Tnesrflow:
https://www.imooc.com/article/details/id/29525
https://blog.youkuaiyun.com/wuzqChom/article/details/74785643
https://www.cnblogs.com/White-xzx/p/9497029.html

3.卷积padding的实战分析
接下来我们通过在TensorFlow中使用卷积和池化函数来分析padding参数在实际中的应用,代码如下:
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import tensorflow as tf
# 首先,模拟输入一个图像矩阵,大小为5*5
# 输入图像矩阵的shape为[批次大小,图像的高度,图像的宽度,图像的通道数]
input = tf.Variable(tf.constant(1.0, shape=[1, 5, 5, 1]))
# 定义卷积核,大小为2*2,输入和输出都是单通道
# 卷积核的shape为[卷积核的高度,卷积核的宽度,图像通道数,卷积核的个数]
filter1 = tf.Variable(tf.constant([-1.0, 0, 0, -1], shape=[2, 2, 1, 1]))
# 卷积操作 strides为[批次大小,高度方向的移动步长,宽度方向的移动步长,通道数]
# SAME
op1_conv_same = tf.nn.conv2d(input, filter1, strides=[1,2,2,1],padding='SAME')
# VALID
op2_conv_valid = tf.nn.conv2d(input, filter1, strides=[1,2,2,1],padding='VALID')
init = tf.global_variables_initializer()
with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(init)
print("op1_conv_same:\n", sess.run(op1_conv_same))
print("op2_conv_valid:\n", sess.run(op2_conv_valid))VALID模式的分析:
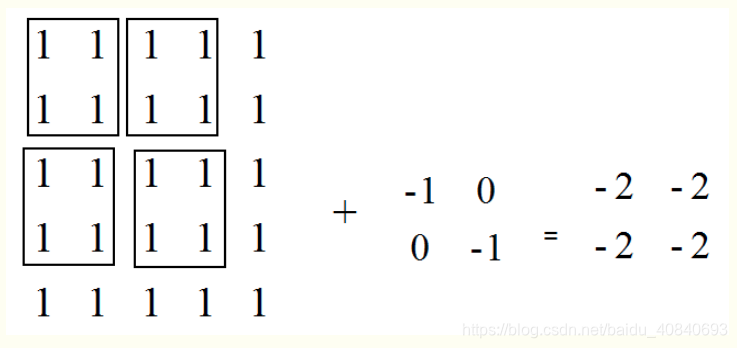
SAME模式分析:
o_w = i_w / s_w = 5/2 = 3
o_h = i_h / s_h = 5/2 = 3
pad_w = max ( (o_w - 1 ) × s_w + f_w - i_w , 0 )
= max ( (3 - 1 ) × 2 + 2 - 5 , 0 ) = 1
pad_left = 1 / 2 =0
pad_right = 1 - 0 =0
# 同理
pad_top = 0
pad_bottom = 1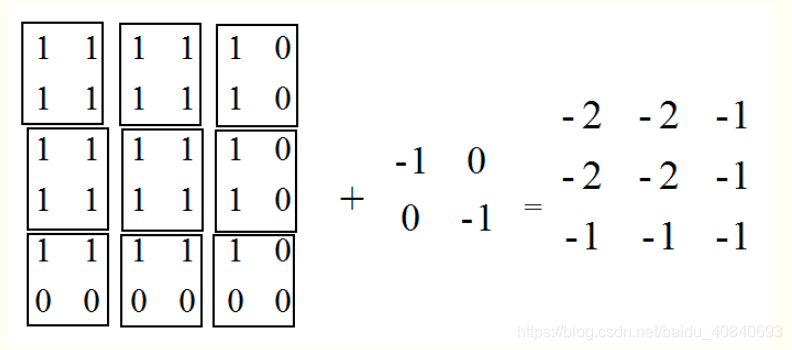
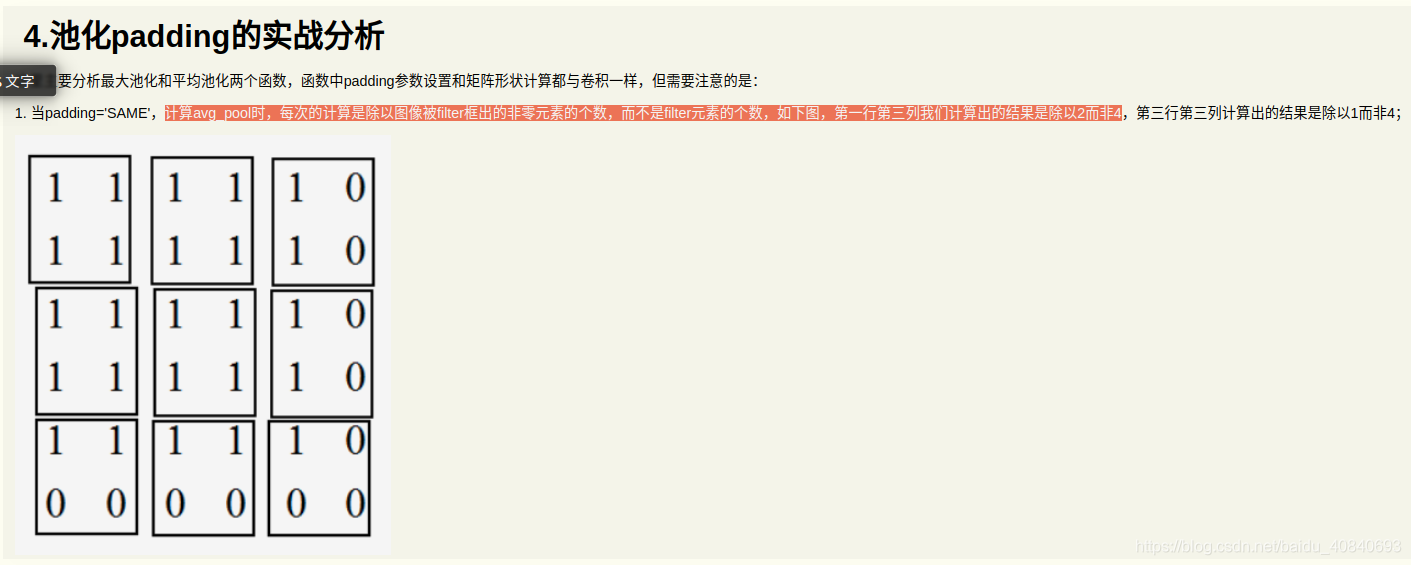
计算avg_pool时,每次的计算是除以图像被filter框出的非零元素的个数,而不是filter元素的个数,如下图,第一行第三列我们计算出的结果是除以2而非4
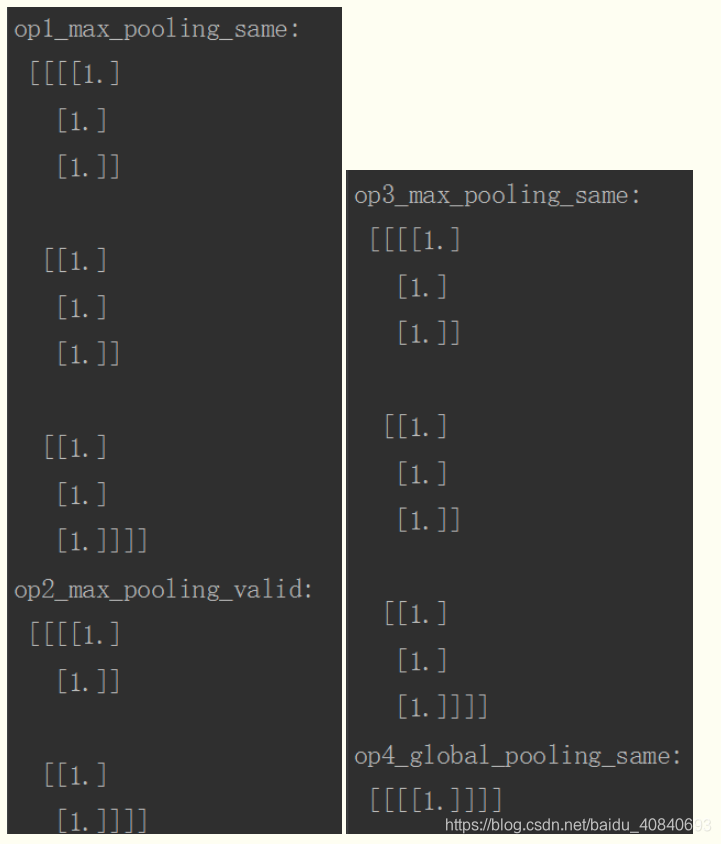
caffe:
template <typename Dtype>
void ConvolutionLayer<Dtype>::compute_output_shape() {
const int* kernel_shape_data = this->kernel_shape_.cpu_data();
const int* stride_data = this->stride_.cpu_data();
const int* pad_data = this->pad_.cpu_data();
const int* dilation_data = this->dilation_.cpu_data();
this->output_shape_.clear();
for (int i = 0; i < this->num_spatial_axes_; ++i) {
// i + 1 to skip channel axis
const int input_dim = this->input_shape(i + 1);
const int kernel_extent = dilation_data[i] * (kernel_shape_data[i] - 1) + 1;
const int output_dim = (input_dim + 2 * pad_data[i] - kernel_extent)
/ stride_data[i] + 1;
this->output_shape_.push_back(output_dim);
}
}template <typename Dtype>
void PoolingLayer<Dtype>::Reshape(const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& bottom,
const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& top) {
CHECK_EQ(4, bottom[0]->num_axes()) << "Input must have 4 axes, "
<< "corresponding to (num, channels, height, width)";
channels_ = bottom[0]->channels();
height_ = bottom[0]->height();
width_ = bottom[0]->width();
if (global_pooling_) {
kernel_h_ = bottom[0]->height();
kernel_w_ = bottom[0]->width();
}
pooled_height_ = static_cast<int>(ceil(static_cast<float>(
height_ + 2 * pad_h_ - kernel_h_) / stride_h_)) + 1;
pooled_width_ = static_cast<int>(ceil(static_cast<float>(
width_ + 2 * pad_w_ - kernel_w_) / stride_w_)) + 1;
if (pad_h_ || pad_w_) {
// If we have padding, ensure that the last pooling starts strictly
// inside the image (instead of at the padding); otherwise clip the last.
if ((pooled_height_ - 1) * stride_h_ >= height_ + pad_h_) {
--pooled_height_;
}
if ((pooled_width_ - 1) * stride_w_ >= width_ + pad_w_) {
--pooled_width_;
}
CHECK_LT((pooled_height_ - 1) * stride_h_, height_ + pad_h_);
CHECK_LT((pooled_width_ - 1) * stride_w_, width_ + pad_w_);
}
top[0]->Reshape(bottom[0]->num(), channels_, pooled_height_,
pooled_width_);
if (top.size() > 1) {
top[1]->ReshapeLike(*top[0]);
}
// If max pooling, we will initialize the vector index part.
if (this->layer_param_.pooling_param().pool() ==
PoolingParameter_PoolMethod_MAX && top.size() == 1) {
max_idx_.Reshape(bottom[0]->num(), channels_, pooled_height_,
pooled_width_);
}
// If stochastic pooling, we will initialize the random index part.
if (this->layer_param_.pooling_param().pool() ==
PoolingParameter_PoolMethod_STOCHASTIC) {
rand_idx_.Reshape(bottom[0]->num(), channels_, pooled_height_,
pooled_width_);
}
}如果是全局池化:
template <typename Dtype>
void PoolingLayer<Dtype>::LayerSetUp(const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& bottom,
const vector<Blob<Dtype>*>& top) {
PoolingParameter pool_param = this->layer_param_.pooling_param();
if (pool_param.global_pooling()) {
CHECK(!(pool_param.has_kernel_size() ||
pool_param.has_kernel_h() || pool_param.has_kernel_w()))
<< "With Global_pooling: true Filter size cannot specified";
} else {
CHECK(!pool_param.has_kernel_size() !=
!(pool_param.has_kernel_h() && pool_param.has_kernel_w()))
<< "Filter size is kernel_size OR kernel_h and kernel_w; not both";
CHECK(pool_param.has_kernel_size() ||
(pool_param.has_kernel_h() && pool_param.has_kernel_w()))
<< "For non-square filters both kernel_h and kernel_w are required.";
}
CHECK((!pool_param.has_pad() && pool_param.has_pad_h()
&& pool_param.has_pad_w())
|| (!pool_param.has_pad_h() && !pool_param.has_pad_w()))
<< "pad is pad OR pad_h and pad_w are required.";
CHECK((!pool_param.has_stride() && pool_param.has_stride_h()
&& pool_param.has_stride_w())
|| (!pool_param.has_stride_h() && !pool_param.has_stride_w()))
<< "Stride is stride OR stride_h and stride_w are required.";
global_pooling_ = pool_param.global_pooling();
if (global_pooling_) {
kernel_h_ = bottom[0]->height();
kernel_w_ = bottom[0]->width();
} else {
if (pool_param.has_kernel_size()) {
kernel_h_ = kernel_w_ = pool_param.kernel_size();
} else {
kernel_h_ = pool_param.kernel_h();
kernel_w_ = pool_param.kernel_w();
}
}
CHECK_GT(kernel_h_, 0) << "Filter dimensions cannot be zero.";
CHECK_GT(kernel_w_, 0) << "Filter dimensions cannot be zero.";
if (!pool_param.has_pad_h()) {
pad_h_ = pad_w_ = pool_param.pad();
} else {
pad_h_ = pool_param.pad_h();
pad_w_ = pool_param.pad_w();
}
if (!pool_param.has_stride_h()) {
stride_h_ = stride_w_ = pool_param.stride();
} else {
stride_h_ = pool_param.stride_h();
stride_w_ = pool_param.stride_w();
}
if (global_pooling_) {
CHECK(pad_h_ == 0 && pad_w_ == 0 && stride_h_ == 1 && stride_w_ == 1)
<< "With Global_pooling: true; only pad = 0 and stride = 1";
}
if (pad_h_ != 0 || pad_w_ != 0) {
CHECK(this->layer_param_.pooling_param().pool()
== PoolingParameter_PoolMethod_AVE
|| this->layer_param_.pooling_param().pool()
== PoolingParameter_PoolMethod_MAX)
<< "Padding implemented only for average and max pooling.";
CHECK_LT(pad_h_, kernel_h_);
CHECK_LT(pad_w_, kernel_w_);
}
}平均池化:
除以所有元素
case PoolingParameter_PoolMethod_AVE:
for (int i = 0; i < top_count; ++i) {
top_data[i] = 0;
}
// The main loop
for (int n = 0; n < bottom[0]->num(); ++n) {
for (int c = 0; c < channels_; ++c) {
for (int ph = 0; ph < pooled_height_; ++ph) {
for (int pw = 0; pw < pooled_width_; ++pw) {
int hstart = ph * stride_h_ - pad_h_;
int wstart = pw * stride_w_ - pad_w_;
int hend = min(hstart + kernel_h_, height_ + pad_h_);
int wend = min(wstart + kernel_w_, width_ + pad_w_);
int pool_size = (hend - hstart) * (wend - wstart);
hstart = max(hstart, 0);
wstart = max(wstart, 0);
hend = min(hend, height_);
wend = min(wend, width_);
for (int h = hstart; h < hend; ++h) {
for (int w = wstart; w < wend; ++w) {
top_data[ph * pooled_width_ + pw] +=
bottom_data[h * width_ + w];
}
}
top_data[ph * pooled_width_ + pw] /= pool_size;
}
}
// compute offset
bottom_data += bottom[0]->offset(0, 1);
top_data += top[0]->offset(0, 1);
}
}
break;pytorch:
池化是向下取整
https://blog.youkuaiyun.com/zxyhhjs2017/article/details/82850842
https://blog.youkuaiyun.com/zz2230633069/article/details/83214308

向下取整:和caffe不一样:







 本文详细解析了在TensorFlow中卷积操作中的Padding参数,并通过具体代码实例展示了SAME与VALID两种模式的区别。同时,还介绍了Caffe和PyTorch中关于Padding及池化的实现细节。
本文详细解析了在TensorFlow中卷积操作中的Padding参数,并通过具体代码实例展示了SAME与VALID两种模式的区别。同时,还介绍了Caffe和PyTorch中关于Padding及池化的实现细节。
















 754
754

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








