
CVPR-2021
文章目录
- 1 Background and Motivation
- 2 Related Work
- 3 Advantages / Contributions
- 4 Method
- 5 Experiments
- 5.1 Datasets
- 5.2 Copy-Paste is robust to training configurations
- 5.3 Copy-Paste helps data-efficiency
- 5.4 Copy-Paste and self-training are additive
- 5.5 Copy-Paste improves COCO state-of-the-art
- 5.6 Copy-Paste produces better representations for PASCAL detection and segmentation
- 5.7 Copy-Paste provides strong gains on LVIS
- 6 Appendix
- 7 Conclusion(own)
1 Background and Motivation
Instance segmentation often data-hungry
人工标注成本较高,本文聚焦 data augmentation 类方法来缓解上述问题
虽然有许多 data augmentation 方法被提出,但 more general-purpose in nature and have not been designed specifically for instance segmentation.
本文作者提出了 Copy-Paste 实例分割数据增广方法,randomly picking objects and pasting them at random locations on the target image
作者方法和类似于 【Cut, Paste and Learn】《Cut, Paste and Learn: Surprisingly Easy Synthesis for Instance Detection》,区别在于
1)not use geometric transformationss (e.g.rotation),find Gaussian blurring of the pasted instances not beneficial
2)拓展到了 semi-supervised learning
3)pasting objects contained in one image into another image already populated with instances(区别于全前景贴全背景)
4)数据集从 CMU 到了应用更广的 COCO 和 LVIS
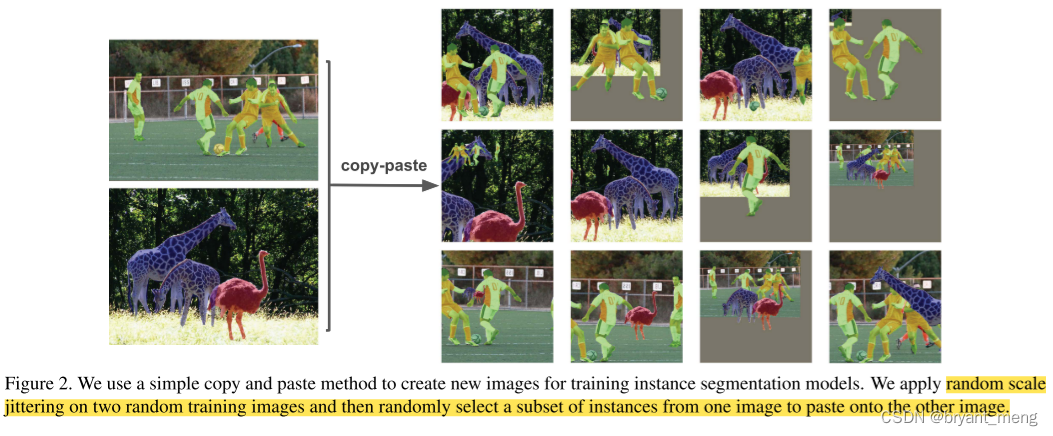

2 Related Work
- Data Augmentations
mainly used for encoding invariances to data transformations, 有利于分类 - Mixing Image Augmentations(mixup, CutMix and Mosaic)
still not object-aware and have not been designed specifically for the task of instance segmentation - Copy-Paste Augmentation
- Instance Segmentation
- Long-Tail Visual Recognition
data re-samplin and loss re-weighting,作者方法 yields significant gains
3 Advantages / Contributions
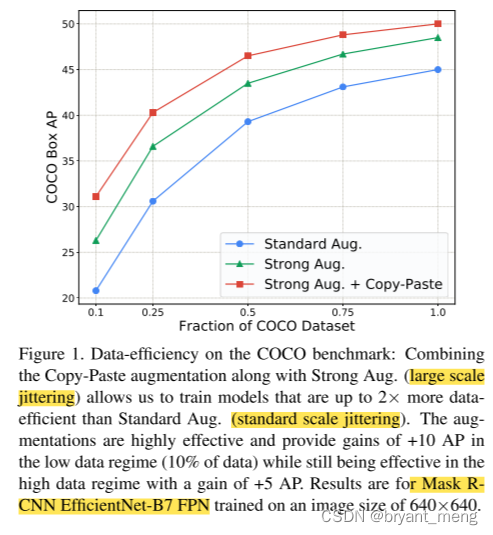
提出了 Copy-Paste 方法,provides a significant boost on top of baselines across multiple settings.
it gives solid improvements across a wide range of settings with variability in backbone architecture, extent of scale jittering, training schedule and image size.
4 Method

-
scale jittering and random horizontal flipping
-
select a random subset of objects from one of the images and paste them onto the other image
-
adjust the ground-truth annotations:remove fully occluded objects and update the masks and bounding boxes of partially occluded objects.
generated images can look very different from real images
1)Blending Pasted Objects
I 1 × α + I 2 × ( 1 − α ) I_1 \times \alpha + I_2 \times (1-\alpha) I1×α+I2×(1−α)
其中 α \alpha α 为 binary mask, I 1 I_1 I1 is the pasted image and I 2 I_2 I2 is the main image
simply composing without any blending has similar performance,不像 【Cut, Paste and Learn】《Cut, Paste and Learn: Surprisingly Easy Synthesis for Instance Detection》 中探索了不同的 composing 方法
2)Large Scale Jittering

-
standard scale jittering (SSJ) :0.8~1.25
-
large scale jittering (LSJ):0.1~2.0
3)Self-training Copy-Paste
标准的 self-training 流程
- train a supervised model with Copy-Paste augmentation on labeled data
- generate pseudo labels on unlabeled data
- paste ground-truth instances into pseudo labeled and supervised labeled images and train a model on this new data
5 Experiments
training a model from scratch with large scale jittering and Copy-Paste augmentation requires 576 epochs while training with only standard scale jittering takes 96 epochs.
加了 scale jittering 和 Copy-Paste 训练的更久更猛
5.1 Datasets
- COCO
- VOC
- LVIS
LVIS has 1203 classes to simulate the long-tail distribution of classes in natural images.

5.2 Copy-Paste is robust to training configurations
robust across a variety of training iterations, models and training hyperparameters.
1)Robustness to backbone initialization
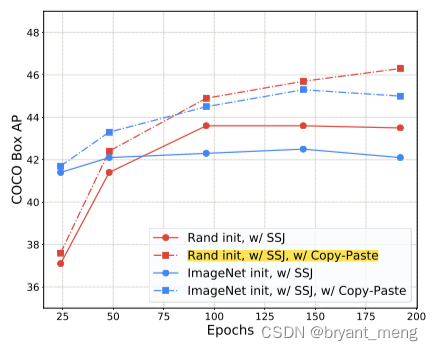
2)Robustness to training schedules
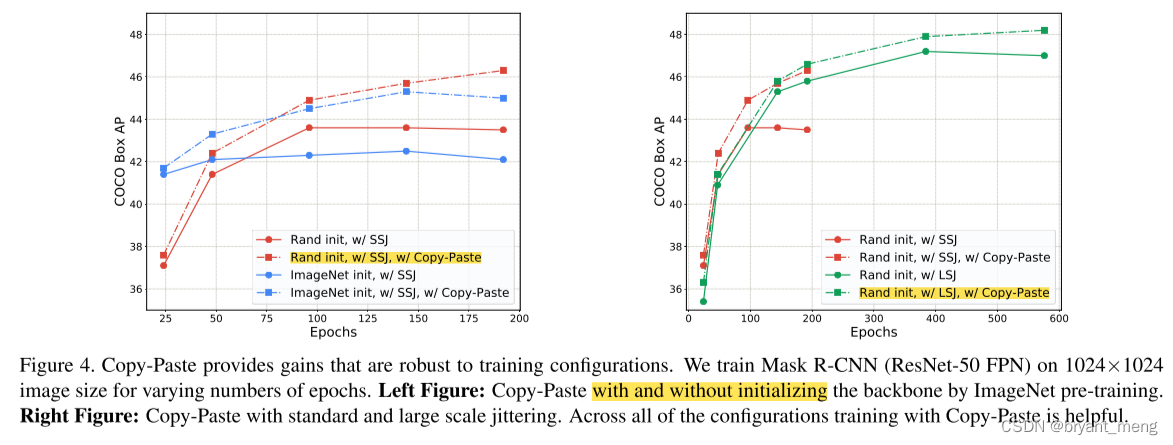
训练更久,性能还能进一步提升
3)Copy-Paste is additive to large scale jittering augmentation
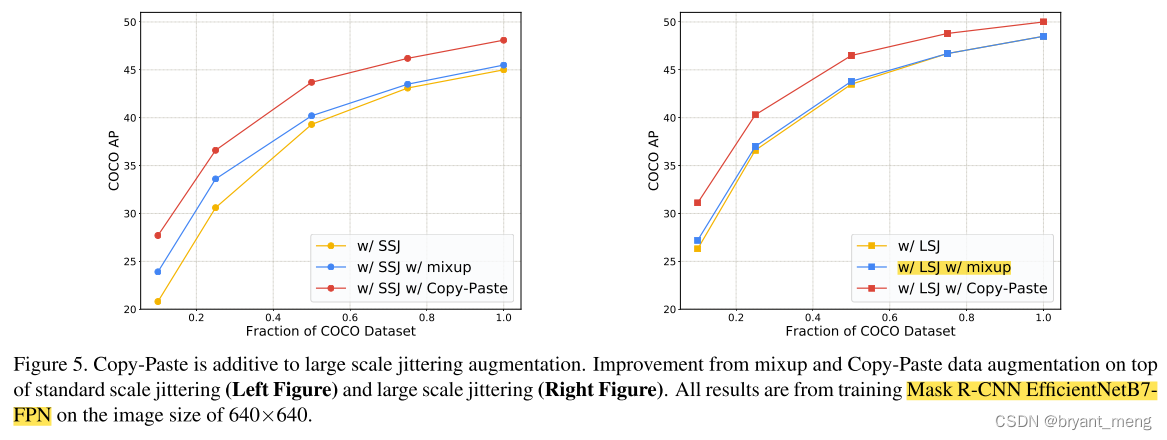
mixup 搭配 SSJ 还行,mixup 搭配 LSJ 效果基本被抵消,但 Copy-Paste 和 LSJ 兼容得不错
4)Copy-Paste works across backbone architectures and image sizes
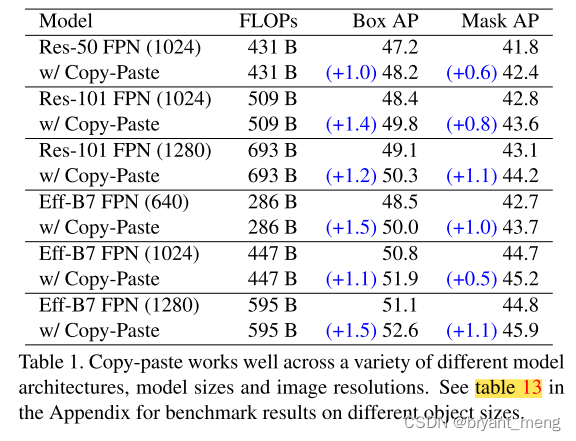
看看不同尺寸的提升
5.3 Copy-Paste helps data-efficiency
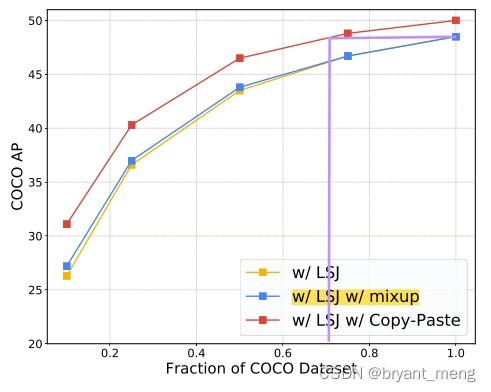
用更少的数据达到同样的效果
a model trained on 75% of COCO with Copy-Paste and LSJ has a similar AP to a model trained on 100% of COCO with LSJ.
5.4 Copy-Paste and self-training are additive
self-training 相关实验,引入了额外的数据集
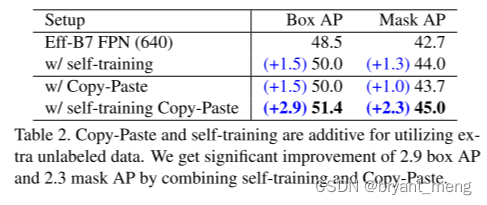
1)Data to Paste on
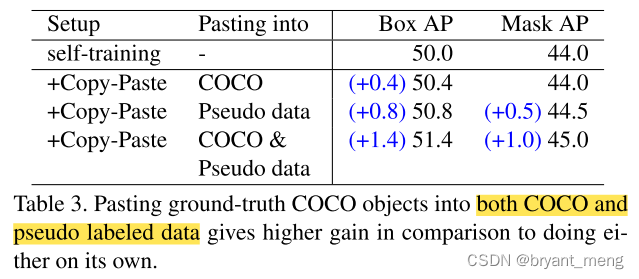
- supervised COCO data (120k images)
- pseudo labeled data (110k images from unlabeled COCO and 610k from Objects365).
表3 的结果可以和表2 对应上
2)Data to Copy from
pasting pseudo labeled objects from an unlabeled dataset directly into the COCO labeled dataset.
反过来贴,no additional AP improvements.
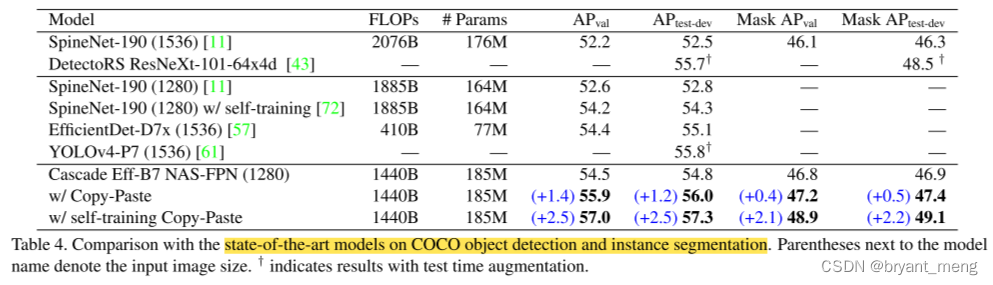
5.5 Copy-Paste improves COCO state-of-the-art
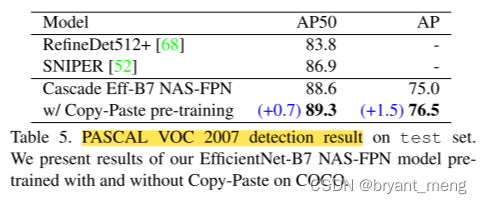
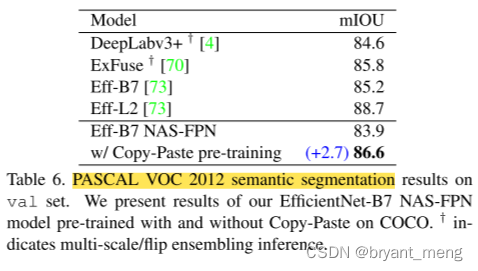
5.6 Copy-Paste produces better representations for PASCAL detection and segmentation
trained with Copy-Paste on COCO.
transfer learning experiments on the PASCAL VOC 2007 dataset.
5.7 Copy-Paste provides strong gains on LVIS
长尾数据集
two different training paradigms typically used for LVIS:
-
single-stage where a detector is trained directly on the LVIS dataset
-
two-stage where the model from the first stage is fine-tuned with class re-balancing losses to help handle the class imbalance.
损失的形式为 ( 1 − β ) / ( 1 − β n ) (1−β)/(1−β^n) (1−β)/(1−βn),where n n n is the number of instances of the class and β = 0.999 β = 0.999 β=0.999
1)Copy-Paste improves single-stage LVIS training
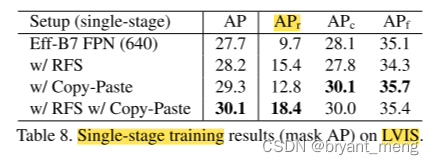
APr (the AP for rare classes)
Repeat Factor Sampling (RFS) are used to handle the class imbalance problem on LVIS
可以看到 Copy-Paste 和 RFS 可兼容
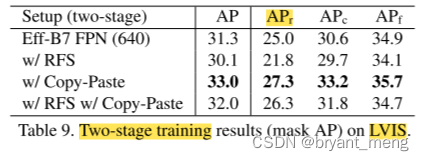
2)Copy-Paste improves two-stage LVIS training
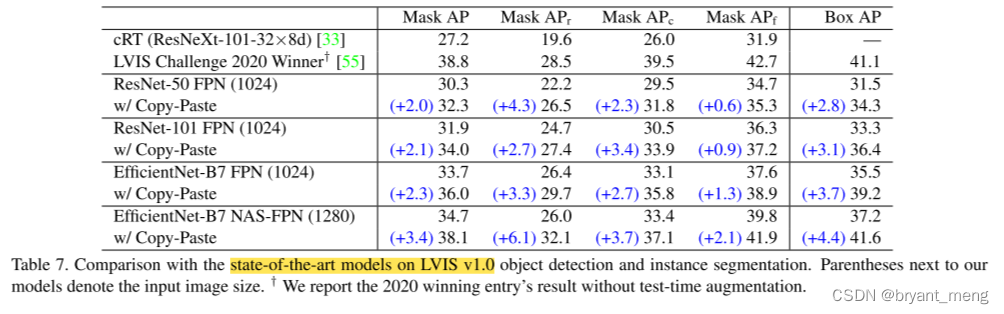
3)Comparison with the state-of-the-art
6 Appendix
6.1 Ablation on the Copy-Paste method
1)Subset of pasted objects
效果最好的是 pasting a random subset of objects,one 或者 all 都没有 random 的好
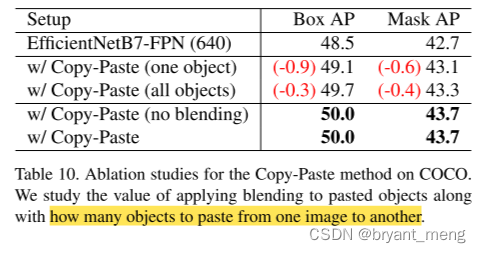
2)Blending
表10 可以看出,不太 care blending 的形式,不用也没有掉点
3)Scale jittering
random scale jittering on both the pasted image (image that pasted objects are being copied from) and the main image.

引入 LSJ 主要的提升来自于对 main image 的增广
6.2 Copy-Paste provides more gain on harder categories of COCO
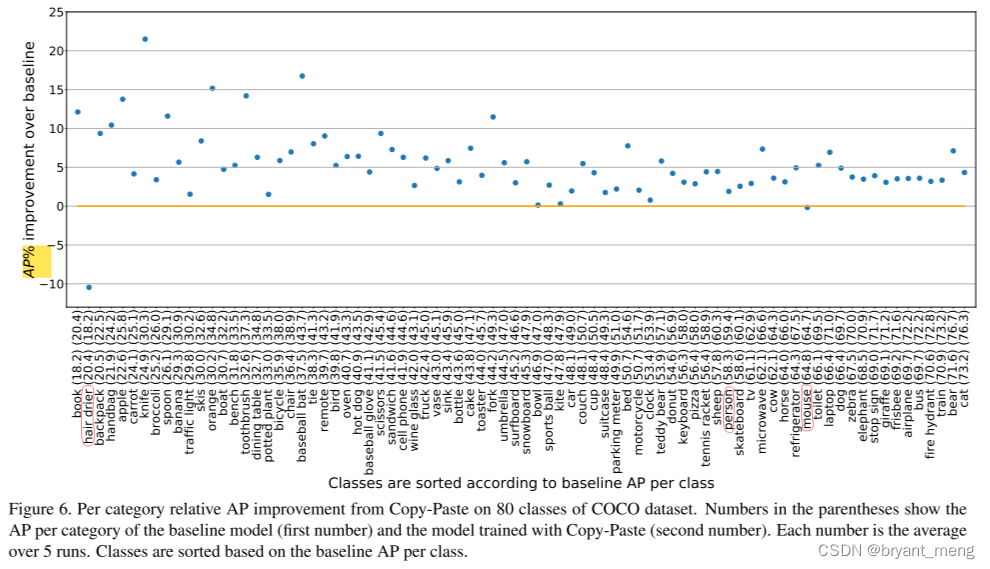
横坐标按 baseline 各类别的 AP 排序的,纵坐标是提升率,不是提升的点
6.3 How likely objects are copied to an un-matched scene?
compute the probability of copying objects to an unmatched scene category
仅区别室内室外场景
We found there are 42538 indoor and 71017 outdoor images (we couldn’t estimate the category of the rest 4732 images).

copy objects to an unmatched scene in about half (46.8%) of generated images.(23.4%+23.4%)
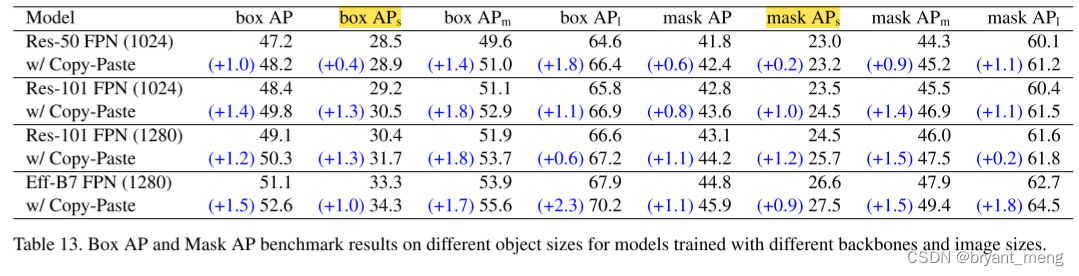
6.4 Benchmark results on different object sizes

7 Conclusion(own)
-
效果确实很惊艳,拿下COCO目标检测和实例分割双料第一名!目标检测数据刷到57.3 AP,实例分割刷到49.1 AP!(Table4)
-
Instaboost: Boosting instance segmentation via probability map guided copypasting. In ICCV, 2019.

-

-
-
-
代码复现:Copy-Paste 数据增强for 语义分割
数据格式是 VOC 版本的
"""
Unofficial implementation of Copy-Paste for semantic segmentation
"""
from PIL import Image
import imgviz
import cv2
import argparse
import os
import numpy as np
import tqdm
def save_colored_mask(mask, save_path):
lbl_pil = Image.fromarray(mask.astype(np.uint8), mode="P")
colormap = imgviz.label_colormap()
lbl_pil.putpalette(colormap.flatten())
lbl_pil.save(save_path)
def random_flip_horizontal(mask, img, p=0.5):
if np.random.random() < p:
img = img[:, ::-1, :]
mask = mask[:, ::-1]
return mask, img
def img_add(img_src, img_main, mask_src):
if len(img_main.shape) == 3:
h, w, c = img_main.shape
elif len(img_main.shape) == 2:
h, w = img_main.shape
mask = np.asarray(mask_src, dtype=np.uint8)
sub_img01 = cv2.add(img_src, np.zeros(np.shape(img_src), dtype=np.uint8), mask=mask) # src 前景抠出来
mask_02 = cv2.resize(mask, (w, h), interpolation=cv2.INTER_NEAREST)
mask_02 = np.asarray(mask_02, dtype=np.uint8)
sub_img02 = cv2.add(img_main, np.zeros(np.shape(img_main), dtype=np.uint8),
mask=mask_02) # img_main 对应的 src 前景区域抠出来
img_main = img_main - sub_img02 + cv2.resize(sub_img01, (img_main.shape[1], img_main.shape[0]),
interpolation=cv2.INTER_NEAREST) # 去掉 main 中的 src前景区域,把 src 前景区域贴上来
return img_main
def rescale_src(mask_src, img_src, h, w):
if len(mask_src.shape) == 3:
h_src, w_src, c = mask_src.shape
elif len(mask_src.shape) == 2:
h_src, w_src = mask_src.shape
max_reshape_ratio = min(h / h_src, w / w_src)
rescale_ratio = np.random.uniform(0.2, max_reshape_ratio)
# reshape src img and mask
rescale_h, rescale_w = int(h_src * rescale_ratio), int(w_src * rescale_ratio)
mask_src = cv2.resize(mask_src, (rescale_w, rescale_h),
interpolation=cv2.INTER_NEAREST)
# mask_src = mask_src.resize((rescale_w, rescale_h), Image.NEAREST)
img_src = cv2.resize(img_src, (rescale_w, rescale_h),
interpolation=cv2.INTER_LINEAR)
# set paste coord
py = int(np.random.random() * (h - rescale_h))
px = int(np.random.random() * (w - rescale_w))
# paste src img and mask to a zeros background
img_pad = np.zeros((h, w, 3), dtype=np.uint8)
mask_pad = np.zeros((h, w), dtype=np.uint8)
img_pad[py:int(py + h_src * rescale_ratio), px:int(px + w_src * rescale_ratio), :] = img_src
mask_pad[py:int(py + h_src * rescale_ratio), px:int(px + w_src * rescale_ratio)] = mask_src
return mask_pad, img_pad
def Large_Scale_Jittering(mask, img, min_scale=0.1, max_scale=2.0):
rescale_ratio = np.random.uniform(min_scale, max_scale)
h, w, _ = img.shape
# rescale
h_new, w_new = int(h * rescale_ratio), int(w * rescale_ratio)
img = cv2.resize(img, (w_new, h_new), interpolation=cv2.INTER_LINEAR)
mask = cv2.resize(mask, (w_new, h_new), interpolation=cv2.INTER_NEAREST)
# mask = mask.resize((w_new, h_new), Image.NEAREST)
# crop or padding
x, y = int(np.random.uniform(0, abs(w_new - w))), int(np.random.uniform(0, abs(h_new - h)))
if rescale_ratio <= 1.0: # padding
img_pad = np.ones((h, w, 3), dtype=np.uint8) * 168
mask_pad = np.zeros((h, w), dtype=np.uint8)
img_pad[y:y+h_new, x:x+w_new, :] = img
mask_pad[y:y+h_new, x:x+w_new] = mask
return mask_pad, img_pad
else: # crop
img_crop = img[y:y+h, x:x+w, :]
mask_crop = mask[y:y+h, x:x+w]
return mask_crop, img_crop
def copy_paste(mask_src, img_src, mask_main, img_main):
mask_src, img_src = random_flip_horizontal(mask_src, img_src)
mask_main, img_main = random_flip_horizontal(mask_main, img_main)
# LSJ, Large_Scale_Jittering
if args.lsj:
mask_src, img_src = Large_Scale_Jittering(mask_src, img_src)
mask_main, img_main = Large_Scale_Jittering(mask_main, img_main)
else:
# rescale mask_src/img_src to less than mask_main/img_main's size
h, w, _ = img_main.shape
mask_src, img_src = rescale_src(mask_src, img_src, h, w)
img = img_add(img_src, img_main, mask_src) # src 的前景抠出来贴 main
mask = img_add(mask_src, mask_main, mask_src)
return mask, img
def main(args):
# input path
segclass = os.path.join(args.input_dir, 'SegmentationClass')
JPEGs = os.path.join(args.input_dir, 'JPEGImages')
# create output path
os.makedirs(args.output_dir, exist_ok=True)
os.makedirs(os.path.join(args.output_dir, 'SegmentationClass'), exist_ok=True)
os.makedirs(os.path.join(args.output_dir, 'JPEGImages'), exist_ok=True)
masks_path = os.listdir(segclass)
tbar = tqdm.tqdm(masks_path, ncols=100)
for mask_path in tbar:
# get source mask and img
mask_src = np.asarray(Image.open(os.path.join(segclass, mask_path)), dtype=np.uint8)
img_src = cv2.imread(os.path.join(JPEGs, mask_path.replace('.png', '.jpg')))
# random choice main mask/img
mask_main_path = np.random.choice(masks_path)
mask_main = np.asarray(Image.open(os.path.join(segclass, mask_main_path)), dtype=np.uint8)
img_main = cv2.imread(os.path.join(JPEGs, mask_main_path.replace('.png', '.jpg')))
# Copy-Paste data augmentation
mask, img = copy_paste(mask_src, img_src, mask_main, img_main) # 调用 copy_paste 方法
mask_filename = "copy_paste_" + mask_path
img_filename = mask_filename.replace('.png', '.jpg')
save_colored_mask(mask, os.path.join(args.output_dir, 'SegmentationClass', mask_filename)) # 保存 mask
cv2.imwrite(os.path.join(args.output_dir, 'JPEGImages', img_filename), img) # 保存合成后的图片
def get_args():
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
parser.add_argument("--input_dir", default="../dataset/VOCdevkit2012/VOC2012", type=str,
help="input annotated directory")
parser.add_argument("--output_dir", default="../dataset/VOCdevkit2012/VOC2012_copy_paste", type=str,
help="output dataset directory")
parser.add_argument("--lsj", default=True, type=bool, help="if use Large Scale Jittering")
return parser.parse_args()
if __name__ == '__main__':
args = get_args()
main(args)





















 2032
2032

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








