(配置)
- finetuning(微调)
- 句子结构:模型训练说明句
- 难点解释:描述了完整的训练过程
- 重点词汇:
[句子4-5]
- 原文:During inference, for each method, we sample as many non-overlapping temporal clips as needed to cover the full temporal extent of a video, e.g., if a single clip spans 8.5 seconds, we would sample 48 test clips to cover a video of 410 seconds. Video-level classification is done by averaging the clip predictions.
- 翻译:在推理过程中,对于每种方法,我们采样所需数量的非重叠时序片段以覆盖视频的完整时间范围,例如,如果单个片段跨越8.5秒,我们会采样48个测试片段来覆盖410秒的视频。视频级别的分类是通过对片段预测取平均值完成的。
- 解释:
- 重点词汇:
- non-overlapping(非重叠)
- temporal extent(时间范围)
- 句子结构:推理过程说明句
- 难点解释:详细说明了推理阶段的具体操作
- 重点词汇:
B. 段落整体理解
这两段介绍了实验的基础采样配置。具体来说,采用1/32的采样率(即每32帧采样1帧),并设置了8、32、64、96帧四种配置来覆盖不同的时间跨度。这种实验设置在视频理解领域是一种常见做法 - SlowFast通过双路径验证了多时间尺度建模的重要性,TSM研究了较小帧数下的时序位移效果,X3D系统地探索了从小到大的帧数配置,而Swin Transformer则进一步验证了更长时序下Transformer架构的优势。这样的多尺度实验设置能够全面评估模型在从短时(如击打动作)到长时(如烹饪过程)等不同时序场景下的性能表现。
4.6. Long-Term Video Modeling 5-6段

A. 段落分解和分析
[段落1]
总句子数:3
[句子1]
- 原文:From the results in Table 8 we first note that, for the same single clip coverage, TimeSformer outperforms the corresponding SlowFast by a large margin of 8 − 11 % 8-11\% 8−11%.
- 翻译:从表8的结果中我们首先注意到,在相同的单片段覆盖范围下,TimeSformer比相应的SlowFast模型有 8 − 11 % 8-11\% 8−11%的显著性能优势。
- 解释:
- 关键词:single clip coverage(单片段覆盖), outperforms(优于)
- 句子结构:结果对比句型
- 重点:强调了TimeSformer相对SlowFast的性能优势
- 难点:single clip coverage的概念理解
[句子2]
- 原文:We also observe that longer-range TimeSformers do better, i.e., our longest-range variant achieves the best video-level classification accuracy.
- 翻译:我们还观察到更长时间范围的TimeSformer表现更好,即我们最长范围的变体获得了最佳的视频级分类准确率。
- 解释:
- 关键词:longer-range(更长范围), video-level classification(视频级分类)
- 句子结构:观察陈述句
- 重点:说明时间范围与性能的关系
- 难点:理解longer-range的具体含义
[句子3]
- 原文:These results suggest that our model is highly suitable for tasks that require long-term video modeling.
- 翻译:这些结果表明我们的模型非常适合需要长期视频建模的任务。
- 解释:
- 关键词:long-term video modeling(长期视频建模)
- 句子结构:结论句
- 重点:模型的应用场景定位
[段落2和3]
总句子数:4
[句子4]
- 原文:We also experimented with finetuning TimeSformer directly from a ViT pretrained on ImageNet-1K and ImageNet-21K (skipping the Kinetics-400 training).
- 翻译:我们还尝试了直接从预训练在ImageNet-1K和ImageNet-21K上的ViT微调TimeSformer(跳过Kinetics-400训练)。
- 解释:
- 关键词:finetuning(微调), pretrained(预训练)
- 句子结构:实验方法描述句
- 重点:描述了一个新的训练策略
- 难点:理解预训练和微调的概念
B. 段落整体理解(第一段)
-
段落主旨:展示TimeSformer的性能优势
-
核心要点:
- TimeSformer比SlowFast性能更好
- 更长时间范围的模型效果更好
- 适合长期视频建模任务
[句子5]
-
原文:We report that when pretrained only on ImageNet-1K, our model achieves top-1 accuracies of 52.8 % , 58.4 % , 59.2 % , 59.4 % 52.8\%, 58.4\%, 59.2\%, 59.4\% 52.8%,58.4%,59.2%,59.4% for 8 , 32 , 64 , 96 8, 32, 64, 96 8,32,64,96 frame inputs, respectively.
-
翻译:实验结果表明,当仅在ImageNet-1K上预训练时,我们的模型在 8 , 32 , 64 , 96 8, 32, 64, 96 8,32,64,96帧输入下分别达到了 52.8 % , 58.4 % , 59.2 % , 59.4 % 52.8\%, 58.4\%, 59.2\%, 59.4\% 52.8%,58.4%,59.2%,59.4%的top-1准确率。
-
解释:
- 关键词:top-1 accuracies, frame inputs
- 句子结构:实验结果陈述句
- 重点:详细列举了不同帧数下的性能数据
- 难点:理解帧数与准确率的关系变化
[句子6]
- 原文:When considering ImageNet-21K pretraining, TimeSformer produces top-1 accuracies of 56.0 % , 59.2 % , 60.2 % , 62.1 % 56.0\%, 59.2\%, 60.2\%, 62.1\% 56.0%,59.2%,60.2%,62.1% for 8 , 32 , 64 , 96 8, 32, 64, 96 8,32,64,96 frame inputs, respectively.
- 翻译:当使用ImageNet-21K预训练时,TimeSformer在 8 , 32 , 64 , 96 8, 32, 64, 96 8,32,64,96帧输入下分别产生了 56.0 % , 59.2 % , 60.2 % , 62.1 % 56.0\%, 59.2\%, 60.2\%, 62.1\% 56.0%,59.2%,60.2%,62.1%的top-1准确率。
- 解释:
- 关键词:ImageNet-21K pretraining
- 句子结构:平行对比句
- 重点:展示了更大数据集预训练的效果
[句子7]
- 原文:These results demonstrate that our model can effectively exploit long-range temporal dependencies regardless of the pretraining dataset that we use.
- 翻译:这些结果表明,无论使用哪种预训练数据集,我们的模型都能有效利用长程时序依赖关系。
- 解释:
- 关键词:long-range temporal dependencies(长程时序依赖关系)
- 句子结构:结论句
- 重点:强调模型的普适性和稳定性
- 难点:理解temporal dependencies概念
4.7. Additional Ablations 第1-2段

A. 段落分解和分析
[句子1]
- 原文:In addition to the “Base” ViT model (Dosovitskiy et al., 2020), we also experimented with the “Large” ViT.
- 翻译:除了"Base" ViT模型(Dosovitskiy等,2020)外,我们还测试了"Large" ViT。
- 解释:
- 关键词:Base ViT, Large ViT
- 句子结构:实验设置引入句
- 重点:引入不同规模模型的对比实验
- 难点:理解不同规模ViT模型的区别
[句子2]
- 原文:We report that this yielded results 1 % 1\% 1% worse on both Kinetics-400, and Something-Something-V2.
- 翻译:我们报告基于Kinetics-400和Something-Something-V2数据集上,这导致了性能下降 1 % 1\% 1%。
[句子3]
- 原文:Given that our “Base” model already has 121M parameters, we suspect that the current datasets are not big enough to justify a further increase in model capacity.
- 翻译:考虑到我们的"Base"模型已经有121M参数,我们怀疑当前数据集的规模不足以支撑进一步增加模型容量。
[句子4]
- 原文:We also tried the “Small” ViT variant, which produced accuracies about 5 % 5\% 5% worse than our default “Base” ViT model.
- 翻译:我们还尝试了"Small" ViT变体,其准确率比我们默认的"Base" ViT模型低约 5 % 5\% 5%。
[段落2 - Patch Size实验]
总句子数:4
[句子5]
- 原文:We also experimented with a different patch size, i.e., P = 32 P = 32 P=32.
- 翻译:我们还实验了不同的patch大小,即 P = 32 P = 32 P=32。
[句子6-8]
- 原文:We report that this variant of our model produced results about 3 % 3\% 3% worse than our default variant using P = 16 P = 16 P=16. We conjecture that the performance decrease with P = 32 P = 32 P=32 is due to the reduced spatial granularity. We did not train any models with P values lower than 16 as those models have a much higher computational cost.
- 翻译:我们报告这个变体的结果比使用 P = 16 P = 16 P=16的默认变体差约 3 % 3\% 3%。我们推测 P = 32 P = 32 P=32时性能下降是由于降低了空间粒度。我们没有训练任何P值小于16的模型,因为这些模型计算成本要高得多。
B. 段落整体理解
[段落1]
- 段落主旨:探讨模型规模对性能的影响
- 核心要点:
- Large模型反而性能略有下降
- 可能是由于数据集规模限制
- Small模型性能显著下降
[段落2]
- 段落主旨:研究patch size参数的影响
- 核心要点:
- 更大的patch size(32)导致性能下降
- 性能下降与空间粒度降低有关
- 更小的patch size计算成本过高
C. 专业知识拓展
-
术语解释:
- ViT (Vision Transformer):用于视觉任务的Transformer架构
- Patch Size:图像分割的基本单元大小
- Spatial granularity:空间细粒度,指模型处理视觉信息的精细程度
- Model capacity:模型容量,指模型的参数量和复杂度
-
背景信息:
- 模型规模与性能并非简单的正相关
- 需要在精度、效率、资源消耗间平衡
4.7. Additional Ablations 第3段

A. 段落分解和分析
[段落1]
总句子数:5
[句子1]
- 原文:Our proposed “Divided Space-Time Attention” scheme applies temporal attention and spatial attention one after the other.
- 翻译:我们提出的"分离式时空注意力"方案依次应用时间注意力和空间注意力。
[句子2]
- 原文:Here, we investigate whether reversing the order of time-space attention (i.e., applying spatial attention first, then temporal) has an impact on our results.
- 翻译:在这里,我们研究反转时空注意力的顺序(即先应用空间注意力,再应用时间注意力)是否会影响我们的结果。
[句子3]
- 原文:We report that applying spatial attention first, followed by temporal attention leads to a 0.5 % 0.5\% 0.5% drop in accuracy on both Kinetics-400, and Something-Something-V2.
- 翻译:我们报告,先应用空间注意力,再应用时间注意力会导致在Kinetics-400和Something-Something-V2数据集上的准确率都下降 0.5 % 0.5\% 0.5%。
[句子4-5]
- 原文:We also tried a parallel space-time self-attention. We report that it produces 0.4 % 0.4\% 0.4% lower accuracy compared to our adopted “Divided Space-Time Attention” scheme.
- 翻译:我们还尝试了并行时空自注意力。我们报告它与我们采用的"分离式时空注意力"方案相比,准确率降低了 0.4 % 0.4\% 0.4%。
B. 段落整体理解
- 段落主旨:研究不同时空注意力应用顺序对模型性能的影响
- 核心要点:
- 默认顺序:先时间后空间
- 反转顺序导致性能轻微下降
- 并行处理方案也略逊于默认顺序
C. 专业知识拓展
-
术语解释:
- Divided Space-Time Attention:分离式时空注意力,将时间和空间注意力机制分开依次处理
- Temporal attention:时间注意力,处理视频序列中的时间维度信息
- Spatial attention:空间注意力,处理每一帧中的空间维度信息
- Parallel space-time self-attention:并行时空自注意力,同时处理时间和空间维度的信息
-
背景信息:
- 注意力机制是Transformer架构的核心组件
- 时空信息处理顺序对视频理解任务很重要
E. 研究意义
这个实验揭示了:
- 时空注意力的处理顺序确实影响模型性能
- 先时间后空间的处理顺序可能更符合视频数据的内在特性
- 即使是较小的实现差异也会导致可测量的性能变化
4.8. Qualitative Results
A. 段落分解和分析
[段落1 - 时空注意力可视化]
总句子数:4
[句子1-2]
- 原文:In Figure 7, we present space-time attention visualizations obtained by applying TimeSformer on Something-Something-V2 videos. To visualize the learned attention, we use the Attention Rollout scheme presented in (Abnar & Zuidema, 2020).
- 翻译:在图7中,我们展示了通过在Something-Something-V2视频上应用TimeSformer得到的时空注意力可视化结果。为了可视化学习到的注意力,我们使用了(Abnar & Zuidema, 2020)提出的注意力展开方案。
[句子3-4]
- 原文:Our results suggest that TimeSformer learns to attend to the relevant regions in the video in order to perform complex spatiotemporal reasoning. For example, we can observe that the model focuses on the configuration of the hand when visible and the object-only when not visible.
- 翻译:我们的结果表明TimeSformer学会了关注视频中的相关区域以执行复杂的时空推理。例如,我们可以观察到模型在手部可见时关注手部构型,在手部不可见时仅关注物体。
[段落2 - 特征嵌入可视化]
总句子数:3
[句子5]
- 原文:In Figure 8, we also visualize the features learned by TimeSformer on Something-Something-V2.
- 翻译:在图8中,我们还可视化了TimeSformer在Something-Something-V2上学习到的特征。
[句子6]
- 原文:The visualization is done using t-SNE (van der Maaten & Hinton, 2008) where each point represents a single video, and different colors depict different action categories.
- 翻译:可视化使用t-SNE (van der Maaten & Hinton, 2008)完成,其中每个点代表一个视频,不同颜色表示不同的动作类别。
[句子7]
- 原文:Based on this illustration, we observe that TimeSformer with divided space-time attention learns semantically more separable features than the TimeSformer with space-only attention or ViT (Dosovitskiy et al., 2020).
- 翻译:基于此图示,我们观察到具有分离式时空注意力的TimeSformer比仅有空间注意力的TimeSformer或ViT学习到了语义上更可分离的特征。
B. 段落整体理解
[段落1]
- 段落主旨:展示和分析模型的注意力机制
- 核心要点:
- 使用Attention Rollout进行可视化
- 模型能够智能定位关键区域
- 注意力分配随场景变化而适应
[段落2]
- 段落主旨:分析模型学习到的特征表示
- 核心要点:
- 使用t-SNE进行特征可视化
- 分离式时空注意力提升特征可分性
- 与其他模型变体的对比优势
C. 专业知识拓展
-
术语解释:
- Attention Rollout:一种注意力机制可视化方法
- t-SNE:t-distributed Stochastic Neighbor Embedding,用于高维数据可视化的算法
- Feature embeddings:特征嵌入,模型学习到的数据表示
- Spatiotemporal reasoning:时空推理,理解视频中时间和空间关系的能力
-
背景信息:
- 可视化分析是理解深度学习模型的重要工具
- 特征可分离性是评估模型效果的重要指标
5. Conclusion
A. 段落分解和分析
[句子1]
- 原文:In this work, we introduced TimeSformer, a fundamentally different approach to video modeling compared to the established paradigm of convolution-based video networks.
- 翻译:在本研究中,我们介绍了TimeSformer,这是一种与传统基于卷积的视频网络范式有根本区别的视频建模方法。
- 解释:
- 关键词:fundamentally different approach
- 句子结构:研究概括句
- 重点:强调方法的创新性
- 难点:理解与传统方法的根本区别
[句子2]
- 原文:We showed that it is possible to design an effective, and scalable video architecture built exclusively on space-time self-attention.
- 翻译:我们证明了可以设计一个完全基于时空自注意力的有效且可扩展的视频架构。
- 解释:
- 关键词:effective, scalable, exclusively
- 句子结构:成果陈述句
- 重点:证明了设计可行性
- 难点:理解可扩展性概念
[句子3]
- 原文:Our method (1) is conceptually simple, (2) achieves state-of-the-art results on major action recognition benchmarks, (3) has low training and inference cost, and (4) can be applied to clips of over one minute, thus enabling long-term video modeling.
- 翻译:我们的方法(1)概念简单,(2)在主要动作识别基准测试中达到了最先进的结果,(3)具有较低的训练和推理成本,(4)可以应用于超过一分钟的视频片段,从而实现长期视频建模。
- 解释:
- 关键词:conceptually simple, state-of-the-art, long-term video modeling
- 句子结构:优点列举句
- 重点:方法的四大优势
- 难点:无
[句子4]
- 原文:In the future, we plan to extend our method to other video analysis tasks such as action localization, video captioning and question-answering.
- 翻译:未来,我们计划将我们的方法扩展到其他视频分析任务,如动作定位、视频描述和问答。
- 解释:
- 关键词:action localization, video captioning, question-answering
- 句子结构:未来展望句
- 重点:方法的潜在应用领域
- 难点:理解各种视频分析任务的概念
B. 段落整体理解
- 段落主旨:总结研究成果并展望未来
- 核心要点:
- 方法的创新性
- 四大主要优势
- 未来应用方向
C. 专业知识拓展
- 术语解释:
- Action recognition:动作识别,识别视频中的人类动作
- Action localization:动作定位,定位视频中动作发生的时空位置
- Video captioning:视频描述,自动生成视频内容的文字描述
- Question-answering:问答系统,回答关于视频内容的问题
附表
表1

[句子1]
- 原文:Video-level accuracy for different space-time attention schemes in TimeSformer. We evaluate the models on the validation sets of Kinetics-400 (K400), and Something-Something-V2 (SSv2). We observe that divided space-time attention achieves the best results on both datasets.
- 翻译:在TimeSformer中不同时空注意力方案的视频级准确率。我们在Kinetics-400 (K400)和Something-Something-V2 (SSv2)的验证集上评估模型。我们观察到分离时空注意力在两个数据集上都取得了最佳结果。(78.0, 59.5)
表2

表3

表4

表5

表6

表7

表8

附图
图3

[句子1]
- 原文:We compare the video classification cost (in TFLOPs) of Joint Space-Time versus Divided Space-Time attention.
- 翻译:我们比较联合时空注意力与分离时空注意力的视频分类计算成本(以TFLOPs计)。
[段落2 - 详细说明]
总句数:1
[句子1]
- 原文:We plot the number of TFLOPs as a function of spatial crop size in pixels (left), and the number of input frames (right). As we increase the spatial resolution (left), or the video length (right), our proposed divided space-time attention leads to dramatic computational savings compared to the scheme of joint space-time attention.
- 翻译:我们绘制了TFLOPs数量与空间裁剪尺寸(左图)和输入帧数(右图)的关系。随着空间分辨率(左图)或视频长度(右图)的增加,我们提出的分离时空注意力机制与联合时空注意力方案相比带来了显著的计算节省。
- 解释:
- 重点词汇:
- spatial crop size:空间裁剪尺寸,指输入图像的分辨率
- computational savings:计算资源节省
- 句子结构:复合句,分别说明两个维度的实验结果
- 与上下文关系:详细解释了图表展示的实验结果
- 难点解释:说明了两种方案在不同条件下的性能差异
- 重点词汇:
图4
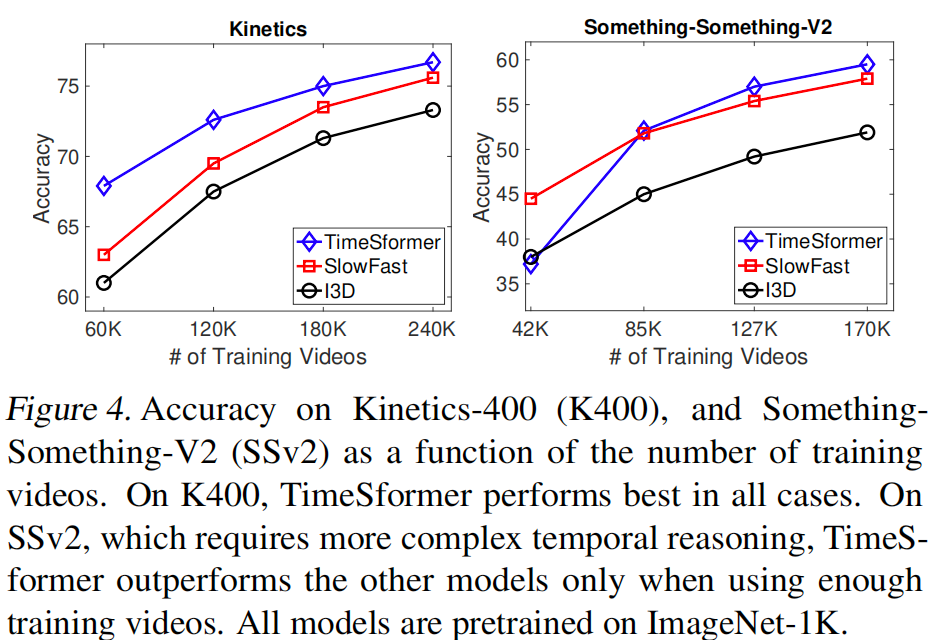
图6

图7

图8
























 2099
2099

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








