摘要:本文详细介绍了KingbaseES数据库的Python专用驱动ksycopg2的使用方法。内容涵盖驱动安装、连接配置、CRUD操作等基础功能,以及事务管理、连接池等高级特性。ksycopg2作为遵循Python DBAPI 2.0规范的线程安全适配器,针对KingbaseES进行了深度优化,支持数据类型映射、批量操作等特性。文章提供了完整的业务表创建示例和员工管理系统实战案例,包含环境配置、性能优化建议和常见问题解决方案,帮助开发者快速掌握该驱动的使用技巧。通过详细的代码示例,展示了如何高效安全地操作KingbaseES数据库。
一、安装ksycopg2:KingbaseES的Python
ksycopg2是专为KingbaseES数据库设计的Python适配器,完全遵循Python DB API 2.0规范,具有线程安全的特性。它不仅提供了高效的数据操作能力,还支持KingbaseES特有的功能特性。
与通用的PostgreSQL驱动psycopg2相比,ksycopg2针对KingbaseES进行了深度优化,特别是在数据类型映射、事务处理和高级功能支持方面表现更加出色。
KingbaseES提供了专门的Python驱动包ksycopg2,它是基于Python DB API 2.0规范实现的线程安全数据库适配器!
1.1 科普ksycopg2知识
ksycopg2是Python编程语言的KingbaseES数据库适配器。它的主要特点是Python DB API 2.0 规范的完整实现和线程安全。
ksycopg2 主要在C程序中作为libkci包装器实现,因此既高效又安全。它拥有客户端和服务端游标,支持异步通信和通知、复制。
ksycopg2驱动需要和python大版本一致,如python3.8的ksycopg2驱动支持python3.8.x的任意小版本。
更多科普请查看金仓官方手册:如何通过 Python 驱动 Ksycopg2 连接和使用 Kingbase 数据库

1.2 官方下载ksycopg2驱动
1、首先需要下载并安装与你的Python版本和系统架构匹配的ksycopg2驱动。驱动可以从KingbaseES官方网站(KES-电科金仓官网)获取,如下图所示:
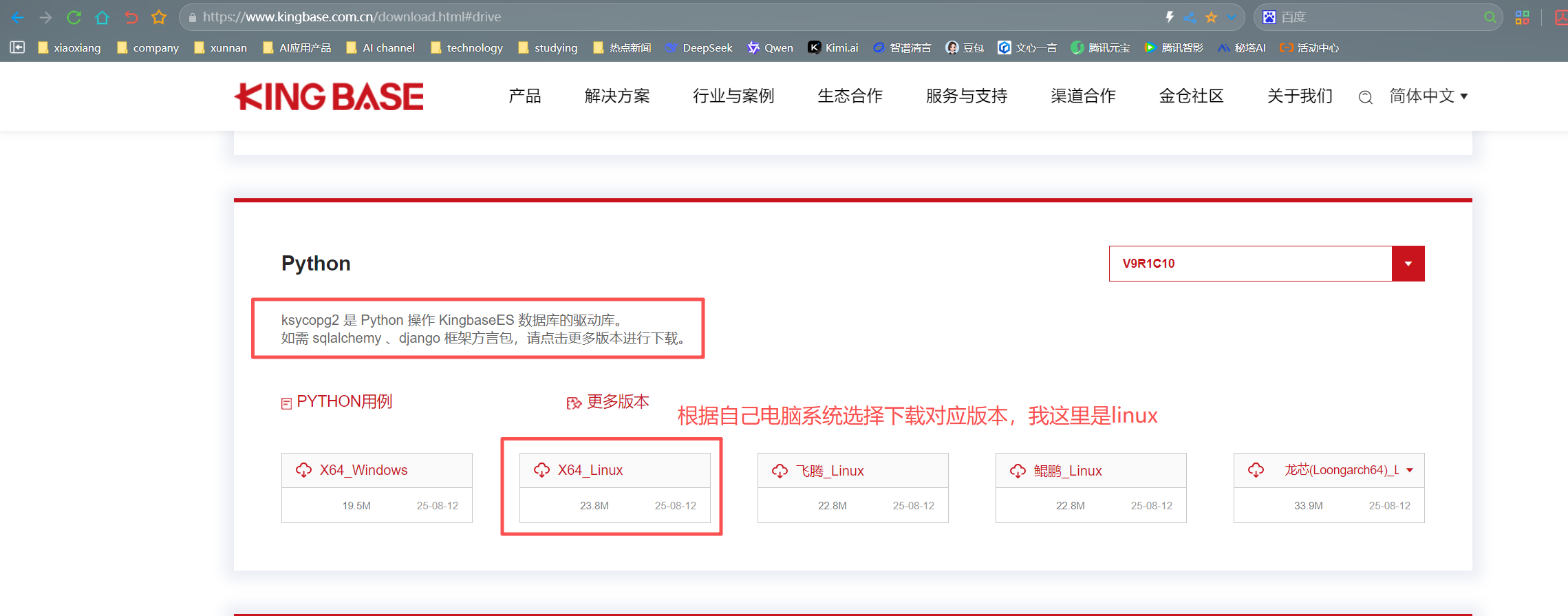
2、这里兄弟盟根据自己电脑系统,选择对应的版本,我这里是linux,下载下来如下图所示:KingbaseES_V009R001C010B0004_X64_Linux_Ksycopg2.tar 解压后可以看到有python2.7、python3.6、python3.7、python3.8、python3.9、python3.10、python3.11、python3.12,准备得真是周到,照顾各位大佬电脑上不同python版本,这一点为国产金仓数据库点赞👍👍👍
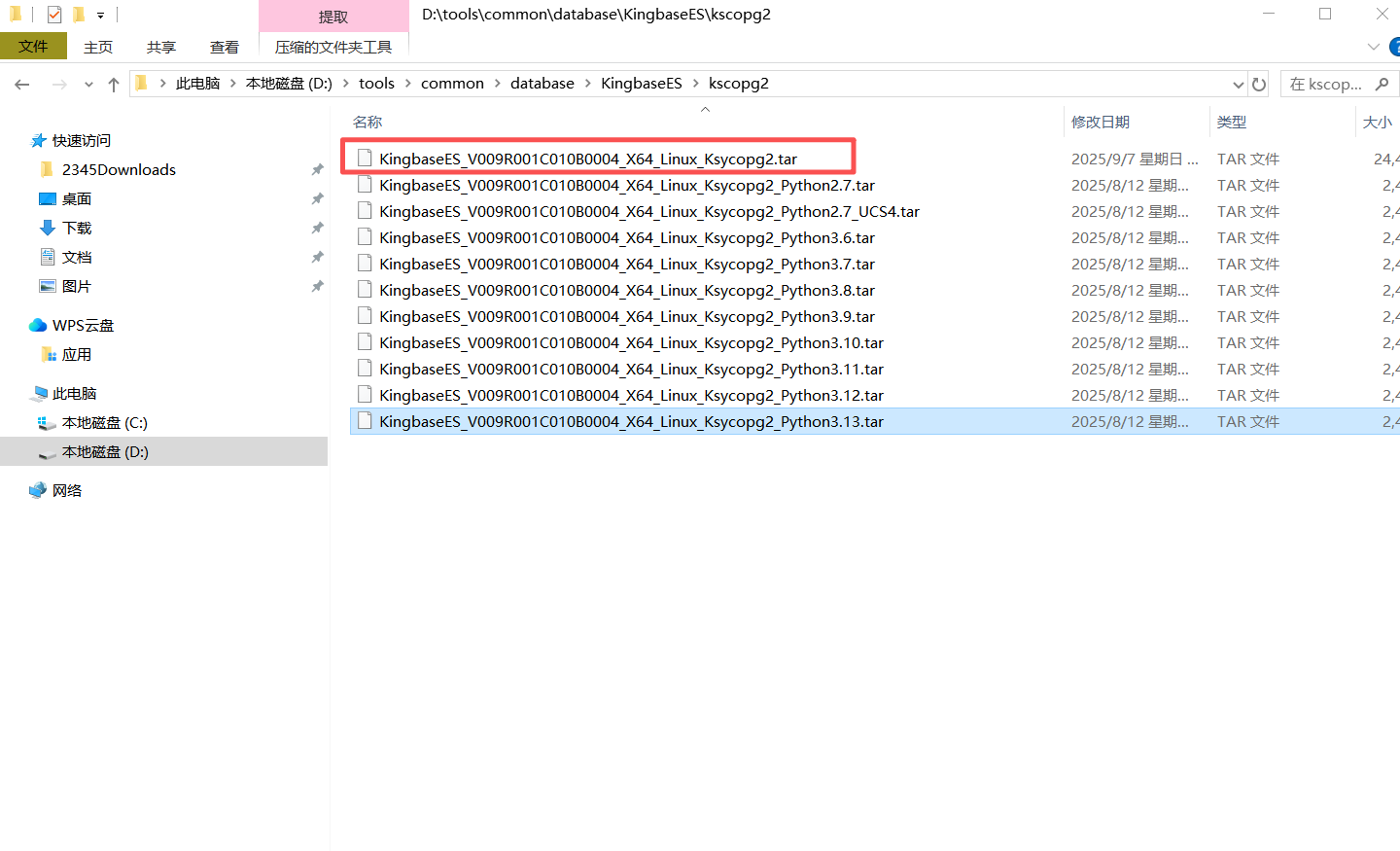
1.3 安装ksycopg2驱动
1、上面下载后解压并将ksycopg2文件夹放置在Python的模块搜索路径中,如果不清楚自己Python的模块在哪里,可以写个简单python代码查看:
import sys
print(sys.path)
2、运行后如下所示,可以查看Python的模块位置:/usr/lib/python3/dist-packages
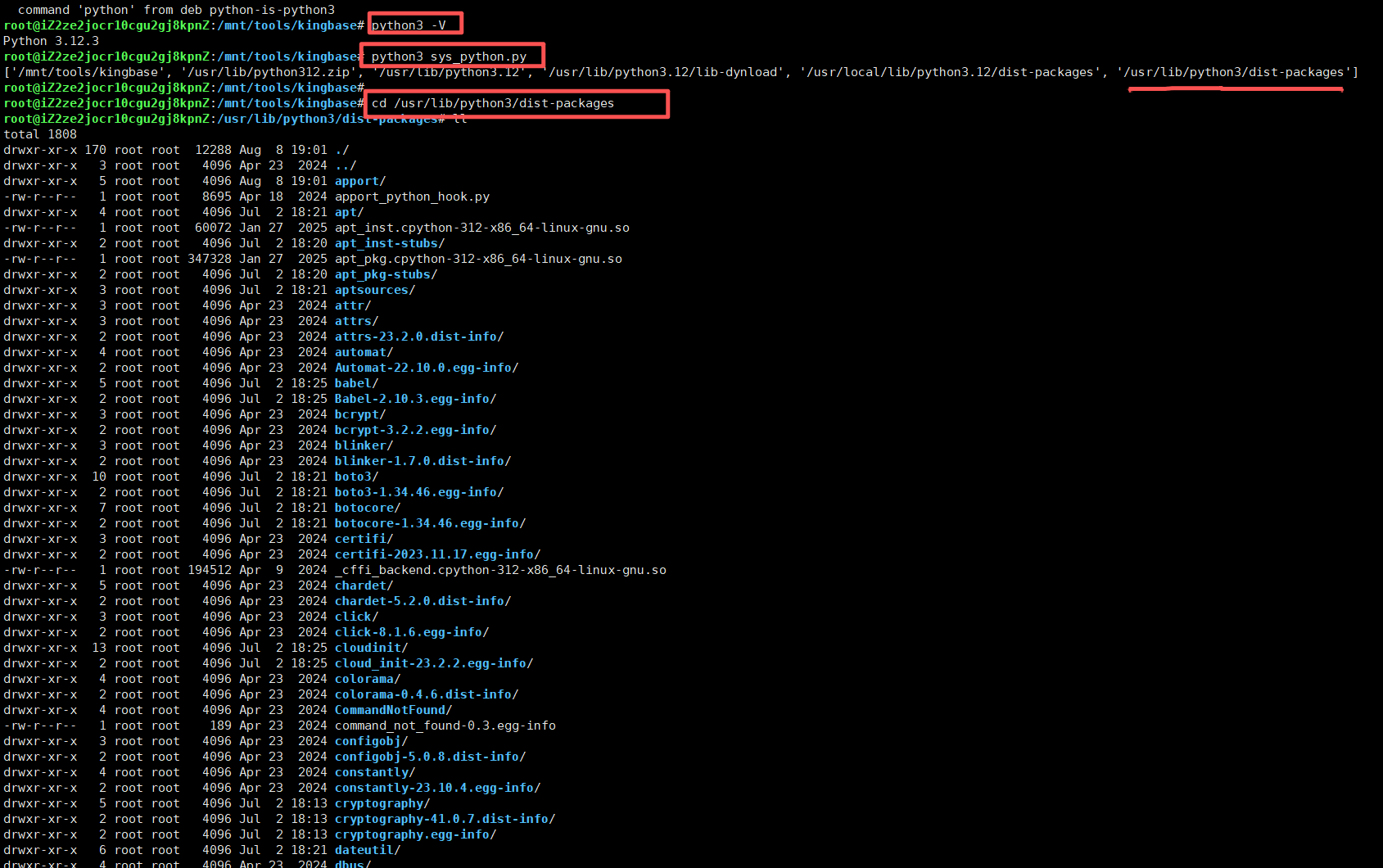
3、开始上传到:/usr/lib/python3/dist-packages
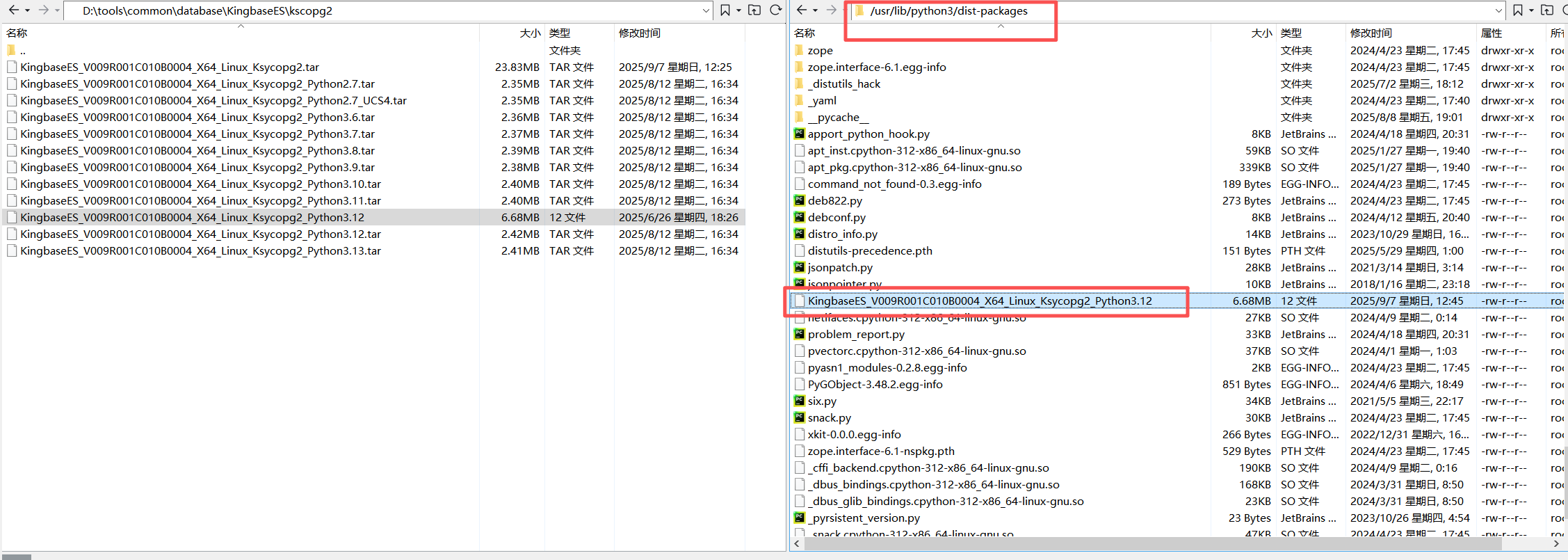
4、此外,还需要将KingbaseES的libkci库文件路径添加到LD_LIBRARY_PATH环境变量中:
export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=/kingbase/data/KESRealPro/V009R002C012/Server/lib:$LD_LIBRARY_PATH如果不清楚自己KingbaseES的libkci库文件路在哪里,可以用这个命令查看:
ps -ef | grep kingbase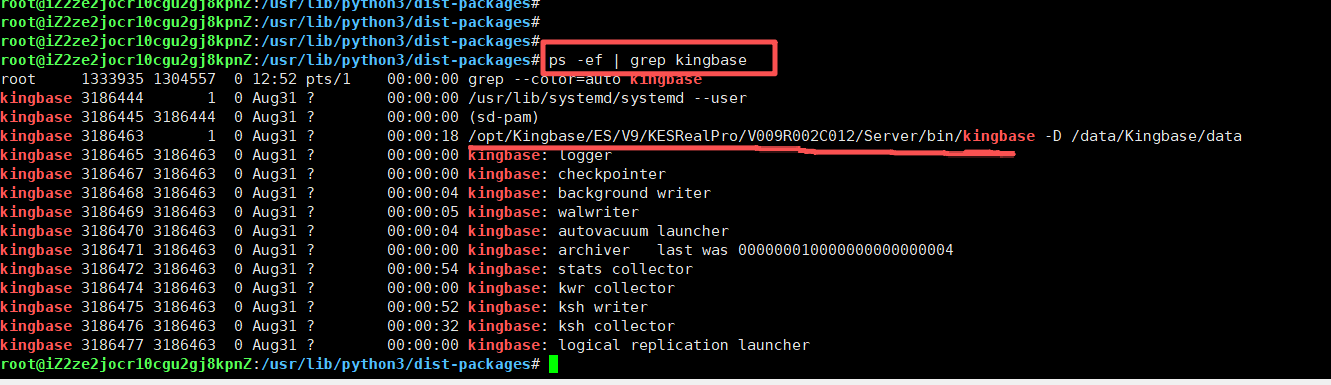
5、验证安装ksycoph2驱动
import ksycopg2
print("ksycopg2驱动安装成功")1.4. 连接KingbaseES数据库
使用ksycopg2连接KingbaseES数据库需要提供数据库名称、用户名、密码、主机地址和端口号等信息。
import ksycopg2
def create_connection():
try:
conn = ksycopg2.connect(
database="TEST",
user="SYSTEM",
password="qwe123!@#",
host="127.0.0.1",
port="54321"
)
print("数据库连接成功")
return conn
except Exception as e:
print(f"连接数据库失败: {e}")
return None
# 建立数据库连接
connection = create_connection()创建一个connect_database.py把上面代码复制进去,然后执行
python connect_database.py
1.5. 创建数据表
在执行增删改查操作前,需要先创建一张测试表,有表才好对后面的案例进行操作。
def create_table(conn):
try:
cursor = conn.cursor()
create_table_sql = """
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS user_info (
id INTEGER PRIMARY KEY,
username VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL,
age INTEGER,
created_time TIMESTAMP DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP
)
"""
cursor.execute(create_table_sql)
conn.commit()
cursor.close()
print("表创建成功")
except Exception as e:
print(f"创建表失败: {e}")
conn.rollback()
# 创建表
if connection:
create_table(connection)同理,在ubuntu服务器上新建一个create_table.py文件,把上面代码丢进去执行:
python create_table.py
二、ksycopg2建立数据库连接

1. 验证安装
# 验证ksycopg2安装
try:
import ksycopg2
print(f"ksycopg2版本: {ksycopg2.__version__}")
print(f"libpq版本: {ksycopg2.__libpq_version__}")
print("✅ ksycopg2驱动安装成功!")
except ImportError as e:
print(f"❌ 导入ksycopg2失败: {e}")2. 连接数据库经典案例
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import ksycopg2
import datetime
database = "test"
user = "username"
password = "123456"
host = "127.0.0.1"
port = "54321"
failed = 0
def check(name, val):
if val is None:
global failed
failed += 1
else:
if isinstance(val, ksycopg2.extensions.connection):
print("close connection")
val.close()
print("test", name, "success !", "\n")
def testConn():
try:
conn = ksycopg2.connect(
"dbname={} user={} password={} host={} port={}".format(database, user, password, host, port))
# conn.set_session(autocommit=True)
except Exception as e:
print(e)
return None
else:
return conn
def testConn2():
try:
conn = ksycopg2.connect(database=database, user=user, password=password, host=host, port=port)
cur = conn.cursor()
cur.execute("select version()")
rows = cur.fetchall()
print("database version:", rows[0])
cur.close()
except Exception as e:
print(e)
return None
else:
return conn
def testExecute():
conn = testConn()
if conn is not None:
cur = conn.cursor()
cur.execute('drop table if exists test_ksy')
cur.execute('create table test_ksy(id integer, name TEXT)')
cur.execute("insert into test_ksy values(%s, %s)", (1, "John"))
cur.execute("insert into test_ksy values(%s, %s)", (2, '中文测试文字'))
cur.execute("insert into test_ksy values(%s, %s)", (3, '!@#¥%……'))
cur.close()
conn.commit()
conn.close()
return 0
else:
return None
def testSelect():
conn = testConn()
if conn is not None:
cur = conn.cursor()
cur.execute("select * from test_ksy")
rows = cur.fetchall()
for c in cur.description:
print(c.name, "\t", end="")
print()
for row in rows:
for cell in row:
print(cell, " ", end="")
print()
cur.close()
conn.commit()
conn.close()
return 0
else:
return None
def testLob():
conn = testConn()
if conn is not None:
cur = conn.cursor()
cur.execute('drop table if exists test_lob')
cur.execute('create table test_lob(id integer, b BLOB, c CLOB, ba bytea)')
ba = bytearray("中文测试字符bytearray", "UTF8")
b = bytes('中文测试字符bytes' * 2, "UTF8")
u = u'中文字unicode' * 3
s = '中文str' * 4
cur.execute("insert into test_lob values(%s, %s, %s, %s)", (1, ba, ba, ba))
cur.execute("insert into test_lob values(%s, %s, %s, %s)", (2, b, b, b))
cur.execute("insert into test_lob values(%s, %s, %s, %s)", (3, u, u, u))
cur.execute("insert into test_lob values(%s, %s, %s, %s)", (4, s, s, s))
cur.execute("select * from test_lob")
rows = cur.fetchall()
for row in rows:
for cell in row:
if isinstance(cell, memoryview):
print(type(cell), cell[:].tobytes().decode('UTF8'), " ", end="")
else:
print(type(cell), cell, " ", end="")
print()
cur.close()
conn.commit()
conn.close()
return 0
else:
return None
def testOID():
conn = testConn()
if conn is not None:
cur = conn.cursor()
cur.execute('drop table if exists test_oid')
cur.execute('create table test_oid(id integer, o OID)')
lo1 = conn.lobject()
lo1.write("raw data")
cur.execute("insert into test_oid values(%s, %s)", (1, lo1.oid))
lo2 = conn.lobject()
lo2.write(b'binary data')
cur.execute("insert into test_oid values(%s, %s)", (3, lo2.oid))
lo3 = conn.lobject()
lo3.write('中文数据 data')
cur.execute("insert into test_oid values(%s, %s)", (3, lo3.oid))
lo1.close()
lo2.close()
lo3.close()
cur.execute("select o from test_oid")
rows = cur.fetchall()
for c in cur.description:
print(c.name, "\t", end="")
print()
for row in rows:
for cell in row:
lo_out = conn.lobject(cell)
r = lo_out.read()
lo_out.close()
print("oid:", cell, ":", r, " ", end="")
print()
cur.close()
conn.commit()
conn.close()
return 0
else:
return None
def testNewType():
conn = testConn()
if conn is not None:
cur = conn.cursor()
cur.execute('drop table if exists test_newtype')
cur.execute(
'create table test_newtype(num INTEGER, bcb bpcharbyte(30), vcb varcharbyte(30), date date, blob BLOB, nclob NCLOB)')
cur.execute("insert into test_newtype values(%s, %s, %s, %s, %s, %s)",
(100, 'bpcharbyte_30', 'varcharbyte_30', '2000-12-01 15:30:12', 'blob', 'nclob'))
cur.execute("insert into test_newtype values(%s, %s, %s, %s, %s, %s)",
(200, u'中文测试数据', u'中文测试数据', datetime.datetime.today(), u'电科金仓数据库', u'电科金仓'))
cur.execute("select * from test_newtype")
rows = cur.fetchall()
for row in rows:
for cell in row:
print(type(cell), cell, " ", end="")
print()
cur.close()
conn.commit()
conn.close()
return 0
else:
return None
if __name__ == "__main__":
print("libpq version:", ksycopg2.__libpq_version__)
print("ksycopg2 version:", ksycopg2.__version__)
check("testConn", testConn())
check("testConn2", testConn2())
check("testExecute", testExecute())
check("testSelect", testSelect())
check("testLob", testLob())
check("testOID", testOID())
check("testNewType", testNewType())
print("failed case:", failed)
三、基础数据库操作实战

1. 数据库连接管理
创建可重用的连接工具类:
import ksycopg2
from ksycopg2 import OperationalError
class KingbaseESManager:
def __init__(self, dbname="TEST", user="SYSTEM", password="your_password",
host="127.0.0.1", port="54321"):
self.db_params = {
"database": dbname,
"user": user,
"password": password,
"host": host,
"port": port,
"charset": "utf8" # 防止中文乱码
}
self.conn = None
def connect(self):
"""建立数据库连接"""
try:
self.conn = ksycopg2.connect(**self.db_params)
print("✅ 数据库连接成功")
return True
except OperationalError as e:
print(f"❌ 连接失败: {e}")
return False
def disconnect(self):
"""关闭数据库连接"""
if self.conn:
self.conn.close()
print("✅ 数据库连接已关闭")
def test_connection(self):
"""测试连接并获取数据库版本"""
try:
cursor = self.conn.cursor()
cursor.execute("SELECT substr(version(), 1, 50) as db_version")
result = cursor.fetchone()
print(f"📊 数据库版本: {result[0]}")
cursor.close()
return True
except Exception as e:
print(f"❌ 连接测试失败: {e}")
return False
# 使用示例
if __name__ == "__main__":
db_mgr = KingbaseESManager(
dbname="TEST",
user="SYSTEM",
password="your_password", # 替换为实际密码
host="localhost",
port="54321"
)
if db_mgr.connect():
db_mgr.test_connection()
db_mgr.disconnect()
2. 数据表创建与管理
创建完整的业务数据表:
def create_business_tables(conn):
"""
创建业务相关的数据表
包含员工表、部门表、工资记录表
"""
cursor = conn.cursor()
# 创建部门表
department_table_sql = """
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS departments (
dept_id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY,
dept_name VARCHAR(100) NOT NULL UNIQUE,
manager VARCHAR(50),
create_time TIMESTAMP DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP,
update_time TIMESTAMP DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP
)
"""
# 创建员工表
employee_table_sql = """
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS employees (
emp_id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY,
emp_code VARCHAR(20) UNIQUE NOT NULL,
name VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL,
gender CHAR(1) CHECK (gender IN ('M', 'F')),
age INT CHECK (age >= 18 AND age <= 65),
position VARCHAR(50),
salary DECIMAL(10,2),
dept_id INT,
hire_date DATE,
active BOOLEAN DEFAULT TRUE,
created_time TIMESTAMP DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP,
CONSTRAINT fk_dept FOREIGN KEY(dept_id) REFERENCES departments(dept_id)
)
"""
# 创建工资记录表
salary_history_sql = """
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS salary_history (
record_id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY,
emp_id INT NOT NULL,
salary_month VARCHAR(7) NOT NULL, -- 格式: YYYY-MM
base_salary DECIMAL(10,2),
bonus DECIMAL(10,2) DEFAULT 0,
deduction DECIMAL(10,2) DEFAULT 0,
total_salary DECIMAL(10,2) GENERATED ALWAYS AS (base_salary + bonus - deduction) STORED,
pay_date DATE,
remark TEXT,
created_time TIMESTAMP DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP,
CONSTRAINT fk_emp FOREIGN KEY(emp_id) REFERENCES employees(emp_id),
CONSTRAINT unique_emp_month UNIQUE(emp_id, salary_month)
)
"""
try:
# 执行建表语句
cursor.execute(department_table_sql)
cursor.execute(employee_table_sql)
cursor.execute(salary_history_sql)
conn.commit()
print("✅ 业务数据表创建成功!")
# 验证表结构
cursor.execute("""
SELECT table_name, column_name, data_type
FROM information_schema.columns
WHERE table_schema = 'public'
AND table_name IN ('departments', 'employees', 'salary_history')
ORDER BY table_name, ordinal_position
""")
tables = cursor.fetchall()
print("\n📋 创建的表结构概览:")
current_table = ""
for table, column, dtype in tables:
if table != current_table:
print(f"\n{table}:")
current_table = table
print(f" - {column} ({dtype})")
except Exception as e:
conn.rollback()
print(f"❌ 创建表失败: {e}")
finally:
cursor.close()
# 执行建表
db_mgr = KingbaseESManager()
if db_mgr.connect():
create_business_tables(db_mgr.conn)
db_mgr.disconnect()3. 数据操作完整示例
完整的CRUD操作封装:
class BusinessDataManager:
def __init__(self, db_manager):
self.db = db_manager
def insert_department(self, dept_name, manager=None):
"""插入部门数据"""
sql = "INSERT INTO departments (dept_name, manager) VALUES (%s, %s) RETURNING dept_id"
try:
cursor = self.db.conn.cursor()
cursor.execute(sql, (dept_name, manager))
dept_id = cursor.fetchone()[0]
self.db.conn.commit()
print(f"✅ 部门 '{dept_name}' 创建成功,ID: {dept_id}")
return dept_id
except Exception as e:
self.db.conn.rollback()
print(f"❌ 插入部门失败: {e}")
return None
def batch_insert_employees(self, employees_data):
"""批量插入员工数据"""
sql = """
INSERT INTO employees (emp_code, name, gender, age, position, salary, dept_id, hire_date)
VALUES (%s, %s, %s, %s, %s, %s, %s, %s)
"""
try:
cursor = self.db.conn.cursor()
cursor.executemany(sql, employees_data)
self.db.conn.commit()
print(f"✅ 批量插入员工成功,影响行数: {cursor.rowcount}")
except Exception as e:
self.db.conn.rollback()
print(f"❌ 批量插入员工失败: {e}")
def query_employees_by_department(self, dept_name=None):
"""根据部门查询员工信息"""
if dept_name:
sql = """
SELECT e.emp_id, e.emp_code, e.name, e.position, e.salary, d.dept_name
FROM employees e
LEFT JOIN departments d ON e.dept_id = d.dept_id
WHERE d.dept_name = %s AND e.active = TRUE
ORDER BY e.salary DESC
"""
params = (dept_name,)
else:
sql = """
SELECT e.emp_id, e.emp_code, e.name, e.position, e.salary, d.dept_name
FROM employees e
LEFT JOIN departments d ON e.dept_id = d.dept_id
WHERE e.active = TRUE
ORDER BY d.dept_name, e.salary DESC
"""
params = None
cursor = self.db.conn.cursor()
cursor.execute(sql, params)
results = cursor.fetchall()
print(f"\n👥 员工查询结果 ({len(results)} 条记录):")
for emp in results:
print(f" 编号: {emp[1]}, 姓名: {emp[2]}, 职位: {emp[3]}, 薪资: {emp[4]:.2f}, 部门: {emp[5]}")
cursor.close()
return results
def update_employee_salary(self, emp_code, new_salary):
"""更新员工薪资"""
update_sql = "UPDATE employees SET salary = %s WHERE emp_code = %s"
history_sql = """
INSERT INTO salary_history (emp_id, salary_month, base_salary, bonus, pay_date)
SELECT emp_id, TO_CHAR(CURRENT_DATE, 'YYYY-MM'), %s, 0, CURRENT_DATE
FROM employees WHERE emp_code = %s
"""
try:
cursor = self.db.conn.cursor()
# 更新员工薪资
cursor.execute(update_sql, (new_salary, emp_code))
if cursor.rowcount == 0:
print("❌ 未找到对应员工")
return False
# 插入薪资历史记录
cursor.execute(history_sql, (new_salary, emp_code))
self.db.conn.commit()
print(f"✅ 员工 {emp_code} 薪资更新成功")
return True
except Exception as e:
self.db.conn.rollback()
print(f"❌ 更新薪资失败: {e}")
return False
# 完整的使用示例
def comprehensive_demo():
"""综合演示示例"""
db_mgr = KingbaseESManager()
if not db_mgr.connect():
return
manager = BusinessDataManager(db_mgr)
# 1. 插入部门数据
dept1 = manager.insert_department("技术研发部", "张经理")
dept2 = manager.insert_department("市场营销部", "李经理")
dept3 = manager.insert_department("人力资源部", "王经理")
# 2. 批量插入员工数据
employees = [
("EMP2024001", "张三", "M", 28, "高级工程师", 15000.00, dept1, "2024-01-15"),
("EMP2024002", "李四", "F", 25, "前端工程师", 12000.00, dept1, "2024-02-20"),
("EMP2024003", "王五", "M", 30, "市场专员", 10000.00, dept2, "2024-01-10"),
("EMP2024004", "赵六", "F", 26, "招聘专员", 9000.00, dept3, "2024-03-01"),
("EMP2024005", "钱七", "M", 32, "架构师", 20000.00, dept1, "2024-02-15"),
]
manager.batch_insert_employees(employees)
# 3. 查询员工信息
print("\n" + "="*50)
print("技术研发部员工列表:")
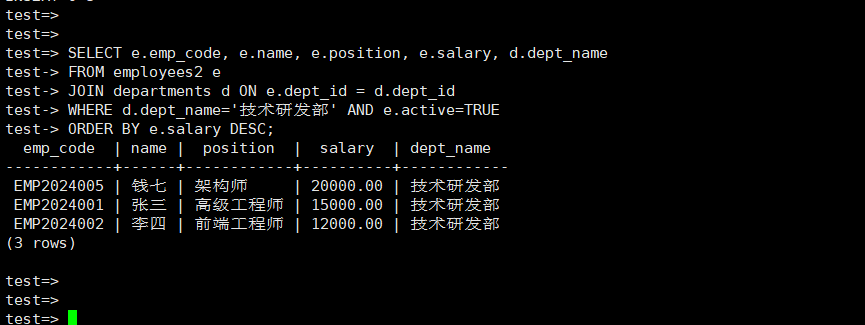
manager.query_employees_by_department("技术研发部")
print("\n所有部门员工列表:")
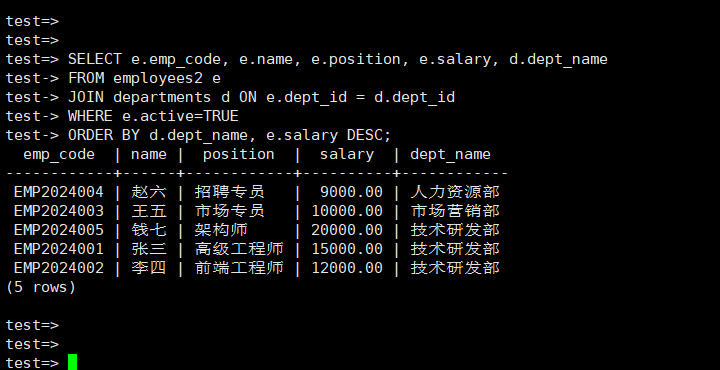
manager.query_employees_by_department()
# 4. 更新薪资
print("\n" + "="*50)
manager.update_employee_salary("EMP2024001", 18000.00)
# 5. 验证更新结果
print("\n更新后的技术研发部员工列表:")
manager.query_employees_by_department("技术研发部")
db_mgr.disconnect()
if __name__ == "__main__":
comprehensive_demo()以上操作,后台查看数据库部分如下图所示:
技术研发部员工列表:
查询全公司列表:
四、高级特性与实战技巧
1. 连接池管理
使用连接池提升性能:
from ksycopg2 import pool
class ConnectionPoolManager:
def __init__(self, minconn=1, maxconn=10, **db_params):
self.db_params = db_params
try:
self.connection_pool = pool.SimpleConnectionPool(
minconn, maxconn, **db_params
)
print("✅ 数据库连接池创建成功")
except Exception as e:
print(f"❌ 连接池创建失败: {e}")
self.connection_pool = None
def get_connection(self):
"""从连接池获取连接"""
if self.connection_pool:
return self.connection_pool.getconn()
return None
def return_connection(self, conn):
"""将连接返回连接池"""
if self.connection_pool and conn:
self.connection_pool.putconn(conn)
def close_all_connections(self):
"""关闭所有连接"""
if self.connection_pool:
self.connection_pool.closeall()
print("✅ 所有连接已关闭")
# 使用连接池的示例
def connection_pool_demo():
db_params = {
"database": "TEST",
"user": "SYSTEM",
"password": "your_password",
"host": "localhost",
"port": "54321"
}
pool_mgr = ConnectionPoolManager(**db_params)
# 从连接池获取连接执行操作
conn = pool_mgr.get_connection()
if conn:
try:
cursor = conn.cursor()
cursor.execute("SELECT COUNT(*) FROM employees")
count = cursor.fetchone()[0]
print(f"当前员工总数: {count}")
cursor.close()
finally:
pool_mgr.return_connection(conn)
pool_mgr.close_all_connections()
2. 事务处理与错误处理
完整的事务管理示例:
def transfer_salary_with_transaction(db_mgr, from_emp, to_emp, amount):
"""
薪资转账事务示例
演示完整的事务回滚机制
"""
conn = db_mgr.conn
cursor = conn.cursor()
try:
# 开始事务
conn.autocommit = False
# 检查转出账户余额
cursor.execute("SELECT salary FROM employees WHERE emp_code = %s", (from_emp,))
from_balance = cursor.fetchone()
if not from_balance:
raise Exception(f"员工 {from_emp} 不存在")
if from_balance[0] < amount:
raise Exception(f"员工 {from_emp} 余额不足")
# 执行转账操作
cursor.execute("UPDATE employees SET salary = salary - %s WHERE emp_code = %s",
(amount, from_emp))
cursor.execute("UPDATE employees SET salary = salary + %s WHERE emp_code = %s",
(amount, to_emp))
# 记录交易日志
cursor.execute("""
INSERT INTO salary_history (emp_id, salary_month, base_salary, bonus, remark)
SELECT emp_id, TO_CHAR(CURRENT_DATE, 'YYYY-MM'), -%s, 0, '转账给员工%s'
FROM employees WHERE emp_code = %s
""", (amount, to_emp, from_emp))
cursor.execute("""
INSERT INTO salary_history (emp_id, salary_month, base_salary, bonus, remark)
SELECT emp_id, TO_CHAR(CURRENT_DATE, 'YYYY-MM'), %s, 0, '收到员工%s转账'
FROM employees WHERE emp_code = %s
""", (amount, from_emp, to_emp))
# 提交事务
conn.commit()
print(f"✅ 转账成功: 从 {from_emp} 向 {to_emp} 转账 {amount} 元")
return True
except Exception as e:
# 回滚事务
conn.rollback()
print(f"❌ 转账失败,已回滚: {e}")
return False
finally:
cursor.close()
conn.autocommit = True五、实战建议与最佳实践
1. 性能优化技巧
-
使用参数化查询:防止SQL注入,提高查询效率
-
合理使用连接池:避免频繁创建关闭连接的开销
-
批量操作:使用
executemany()进行批量插入更新
2. 错误处理策略
def robust_query(db_mgr, sql, params=None):
"""健壮的查询函数"""
max_retries = 3
for attempt in range(max_retries):
try:
cursor = db_mgr.conn.cursor()
cursor.execute(sql, params)
results = cursor.fetchall()
cursor.close()
return results
except OperationalError as e:
if attempt == max_retries - 1:
raise e
print(f"数据库操作失败,重试 {attempt + 1}/{max_retries}")
db_mgr.connect() # 重新连接六、常见问题

-
驱动包 SSL 库与系统环境的 SSL 库冲突
原因:系统环境的依赖库版本过高,或应用程序运行时错误加载了系统环境的SSL库。
解决:通过
ldd _ksycopg 开头的驱动, 查看当前环境下的依赖关系,确保运行应用程序时加载驱动包提供的 SSL 库,若仍然有 SSL 相关报错,则确定是驱动包提供的 SSL 库无法在当前环境下使用,此时请联系技服获取 Ksycopg2静态依赖 SSL 库的驱动包来解决 SSL 依赖冲突问题。 -
Ksycopg2 加载失败,报错 No module named 'ksycopg2._ksycopg'
原因:使用与当前环境架构不符或 Python 版本不一致的驱动包,也有可能是驱动包安装路径不对,Python 无法识别。
解决:先确保使用对应架构及对应 Python 版本的驱动包,若确认驱动包无误,则可能是 Python 未成功识别到对应 Ksycopg2 模块,可通过在 Python 强制设置模块搜索路径解决:
>>> import sys >>> sys.path.insert(0, "Ksycopg2 驱动包的父目录")
七、总结

ksycopg2作为KingbaseES的专用Python驱动,提供了完整、高效、安全的数据库操作解决方案。通过本文的实战示例,您可以快速掌握:
-
环境配置:正确安装和配置ksycopg2驱动
-
基础操作:连接管理、CRUD操作、事务处理
-
高级特性:连接池、批量操作、错误处理
-
最佳实践:性能优化和安全建议
建议您在实际环境中运行这些代码示例,根据具体业务需求进行调整和优化。KingbaseES的官方文档提供了更详细的功能说明和API参考,是深入学习的重要资源。

关于本文,博主还写了相关文章,欢迎关注《电科金仓》分类:
第一章:基础与入门
1、【金仓数据库征文】政府项目数据库迁移:从MySQL 5.7到KingbaseES的蜕变之路
2、【金仓数据库征文】学校AI数字人:从Sql Server到KingbaseES的数据库转型之路
3、电科金仓2025发布会,国产数据库的AI融合进化与智领未来
5、《一行代码不改动!用KES V9 2025完成SQL Server → 金仓“平替”迁移并启用向量检索》
6、《赤兔引擎×的卢智能体:电科金仓如何用“三骏架构”重塑AI原生数据库一体机》
7、探秘KingbaseES在线体验平台:技术盛宴还是虚有其表?
9、KDMS V4 一键搞定国产化迁移:零代码、零事故、零熬夜——金仓社区发布史上最省心数据库迁移评估神器
10、KingbaseES V009版本发布:国产数据库的新飞跃
11、从LIS到全院云:浙江省人民医院用KingbaseES打造国内首个多院区异构多活信创样板
第二章:能力与提升
1、零改造迁移实录:2000+存储过程从SQL Server滑入KingbaseES V9R4C12的72小时
3、在Ubuntu服务器上安装KingbaseES V009R002C012(Orable兼容版)数据库过程详细记录
4、金仓数据库迁移评估系统(KDMS)V4 正式上线:国产化替代的技术底气
5、Ubuntu系统下Python连接国产KingbaseES数据库实现增删改查
7、Java连接电科金仓数据库(KingbaseES)实战指南
8、使用 Docker 快速部署 KingbaseES 国产数据库:亲测全过程分享
9、【金仓数据库产品体验官】Oracle兼容性深度体验:从SQL到PL/SQL,金仓KingbaseES如何无缝平替Oracle?
10、KingbaseES在Alibaba Cloud Linux 3 的深度体验,从部署到性能实战
第三章:实践与突破
2、【金仓数据库产品体验官】实战测评:电科金仓数据库接口兼容性深度体验
3、KingbaseES与MongoDB全面对比:一篇从理论到实战的国产化迁移指南
4、从SQL Server到KingbaseES:一步到位的跨平台迁移与性能优化指南
5、ksycopg2实战:Python连接KingbaseES数据库的完整指南
后期作品正在准备中,敬请关注......























 3054
3054












