PRIS: Practical robust invertible network for image steganography
PRIS:用于图像隐写术的实用鲁棒可逆网络
https://arxiv.org/html/2309.13620?_immersive_translate_auto_translate=1
Image steganography is a technique of hiding secret information inside another image, so that the secret is not visible to human eyes and can be recovered when needed. Most of the existing image steganography methods have low hiding robustness when the container images affected by distortion. Such as Gaussian noise and lossy compression. This paper proposed PRIS to improve the robustness of image steganography, it based on invertible neural networks, and put two enhance modules before and after the extraction process with a 3-step training strategy. Moreover, rounding error is considered which is always ignored by existing methods, but actually it is unavoidable in practical. A gradient approximation function (GAF) is also proposed to overcome the undifferentiable issue of rounding distortion. Experimental results show that our PRIS outperforms the state-of-the-art robust image steganography method in both robustness and practicability. Codes are available at https://github.com/yanghangAI/PRIS, demonstration of our model in practical at http://yanghang.site/hide/.
图像隐写术是一种将秘密信息隐藏在另一张图像中的技术,使人眼不可见秘密,并且可以在需要时恢复。现有的大多数图像隐写方法在容器图像受畸变影响时隐藏鲁棒性较低。例如高斯噪声和有损压缩。该文提出了 PRIS 来提高图像隐写术的鲁棒性,该方法基于可逆神经网络,在提取过程前后放置两个增强模块,采用三步训练策略。此外,考虑到舍入误差,这在现有方法中总是被忽略,但实际上在实践中是不可避免的。还提出了梯度逼近函数(GAF)来克服舍入畸变的不可微分问题。实验结果表明,我们的 PRIS 在鲁棒性和实用性方面都优于最先进的鲁棒图像隐写法。代码可在 https://github.com/yanghangAI/PRIS 获得,http://yanghang.site/hide/ 实际演示我们的模型。
,
1Introduction 1 介绍
Steganography is the art of concealing information. The goal of steganography is to hide a secret message within a host medium [1, 2]. The host medium containing the hidden secret message is called the container [3]. The container is typically publicly visible, but the difference between the host and container should be invisible to third parties. There are some good introductions to steganography in [1, 4, 5]. Image steganography aims to hide message such as image, audio, and text within a host image in an undetectable way [6], meaning the host medium in image steganography is an image. Nowadays, image steganography is widely used in fields such as copyright protection, digital communication, information certification, and more [7].
隐写术是隐藏信息的艺术。隐写术的目标是在宿主培养基中隐藏秘密信息 [1,2]。 包含隐藏秘密消息的主机介质称为容器 [3]。 容器通常是公开可见的,但主机和容器之间的差异应该对第三方不可见。[1, 4, 5] 中有一些关于隐写术的很好的介绍。图像隐写术旨在以无法检测的方式将图像、音频和文本等信息隐藏在主机图像中[6],这意味着图像隐写术中的宿主介质是图像。如今,图像隐写术广泛应用于版权保护、数字通信、信息认证等领域 [7]。
Traditional image steganographic methods have the ability to hide only a small amount of information [8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13]. They conceal secret messages in the spatial or adaptive domains [14] with capacities of 0.2∼4 bits per pixel (bpp). In recent years, some researchers have attempted to hide an image containing more information than the secret message in traditional image steganographic methods within a host image [15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 20]. They introduced deep learning into image steganography by using two separate networks to realize the embedding and extraction processes. Lu [3] and Jing [21] achieved state-of-the-art performance in image steganography by using an invertible network to embed a secret image into a host image. Since the extraction process is the inverse of the embedding process, the secret image can be fully recovered.
In practical applications, the container image is often subject to various forms of attacks due to factors such as lossy image compression for storage savings. These attacks can distort the container image, potentially affecting the ability to extract the secret information. Robustness refers to the ability of the secret information to remain unchanged when the container is distorted [22]. In other words, it measures how similar the secret and extracted messages will be when the container image is attacked.
在实际应用中,容器镜像经常会受到各种形式的攻击,例如为了节省存储而进行有损镜像压缩等因素。这些攻击可能会扭曲容器映像,从而可能影响提取机密信息的能力。鲁棒性是指当容器失真时,秘密信息保持不变的能力 [22]。 换句话说,它衡量容器映像受到攻击时机密消息和提取消息的相似程度。
However, state-of-the-art image steganography methods [3, 21] did not take into account the effect of container images being attacked. As a result, they failed to extract secret images when container images were distorted. To address this issue, Xu [6] proposed robust invertible image steganography. This method improved the robustness of image steganography by taking image distortion into account, allowing for the successful extraction of secret information even when the container image is distorted.
然而,最先进的图像隐写方法 [3,21] 没有考虑到容器图像受到攻击的影响。因此,当容器镜像失真时,他们无法提取机密镜像。为了解决这个问题,Xu [6] 提出了鲁棒的可逆图像隐写术。该方法通过考虑图像失真来提高图像隐写术的鲁棒性,即使在容器图像失真的情况下也能成功提取秘密信息。
Moreover, since the current mainstream deep learning frameworks have a numerical precision of 32 bits, while images are usually 8 bits, there is an inevitable rounding error when saving the container images. However, to the best of our knowledge, the existing deep steganography methods ignore this problem [23, 6, 21, 3], which is not practical in real application, we also give a method to illustrate the importance to consider rounding error in section 3.7.
而且,由于目前主流的深度学习框架的数值精度为 32 位,而图像通常为 8 位,因此在保存容器图像时不可避免地会出现舍入误差。然而,据我们所知,现有的深度隐写术方法忽略了这个问题 [23,6,21,3],这在实际应用中并不实用,我们还在第 3.7 节中给出了一种方法来说明考虑舍入误差的重要性。
In this paper, we designed a practical robust invertible network called PRIS based on HiNet [21]. We introduce two enhancement modules and a 3-step training strategy into invertible neural network to improve its robustness. In addition, we take rounding distortion into account and propose a gradient approximation function (GAF) to deal with the undifferentiable problem of rounding operation. The main contributions are listed as follows:
在本文中,我们设计了一种基于 HiNet 的实用鲁棒可逆网络 PRIS[21]。 在可逆神经网络中引入两个增强模块和三步训练策略,以提高其鲁棒性。此外,我们还考虑了舍入失真,并提出了梯度近似函数(GAF)来处理舍入运算的不可微分问题。主要贡献如下:
1. A practical robust invertible network is proposed for image steganography under diverse attacks.
1. 提出了一种实用的鲁棒可逆网络,用于多种攻击下的图像隐写术。
2. We introduce a 3-step training strategy into our training process to achieve a better robustness.
2. 我们在训练过程中引入三步训练策略,以实现更好的鲁棒性。
3. A gradient approximate function is proposed to solve the undifferentiable problem caused by rounding operation, and take rounding error into consideration.
3. 提出梯度近似函数,解决舍入运算导致的不可微问题,并考虑舍入误差。
4. Experiments results demonstrate that our proposed PRIS outperforms the existing state-of-the-art method RIIS in both robustness and practicability.
4. 实验结果表明,我们提出的 PRIS 在鲁棒性和实用性方面都优于现有的先进方法 RIIS。
2Related work 阿拉伯数字 相关工作
2.1Traditional image steganography
2.1 传统图像隐写术
Traditional image steganography can be divided into two categories based on the whether the hiding process happen in spatial or frequency domain. Spatial domain: The most popular spatial-based method called Least Significant Bit (LSB) [24, 25], it changes n least significant bits of host image to embed secret messages. However, the change of picked bits make it easy to be detected by some steganalysis methods [9, 26, 27]. In addition, Pan [28] utilizes pixel value differencing (PVD), Tsai [29] introduces histogram shifting, Nguyen [30] use multiplebit-planes and Imaizumi [31] propose palettes in image steganography. Frequency domain: Those methods hide secret messages in frequency domains, such as discrete cosine transform (DCT) [10], discrete Fourier transform (DFT) [13], and discrete wavelet transform (DWT) [8] domains. Although they are more robust and undetectable than LSB methods, they still suffered from limited payload capacity.
传统的图像隐写术可以根据隐藏过程发生在空间域还是频域中分为两类。 空域: 最流行的基于空间的方法称为最低有效位(LSB)[24,25],它更改 n 主机图像的最低有效位以嵌入秘密消息。然而,拾取位的变化使得一些隐写分析方法很容易检测到[9,26,27]。 此外,Pan [28] 利用像素值差分(PVD),Tsai [29] 引入直方图移位,Nguyen [30] 使用多位平面,Imaizumi [31] 提出了图像隐写术中的调色板。 频域: 这些方法隐藏了频域中的秘密信息,例如离散余弦变换(DCT)[10]、离散傅里叶变换(DFT)[13] 和离散小波变换(DWT)[8] 域。尽管它们比 LSB 方法更稳健且难以检测,但它们仍然受到有效载荷能力有限的影响。
2.2Deep learning-based image steganography
2.2 基于深度学习的图像隐写术
Recently, many researchers have applied deep learning methods to image steganography and achieved better performance than traditional methods. HiDDeN [32] and SteganoGAN [33] utilize the encoder-decoder architecture to realize the embedding and extraction of secret messages and employ a third network to resist steganalysis adversarially. Shi [34] proposes Ssgan for image steganography, which is based on generative adversarial networks. Baluja [17, 15] and Zhang [16] hide a secret image of the same size as the host image with deep learning method, achieve a much higher payload capacity than traditional methods.
近年来,许多研究人员将深度学习方法应用于图像隐写术,并取得了比传统方法更好的性能。HiDDeN[32] 和 SteganoGAN[33] 利用编码器-解码器架构实现秘密消息的嵌入和提取,并采用第三个网络对抗隐写分析。Shi [34] 提出了基于生成对抗网络的图像隐写术的 Ssgan。Baluja [17, 15] 和 Zhang [16] 采用深度学习方法隐藏了与主机图像大小相同的秘密图像,实现了比传统方法高得多的有效载荷能力。
2.3Invertible neural network
2.3 可逆神经网络
Dinh [35] proposed Invertible neural network (INN) in 2014. It learns a stable bijective mapping between a data distribution pX and a latent distribution pZ. Unlike CycleGAN [36], which uses two generators and a cycle loss to achieve bidirectional mapping, INN performs both forward and backward propagation within the same network, acting as both feature encoder and image generator. INNs are also useful for estimating the posterior of an inverse problem [37]. More flexible INNs are built with masked convolutions under some composition rules in [38]. An unbiased flow-based generative model is proposed in [39]. Other works improve the coupling layer for density estimation, such as Glow [40] and i-ResNet [41], resulting in better generation quality.
Dinh [35] 在 2014 年提出了可逆神经网络(INN)。它学习数据分布 pX 和潜在分布 pZ 之间的稳定双射映射。与 CycleGAN [36]不同,CycleGAN [36] 使用两个生成器和一个周期损耗来实现双向映射,INN 在同一网络内同时执行前向和后向传播,既充当特征编码器又充当图像生成器。INN 也可用于估计逆问题的后验[37]。 在 [38] 中的一些组成规则下,使用掩码卷积构建了更灵活的 INN。[39] 提出了一种基于无偏流的生成模型。其他工作改进了耦合层以进行密度估计,例如 Glow [40] 和 i-ResNet [41],从而提高了生成质量。
Lu [3], Jing [21] and Jia [42] introduced INN into image steganography. The strict invertibility of INN just meets the requirement that embedding and extraction are mutually inverse processes. Therefore they gain state-of-the-art performance in image steganography. However, the strict invertibility also means that when the container image is attacked, the noise is also transmitted to the extracted image, which make it vulnerable to attack. Xu [6] proposed robust invertible image steganography (RIIS) and improve the robustness of the aforementioned invertible neural networks.
Lu [3]、Jing [21] 和 Jia [42] 将 INN 引入图像隐写术。INN 的严格可逆性恰好满足了嵌入和提取是相互逆过程的要求。因此,它们在图像隐写术中获得了最先进的性能。然而,严格的可逆性也意味着,当容器镜像受到攻击时,噪声也会传递到提取的镜像上,这使得它容易受到攻击。Xu [6] 提出了鲁棒可逆图像隐写术(RIIS),提高了上述可逆神经网络的鲁棒性。
In the field of image steganography, the invertible network has shown its great potential. It achieves state-of-the-art performance by utilizing the prior knowledge that hiding and extraction are inverse processes [3, 21], along with the strict reversibility of its own network. However, due to its strictly reversible nature, when the container image is perturbed, the inverse process of its network will also be perturbed. This implies that the extracted image will also be distorted. To address this issue, we proposed our model PRIS, by introducing two new modules: pre-enhance and post-enhance, which are added before and after the extraction process respectively, and through a 3-step training strategy, we improve its robustness to state-of-the-art level. Moreover, rounding error is considered in our PRIS since it is unavoidable in practice, and a gradient approximate function is proposed to address the undifferentiable problem of rounding operation.
在图像隐写术领域,可逆网络已经展现出了其巨大的潜力。它利用隐藏和提取是逆过程的先验知识[3,21],以及其自身网络的严格可逆性,实现了最先进的性能。但是,由于其严格可逆的特性,当容器镜像受到扰动时,其网络的逆过程也会受到扰动。这意味着提取的图像也会失真。为了解决这个问题,我们提出了我们的模型 PRIS,通过引入两个新模块:预增强和后增强,分别在提取过程之前和之后添加,并通过三步训练策略,将其鲁棒性提高到最先进的水平。此外,我们的 PRIS 考虑了舍入误差,因为它在实践中是不可避免的,并提出了梯度近似函数来解决舍入运算的不可微分问题。
3Method 3、方法
3.1Overview 3.1 概述
Let xh, xs, xc and xe denote the host, secret, container and extracted image respectively. The architecture of our model is shown as Fig. 1. In the embedding process, the xh and xs are first transformed to the frequency domain by discrete wavelet transform (DWT), and then fed into N invertible blocks, which output two images. The output corresponding to image xh is further transformed to the spatial domain by IWT, resulting in xc. The output z^ corresponding to image xs is inaccessible in the extraction process, and we hope that it follows a Gaussian distribution, so that we can input a Gaussian distribution in the extraction process. In practical, xc will be attacked by different distortion and becomes image xd. In the extraction process, if pre-enhance module is enabled, xd is enhanced by pre-enhance first and then transformed by DWT before being sent to the inverse process of invertible blocks. Meanwhile, a Gaussian distributed image z is also sent to the invertible blocks. Finally, we obtain two images, revealed host and extracted secret in the frequency domain. The latter is transformed to the xe by inverse wavelet transform (IWT). If post-enhance is enabled, this image will be further enhanced by a post-enhance module.
让 xh 、 xs 和 分别 xc xe 表示主机、密钥、容器和提取的镜像。我们模型的架构如图所示。1、在嵌入过程中, xh 首先通过离散小波变换(DWT)将和变 xs 换到频域,然后馈入可逆块中 N ,输出两张图像。图像 xh 对应的输出通过 IWT 进一步转换为空间域,得到 xc 。图像 xs 对应的输出 z^ 在提取过程中是无法访问的,我们希望它遵循高斯分布,这样我们就可以在提取过程中输入高斯分布。在实践中, xc 会受到不同畸变的攻击而成为图像 xd 。在提取过程中,如果启用了预增强模块, xd 则先通过预增强进行增强,然后通过 DWT 进行变换,然后发送到可逆块的逆过程。同时,高斯分布式图像 z 也被发送到可逆块。最后,我们获得了两张图像,揭示了主机,并提取了频域中的秘密。后者通过逆小波变换 (IWT) xe 进行变换。如果启用了后期增强,则此图像将通过后期增强模块进一步增强。
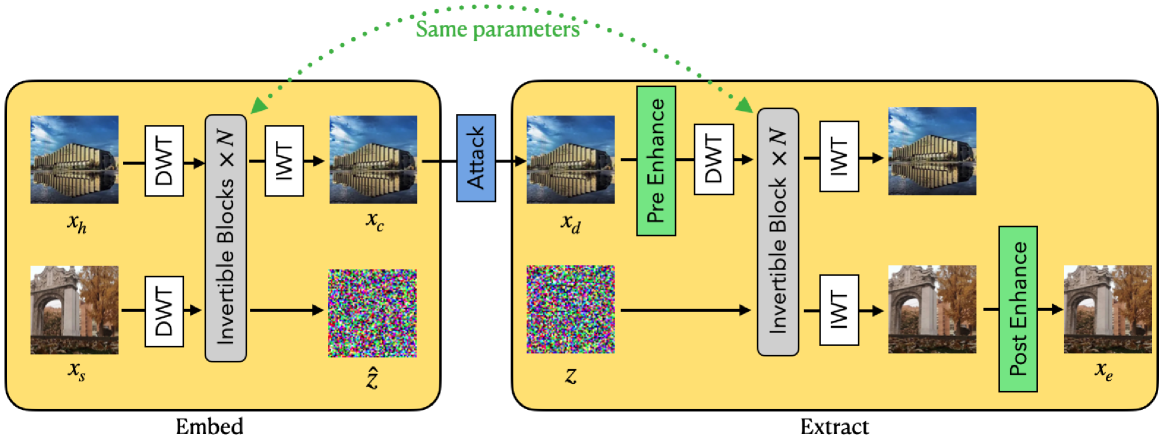
Figure 1:The framework of PRIS, it contains two main parts, invertible blocks and enhance modules, DWT and IWT denote discrete wavelet transform and inverse wavelet transform respectively. The left block is the embedding process and the right block is the extraction process. z is a random noise that follows a normal distribution.
图 1:PRIS 的框架 ,它包含两个主要部分,可逆块和增强模块,DWT 和 IWT 分别表示离散小波变换和逆小波变换。左边的块是嵌入过程,右边的块是提取过程。 z 是遵循正态分布的随机噪声。
3.2Invertible block
3.2 可倒积块
Fig. 2 shows the overview of invertible block. In the forward process, it takes xhi and xsi as input, and outputs xhi+1 and xsi+1 with the same size as the input. Eq. (1) gives the formula of it.
无花果。 图 2 示出了可逆块的概述。在正向过程中,它采用 xhi 和 xsi 作为输入,输出 xhi+1 和 xsi+1 与输入大小相同。式(1)给出了它的公式。
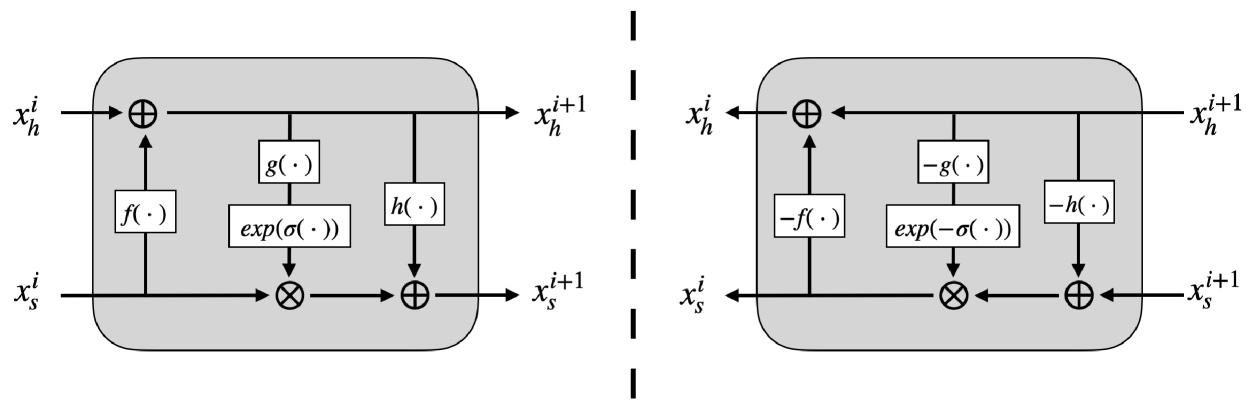
Figure 2:Network architecture of an invertible block. The left part shows the forward process, i.e., the embedding process. The right part shows the backward process, i.e., the extraction process. f(⋅), g(⋅) and h(⋅) represent three convolutional networks that share the same architecture, σ denotes sigmoid activate function, ⊗ and ⊕ denote element-wise multiply and add.
图 2: 可逆块的网络架构。 左侧部分显示了正向过程,即嵌入过程。右侧部分显示了向后过程,即提取过程。 f(⋅) , g(⋅) 表示 h(⋅) 共享相同架构的三个卷积网络, σ 表示 sigmoid 激活函数, ⊗ 表示 ⊕ 元素乘法和加法。
| xhi+1 | =xhi+f(xsi) | |||
| xsi+1 | =xsi⊗exp(σ(g(xhi+1)))+h(xhi+1) | (1) |
By transforming Eq. (1), we can easily obtain their inverse processes. The result is shown as below:
通过变换式(1),我们可以很容易地得到它们的逆过程。结果如下图所示:
| xsi | =(xsi+1−h(xhi+1))⊗exp(−σ(g(xhi+1))) | |||
| xhi | =xhi+1−f(xsi) | (2) |
The invertible block takes two images as input and outputs two images for both forward and inverse processes, as implied by Eqs. (1) and (2). However, in image steganography, only one container image is transferred in communication. To address this issue, an auxiliary variable z∼N(0,1) is taken as the second image and fed into the inverse process with the container image xc.
如 Eqs 所暗示的那样,可逆块采用两个图像作为输入,并输出两个正向和反向过程的图像。(1)和(2)。然而,在图像隐写术中,在通信中仅传输一个容器图像。为了解决这个问题,将辅助变量 z∼N(0,1) 作为第二个映像,并输入到容器映像 xc 的逆向进程中。
3.3Enhance module
3.3 增强模块
We introduced pre-enhance and post-enhance modules at the beginning and end of the backward process respectively. Both modules share the same architecture of densenet [43]. The pre-enhance module takes the distorted container image as input and outputs an enhanced container image that facilitates the extraction by the invertible block. The post-enhance module takes the extracted image as input and outputs an enhanced extracted image that is more similar to the original secret image.
我们分别在向后过程的开始和结束时引入了预增强和后增强模块。两个模块共享相同的 Densenet 架构 [43]。 预增强模块将扭曲的容器图像作为输入,输出增强的容器图像,便于可逆块提取。后增强模块将提取的图像作为输入,输出与原始秘密图像更相似的增强提取图像。
The pre-enhance module aims to reduce the perturbation of the container image before feeding it into the extraction network, while the post-enhance module aims to restore the quality of the extracted image after getting it from the extraction network. In this way, we can mitigate the negative effects of perturbation on both ends of the extraction process and enhance the robustness of our method.
预增强模块旨在减少容器图像在馈入提取网络之前的扰动,而后增强模块旨在恢复从提取网络获取提取图像后的质量。通过这种方式,我们可以减轻扰动对提取过程两端的负面影响,并增强我们方法的鲁棒性。
Meanwhile, the pre-enhance and post-enhance modules can also weaken the strict reversibility of the invertible network, so that it can better resist noise. We use the analogy of a stiff stick and a soft rope to illustrate the relationship between the strict reversibility and the noise transmission. A stiff stick will transmit all the perturbations from one side to the other, while a soft rope will dampen most of the perturbations from the other side. Therefore, we introduce the enhance modules to relax the strict reversibility of INNs. By weakening the reversibility of the network, we can reduce the impact of noise on both ends of the extraction process and enhance the robustness of our method.
同时,预增强和后增强模块还可以削弱可逆网络的严格可逆性,使其能够更好地抵抗噪声。我们用硬棍和软绳的类比来说明严格的可逆性和噪声传输之间的关系。一根硬棍会将所有扰动从一侧传递到另一侧,而软绳会抑制另一侧的大部分扰动。因此,我们引入了增强模块来放宽 INN 的严格可逆性。通过削弱网络的可逆性,我们可以减少噪声对提取过程两端的影响,增强我们方法的鲁棒性。
3.4Loss function
3.4 损失函数
We are concerned with two types of similarity: one is the similarity between the host image xh and the container image xc, i.e., c-pair; the other is the similarity between the secret images xs and the extracted images xe, i.e., s-pair. We use the PSNR (Peak Signal to Noise Ratio) [44] metric to measure this similarity. Higher PSNR means higher similarity. PSNR-C and PSNR-S denote the PSNR values of c-pair and s-pair, respectively. Our goal is to maximize PSNR-C and PSNR-S. To achieve this, we introduce the following two losses, Lc and Ls:
我们关注两种相似性:一种是主机镜像 xh 和容器镜像 xc 之间的相似性,即 c 对;另一个是秘密图像 xs 和提取图像之间的相似性 xe ,即 S 对。我们使用 PSNR(峰值信噪比)[44] 指标来衡量这种相似性。PSNR 越高意味着相似度越高。PSNR-C 和 PSNR-S 分别表示 c 对和 s 对的 PSNR 值。我们的目标是最大限度地提高 PSNR-C 和 PSNR-S。为了实现这一目标,我们引入了以下两种损失, Lc 以及 Ls :
| Lc=∑p(xc(p)−xh(p))2,Ls=∑p(xs(p)−xe(p))2 | (3) |
where x(p) represents the pixel value at position p for image x, and Lc and Ls measure the similarity of c-pair and s-pair respectively. The total loss is a weighted sum of the two losses:
其中 x(p) 表示图像 x 位置 p 的像素值, Lc 并 Ls 分别测量 c 对和 s 对的相似度。总损失是两个损失的加权总和:
| L=λcLc+λsLs | (4) |
There is a trade-off between Lc and Ls. By increasing λc, we give more influence to Lc in the total loss, which improves the PSNR-C at the expense of reducing the PSNR-S. Conversely, we can enhance the PSNR-S by sacrificing some PSNR-C by increasing λs.
和 Ls 之间 Lc 有一个权衡。通过增加 λc ,我们对总损耗 Lc 产生更大的影响,从而以降低 PSNR-S 为代价提高 PSNR-C。相反,我们可以通过增加 λs 来牺牲一些 PSNR-C 来增强 PSNR-S。
3.53-step training strategy
3.5 三步训练策略
The strict invertibility is vulnerable to attack, but meets the demand of image steganography, therefore, we need to find a balance point between strict invertiblity and non-invertiblity. The existence of enhance modules breaks too much invertiblity, in order to balance it, we proposed 3-step training strategy. It splits whole training process into 3 steps.
严格可逆性容易受到攻击,但满足了图像隐写术的需求,因此,我们需要在严格可逆性和不可逆性之间找到一个平衡点。增强模块的存在打破了太多的可逆性,为了平衡它,我们提出了三步训练策略。它将整个训练过程分为 3 个步骤。
Step 1: Pre-train invertible blocks. In this step, only the invertible blocks are enabled, the enhance modules are not computed both in forward and backward process. This will guarantee the invertiblity of whole networks.
步骤 1: 预训练可逆块。在此步骤中,仅启用可逆块,在前向和后向过程中都不计算增强模块。这将保证整个网络的可逆性。
Step 2: Pre-train enhance modules. In this step, all parts of the PRIS are enabled, but the parameters of invertible block are frozen, by doing this, it will weaken the invertiblity, while make sure it will not damage the performance.
步骤 2: 预训练增强模块。在这一步中,PRIS 的所有部分都启用了,但可逆块的参数被冻结了,这样做会削弱可逆性,同时确保它不会损害性能。
Step 3: Finetune invertible blocks and enhance modules together. In this step, all parameters are enabled and will be updated during the back-propagation. It will help to improve the robustness furthermore.
步骤 3: 微调可逆块并一起增强模块。在此步骤中,所有参数都已启用,并将在反向传播期间更新。这将有助于进一步提高鲁棒性。
3.6Why rounding error is so important?
3.6 为什么舍入误差如此重要?
In this section, we present a method to demonstrate that we can embed an 8-bit secret image into an 8-bit host image and obtain a 32-bit container image with a guaranteed PSNR-C of more than 144.52dB and a lossless extraction if we neglect the rounding error. The overview of this method is shown as Fig.3.
在本节中,我们提出了一种方法来演示我们可以将 8 位秘密图像嵌入到 8 位主机图像中,并获得一个 32 位容器图像,如果我们忽略舍入误差,则保证 PSNR-C 大于 144.52dB 和无损提取。该方法的概述如图所示。3.
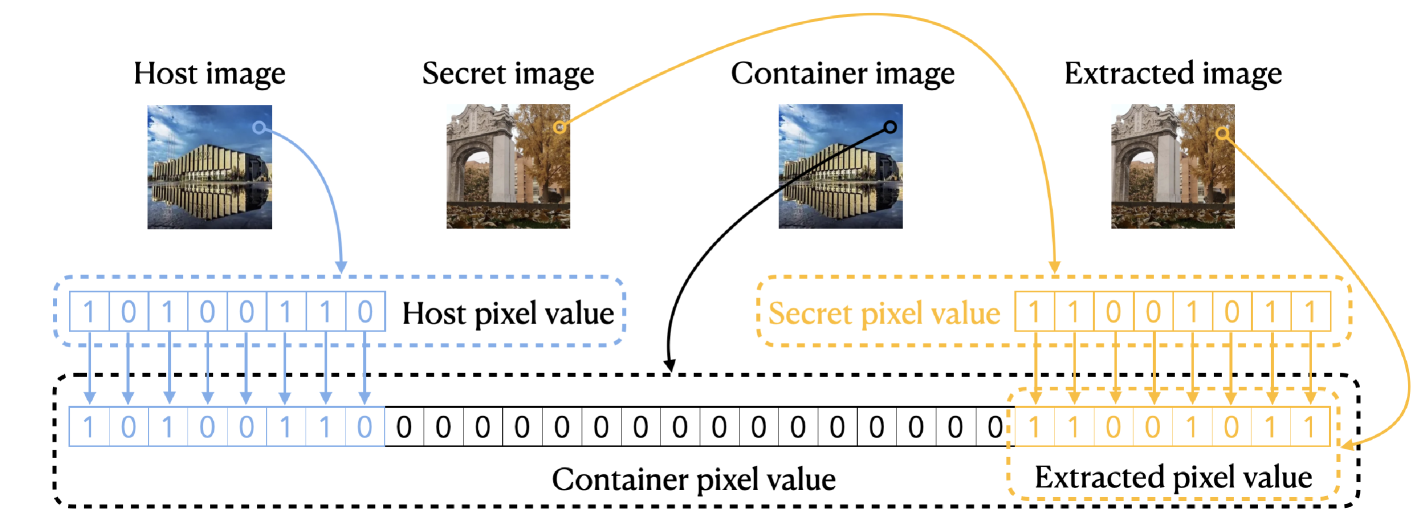
Figure 3:The method to hide and extract if the rounding error is ignored. All the pixel value is shown in binary way.
图 3: 如果忽略舍入误差,则隐藏和提取的方法。所有像素值都以二进制方式显示。
Let xhi, xsi, xci and xei denote the i-th pixel of host, secret, container and extracted image respectively. xhi, xsi and xei are integers ranging from 0 to 28−1, and xci is an integer ranging from 0 to 232−1. The formulas to compute xci and xei are given by Eqs. (5) and (6). It is clear that xei=xsi, so the extraction is a lossless process.
设 xhi 、 xsi 和 分别 xci xei 表示主机、密钥、容器和提取图像的第 i 个像素。 xhi , xsi 是 xei 0 到 28−1 的整数, xci 是 的整数,是 的整数,范围从 0 到 232−1 。要计算的公式 xci 由 xei Eqs 给出。(5)和(6)。很明显 xei=xsi ,因此提取是一个无损过程。
| xci | =224⋅xhi+xsi | (5) | ||
| xei | =xci−224⋅⌊xci⋅2−24⌋ | (6) |
Moreover, the PSNR-C is greater than 144.52dB according to Eqs. (7) and (8).
此外,根据 Eqs,PSNR-C 大于 144.52dB。(7) 和 (8)。
| MSE | =1N∑i=1N(224⋅xhi−xci)2=1N∑i=1Nxsi2≤2552 | (7) | ||
| PSNR | =10⋅log10MAX2MSE≥10⋅log10(232−1)22552>144.52 | (8) |
Where N denotes the total pixels number of the host (secret) image.
其中 表示 N 主机(秘密)图像的总像素数。
3.7Differentiable rounding function
3.7 可微舍入函数
The rounding function round has a zero gradient almost everywhere, which leads to gradient vanishing during the training process. To address this issue, we tried two ways to replace the gradient of round. First, we used 1 as the gradient of round, which means during the backward stage, we computed the gradient with y=x. Second, we proposed a modified gradient approximation function (GAF), defined by Eqs. (9) and (10).
舍入函数 round 几乎无处不在的梯度为零,这会导致训练过程中梯度消失。为了解决这个问题,我们尝试了两种方法来替换 round 的梯度。首先,我们使用 1 作为 的 round 梯度,这意味着在向后阶段,我们用 计算 y=x 梯度。其次,我们提出了一个修正的梯度近似函数(GAF),由 Eqs 定义。(9)和(10)。
| sign(x)={1,if⌊x⌋isodd−1,else | (9) | |||
| GAF(x)=sign(x)⋅0.5⋅cos(π⋅x)+0.5+⌊x⌋ | (10) |
We designed GAF based on the following two features that it shares with the rounding function:
我们根据与舍入函数共享的以下两个特性设计了 GAF:
1. It acts as an identity mapping when the input is an integer, so the gradient is zero.
1. 当输入为整数时,它充当恒等映射,因此梯度为零。
2. The gradient reaches its maximum value when the input is at the midpoint between two consecutive integers.
2. 当输入位于两个连续整数之间的中点时,梯度达到最大值。
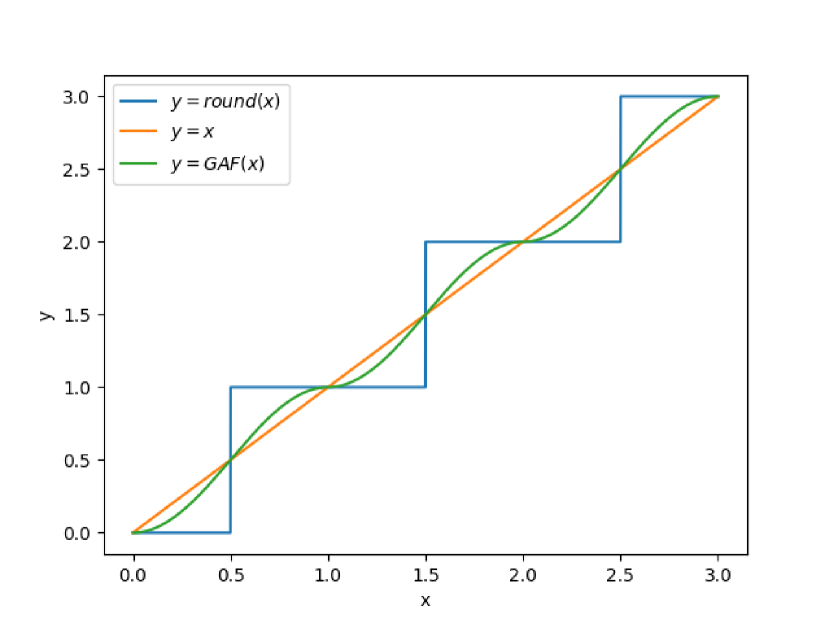
Figure 4:Round and its approximate function.
图 4:Round 及其近似函数。
4Experiment 4、实验
4.1Implementation details
4.1 实现细节
We train our model on the DIV2K training dataset [45] and evaluate it on the DIV2K testing dataset on RTX3090. The input images are cropped to a resolution of 224 × 224 pixels. For the training dataset, we apply random cropping for better generalization. For the testing dataset, we use center cropping to avoid randomness in evaluation. Each stage consists of 1600 epochs and we use the Adam optimizer with β1=0.9 and β2=0.99. The initial learning rates are 10−4.5 and 10−5.5 for steps 1, 2 and step 3 respectively, reducing them by half every 200 epochs for all steps. We set λc and λs to 1 unless otherwise specified.
我们在 DIV2K 训练数据集 [45] 上训练模型,并在 RTX3090 上的 DIV2K 测试数据集上对其进行评估。输入图像被裁剪为 224 × 224 像素的分辨率。对于训练数据集,我们应用随机裁剪以获得更好的泛化。对于测试数据集,我们使用中心裁剪来避免评估中的随机性。每个阶段由 1600 个纪元组成,我们将 Adam 优化器与 β1=0.9 和 β2=0.99 一起使用。步骤 1、2 和步骤 3 的初始学习率分别为 10−4.5 和 10−5.5 ,所有步骤每 200 个 epoch 降低一半。除非另有说明,否则我们将 and λs 设置为 λc 1。
4.2Ablation experiments
4.2 消融实验
Effectiveness of enhance module, 3-step training strategy and domain selection. As shown in the second and third rows of Table 1, both pre-enhance and post-enhance modules improved PSNR-C and PSNR-S compared to the baseline in the first row. Moreover, applying both modules together achieved further improvement. This indicates that the enhance modules can effectively reduce the noise of the distorted container image before and after the inverse process of the invertible blocks. The pre-enhance module can help the invertible blocks to resist the noise from distortion, while the post-enhance module can further refine the extracted image and remove some residual noise.
增强模块、三步训练策略和领域选择的有效性。 如表 1 的第二行和第三行所示,与第一行的基线相比,增强前和增强后模块都改善了 PSNR-C 和 PSNR-S。此外,将这两个模块一起使用实现了进一步的改进。这表明增强模块能够有效降低可逆块逆过程前后扭曲容器图像的噪声。预增强模块可以帮助可逆块抵抗失真的噪声,而后增强模块可以进一步细化提取的图像并去除一些残留噪声。
Table 1:Ablation studies for every model design, including pre-enhance, post-enhance, 3-step strategy and domain selection in PRIS under Gaussian σ=10 distortion.
表 1: 每个模型设计的消融研究,包括高斯 σ=10 畸折下 PRIS 中的预增强、后增强、三步策略和域选择。
| 3-step 3步 | Pre-en. 预语。 | Post-en. 后 en. | Domain 域 | PSNR-C | PSNR-S |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| - | × | × | - | 30.79 | 28.99 |
| ✓ | × | ✓ | Spatial 空间 | 31.02 | 29.24 |
| ✓ | ✓ | × | Spatial 空间 | 31.11 | 29.28 |
| × | ✓ | ✓ | Spatial 空间 | 30.97 | 27.63 |
| ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | Frequency 频率 | 31.09 | 29.03 |
| ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | Spatial 空间 | 31.13 | 29.34 |
Spatial domain or frequency domain?
空间域还是频域?
Junpeng Jing et al. [21] applied discrete wavelet transform (DWT) to convert images from spatial domain to frequency domain before sending them to the invertible block. Then, they used inverse wavelet transform (IWT) to convert images back from frequency domain to spatial domain after the invertible block. This means that the invertible blocks processed images in frequency domain. Their research demonstrated that hiding images in frequency domain is more effective than in spatial domain. However, weather frequency domain still the better option for enhance modules needs to be checked, therefore we did the ablation study of different domains.
Junpeng Jing 等[21] 应用离散小波变换(DWT)将图像从空间域转换为频域,然后再将其发送到可逆块。然后,他们使用逆小波变换(IWT)将可逆块后的图像从频域转换回空间域。这意味着可逆块在频域中处理过的图像。他们的研究表明,在频域中隐藏图像比在空间域中隐藏图像更有效。然而,天气频域仍然是增强模块的更好选择,因此我们对不同域进行了消融研究。
The comparison between the fifth and sixth rows of Table 1 shows that the spatial domain has a better performance than the frequency domain. Therefore, the enhance modules will process images in the spatial domain in other experiments. This may be because the spatial domain is more suitable for capturing the local features and edges of the image, which are important for image restoration. The frequency domain, on the other hand, may introduce some artifacts or distortions when transforming the image back to the spatial domain.
表 1 第五行和第六行的对比表明,空间域的性能优于频域。因此,增强模块将在其他实验中处理空间域中的图像。这可能是因为空间域更适合捕捉图像的局部特征和边缘,这对于图像恢复很重要。另一方面,在将图像转换回空间域时,频域可能会引入一些伪影或失真。
Different ways to compute the gradient of rounding function. We experimented with three different ways to compute the gradient of rounding function – setting all gradients to 0, setting all gradients to 1, and replacing round with GAF during backward propagation. Table 2 shows the results of each method. When we set the gradient of rounding function to 0, it means that the loss of secret-pair will not propagate to the embedding process, and thus it will not take extraction into account. The visual results in Fig. 5 demonstrate that it completely ignores the extraction task, and essentially, the goal becomes learning an identical mapping function. From Table 2, we can see that GAF is generally better than other methods. Therefore, we choose GAF to compute the gradient. The GAF can provide a smooth approximation of the rounding function and preserve more information during backpropagation, which can contribute to the learning process of the network.
计算舍入函数梯度的不同方法。 我们尝试了三种不同的方法来计算舍入函数的梯度——将所有梯度设置为 0,将所有梯度设置为 1,并在向后传播期间替换 round 为 GAF。表 2 显示了每种方法的结果。当我们将舍入函数的梯度设置为 0 时,这意味着 secret-pair 的丢失不会传播到嵌入过程中,因此不会考虑提取。视觉结果如图所示。5 表明它完全忽略了提取任务,从本质上讲,目标变成了学习相同的映射函数。从表 2 中我们可以看出,GAF 总体上优于其他方法。因此,我们选择 GAF 来计算梯度。GAF 可以提供舍入函数的平滑近似,并在反向传播过程中保留更多信息,这有助于网络的学习过程。
Table 2:Comparison (PSNR-C / PSNR-S) with different gradients of rounding function.
表 2: 与不同梯度的舍入函数的比较 (PSNR-C / PSNR-S)。
| gradient 梯度 | Round 圆 | JPEG Q=90 | JPEG Q=80 |
| all 0 全部 0 | 78.32 / 11.76 | 82.19 / 11.76 | 81.98 / 11.76 |
| all 1 全部 1 | 41.15 / 40.28 | 31.46 / 29.85 | 29.48 / 27.91 |
| GAF | 41.39 / 40.71 | 31.36 / 29.76 | 29.51 / 28.01 |

Figure 5:The visual result of setting the gradient of rounding function to 0, it achieves a high PSNR-C by ignoring extraction task, essentially, it tries to learn an identical mapping function.
图 5: 将舍入函数的梯度设置为 0 的视觉结果,它通过忽略提取任务来实现高 PSNR-C,本质上是尝试学习相同的映射函数。
The influence of λc and λs. Table 3 illustrates how PSNR-C and PSNR-S vary inversely with each other. A higher proportion of λc leads to a higher PSNR-C but a lower PSNR-S, while a lower proportion of λc results in a lower PSNR-C but a higher PSNR-S. This implies that in practical applications, we can adjust the ratio of these two parameters according to different tasks.
λc 下标λc\lambda_{c}italic_λ start_POSTSUBSCRIPT italic_c end_POSTSUBSCRIPT 和λs 下标λs\lambda_{s}italic_λ start_POSTSUBSCRIPT italic_s end_POSTSUBSCRIPT 的影响。表 3 说明了 PSNR-C 和 PSNR-S 如何相互反比变化。比例 λc 越高,PSNR-C 越高,PSNR-S 越低,PSNR-S 越低, λc PSNR-C 越低,PSNR-S 越高。这意味着在实际应用中,我们可以根据不同的任务来调整这两个参数的比例。
Table 3:Performance comparison with different λc and λs under Gaussian σ=10.
表 3: 与不同和 λc λs 高斯下的性能比较 σ=10 。
| (λc-λs) | (0.1-1.9) | (0.5-1.5) | (1.0-1.0) | (1.5-0.5) | (1.9-0.1) |
| PSNR-C | 23.61 | 27.66 | 31.13 | 34.23 | 39.54 |
| PSNR-S | 34.89 | 30.73 | 29.34 | 27.32 | 22.97 |
4.3Comparison with other methods
4.3 与其他方法的比较
We categorize the task into four levels of difficulty and practicality, as shown below, and compare different methods across these levels. Fig. 6 illustrates the difference between level 2 and 3.
我们将任务分为四个难度和实用性级别,如下所示,并比较了这些级别的不同方法。无花果。6 说明了 2 级和 3 级之间的区别。
Level 1: Only deal with one specific attack method with one model.
1 级: 只用一种模型处理一种特定的攻击方法。
Level 2: Deal with multiple attack methods with one model, but the attack information is required during both embedding and extraction.
2 级: 用一个模型处理多种攻击方式,但在嵌入和提取过程中都需要攻击信息。
Level 3: Deal with multiple attack methods with one model, but the attack information is only required during extraction.
3 级: 用一个模型处理多种攻击方式,但攻击信息仅在提取时才需要。
Level 4: Deal with multiple attack methods with one model, and the attack information is not required.
4 级: 用一种模型应对多种攻击方式,不需要攻击信息。

Figure 6:The difference between level 2 and 3. Level 2 requires the attack info both in embedding and extraction process, level 3 only need attack info in extraction process, which means level 2 needs to know which attack and the attack level before the attack actual happen.
图 6:2 级和 3 级的区别。2 级在嵌入和提取过程中都需要攻击信息,3 级只需要在提取过程中的攻击信息,这意味着 2 级在攻击实际发生之前需要知道是哪种攻击和攻击级别。
We evaluate our PRIS method against several methods on different levels. To handle level 4 task, PRIS is trained for all attack methods with a 3-step strategy. To handle level 3 task, we take the trained PRIS model from level 4 task, and finetune different enhancement modules for different attack methods, i.e., the second step in the 3-step strategy. This means that in practice, we can select different enhancement modules for different attacks during the extraction process.
我们根据不同层面的几种方法评估我们的 PRIS 方法。为了处理 4 级任务,PRIS 采用 3 步策略针对所有攻击方法进行了训练。为了处理 3 级任务,我们从 4 级任务中获取训练好的 PRIS 模型,并针对不同的攻击方式微调不同的增强模块,即 3 步策略的第二步。这意味着在实践中,我们可以在提取过程中针对不同的攻击选择不同的增强模块。
Table 4 displays the performance results of PRIS and several other methods on the level 1 task. Our PRIS exhibits superior performance when compared to the latest methods, establishing it as the most robust model. Fig. 7 is the visual results of PRIS in different type of attacks on level 1, the cover-pair and secret-pair are undistinguished from human eyes under different distortions.
表 4 显示了 PRIS 和其他几种方法在 1 级任务上的表现结果。与最新方法相比,我们的 PRIS 表现出卓越的性能,使其成为最稳健的型号。无花果。 图 7 是 PRIS 在 1 级不同类型攻击中的视觉结果,掩体对和秘密对在不同畸变下与人眼无区别。
Table 4:Comparison (PSNR-C / PSNR-S) between different methods on level 1.
表 4:1 级不同方法之间的比较 (PSNR-C / PSNR-S)。
| Method 方法 | Gaussian σ=1 高斯 σ =1 | Gaussian σ=10 | JPEG QF=90 | JPEG QF=80 | Round 圆 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baluja [17] 巴鲁贾 [17] | 21.94 / 20.64 | 21.36 / 19.86 | 21.86 / 20.14 | 21.53 / 19.81 | 22.05 / 20.68 |
| HiNet [21] | 37.69 / 36.70 | 30.79 / 28.99 | 31.28 / 29.60 | 29.34 / 27.66 | 40.45 / 39.78 |
| ISN [3] 国际标准网 [3] | - / 28.98 | - / 27.12 | - / 27.48 | - / 27.15 | - |
| RIIS [6] | 29.67 / 30.39 | 27.77 / 28.11 | 28.17 / 28.53 | 27.73 / 28.19 | - |
| PRIS | 37.99 / 36.97 | 31.13 / 29.34 | 31.36 / 29.76 | 29.51 / 28.01 | 41.39 / 40.71 |
Table 5 compares the results of RIIS (RIIS on level 2) and PRIS (level 4). Although level 3 requires less information than level 2, which means that level 3 is more challenging than level 2, PRIS still performance better than RIIS.
表 5 比较了 RIIS(2 级 RIIS)和 PRIS(4 级)的结果。尽管 3 级比 2 级需要更少的信息,这意味着 3 级比 2 级更具挑战性,但 PRIS 的性能仍然优于 RIIS。
Table 5:Comparison (PSNR-C / PSNR-S) between different methods, where RIIS and PRIS are trained and evaluated on level 2 and 3 respectively.
表 5: 不同方法之间的比较 (PSNR-C / PSNR-S),其中 RIIS 和 PRIS 分别在 2 级和 3 级进行训练和评估。
| Method 方法 | Gaussian σ=1 高斯 σ =1 | Gaussian σ=10 | JPEG QF=90 | JPEG QF=80 | Round 圆 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RIIS [6] | - / 30.01 | - / 28.03 | - / 28.44 | - / 28.10 | - |
| PRIS | 29.69 / 33.32 | 29.69 / 28.65 | 29.69 / 30.25 | 29.69 / 27.74 | 29.69 / 33.70 |
Table 6 shows the results of HiNet, RIIS and PRIS on level 4 task. PRIS outperformed RIIS by 0.74 dB on PSNR-S in average. HiNet has the highest PSNR-C because it did not consider attacks during training, and the attacks occurred after the embedding process, so they did not affect PSNR-C. However, the PSNR-S of HiNet was unacceptable, especially for Gaussian σ=10 and JPEG distortions. Which indicates HiNet is fragile to attacks.
表 6 显示了 HiNet、RIIS 和 PRIS 在 4 级任务上的结果。PRIS 在 PSNR-S 上的平均表现比 RIIS 高出 0.74 dB。HiNet 的 PSNR-C 最高,因为它在训练过程中没有考虑攻击,而且攻击发生在嵌入过程之后,因此不会影响 PSNR-C。然而,HiNet 的 PSNR-S 是不可接受的,特别是对于高斯 σ=10 和 JPEG 失真。这表明 HiNet 很容易受到攻击。
Table 6:Comparison (PSNR-C / PSNR-S) between different methods on level 4.
表 6:4 级不同方法之间的比较 (PSNR-C / PSNR-S)。
| Method 方法 | Gaussian σ=1 高斯 σ =1 | Gaussian σ=10 高斯 σ =10 | JPEG QF=90 | JPEG QF=80 | Round 圆 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baluja [17] 巴鲁贾 [17] | 22.12 / 20.95 | 22.12 / 20.1 | 22.12 / 20.45 | 22.12 / 19.96 | 22.12 / 20.96 |
| HiNet [21] | 43.64 / 24.55 | 43.64 / 8.470 | 43.64 / 11.44 | 43.64 / 11.39 | 43.64 / 34.36 |
| ISN [21] 国际标准网 [21] | - / 25.19 | - / 8.55 | - / 11.25 | - | - |
| RIIS [6] | - / 29.78 | - / 27.65 | - / 28.00 | - / 27.65 | - |
| PRIS | 29.69 / 30.61 | 29.69 / 28.43 | 29.69 / 29.40 | 29.69 / 27.61 | 29.69 / 30.18 |

Figure 7:Visual results of PRIS in different type of attacks.
图 7:PRIS 在不同类型攻击中的可视化结果。
4.4Experiments in Practice
4.4 实践实验
Rounding is an inevitable distortion in practice, and it is the first attack will occur once the embedding is done. Thus, we applied rounding error prior to Gaussian or JPEG distortion respectively, which is more realistic, and labelled these two errors RGaussian and RJPEG. Furthermore, since the type of distortion that occurs when embedding the secret image is unpredictable, we trained our PRIS on level 3 and 4 with these realistic distortion. Table 7 shows that the PNSR-C is 30.3 dB and the lowest PNSR-S on level 3 and 4 are 27.00 and 26.79 dB respectively, which are satisfactory. We also deployed PRIS in http://yanghang.site/hide/, where users can embed a secret image into a host image and retrieve it by simply clicking the mouse.
舍入在实践中是不可避免的失真,一旦嵌入完成,就会发生第一次攻击。因此,我们分别在高斯或 JPEG 失真之前应用舍入误差,这更真实,并将这两个误差标记为 RGaussian 和 RJPEG。此外,由于嵌入秘密图像时发生的失真类型是不可预测的,因此我们在 3 级和 4 级上使用这些逼真的失真训练了我们的 PRIS。表 7 显示,PNSR-C 为 30.3 dB,3 级和 4 级的 PNSR-S 最低值分别为 27.00 和 26.79 dB,令人满意。我们还在 http://yanghang.site/hide/ 中部署了 PRIS,用户可以将秘密映像嵌入到主机映像中,只需单击鼠标即可检索它。




















 1517
1517

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








