目录
摘要:
解析influxdb集群写数据writeToShard, 分析出influxdb集群如何处理数据.
源码:
顶层writeToShard
// writeToShards writes points to a shard and ensures a write consistency level has been met. If the write
// partially succeeds, ErrPartialWrite is returned.
func (w *PointsWriter) writeToShard(shard *meta.ShardInfo, database, retentionPolicy string,
consistency ConsistencyLevel, points []models.Point) error {
atomic.AddInt64(&w.stats.PointWriteReqLocal, int64(len(points)))
// The required number of writes to achieve the requested consistency level
required := len(shard.Owners)
switch consistency {
case ConsistencyLevelAny, ConsistencyLevelOne:
required = 1
case ConsistencyLevelQuorum:
required = required/2 + 1
}
// response channel for each shard writer go routine
type AsyncWriteResult struct {
Owner meta.ShardOwner
Err error
}
ch := make(chan *AsyncWriteResult, len(shard.Owners))
for _, owner := range shard.Owners {
go func(shardID uint64, owner meta.ShardOwner, points []models.Point) {
if w.Node.ID == owner.NodeID {
atomic.AddInt64(&w.stats.PointWriteReqLocal, int64(len(points)))
err := w.TSDBStore.WriteToShard(shardID, points)
// If we've written to shard that should exist on the current node, but the store has
// not actually created this shard, tell it to create it and retry the write
if err == tsdb.ErrShardNotFound {
err = w.TSDBStore.CreateShard(database, retentionPolicy, shardID, true)
if err != nil {
ch <- &AsyncWriteResult{owner, err}
return
}
err = w.TSDBStore.WriteToShard(shardID, points)
}
ch <- &AsyncWriteResult{owner, err}
return
}
atomic.AddInt64(&w.stats.PointWriteReqRemote, int64(len(points)))
err := w.ShardWriter.WriteShard(shardID, owner.NodeID, points)
if err != nil && tsdb.IsRetryable(err) {
// The remote write failed so queue it via hinted handoff
atomic.AddInt64(&w.stats.WritePointReqHH, int64(len(points)))
hherr := w.HintedHandoff.WriteShard(shardID, owner.NodeID, points)
if hherr != nil {
ch <- &AsyncWriteResult{owner, hherr}
return
}
// If the write consistency level is ANY, then a successful hinted handoff can
// be considered a successful write so send nil to the response channel
// otherwise, let the original error propagate to the response channel
if hherr == nil && consistency == ConsistencyLevelAny {
ch <- &AsyncWriteResult{owner, nil}
return
}
}
ch <- &AsyncWriteResult{owner, err}
}(shard.ID, owner, points)
}
var wrote int
timeout := time.After(w.WriteTimeout)
var writeError error
for range shard.Owners {
select {
case <-w.closing:
return ErrWriteFailed
case <-timeout:
atomic.AddInt64(&w.stats.WriteTimeout, 1)
// return timeout error to caller
return ErrTimeout
case result := <-ch:
// If the write returned an error, continue to the next response
if result.Err != nil {
atomic.AddInt64(&w.stats.WriteErr, 1)
w.Logger.Info("write failed", zap.Uint64("shard", shard.ID), zap.Uint64("node", result.Owner.NodeID), zap.Error(result.Err))
// Keep track of the first error we see to return back to the client
if writeError == nil {
writeError = result.Err
}
continue
}
wrote++
// We wrote the required consistency level
if wrote >= required {
atomic.AddInt64(&w.stats.WriteOK, 1)
return nil
}
}
}
if wrote > 0 {
atomic.AddInt64(&w.stats.WritePartial, 1)
return ErrPartialWrite
}
if writeError != nil {
return fmt.Errorf("write failed: %v", writeError)
}
return ErrWriteFailed
}
向远端shard写入:
// WriteShard writes time series points to a shard
func (w *ShardWriter) WriteShard(shardID, ownerID uint64, points []models.Point) error {
c, err := w.dial(ownerID)
if err != nil {
return err
}
conn, ok := c.(*pooledConn)
if !ok {
panic("wrong connection type")
}
defer func(conn net.Conn) {
conn.Close() // return to pool
}(conn)
// Determine the location of this shard and whether it still exists
db, rp, sgi := w.MetaClient.ShardOwner(shardID)
if sgi == nil {
// If we can't get the shard group for this shard, then we need to drop this request
// as it is no longer valid. This could happen if writes were queued via
// hinted handoff and we're processing the queue after a shard group was deleted.
return nil
}
// Build write request.
var request WriteShardRequest
request.SetShardID(shardID)
request.SetDatabase(db)
request.SetRetentionPolicy(rp)
request.AddPoints(points)
// Marshal into protocol buffers.
buf, err := request.MarshalBinary()
if err != nil {
return err
}
// Write request.
conn.SetWriteDeadline(time.Now().Add(w.timeout))
if err := WriteTLV(conn, writeShardRequestMessage, buf); err != nil {
conn.MarkUnusable()
return err
}
// Read the response.
conn.SetReadDeadline(time.Now().Add(w.timeout))
_, buf, err = ReadTLV(conn)
if err != nil {
conn.MarkUnusable()
return err
}
// Unmarshal response.
var response WriteShardResponse
if err := response.UnmarshalBinary(buf); err != nil {
return err
}
if response.Code() != 0 {
return fmt.Errorf("error code %d: %s", response.Code(), response.Message())
}
return nil
}寻找到shard的映射:
// MapShards maps the points contained in wp to a ShardMapping. If a point
// maps to a shard group or shard that does not currently exist, it will be
// created before returning the mapping.
func (w *PointsWriter) MapShards(wp *WritePointsRequest) (*ShardMapping, error) {
rp, err := w.MetaClient.RetentionPolicy(wp.Database, wp.RetentionPolicy)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
} else if rp == nil {
return nil, freetsdb.ErrRetentionPolicyNotFound(wp.RetentionPolicy)
}
// Holds all the shard groups and shards that are required for writes.
list := make(sgList, 0, 8)
min := time.Unix(0, models.MinNanoTime)
if rp.Duration > 0 {
min = time.Now().Add(-rp.Duration)
}
for _, p := range wp.Points {
// Either the point is outside the scope of the RP, or we already have
// a suitable shard group for the point.
if p.Time().Before(min) || list.Covers(p.Time()) {
continue
}
// No shard groups overlap with the point's time, so we will create
// a new shard group for this point.
sg, err := w.MetaClient.CreateShardGroup(wp.Database, wp.RetentionPolicy, p.Time())
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
if sg == nil {
return nil, errors.New("nil shard group")
}
list = list.Append(*sg)
}
mapping := NewShardMapping(len(wp.Points))
for _, p := range wp.Points {
sg := list.ShardGroupAt(p.Time())
if sg == nil {
// We didn't create a shard group because the point was outside the
// scope of the RP.
mapping.Dropped = append(mapping.Dropped, p)
atomic.AddInt64(&w.stats.WriteDropped, 1)
continue
}
sh := sg.ShardFor(p.HashID())
mapping.MapPoint(&sh, p)
}
return mapping, nil
}时序图:
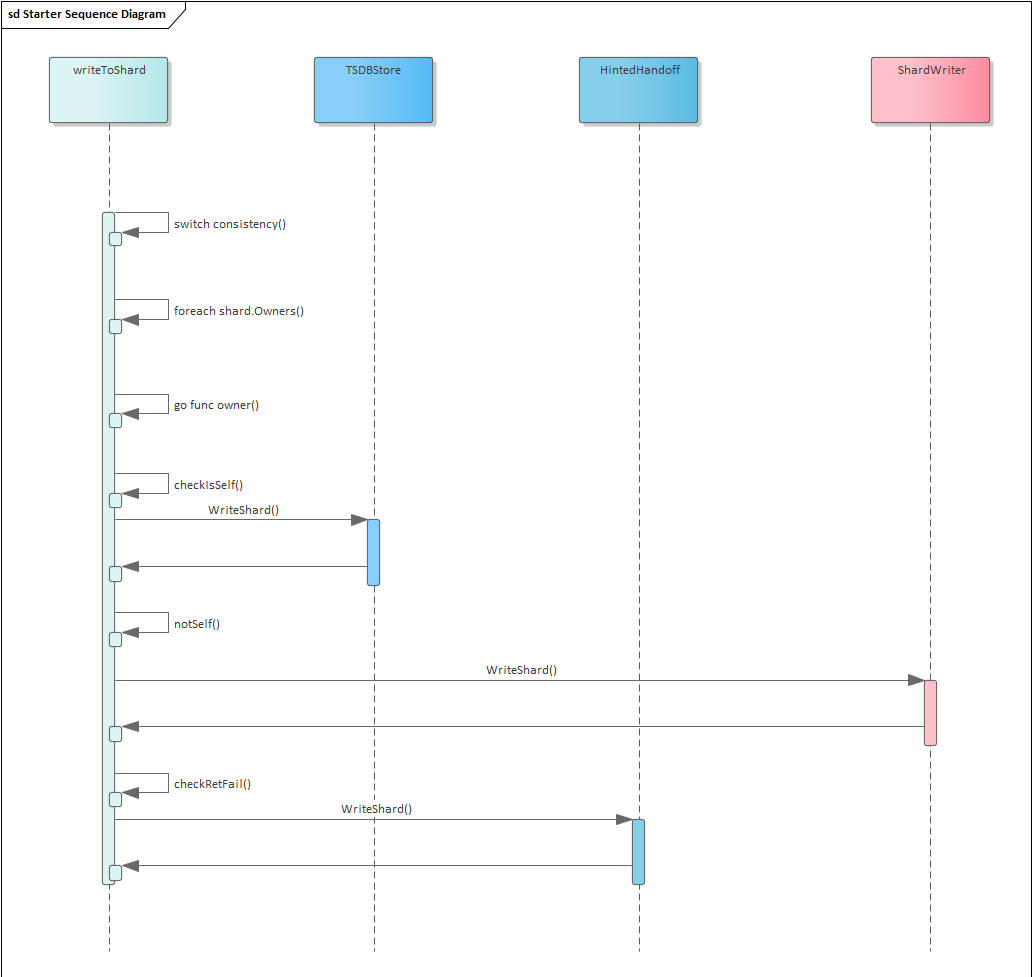
分析:
从逻辑流程上:
- 到该函数时, 已经完成了key -> shard之间映射关系的查找
- 遍历内存中保存的shard列表
- 需要注意shard中的每个shard都开创一个协程去处理
- 如果shard是自己, 调用tsdb写
- 如果是远端shard
- 向远端写, 如果写失败
- 写入内存中的hinted handoff
- 收集处理结果
从架构上:
- 可以看出将key换算成shardID, 分布到整个集群中存储
- 一旦远端shard写失败, 使用HH保存在本shard
- 需要注意该函数对协程的使用技巧








 本文详细解析了InfluxDB集群中数据写入的逻辑流程和架构设计。从`writeToShard`函数开始,介绍了如何根据shard映射向远端节点写入数据,包括错误处理和一致性保证。当远端写入失败时,数据会被暂存到hinted handoff中。同时,还展示了如何查找和创建shard映射的过程。整个过程涉及并发处理、故障恢复和数据一致性策略。
本文详细解析了InfluxDB集群中数据写入的逻辑流程和架构设计。从`writeToShard`函数开始,介绍了如何根据shard映射向远端节点写入数据,包括错误处理和一致性保证。当远端写入失败时,数据会被暂存到hinted handoff中。同时,还展示了如何查找和创建shard映射的过程。整个过程涉及并发处理、故障恢复和数据一致性策略。



















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










