1. 深入理解二维卷积,采用手算的方式实现以下卷积操作,然后用代码验证。

1)采用2个尺寸为33的卷积核对3通道的55图像进行卷积,padding=0, stride=1,dilation=0
其中 input shape = (3, 5, 5),数据如下
kernel size = 3*3, 第一个卷积核所有权值均为1, 第二个卷积核所有权值均为2,
计算输出的feature map尺寸以及所有像素值
flag = 1
# flag = 0
if flag:
tensor1 = torch.ones(1, 1, 5, 5)
tensor2 = tensor1 * 2
tensor3 = tensor1 * 3
input_tensor = torch.cat([tensor1, tensor2, tensor3], dim=1)
kernel1 = [[1., 1., 1.],
[1., 1., 1.],
[1., 1., 1.]]
kernel1 = torch.FloatTensor(kernel1).unsqueeze(0).unsqueeze(0)
kernel1 = torch.cat([kernel1, kernel1, kernel1], dim=1)
kernel2 = kernel1 * 2
kernel = torch.cat([kernel1, kernel2], dim=0)
out_conv = nn.functional.conv2d(input_tensor, kernel, padding=1)
print(out_conv.shape)
print(out_conv)
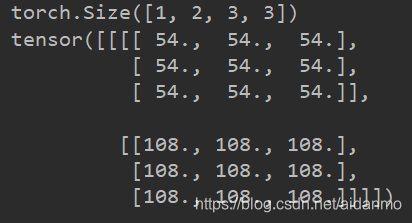
2)接1)题,上下左右四条边均采用padding,padding=1,填充值为0,计算输出的feature map尺寸以及所有像素值

2. 对lena图进行3333d卷积,提示:padding=(1, 0, 0)
# ================ 3d
# flag = 1
flag = 0
if flag:
conv_layer = nn.Conv3d(3, 1, 3, padding=(1, 0, 0))
nn.init.xavier_normal_(conv_layer.weight.data)
# calculation
img_tensor.unsqueeze_(dim=2) # B*C*H*W to B*C*D*H*W
img_conv = conv_layer(img_tensor)






 本文深入探讨二维卷积操作,通过手算和代码实现,详细解析不同参数设置下卷积核对图像的处理过程。从理论到实践,全面理解卷积神经网络中的关键组件。
本文深入探讨二维卷积操作,通过手算和代码实现,详细解析不同参数设置下卷积核对图像的处理过程。从理论到实践,全面理解卷积神经网络中的关键组件。

















 2万+
2万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










