1.Yang 中涉及到的 RPC 和Notification概念
对一个对象进行建模基本都包含三个部分:
一:对象的数据结构
二:可以对该对象进行的操作(rpc)
三:该对象可以做出响应(notification)
而yang里面的rpc就是定义了一系列操作,而notification就是定义了一系列的通知事件。
而rpc和notification的机制,简单理解就是:rpc是函数调用,notification是事件监听。
这是简单的理解。
2.Yang例子简析, “#”--添加的专门注释
例:
// vi: set smarttab et sw=4 tabstop=4:
module toaster-provider-impl {
# Yang的版本
yang-version 1;
# 命名空间,此地址重要,Yang自动生成的文件会放在这个 namespace+Version版本生成的目录下面
# 但是这边举例有些特殊,待会会说到这个情况。
namespace "urn:opendaylight:params:xml:ns:yang:controller:config:toaster-provider:impl";
#此处是说明此Yang文件的前缀
prefix "toaster-provider-impl";
#import 导入,和Java导入的一样。此处导入的是分别是config.yang,rpc-context.yang,opendaylight-md-sal-binding
#同时标注好了相应的简称和版本,列如rpc-context.yang就可以用“rpcx”替代。(注:这里是怎么通过import找到要导入的文件?bundle是如何启动 时处理的?这些暂时不说明,这个涉及到bundle启动时的机制)
import config { prefix config; revision-date 2013-04-05; }
import rpc-context { prefix rpcx; revision-date 2013-06-17; }
import opendaylight-md-sal-binding { prefix mdsal; revision-date 2013-10-28; }
#描述信息,作为一个Yang语言中的注释,就好像Java中的@doc
description
"This module contains the base YANG definitions for
toaster-provider impl implementation.";
#版本信息,一般是XXXX-XX-XX 格式的时间。
revision "2014-01-31" {
description
"Initial revision.";
}
#这边namespace和revision已经给出,一般来说,生成的Java文件会放到如下的文件目录
#org.opendaylight.yang.gen.v1.urn.opendaylight.params.xml.ns.yang.controller.config.toaster.provider.impl.rev140131
#这下面是Yang语言作为数据建模语言的主要内容了,接下来的内容分析比较多,看下面具体的分析。
// This is the definition of the service implementation as a module identity.
identity toaster-provider-impl {
base config:module-type;
// Specifies the prefix for generated java classes.
config:java-name-prefix ToasterProvider;
}
// Augments the 'configuration' choice node under modules/module.
augment "/config:modules/config:module/config:configuration" {
case toaster-provider-impl {
when "/config:modules/config:module/config:type = 'toaster-provider-impl'";
container rpc-registry {
uses config:service-ref {
refine type {
mandatory true;
config:required-identity mdsal:binding-rpc-registry;
}
}
}
container notification-service {
uses config:service-ref {
refine type {
mandatory true;
config:required-identity mdsal:binding-notification-service;
}
}
}
container data-broker {
uses config:service-ref {
refine type {
mandatory false;
config:required-identity mdsal:binding-async-data-broker;
}
}
}
}
}
augment "/config:modules/config:module/config:state" {
case toaster-provider-impl {
when "/config:modules/config:module/config:type = 'toaster-provider-impl'";
leaf toasts-made {
type uint32;
}
rpcx:rpc-context-instance "clear-toasts-made-rpc";
}
}
identity clear-toasts-made-rpc;
rpc clear-toasts-made {
description
"JMX call to clear the toasts-made counter.";
input {
uses rpcx:rpc-context-ref {
refine context-instance {
rpcx:rpc-context-instance clear-toasts-made-rpc;
}
}
}
}
}
3、YANG数据节点
leaf
leaf定义的节点只有一个值,是一个叶子节点,只能有一个实例。
例如:
leaf-list
leaf-list定义一组相同类型的叶节节点,类似数组。与leaf区别在于leaf只有一个实例,而leaf-list可以有多个实例。例如:
container
container主要定义一个schema树的内部节点,它本身没有任何值和意义,只是作为一系列子节点的父亲存在,只有一个实例。例如
list
list描述了一组节点的集合,它像一张数据库表一样,表的每一行用key来标识其主键,有多个实例。例如
grouping
一个grouping定义一个可以重复使用的节点集合,使用时通过use语句,并可通过refine语句进行改进。例如
使用grouping时,通过use语句,它会将grouping定义的节点复制到当前的schema树(如果有refine,并进行更新)。
choice
一个choice节点定义了一个可供选择项的集合,每一个选择项都会在某种情况下存在。一个choice由许多分枝,通过case子语句定义。比如
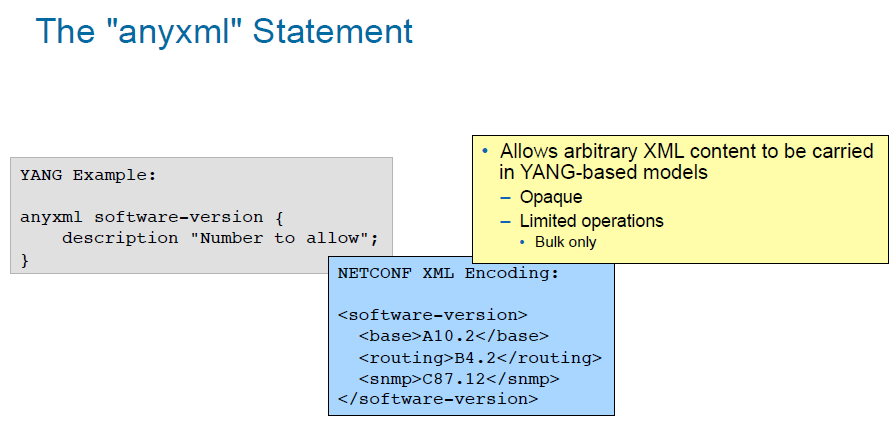
anyxml
augment
YANG提供augment语句,扩大一个模块层次,将节点添加到一个已存在的模块或子模块当中。目标结点可以是一个container, list, choice, case, rpc, input, output, notification等。
augment可以是条件的,使用when语句,当特定条件满足时,新节点才会出现。
notification
notification语句用来定义Notification内容,内容数据的定义同YANG数据定义一样。下面例子使用上文例子定义的connection。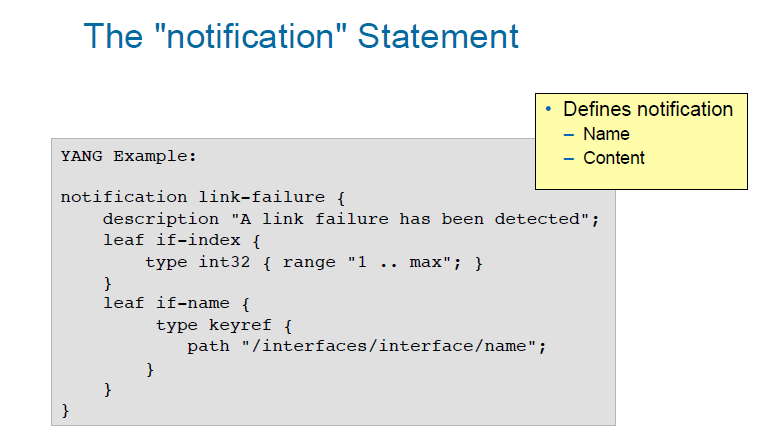
rpc
rpc语句用来定义NETCONF协议的RPCs,input和output使用YANG数据定义语句。如下例子,建模一个激活软件图片的RPC:
4.Yang中typedef关键字
typedef这个关键字简单理解就是把一个基类包装成一个包装类的意思。做个类比就像 java里有int类型,对应的包装类是Integer类。
typedef DisplayString {
type string {
length "0 .. 255";
}
description
"YANG version of the SMIv2 DisplayString TEXTUAL-CONVENTION.";
reference
"RFC 2579, section 2.";
}
将这个sring变量赋予了实际意义,增加了代码可读性,并且增加了对其的限制(length)





 本文围绕Yang语言展开,介绍了Yang中RPC和Notification概念,前者类似函数调用,后者类似事件监听。通过具体例子简析Yang文件结构,还阐述了YANG数据节点如leaf、leaf - list等的特点,最后说明了typedef关键字可包装基类,增加代码可读性和限制。
本文围绕Yang语言展开,介绍了Yang中RPC和Notification概念,前者类似函数调用,后者类似事件监听。通过具体例子简析Yang文件结构,还阐述了YANG数据节点如leaf、leaf - list等的特点,最后说明了typedef关键字可包装基类,增加代码可读性和限制。
















 9784
9784










