一、格式化输出的 格式说明符 列表
1、通用格式说明符
| 说明符 | 作用 | 示例 | 输出 |
|---|---|---|---|
| %s | 字符串(自动调用 toString()) | String.format(“%s”, “Java”) | Java |
| %c | 单个字符(Unicode 字符) | String.format(“%c”, ‘A’) | A |
| %b | 布尔值(true / false) | String.format(“%b”, null) | false |
| %h | 对象的哈希码(十六进制) | String.format(“%h”, “Hi”) | e6e |
| %% | 转义输出 % | String.format(“%%”) | % |
| %n | 换行符(平台无关) | String.format(“Line1%nLine2”) | Line1\nLine2 |
2、整数格式化
| 说明符 | 作用 | 示例 | 输出 |
|---|---|---|---|
| %d | 十进制整数 | String.format(“%d”, 42) | 42 |
| %o | 八进制整数 | String.format(“%o”, 10) | 12 |
| %x / %X | 十六进制整数(小写/大写) | String.format(“%x”, 255) | ff |
| %,d | 带千位分隔符的整数 | String.format(“%,d”, 100000) | 100,000 |
3、浮点数格式化
| 说明符 | 作用 | 示例 | 输出 |
|---|---|---|---|
| %f | 十进制浮点数 | String.format(“%.2f”, 3.1415) | 3.14 |
| %e/%E | 科学计数法(小写 e /大写 E) | String.format(“%.2e”, 12345) | 1.23e+04 |
| %g/%G | 自动选择 %f 或 %e (更紧凑) | String.format(“%.2g”, 0.0123) | 0.012 |
4、日期时间格式化
- 日期时间说明符需与 %t 或 %T 结合使用(%T 强制大写)。
- 如::%tH(小时)、%tY(年份)等。
| 说明符 | 作用 | 示例 | 输出 |
|---|---|---|---|
| %tF | ISO 日期 (yyyy-MM-dd) | String.format(“%tF”, new Date()) | 2023-08-25 |
| %tT | 24小时时间 (HH:mm:ss) | String.format(“%tT”, new Date()) | 15:30:45 |
| %tD | 短日期(MM/dd/yy) | String.format(“%tD”, new Date()) | 08/25/23 |
| %tc | 完整日期时间(默认格式) | String.format(“%tc”, new Date()) | Fri Aug 25 15:30:45 CST 2025 |
| %tH | 小时(00-23) | String.format(“%tH”, new Date()) | 15 |
| %tM | 分钟(00-59) | String.format(“%tM”, new Date()) | 30 |
| %tS | 秒(00-60) | String.format(“%tS”, new Date()) | 45 |
5、格式标志(Flags)
| 标志 | 作用 | 示例 | 输出 |
|---|---|---|---|
| - | 左对齐 | String.format(“%-10s”, “Hi”) | Hi |
| 0 | 前导零填充 | String.format(“%05d”, 42) | 00042 |
| + | 显示正负号 | String.format(“%+d”, 42) | +42 |
| 正数前加空格 | String.format(“% d”, 42) | 42 | |
| , | 添加千位分隔符(数字) | String.format(“%,d”, 100000) | 100,000 |
| ( | 负数用括号包裹 | String.format(“%(d”, -42) | (42) |
| # | 显示进制前缀 (如:0x) | String.format(“%#x”, 255) | 0xff |
6、参数索引 与 宽度/精度
- 参数索引:
- 使用 n$ 指定参数位置(如 %1$s 表示第一个参数)。
String.format("%1$s 的年龄是 %2$d 岁,%1$s 的成绩是 %3$.1f", "Alice", 25, 90.5);
// 输出:Alice 的年龄是 25 岁,Alice 的成绩是 90.5
- 宽度:
- 控制输出最小长度(如:%10s)。
- 精度:
- 控制浮点数小数位数或字符串最大长度(如:%.2f)。
String.format("%10.2f", 3.1415); // 输出: 3.14
String.format("%.3s", "Hello"); // 输出:Hel
二、System.out.format() 与 System.out.printf()
- System.out.format() 与 System.out.printf() 是 等价的 。
- 只需要一个简单的 格式化字符串,加上一串参数即可,每个参数对应一个 格式修饰符。
1、基础格式化
- 示例:
public static void baseFormat() {
String name = "Alice";
int age = 25;
double score = 85.5;
// 格式化输出:字符串、整数、浮点数
// 输出:Name: Alice, Age: 25, Score: 85.5
System.out.format("Name: %s, Age: %d, Score: %.1f%n", name, age, score);
System.out.printf("Name: %s, Age: %d, Score: %.1f%n", name, age, score);
}
2、控制宽度与对齐
- 示例:
public static void baseFormat() {
String item = "Apple";
double price = 3.99;
// 左对齐(-)、固定宽度(10)、浮点数固定宽度为 8,保留 2 位小数(8.2)。
// %n 表示换行。
// 输出:Apple | 3.99
// Apple 后边 5 个空格。 3.99前边4个空格。
System.out.format("%-10s|%8.2f%n", item, price);
// 输出: Apple| 3.99
// Apple 前边 5 个空格。 3.99前边4个空格。
System.out.printf("%10s|%8.2f%n", item, price);
double x = 10000.0 / 3.0;
// 3333.3333333333335
System.out.println(x);
// 打印 x 时字段宽度 (field width) 为 8 个字符,精度为 2 个字符。
// 输出结果为 " 3333.33" 。即:结果包含一个前导的空格和 7 个字符。
System.out.printf( "%8.2f%n", x);
// 如果结果超过了指定的 字段宽度 (field width) 为 2 个字符。则 字段宽度 无效。按照实际长度进行显式。
System.out.printf( "%2.2f%n", x);
// 打印 x 时字段宽度 (field width) 为 9 个字符,精度为 2 个字符。
// 输出结果为:" 3.33E+03" 。即:结果包含一个前导的空格和 8 个字符。
System.out.printf("%9.2E", x);
}
3、多参数与参数索引
- 示例:
public static void baseFormat(){
int x = 10, y = 20;
// 重复使用参数索引(1$:表示第一个参数,2$:表示第二个参数,3$:表示第三个参数,)
// 输出:x = 10, y = 20, x + y = 10 + 20 = 30
System.out.format("x = %1$d, y = %2$d, x + y = %1$d + %2$d = %3$d%n", x, y, x + y);
}
4、日期时间格式化
- 示例:
public static void baseFormat(){
Date now = new Date();
// 格式化日期时间
// 输出:当前时间:2025-05-16 14:16:30
System.out.format("当前时间:%tF %tT%n", now, now);
}
5、进制转换
- 示例:
public static void baseFormat(){
int number = 255;
// 十六进制、八进制、二进制
// Hex: ff, Octal: 377, Binary: 11111111
System.out.format("Hex: %x, Octal: %o, Binary: %s%n", number, number, Integer.toBinaryString(number));
}
6、填充与特殊符号
- 示例:
public static void baseFormat(){
int value = 42;
// 前导 0 填充(%04d)、每三位添加分隔符(%,d)
// 输出:ID: 0042 | Salary: ¥1,000,000
System.out.format("ID: %04d | Salary: ¥%,d%n", value, 1000000);
}
7、科学计数法
- 示例:
public static void baseFormat(){
double distance = 149600000;
// 科学计数法,保留 3 位有效小数(%.3e)
// 输出:地球到太阳的距离:1.496e+08 公里
System.out.format("地球到太阳的距离:%.3e 公里%n", distance);
}
8、本地化格式(Locale)
- 示例:
public static void baseFormat(){
double amount = 1234567.89;
// 使用中国本地化格式(分隔符为 , ,小数点为. )
// 金额:1,234,567.89 人民币
System.out.format(Locale.CHINA, "金额:%,.2f 人民币%n", amount);
}
三、String.format() 与 java.util.Formatter 类
- String.format() 使用的就是 java.util.Formatter 来实现的。
public static String format(String format, Object... args) {
return new Formatter().format(format, args).toString();
}
1、String.format()
- 直接返回格式化后的字符串,适用于快速生成格式化结果。
- 示例:
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 基本格式化
String name = "Bob";
int age = 30;
String result = String.format("Name: %s, Age: %d", name, age);
// 输出:Name: Bob, Age: 30
System.out.println(result);
// 浮点数与对齐
double price = 99.95;
// 宽度10,保留2位小数
String formatted = String.format("价格: %10.2f 元", price); /
// 输出:价格: 99.95 元
System.out.println(formatted);
// 日期格式化
Date now = new Date();
// %<tT 复用前一个参数
String dateStr = String.format("当前时间: %tF %<tT", now);
// 输出:当前时间: 2025-05-16 14:42:26
System.out.println(dateStr);
}
2、Formatter 类
- 更灵活,可指定输出目标(如:StringBuilder、文件、流 等),适合需要复用或复杂输出的场景。
- 示例:
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 输出到 StringBuilder
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
try (Formatter formatter = new Formatter(sb)) {
formatter.format("商品: %s\n", "Coffee");
formatter.format("单价: %.2f 元\n", 25.5);
formatter.format("数量: %d 杯", 3);
}
System.out.println(sb.toString());
// 输出到文件
try (Formatter fileFormatter = new Formatter("data.txt")) {
fileFormatter.format("用户: %s\n", "Alice");
fileFormatter.format("积分: %d", 1000);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
四、java.util.HexFormat – (Java 17)
- HexFormat类 – (非线程安全 )
1、将 byte[] 数组 转换为 十六进制 字符串
- 代码
/**
* 将 字符串 按照指定编码,转成 十六进制 字符串
*/
public static String getHexStringForString(String param, String charsetName){
byte[] bytes = null;
try {
bytes = String.valueOf(param).getBytes(charsetName);
// 若必须使用 UTF-16,可手动去除 BOM(Byte Order Mark)以标识字节顺序(大端序或小端序)。
// BOM(字节顺序标记):UTF-16 编码默认添加 BOM 即:FE FF(大端序),对应有符号字节为 -2 和 -1。
if (bytes.length >= 2 && bytes[0] == -2 && bytes[1] == -1) {
bytes = Arrays.copyOfRange(bytes, 2, bytes.length);
}
/*StringBuffer buffer = new StringBuffer();
for (byte b : bytes){
// 将 字节 进行 十六进制格式化
buffer.append(String.format("%02X", b));
}
return buffer.toString();*/
// 下边两行代码 等价于 上边 5 行代码
HexFormat hf = HexFormat.of();
// 将 byte[] 数组转换为 十六进制字符串
return hf.formatHex(bytes);
} catch (UnsupportedEncodingException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 3042
System.out.println(getHexStringForString("あ", String.valueOf(StandardCharsets.UTF_16)));
// 003100310031
System.out.println(getHexStringForString("111", String.valueOf(StandardCharsets.UTF_16)));
}
- 定制 转换格式
// 分隔符为空格,添加前缀 0x,大写字母(如:0x6F):
HexFormat hf = HexFormat.ofDelimiter(" ").withPrefix("0x").withUpperCase();
// 0x31 0x31 0x31
System.out.println(hf.formatHex("111".getBytes()));
2、从 十六进制 字符串 到 byte[] 数组 转换
- 代码
byte[] bs = HexFormat.of().parseHex("003100310031");
// [0, 49, 0, 49, 0, 49]
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(bs));
// 111
System.out.println(new String(bs, StandardCharsets.UTF_16));
五、java.text.NumberFormat – 数字的 格式化 与 解析
- 用于对数字进行 本地化 的 格式化 与 解析,支持数字、货币、百分比等格式。
- 可以实现 国际化 的数字处理需求。
- NumberFormat 类 – (非线程安全 )
核心功能
- 格式化数字:将数值转换为符合特定地区习惯的字符串。
- 解析字符串:将 本地化 的字符串 解析 为 Number 对象。
- 支持类型:数字、货币、百分比。
1、对 数字 进行格式化 和 解析
public static void main(String[] args) {
// getIntegerInstance() 省略 Locale,使用默认地区(Locale.getDefault())。
double number = 956123.456;
// 1、格式化成整数字符串。
NumberFormat cnInteger = NumberFormat.getIntegerInstance();
// 956,123
System.out.println(cnInteger.format(number));
// 禁用千分位分隔符
cnInteger.setGroupingUsed(false);
// 956123
System.out.println(cnInteger.format(number));
// 使用 setMinimumIntegerDigits 时,如果数字本身的整数部分长度小于指定的最小整数位数,则会在前面补零。
cnInteger.setMinimumIntegerDigits(10);
// 0000956123
System.out.println(cnInteger.format(number));
// 2、长短风格。
// 短风格
NumberFormat shortFormat = NumberFormat.getCompactNumberInstance(Locale.ENGLISH, NumberFormat.Style.SHORT);
// 956K
System.out.println(shortFormat.format(number));
// 长风格
NumberFormat longFormat = NumberFormat.getCompactNumberInstance(Locale.ENGLISH, NumberFormat.Style.LONG);
// 956 thousand
System.out.println(longFormat.format(number));
// 3、设置 整数 和 小数 的位数
NumberFormat numberFormat = NumberFormat.getNumberInstance();
// 设置小数部分的位数为 小数点后 4 位。
numberFormat.setMinimumFractionDigits(4);
// 设置整数部分的位数为 10 位。
numberFormat.setMinimumIntegerDigits(10);
// 0,000,956,123.4560
System.out.println(numberFormat.format(number));
// 4、禁用千分位分隔符
numberFormat.setGroupingUsed(false);
//0000956123.4560
System.out.println(numberFormat.format(number));
// 解析字符串
try {
NumberFormat usFormat = NumberFormat.getNumberInstance(Locale.CHINA);
Number parse = usFormat.parse("956,123.46");
// 956123.46
System.out.println(parse.doubleValue());
} catch (ParseException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
2、对 货币量 进行格式化 和 解析
- NumberFormat.getCurrencyInstance() 返回的是一个只针对一种货币的格式器。
public static void main(String[] args) throws ParseException {
double amount = 1234.56;
// 1、货币格式化
// 中文(简体,中国)的货币格式
NumberFormat cnFormat = NumberFormat.getCurrencyInstance(Locale.CHINA);
cnFormat = NumberFormat.getCurrencyInstance(
new Locale.Builder().setLanguage("zh").setRegion("CN").setScript("Hans").build());
// 使用 setMinimumFractionDigits 时,如果数字的小数部分长度小于指定的最小小数位数,则会在后面补零。
cnFormat.setMinimumFractionDigits(3);
String price = cnFormat.format(amount);
// 中国:¥1,234.560
System.out.println("中国:" + price);
// 2、货币字符串 解析为 数字。
Number number = cnFormat.parse("¥1,234.560");
// 中国货币格式解析为数字:1234.56
System.out.println("中国货币格式解析为数字:" + number.doubleValue());
// 美元格式(美国)
NumberFormat usFormat = NumberFormat.getCurrencyInstance(Locale.US);
// 美国:$1,234.56
System.out.println("美国:" + usFormat.format(amount));
// 2、货币字符串 解析为 数字。
number = usFormat.parse("$1,234.56");
// 美国货币格式解析为数字:1234.56
System.out.println("美国货币格式解析为数字:" + number.doubleValue());
// 欧元格式(德国)
NumberFormat deFormat = NumberFormat.getCurrencyInstance(Locale.GERMANY);
// 德国:1.234,56 €
System.out.println("德国:" + deFormat.format(amount));
// 2、货币字符串 解析为 数字。
// 直接用 NumberFormat.getCurrencyInstance(Locale.GERMANY) 。
// 提示 Unparseable number: "1.234,56 €"
number = NumberFormat.getNumberInstance(Locale.GERMANY).parse("1.234,56 €");
// 德国货币格式解析为数字:1234.56
System.out.println("德国货币格式解析为数字:" + number.doubleValue());
}
- 假如有一张货物单,货物单中有些货物的金额是用美元表示的,有些是用欧元表示的。
- 处理这样的情况,应该使用 Currency 类来控制被格式器处理的货币。
- 将一个货币标识符传给静态的 Currency.getlnstance 方法来得到一个 Currency 对象。
- 然后,对每一个格式器都调用 setcurrency 方法。
public class CurrencyFormattingExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
double amount = 1234.56;
// 场景 1:以美国格式显示欧元金额(符号在前,千分位逗号,小数点)
// 英语 (美国) 格式的欧元金额: €1,234.56
formatCurrency(amount, Locale.US, "EUR");
// 场景 2:以法国格式显示欧元金额(符号在后,千分位空格,小数点逗号)
// 法语 (法国) 格式的欧元金额: 1 234,56 €
formatCurrency(amount, Locale.FRANCE, "EUR");
// 场景 3:以中国格式显示欧元金额(符号在前,千分位逗号)
// 中文 (中国) 格式的欧元金额: €1,234.56
formatCurrency(amount, Locale.CHINA, "EUR");
}
/**
* 将金额格式化为指定区域风格 + 指定货币
* @param amount 金额
* @param locale 区域(控制格式风格)
* @param currency 货币代码(如 "EUR")
*/
public static void formatCurrency(double amount, Locale locale, String currency) {
try {
// 1. 创建指定区域的货币格式化器
NumberFormat formatter = NumberFormat.getCurrencyInstance(locale);
// 2. 设置货币为欧元(覆盖区域默认货币)
Currency euro = Currency.getInstance(currency);
formatter.setCurrency(euro);
// 3. 格式化输出
String formatted = formatter.format(amount);
System.out.println(locale.getDisplayName() + " 格式的欧元金额: " + formatted);
} catch (IllegalArgumentException e) {
System.out.println("无效货币代码: " + currency);
}
}
}
3、对 百分比 进行格式化 和 解析
public static void main(String[] args) throws ParseException {
double amount = 1234.56;
// 1、格式化成百分号字符串。
NumberFormat cnPercent = NumberFormat.getPercentInstance();
// 设置小数部分的位数为 小数点后 2 位。
cnPercent.setMinimumFractionDigits(2);
// 设置整数部分的位数为 10 位。
cnPercent.setMinimumIntegerDigits(10);
// 0,000,123,456.00%
System.out.println(cnPercent.format(amount));
// 禁用千分位分隔符
cnPercent.setGroupingUsed(false);
// 0000123456.00%
System.out.println(cnPercent.format(amount));
// 2、百分号字符串 解析为 数字。
Number number = cnPercent.parse("0000123456.00%");
// 1234.56
System.out.println(number.doubleValue());
}
4、子类 – DecimalFormat 类(非线程安全)
- DecimalFormat 描述了世界各地的各种格式化机制 。
- 可以修改现有对象的每个设置项,也可以创建全新的格式器。
- 模式语法 使这种设置变得更简便了。
- 模式描述了必需的和可选的数字位数,以及正数和负数的前缀与后缀****。
// 模式语法:模式中的分号将正数和可选的负数部分分隔开。
DecimalFormat df = new DecimalFormat("#,##0.00;(#,##0.00)");
// 输出:12.35
System.out.println(df.format(12.345));
// 输出:(12.35)
System.out.println(df.format(-12.345));
- 代码:
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 1、基本数值格式化
DecimalFormat df = new DecimalFormat("#,##0.00");
// 输出:12,345.68(自动四舍五入)
System.out.println(df.format(12345.678));
// 输出:0.50
System.out.println(df.format(0.5));
// 2、处理负数
// 正数显示为 12.35,负数显示为 (12.35)
df = new DecimalFormat("#,##0.00;(#,##0.00)");
// 输出:12.35
System.out.println(df.format(12.345));
// 输出:(12.35)
System.out.println(df.format(-12.345));
// 3、百分比格式
df = new DecimalFormat("0.00%");
// 输出:85.60%(自动乘以100)
System.out.println(df.format(0.856));
// 4、科学计数法
df = new DecimalFormat("0.###E0");
// 输出:1.2345E4
System.out.println(df.format(12345));
// 5、自定义符号
df = new DecimalFormat("¥#,##0.00;¥-#");
// 覆盖模式中的负数前缀
df.setNegativePrefix("欠款¥");
// 输出:¥1,234.50
System.out.println(df.format(1234.5));
// 输出:欠款¥1234.5
System.out.println(df.format(-1234.5));
double number = 123.45;
DecimalFormat decimalFormat = new DecimalFormat();
// 6、设置最小整数位数为 6,最小小数位数为 3 。
decimalFormat.setMinimumIntegerDigits(6);
decimalFormat.setMinimumFractionDigits(3);
String formattedNumber = decimalFormat.format(number);
// 输出: 000,123.450
System.out.println(formattedNumber);
// 7、设置舍入模式
df = new DecimalFormat("#,##0.00");
// 四舍五入(默认)
df.setRoundingMode(RoundingMode.HALF_UP);
// 0.86
System.out.println(df.format(0.856));
// 直接截断
df.setRoundingMode(RoundingMode.DOWN);
// 0.85
System.out.println(df.format(0.856));
// 8、本地化适配
// 结合Locale设置符号(如小数点、千分位符)
NumberFormat nf = NumberFormat.getNumberInstance();
df = (DecimalFormat) nf;
df.applyPattern("#,##0.00");
// 输出:1,234.50
System.out.println(df.format(1234.5));
}
六、日期格式化
- 当格式化 日期和时间 时,需要考虑 4 个与 locale 相关的问题:
- 月份和星期应该用本地语言来表示。
- 年、月、日的顺序要符合本地习惯。
- 公历可能不是 本地首选的 日期表示方法。
- 必须要考虑本地的时区。
1、java.text.DateFormat 类
- 格式化日期:就是将日期转换成相应的字符串。
- 它提供如下方法来获取 DateFormat 实例。
- getDateInstance():得到一个日期格式,格式化出来的字符串只有日期。
- getTimeInstance():得到一个时间格式,格式化出来的字符串只有时间。
- getDateTimeInstance():格式化出来的字符串既有日期、时间。
- 可以指定日期、时间的风格:FULL/LONG/NEDIUM/SHORT
- 还传入 Locale,用于指定格式化适应哪个国家的字符串。
- 得到实例之后,调用它的如下方法
- String format(Date date)
import java.text.DateFormat;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.Locale;
public class DateFormatTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Date date = new Date();
// Wed May 21 16:27:28 CST 2025
System.out.println(date);
//为了让这个日期显示的更人性化,于是要将日期格式化成日期字符串
DateFormat dateFormat = DateFormat.getDateInstance();
DateFormat timeFormat = DateFormat.getTimeInstance();
DateFormat datetimeFormat = DateFormat.getDateTimeInstance();
// 2025年5月21日
System.out.println(dateFormat.format(date));
// 16:27:28
System.out.println(timeFormat.format(date));
// 2025年5月21日 16:27:28
System.out.println(datetimeFormat.format(date));
//中国的,当前计算机默认的。
System.out.println("-------中国的----------------");
DateFormat fcndatetimeFormat = DateFormat.getDateTimeInstance(DateFormat.FULL,DateFormat.FULL);
DateFormat lcndatetimeFormat = DateFormat.getDateTimeInstance(DateFormat.LONG,DateFormat.LONG);
DateFormat mcndatetimeFormat = DateFormat.getDateTimeInstance(DateFormat.MEDIUM,DateFormat.MEDIUM);
DateFormat scndatetimeFormat = DateFormat.getDateTimeInstance(DateFormat.SHORT,DateFormat.SHORT);
// 2025年5月21日星期三 中国标准时间 16:27:28
System.out.println(fcndatetimeFormat.format(date));
// 2025年5月21日 CST 16:27:28
System.out.println(lcndatetimeFormat.format(date));
// 2025年5月21日 16:27:28
System.out.println(mcndatetimeFormat.format(date));
// 2025/5/21 16:27
System.out.println(scndatetimeFormat.format(date));
//美国的
System.out.println("-------美国的----------------");
DateFormat fusdatetimeFormat = DateFormat.getDateTimeInstance(DateFormat.FULL,DateFormat.FULL,Locale.US);
DateFormat lusdatetimeFormat = DateFormat.getDateTimeInstance(DateFormat.LONG,DateFormat.LONG,Locale.US);
DateFormat musdatetimeFormat = DateFormat.getDateTimeInstance(DateFormat.MEDIUM,DateFormat.MEDIUM,Locale.US);
DateFormat susdatetimeFormat = DateFormat.getDateTimeInstance(DateFormat.SHORT,DateFormat.SHORT,Locale.US);
// Wednesday, May 21, 2025, 4:27:28 PM China Standard Time
System.out.println(fusdatetimeFormat.format(date));
// May 21, 2025, 4:27:28 PM CST
System.out.println(lusdatetimeFormat.format(date));
// May 21, 2025, 4:27:28 PM
System.out.println(musdatetimeFormat.format(date));
// 5/21/25, 4:27 PM
System.out.println(susdatetimeFormat.format(date));
}
}
2、java.text.SimpleDateFormat 类
- 将日期对象(Date)转换为特定格式的字符串,或将字符串解析为日期对象 。
- 注意:SimpleDateFormat 非线程安全,多线程环境下需谨慎使用。
- 常用日期模式符号:
| 符号 | 含义 | 示例 |
|---|---|---|
| y | 年(Year) | yyyy → 2023 |
| M | 月(Month) | MM → 09(数字)、MMM → Sep(英文缩写) |
| d | 日(Day) | dd → 05 |
| H | 小时(24 小时制) | HH → 15 |
| h | 小时(12 小时制) | hh → 03 |
| m | 分钟(Minute) | mm → 30 |
| s | 秒(Second) | ss → 45 |
| S | 毫秒(Millisecond) | SSS → 123 |
| E | 星期(Day of week) | EEE → Mon |
| a | 上午/下午(AM/PM) | a → PM |
| z | 时区(Time zone) | z → CST |
public class SimpleDateFormatExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 1、格式化日期(Date → 字符串)
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
String formattedDate = sdf.format(new Date());
// 当前时间: 2025-05-21 16:22:03
System.out.println("当前时间: " + formattedDate);
// 2、解析字符串(字符串 → Date)
sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("dd/MM/yyyy");
try {
Date date = sdf.parse("05/10/2025");
// 解析后的日期: Sun Oct 05 00:00:00 CST 2025
System.out.println("解析后的日期: " + date);
} catch (ParseException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
// 3、设置时区
sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss z");
// 设置为 UTC 时区
sdf.setTimeZone(TimeZone.getTimeZone("UTC"));
String utcTime = sdf.format(new Date());
// UTC时间: 2025-05-21 08:25:15 UTC
System.out.println("UTC 时间: " + utcTime);
}
}
3、java.time.format.DateTimeFormatter 类
- 用于将日期时间对象(如:LocalDate、LocalDateTime、ZonedDateTime 等)格式化为字符串。
- 用于将字符串解析为日期时间对象 。
- 替代旧版的 SimpleDateFormat,具有 线程安全、丰富的预定义格式、灵活的本地化支持 等特性。
- 模式字母大小写敏感:
- yyyy:4 位年份。
- MM:2 位月份(01-12)。
- dd:2 位天数。
- HH:24 小时制小时(00-23)。
- mm:分钟。
- ss:秒。
- SSS:毫秒。
- z:时区缩写(如 CST)。
- 特点:
- 预定义格式:内置 ISO 标准格式(如 ISO_LOCAL_DATE、ISO_DATE_TIME)。
- 模式化格式:通过模式字符串(如 “yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss”)自定义格式。
- 本地化格式:根据区域设置自动适配日期时间显示样式(如:中文、英文)。
- 复杂格式构建:使用 DateTimeFormatterBuilder 实现多段拼接、文本填充等高级功能。
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 1. 预定义格式
LocalDateTime now = LocalDateTime.now();
// ISO格式: 2025-05-21T16:00:41.053032
System.out.println("ISO格式: " + now.format(DateTimeFormatter.ISO_LOCAL_DATE_TIME));
// 解析 ISO 格式字符串
LocalDateTime parsed = LocalDateTime.parse("2024-05-31T15:30:45", DateTimeFormatter.ISO_LOCAL_DATE_TIME);
// 2024-05-31T15:30:45
System.out.println(parsed);
// 2. 自定义模式
DateTimeFormatter customFormatter = DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
String customFormatted = now.format(customFormatter);
// 自定义格式: 2025/05/21 16:00
System.out.println("自定义格式: " + customFormatted);
// 解析字符串为日期时间
LocalDateTime parsedDateTime = LocalDateTime.parse("2024-05-31 15:30:45", customFormatter);
// 2024-05-31T15:30:45
System.out.println(parsedDateTime);
// 3. 本地化格式(中文)
DateTimeFormatter chineseFormatter = DateTimeFormatter
.ofLocalizedDateTime(FormatStyle.MEDIUM)
.withLocale(Locale.CHINA);
// 中文长格式: 2025年5月21日 16:06:08
System.out.println("中文长格式: " + now.format(chineseFormatter));
// 4. 解析带时区的字符串
DateTimeFormatter zoneFormatter = DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss z");
ZonedDateTime zoned = ZonedDateTime.parse("2024-05-31 15:30:45 CST", zoneFormatter);
// 解析后的时区时间: 2024-05-31T15:30:45-05:00[America/Chicago]
System.out.println("解析后的时区时间: " + zoned);
// 5. 复杂格式构建
DateTimeFormatter complex = new DateTimeFormatterBuilder()
.appendLiteral("Event Time: ")
.appendPattern("yyyy-MM-dd")
.appendLiteral(" at ")
.appendPattern("HH:mm")
.toFormatter();
// 复杂格式: Event Time: 2025-05-21 at 16:06
System.out.println("复杂格式: " + now.format(complex));
}
4、Java 日期格式中 YYYY 与 yyyy 的区别?
- yyyy:基于日历年(Calendar Year)
- 即通常理解的年份(如:2023 年 1 月 1 日至 2023 年 12 月 31 日)。
- 行为:
- 严格按照日期的实际年份格式化。
- 始终与日期所在的自然年一致。
- 适用场景:日常日期格式化(如:2025-12-31)。
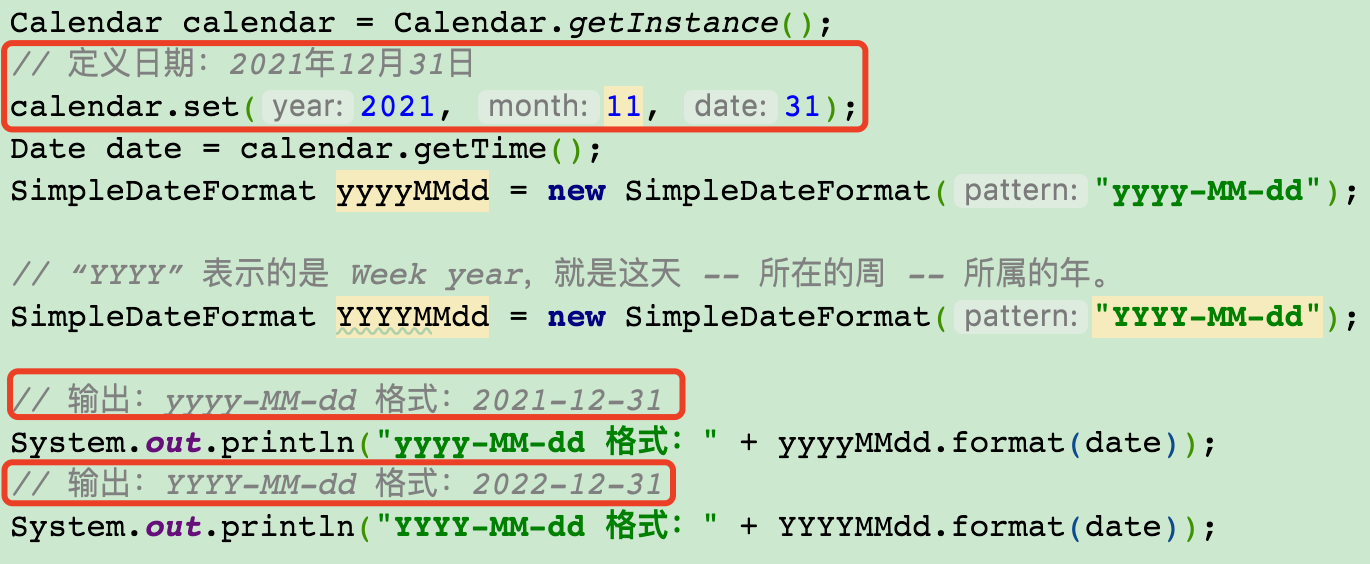
- YYYY:基于周年(Week Year)
- 表示 ISO 8601 标准的周年,即 基于周的年份。
- 每年从第一个完整的周(周一到周日)开始,且该周必须包含至少 4 天属于新年。
- 行为:
- 如果某天的自然年日期属于上一年的最后一周或下一年的第一周,其 YYYY 可能显示为相邻年份。
- 容易在跨年周时,出现 年份跳变。
- 适用场景:需要按周统计的场景(如:财务年度、周报系统)。
5、SimpleDateFormat 为什么线程不安全?
- SimpleDateFormat 类不是线程安全的根本原因是:
- SimpleDateFormat 类继承了 DateFormat 抽象类。
- 在 DateFormat 抽象类中有一个 Calendar 类型的属性 calendar。
- 在多个线程共用同一 SimpleDateFormat 时,DateFormat 中的 calendar 就被多个线程共享,而 Calendar 对象本身不支持线程安全。
- SimpleDateFormat 的 format 方法和 parse 方法都因为使用 calendar 来操作时间。
- format 方法的线程不安全
- 当多个线程同时使用同一 SimpleDateFormat 对象调用 format 方法时,多个线程同时调用 calendar.setTime 方法,可能一个线程刚设置好 time 值,另外的一个线程马上把设置的 time 值给修改了导致返回的格式化时间可能是错误的。
- prase 方法的线程不安全
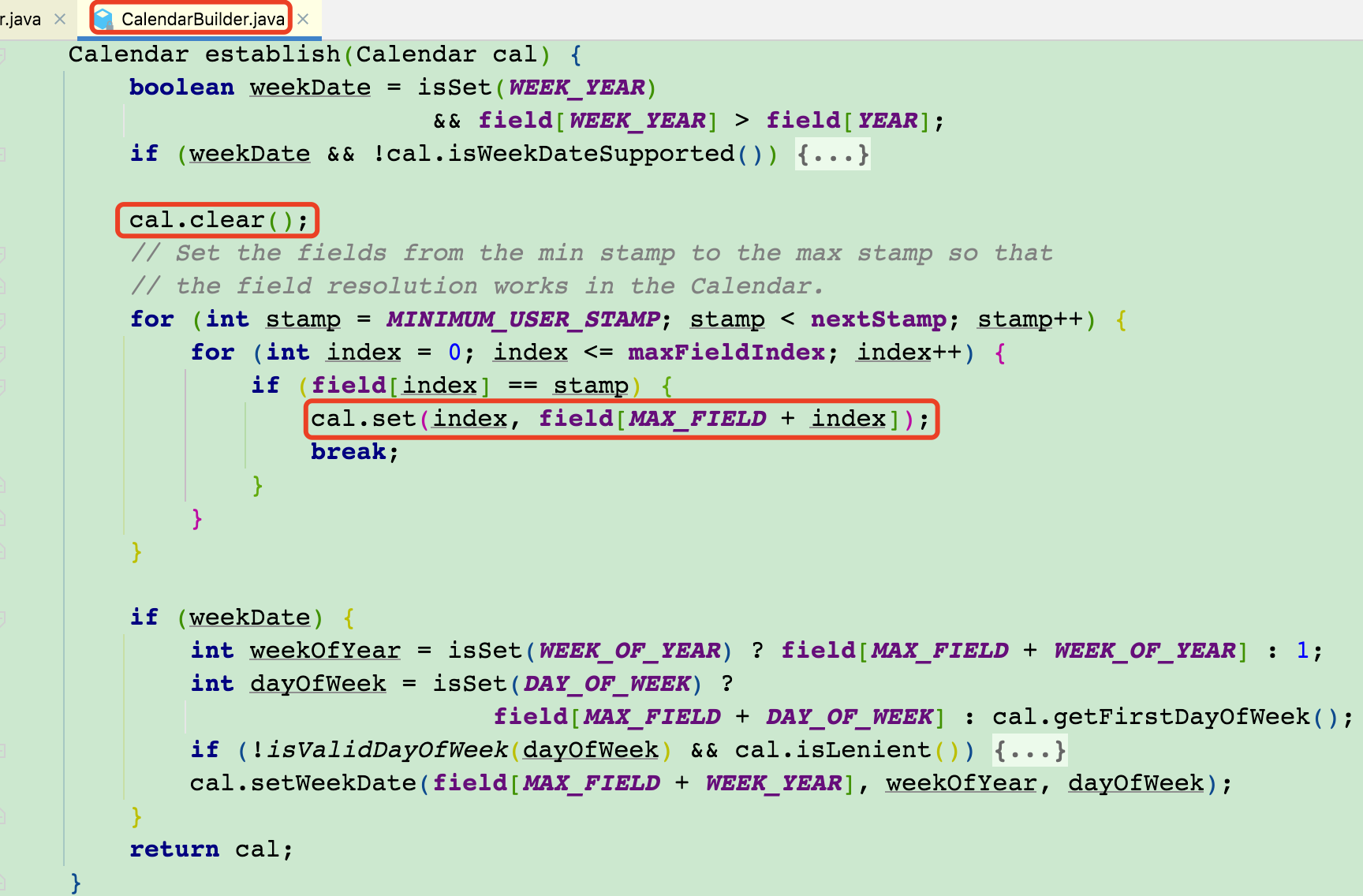
- Calendar 是用来承载字符串转化成日期对象的容器。
- 在 CalendarBuilder 类的 establish 方法中,先后调用 Calendar 的 clear 和 set 方法,先清除 cal 对象中设置的值,再重新设置新的值。
- 由于 Calendar 内部没有线程安全机制,并且这俩操作也不是原子性的,所以,当多个线程共用同一 SimpleDateFormat 时,引起 cal 值混乱。
public class UnSafeSimpleDateFormat {
// SimpleDateFormat 类继承了DateFormat 抽象类,
// 在 DateFormat 抽象类中有一个 Calendar 类型的属性 calendar
// 它就是导致 SimpleDateFormat 线程不安全的关键。
static SimpleDateFormat format = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
private static final int COUNTER = 200;
private static final CountDownLatch COUNT_DOWN_LATCH = new CountDownLatch(COUNTER);
/**
* 测试 SimpleDateFormat 的 format 方法非线程安全
* dates 容器中的元素数量 < 200 证明非线程安全。
* DateFormat 中的 calendar 同一个 SimpleDateFormat 的多环境下编程共享的了。
* format 方法中的 calendar.setTime(date); 编程非线程安全的了。
*
* @throws InterruptedException 中断异常
*/
public static void testFormatUnsafe() throws InterruptedException {
ExecutorService service = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(COUNTER);
// 定义一个线程安全的 HashSet
Set<String> dates = Collections.synchronizedSet(new HashSet<String>());
for (int i = 0; i < COUNTER; i++) {
// 获取当前时间
Calendar calendar = Calendar.getInstance();
int finalI = i;
service.execute(() -> {
try {
// 时间增加
calendar.add(Calendar.DATE, finalI);
// 通过 simpleDateFormat 把时间转换成字符串
String dateString = format.format(calendar.getTime());
// 把字符串放入 Set 中
dates.add(dateString);
} finally {
// countDown
COUNT_DOWN_LATCH.countDown();
}
});
}
// 阻塞,直到 countDown 数量为0
COUNT_DOWN_LATCH.await();
// 输出去重后的时间个数
System.out.println(dates.size());
service.shutdown();
}
/**
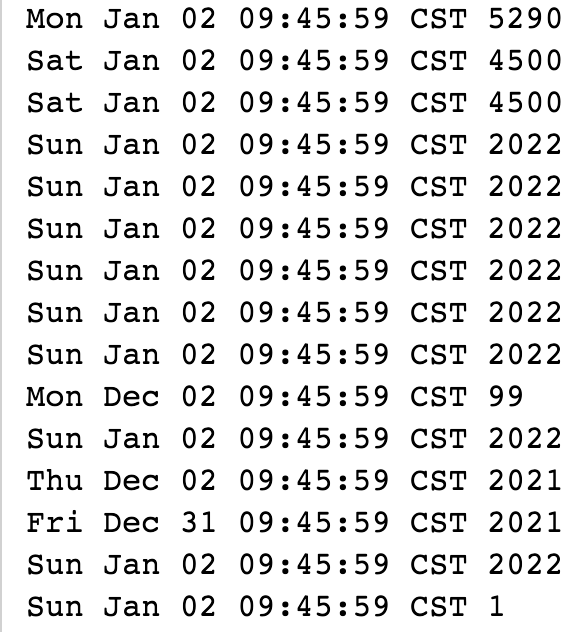
* 测试 SimpleDateFormat 的 parse 方法非线程安全
* 1、可能会抛出各种 NumberFormatException 【empty String、multiple points、""、452022.E4520224E4、E.22202】
* 2、显示不正常的数据:
* Tue Jan 02 09:45:59 CST 20
* Fri Dec 31 09:45:59 CST 2021
* Sun Aug 06 03:01:59 CST 2023
* Fri Jan 02 09:45:59 CST 1
*
* @throws InterruptedException 中断异常
*/
public static void testParseUnsafe() throws InterruptedException {
ExecutorService service = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(100);
for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) {
service.execute(() -> {
for (int j = 0; j < 5; j++) {
try {
System.out.println(format.parse("2022-01-02 09:45:59"));
} catch (ParseException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
});
}
// 启动有序关闭,其中执行先前提交的任务,但不会接受新任务。 如果已经关闭,调用没有额外的效果。
// 此方法不等待先前提交的任务完成执行。 使用awaitTermination来做到这一点。
service.shutdown();
// 阻塞直到所有任务在关闭请求后完成执行,或发生超时,或当前线程被中断,以先发生者为准
service.awaitTermination(1, TimeUnit.DAYS);
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
testFormatUnsafe();
testParseUnsafe();
}
}

6、解决 SimpleDateFormat 线程不安全的方法有哪些?
- 低效方案:
- 局部变量法:
- 每次都生成一个新的 SimpleDateFormat 对象,缺点是低效,创建大量的临时对象。
- 使用 synchronized 关键字方式 或 Lock 锁方式
- 缺点是:降低了并发性,大量并发时进程阻塞。
- 推荐方案:
- Jdk1.8 以上版本:
- DateTimeFormatter: This class is immutable and thread-safe.
- Jdk1.8 以下版本:
- ThreadLocal 存储每个线程拥有的 SimpleDateFormat 对象的副本,能够有效的避免多线程造成的线程安全问题。
- 运行效率比较高
public class SafeSimpleDateFormat{
// 使用ThreadLocal包装一下,每个线程都有自己的SimpleDateFormat实例对象,这样多线程并发的情况下就不会出现线程不安全的问题了。
private static final ThreadLocal<SimpleDateFormat> THREAD_LOCAL = ThreadLocal.withInitial(()-> {
SimpleDateFormat format = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
System.out.println(format + "\t\t" + System.identityHashCode(format) + "\t\t" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t\t" + "###########");
return format;
});
private static final int COUNTER = 200;
static CountDownLatch latch = new CountDownLatch(COUNTER);
public static void testFormatSafe() throws InterruptedException {
ExecutorService service = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(COUNTER);
Set<String> dates = Collections.synchronizedSet(new HashSet<>());
for (int i = 0; i < COUNTER; i++){
Calendar calendar = Calendar.getInstance();
int finalI = i;
service.execute(()->{
try {
calendar.add(Calendar.DATE, finalI);
dates.add(THREAD_LOCAL.get().format(calendar.getTime()));
} finally {
// 线程用完了SimpleDateFormat,如果不调用remove方法将其清除,
// 可能会引发因使用ThreadLocal而导致的内存泄漏。
THREAD_LOCAL.remove();
latch.countDown();
}
});
}
latch.await();
System.out.println(dates.size());
service.shutdown();
}
public static void testPraseSafe() throws InterruptedException {
ExecutorService service = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(COUNTER);
for (int i = 0; i < COUNTER; i++){
int finalI = i;
service.execute(() -> {
for (int j = 0; j < 5; j++) {
try {
/*
Sun Jan 02 09:45:59 CST 2022 95 pool-2-thread-96 java.text.SimpleDateFormat@4f76f1a0 530424907
Sun Jan 02 09:45:59 CST 2022 114 pool-2-thread-115 java.text.SimpleDateFormat@4f76f1a0 1742859816
Sun Jan 02 09:45:59 CST 2022 181 pool-2-thread-182 java.text.SimpleDateFormat@4f76f1a0 1272576190
Sun Jan 02 09:45:59 CST 2022 161 pool-2-thread-162 java.text.SimpleDateFormat@4f76f1a0 388431896
Sun Jan 02 09:45:59 CST 2022 54 pool-2-thread-55 java.text.SimpleDateFormat@4f76f1a0 928001102
输出的 THREAD_LOCAL.get() 对象:都是 java.text.SimpleDateFormat@4f76f1a0
原因是 SimpleDateFormat 重写了 hashCode() 方法。
public int hashCode(){ return pattern.hashCode(); }
pattern 都是为:"yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss" 因此,hashCode 都是一样的。
toString 方法继承的 Object 的 toString() 方法。
public String toString() { return getClass().getName() + "@" + Integer.toHexString(hashCode()); }
System.identityHashCode(THREAD_LOCAL.get()) :输出的是与内存地址相关的值,由于对象不是同一个。所以值不一样。
*/
System.out.println(THREAD_LOCAL.get().parse("2022-01-02 09:45:59") + "\t\t" + finalI + "\t\t" + Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t\t" + THREAD_LOCAL.get() + "\t\t" + System.identityHashCode(THREAD_LOCAL.get()) + "\t\t");
} catch (ParseException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
// 线程用完了SimpleDateFormat,如果不调用 remove 方法将其清除,
// 可能会引发因使用 ThreadLocal 而导致的内存泄漏。
THREAD_LOCAL.remove();
}
}
});
}
service.shutdown();
service.awaitTermination(1, TimeUnit.DAYS);
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
testFormatSafe();
testPraseSafe();
}
}
- 第三方包
- joda-time 是第三方处理日期和时间的类库,线程安全,性能经过高并发的考验,推荐在高并发场景下的生产环境使用。
public class T003_DateTimeFormatter {
private static final DateTimeFormatter formatter = DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
public static String formatDate(LocalDateTime date) {
return formatter.format(date);
}
public static LocalDateTime parse(String dateNow) {
return LocalDateTime.parse(dateNow, formatter);
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException, ParseException {
ExecutorService service = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(100);
// 20个线程
for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) {
service.execute(() -> {
for (int j = 0; j < 10; j++) {
try {
System.out.println(parse(formatDate(LocalDateTime.now())));
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
});
}
// 等待上述的线程执行完
service.shutdown();
service.awaitTermination(1, TimeUnit.DAYS);
}
}





















 4330
4330

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








