In contemporary VLSI chip industry, the software tools used by electrical engineers perform many optimizations. Your task is to implement one specific optimization of some chip design. Your tool is given an acyclic net of NAND gates (NAND gate computes the negated conjunction of its inputs, i.e. the output value of the gate is 0 if and only if its both input values are 1). The net is a part of already synthesized component and cannot be changed. All the inputs of the net are connected to one signal x. The objective is to disconnect x from some inputs and to assign constant signals 0 and/or 1 to those inputs in such a way that the function implemented by the design remains unchanged.
We say that an assignment of x's and/or 0's and/or 1's to the inputs of the net is optimal if the number of inputs connected to x is the smallest possible but the net still computes the same function as if all the inputs were connected to x.
Example
Look at the following design.
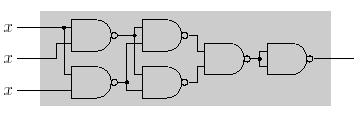
We can change it to the design with only one variable input, for example:

(Observe that there are other ways of connecting the inputs to just one x and to some number of 0's and 1's that implement the same function).
Task
Write a program which for each data set:
- reads the description of the net,
- computes an optimal assignment of x's and/or 0's and/or 1's to the inputs of the net,
- writes the result.
Input
The first line of the input contains exactly one positive integer d equal to the number of data sets, 1 ≤ d ≤ 20. The data sets follow.
Each data set consists of two consecutive lines. The rst of those lines contains exactly two positive integers n and m separated by single space, 1 ≤ n ≤ 100.000, 1 ≤ m ≤ 200.000. Integer n is the number of the net inputs and integer m is the number of the gates in the net.
The second of those lines contains exactly 2m nonzero integers, separated by single spaces. The numbers on positions 2j - 1 and 2j describe the signal sources for the inputs to gate j. The positive number s means the output of gate s. The negative number s means the (-s)-th input to the net. The gates and the net inputs are numbered starting from one. The input of each gate is connected to an input of the net or to an output of a gate whose description occurred earlier in the sequence. Each net input is connected to at least one gate input. Each gate output is connected to at least one gate input except the output of the last gate that is connected to the output of the net.
Output
The output should consist of exactly d lines, one line for each data set. The line number i should contain the answer to the i-th data set.
The answer to one data set should consist of a sequence of exactly k characters terminated by the end of line (with no spaces in between). Each of those characters should be 0 (the digit `zero' ) or 1 (the digit `one') or x (lower-case letter `x' ). The i-th symbol of the sequence denotes the assignment to the i-th input of the net.
If there are more than one optimal assignment then your program should output any of them (but only one).
Sample Input
1 3 6 -1 -3 -1 -2 1 2 1 2 4 3 5 5
Sample Output
10x
#include <cstdio> #include <cstring> using namespace std; // 门电路结构体 typedef struct gate_node { int input1, input2; int output; }gate_node; int input[100010]; gate_node gate[200010]; //int output_num; int main() { int d; scanf("%d",&d); int count = 0; while(count < d) { int n, m; scanf("%d %d", &n, &m); for(int i = 1; i <= m; i++) { scanf("%d", &gate[i].input1); scanf("%d", &gate[i].input2); } // 先确定输出是否为常数 // 尝试输入全为1的情况 memset(input, 1, sizeof(int)*(n+1)); for(int i = 1; i <= m; i++) { int in1, in2; if(gate[i].input1 < 0) in1 = input[-gate[i].input1]; else in1 = gate[gate[i].input1].output; if(gate[i].input2 < 0) in2 = input[-gate[i].input2]; else in2 = gate[gate[i].input2].output; gate[i].output = ~(in1 & in2); } int output_one = gate[m].output; // 尝试全为0的情况 memset(input, 0, sizeof(int)*(n+1)); for(int i = 1; i <= m; i++) { int in1, in2; if(gate[i].input1 < 0) in1 = input[-gate[i].input1]; else in1 = gate[gate[i].input1].output; if(gate[i].input2 < 0) in2 = input[-gate[i].input2]; else in2 = gate[gate[i].input2].output; gate[i].output = ~(in1 & in2); } int output_zero = gate[m].output; // 如果输出为常数,输出全0的情况即可 if(output_zero == output_one) { for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) printf("0"); printf("\n"); } // 否则,从全0至全1检查是否可行(二分检查) else { int begin = 1, end = n; while(begin < end) { int mid = (begin+end)/2; for(int i = 1; i <= m; i++) { int in1, in2; if(gate[i].input1 < 0) { if(-gate[i].input1 <= mid) in1 = 1; else in1 = 0; } else in1 = gate[gate[i].input1].output; if(gate[i].input2 < 0) { if(-gate[i].input2 <= mid) in2 = 1; else in2 = 0; } else in2 = gate[gate[i].input2].output; gate[i].output = ~(in1 & in2); } if(gate[m].output == output_zero) begin = mid+1; else end = mid; } for(int k = 1; k < begin; k++) printf("1"); printf("x"); for(int k = begin+1; k <= n; k++) printf("0"); printf("\n"); /* for(int j = 1; j <= n; j++) { input[j] = 1; for(int i = 1; i <= m; i++) { int in1, in2; if(gate[i].input1 < 0) in1 = input[-gate[i].input1]; else in1 = gate[gate[i].input1].output; if(gate[i].input2 < 0) in2 = input[-gate[i].input2]; else in2 = gate[gate[i].input2].output; gate[i].output = ~(in1 & in2); } if(gate[m].output != output_zero) { for(int k = 1; k < j; k++) printf("%d", input[k]); printf("x"); for(int k = j+1; k <= n; k++) printf("%d", input[k]); printf("\n"); break; } } */ } count++; } return 0; }
一道好题。自己分情况考虑x为0,1时,可以总结出来,结果无非是常数(0或1), x,或非x. 但是不知如何找到解。
看了答案,学习了方法是考虑x全0和全1的情况。如果最终输出一样,证明结果必为常数。
如果最终输出不一样,证明结果为x或非x,由x全0开始逐位变为1,如果某一次的结果和全0时不一样,代表找到解,因为x全1时和x全0时不一样,所以必有解。
然后逐位变换为1检查,TLE.
二分确定位置,中间位置以前的元素全为1,以后的元素全为0. 因为存在一个由全0的结果变为全1的结果的情况。所以总能找到解。




 本文介绍了一种针对VLSI芯片设计中NAND门电路的优化算法。该算法能够在确保电路功能不变的前提下,减少与变量信号相连的输入数量,从而达到优化电路设计的目的。
本文介绍了一种针对VLSI芯片设计中NAND门电路的优化算法。该算法能够在确保电路功能不变的前提下,减少与变量信号相连的输入数量,从而达到优化电路设计的目的。
















 597
597

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








