引言
线性回归擅长推断趋势,但无法学习相互作用。 XGBoost 擅长学习相互互,但无法推断趋势。 在本课中,我们将学习如何创建“混合”预测器,将互补的学习算法结合起来,让一个的优势弥补另一个的弱点。
组件(Components)和残差(Residuals)
为了设计出有效的混合模型,我们需要更好地理解时间序列是如何构建的。 到目前为止,我们已经研究了三种依赖模式:趋势、季节和周期。 许多时间序列可以通过仅由这三个组件加上一些本质上不可预测的、完全随机的错误的相加模型来描述:
series = trend + seasons + cycles + error
这个模型中的每一项我们都可以称为时间序列的组件。
模型的残差是模型训练的目标与模型做出的预测之间的差异 – 换句话说,真实曲线和拟合曲线之间的差异。 针对一个特征绘制残差,你会得到目标值的“剩余”部分,或者叫模型未能从该特征中学习到的内容。

上图左侧是Tunnel Traffic系列的一部分和第3课中的趋势-季节性曲线。减去拟合曲线后,残差在右侧。 残差包含趋势季节性模型没有学习到的Tunnel Traffic 中的所有内容。
我们可以将学习时间序列的组件想象为一个迭代过程:首先学习趋势并将其从序列中减去,然后从去趋势的残差中学习季节性并减去季节,然后学习周期并减去周期 ,最后只剩下不可预知的错误。

将我们学习到的所有组件加在一起,就得到了完整的模型。 如果您在一组完整的趋势、季节和周期特征上对其进行训练建模,这基本上就是线性回归要做的事情。

使用残差进行混合预测
在之前的课程中,我们使用单一算法(线性回归)一次学习所有组件。 但也可以对某些组件使用一种算法,而对其余组件使用另一种算法。 这样,我们总是可以为每个组件选择最佳算法。 为此,我们使用一种算法来拟合原始序列,然后使用第二种算法来拟合残差序列。
详细来说,流程是这样的:
# 1. Train and predict with first model
model_1.fit(X_train_1, y_train)
y_pred_1 = model_1.predict(X_train)
# 2. Train and predict with second model on residuals
model_2.fit(X_train_2, y_train - y_pred_1)
y_pred_2 = model_2.predict(X_train_2)
# 3. Add to get overall predictions
y_pred = y_pred_1 + y_pred_2
我们通常会根据我们希望每个模型学习的内容,来使用不同的特征集(上面的X_train_1和X_train_2)。 例如,如果我们使用第一个模型来学习趋势,那我们的第二个模型通常不需要趋势的特征。
虽然可以使用两个以上的模型,但实际上它似乎并不是特别有用。 事实上,构建混合模型的最常见策略就是我们刚刚描述的:一个简单(通常是线性)学习算法,然后是一个复杂的非线性学习器,如 GBDT 或深度神经网络,简单模型通常设计为 后面强大算法的“助手”。
设计混合模型
除了我们在本课程中概述的方式之外,还有很多方法可以组合机器学习模型。然而,成功地组合模型需要我们更深入地研究这些算法是如何运作的。
回归算法通常可以通过两种方式进行预测:要么转换特征,要么转换目标。 特征转换学习算法一些将特征作为输入的数学函数,然后将它们组合和转换以产生与训练集中的目标值匹配的输出。 线性回归和神经网络就是这种类型。
目标转换算法使用特征对训练集中的目标值进行分组,并通过对组中的值进行平均来进行预测; 一组特征只是表明要平均哪个组。 决策树和最近邻就是这种类型。
重要的是:在给定适当的特征作为输入的情况下,特征变换通常可以推断超出训练集的目标值,但目标变换的预测将始终限制在训练集的范围内。 如果时间虚拟变量(time dummy)继续计算时间步长,则线性回归继续绘制趋势线。 给定相同的时间虚拟变量(time dummy),决策树将按照训练数据的最后一步所表明的趋势来预测未来的趋势。 决策树无法推断趋势。 随机森林和梯度提升决策树(如 XGBoost)是决策树的集合,因此它们也无法推断趋势。

这种差异是本课使用混合设计(hybrid design)的动机:使用线性回归来推断趋势,转换目标以消除趋势,并将 XGBoost 应用于去掉趋势的残差。 要混合神经网络(特征转换)的话,您可以将另一个模型的预测作为特征包含在内,然后神经网络会将其作为其自身预测的一部分。 对残差的拟合方法其实和梯度提升算法使用的方法是一样的,所以我们称这些为boosted hybrids; 使用预测作为特征的方法称为“堆叠”,因此我们将这些称为stacked hybrids。
在Kaggle 比赛中获胜的混合模型为了获得灵感,这里有一些过去比赛中得分最高的解决方案:
- STL boosted with exponential smoothing - Walmart Recruiting - Store Sales Forecasting
- ARIMA and exponential smoothing boosted with GBDT - Rossmann Store Sales
- An ensemble of stacked and boosted hybrids - Web Traffic Time Series Forecasting
- Exponential smoothing stacked with LSTM neural net - M4 (non-Kaggle)
示例 - 美国零售销售额(US Retail Sales)
US Retail Sales 数据集包含美国人口普查局收集的 1992 年至 2019 年各个零售行业的月度销售数据。 我们的目标是根据早些年的销售额预测 2016-2019 年的销售额。 除了创建线性回归 + XGBoost 混合,我们还将了解如何设置用于 XGBoost 的时间序列数据集。
from pathlib import Path
from warnings import simplefilter
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import pandas as pd
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from statsmodels.tsa.deterministic import CalendarFourier, DeterministicProcess
from xgboost import XGBRegressor
simplefilter("ignore")
# Set Matplotlib defaults
plt.style.use("seaborn-whitegrid")
plt.rc(
"figure",
autolayout=True,
figsize=(11, 4),
titlesize=18,
titleweight='bold',
)
plt.rc(
"axes",
labelweight="bold",
labelsize="large",
titleweight="bold",
titlesize=16,
titlepad=10,
)
plot_params = dict(
color="0.75",
style=".-",
markeredgecolor="0.25",
markerfacecolor="0.25",
)
data_dir = Path("./ts-course-data/")
industries = ["BuildingMaterials", "FoodAndBeverage"]
retail = pd.read_csv(
data_dir / "us-retail-sales.csv",
usecols=['Month'] + industries,
parse_dates=['Month'],
index_col='Month',
).to_period('D').reindex(columns=industries)
retail = pd.concat({'Sales': retail}, names=[None, 'Industries'], axis=1)
retail.head()

首先让我们使用线性回归模型来学习每个系列的趋势。 为了演示,我们将使用二次(2 阶)趋势。 (这里的代码和上一课的代码基本相同。)虽然fit并不完美,但足以满足我们的需要。
y = retail.copy()
# Create trend features
dp = DeterministicProcess(
index=y.index, # dates from the training data
constant=True, # the intercept
order=2, # quadratic trend
drop=True, # drop terms to avoid collinearity
)
X = dp.in_sample() # features for the training data
# Test on the years 2016-2019. It will be easier for us later if we
# split the date index instead of the dataframe directly.
idx_train, idx_test = train_test_split(
y.index, test_size=12 * 4, shuffle=False,
)
X_train, X_test = X.loc[idx_train, :], X.loc[idx_test, :]
y_train, y_test = y.loc[idx_train], y.loc[idx_test]
y_train

X_train

# Fit trend model
model = LinearRegression(fit_intercept=False)
model.fit(X_train, y_train)
# Make predictions
y_fit = pd.DataFrame(
model.predict(X_train),
index=y_train.index,
columns=y_train.columns,
)
y_pred = pd.DataFrame(
model.predict(X_test),
index=y_test.index,
columns=y_test.columns,
)
y_fit

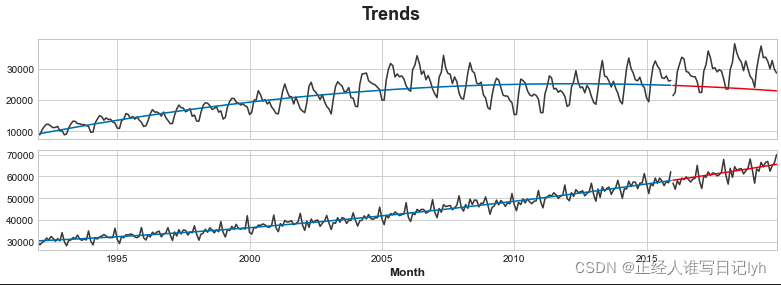
# Plot
axs = y_train.plot(color='0.25', subplots=True, sharex=True)
axs = y_test.plot(color='0.25', subplots=True, sharex=True, ax=axs)
axs = y_fit.plot(color='C0', subplots=True, sharex=True, ax=axs)
axs = y_pred.plot(color='C3', subplots=True, sharex=True, ax=axs)
for ax in axs: ax.legend([])
_ = plt.suptitle("Trends")
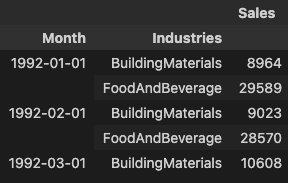
虽然线性回归算法能够进行多输出回归,但 XGBoost 算法却不能。为了使用 XGBoost 一次预测多个系列,我们将把这些系列从 wide 格式(每列一个时间系列)转换为 long 格式,系列按行的类别索引。
# The `stack` method converts column labels to row labels, pivoting from wide format to long
X = retail.stack() # pivot dataset wide to long
display(X.head())
y = X.pop('Sales') # grab target series
为了让 XGBoost 能够学会区分我们的两个时间序列,我们将“行业”的行标签转换为带有标签编码的分类特征。 我们还将通过从时间索引中提取月份数字来创建年度季节性特征。
# Turn row labels into categorical feature columns with a label encoding
X = X.reset_index('Industries')
# Label encoding for 'Industries' feature
for colname in X.select_dtypes(["object", "category"]):
X[colname], _ = X[colname].factorize()
# Label encoding for annual seasonality
X["Month"] = X.index.month # values are 1, 2, ..., 12
# Create splits
X_train, X_test = X.loc[idx_train, :], X.loc[idx_test, :]
y_train, y_test = y.loc[idx_train], y.loc[idx_test]
X_train

y_train

现在我们将之前所做的趋势预测转换为长格式,然后从原始系列中减去它们。 这将为我们提供 XGBoost 可以学习的去趋势(残差)系列。
# Pivot wide to long (stack) and convert DataFrame to Series (squeeze)
y_fit = y_fit.stack().squeeze() # trend from training set
y_pred = y_pred.stack().squeeze() # trend from test set
# Create residuals (the collection of detrended series) from the training set
y_resid = y_train - y_fit
y_fit
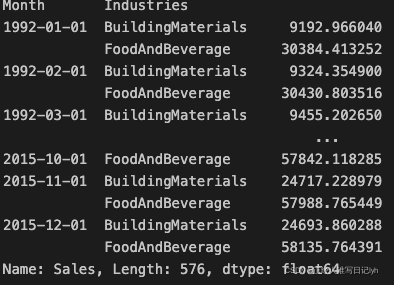
y_train

y_resid
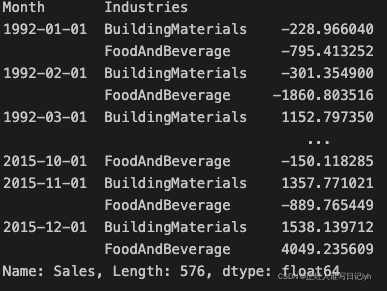
# Train XGBoost on the residuals
xgb = XGBRegressor()
xgb.fit(X_train, y_resid)
# Add the predicted residuals onto the predicted trends
y_fit_boosted = xgb.predict(X_train) + y_fit
y_pred_boosted = xgb.predict(X_test) + y_pred
拟合看起来相当不错,尽管我们可以看到 XGBoost 学习的趋势与线性回归学习的趋势一样好 – 特别注意的是 XGBoost 无法弥补'BuildingMaterials'系列中拟合不佳的趋势。
axs = y_train.unstack(['Industries']).plot(
color='0.25', figsize=(11, 5), subplots=True, sharex=True,
title=['BuildingMaterials', 'FoodAndBeverage'],
)
axs = y_test.unstack(['Industries']).plot(
color='0.25', subplots=True, sharex=True, ax=axs,
)
axs = y_fit_boosted.unstack(['Industries']).plot(
color='C0', subplots=True, sharex=True, ax=axs,
)
axs = y_pred_boosted.unstack(['Industries']).plot(
color='C3', subplots=True, sharex=True, ax=axs,
)
for ax in axs: ax.legend([])

轮到你了
使用 XGBoost 混合模型预测商店销售额(Forecast Store Sales) 并尝试其他 ML 算法组合。





 本文探讨了如何创建混合预测器,结合线性回归和XGBoost的优势,以处理时间序列数据。线性回归擅长趋势分析,而XGBoost擅长学习相互作用。通过训练线性回归模型学习趋势,然后用XGBoost学习残差,可以构建互补的预测模型。在案例中,展示了如何使用此方法预测美国零售销售额,先用线性回归拟合趋势,再用XGBoost学习去趋势后的残差,从而提高预测准确性。
本文探讨了如何创建混合预测器,结合线性回归和XGBoost的优势,以处理时间序列数据。线性回归擅长趋势分析,而XGBoost擅长学习相互作用。通过训练线性回归模型学习趋势,然后用XGBoost学习残差,可以构建互补的预测模型。在案例中,展示了如何使用此方法预测美国零售销售额,先用线性回归拟合趋势,再用XGBoost学习去趋势后的残差,从而提高预测准确性。

















 1208
1208

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








