.contents()
返回: jQuery
描述: 获得匹配元素集合中每个元素的子元素,包括文字和注释节点。
给定一个jQuery对象,表示一个DOM元素的集合,.contents()方法允许我们通过DOM树中查找集合中的直接子元素,并根据匹配的元素创建一个新的 jQuery 对象。.contents()和.children()方法类似,只不过前者包括文本节点和注释节点,以及jQuery对象中产生的HTML元素。请注意,虽然这种方式可以传递文本节点和注释节点给一个jQuery集合,但是大多数操作不会支持他们。少数几个支持的操作将在他们的API文档页面中有一个明确的说明。
如果iframe与主页同域,.contents()方法也可用于获取iframe中的文件内容。
考虑一个简单<div>中一些文本节点,其中每个元素是相隔两换行符(<br />):
<div class="container">
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipisicing elit, sed
do eiusmod tempor incididunt ut labore et dolore magna aliqua.
<br /><br />
Ut enim ad minim veniam, quis nostrud exercitation ullamco
laboris nisi ut aliquip ex ea commodo consequat.
<br /> <br />
Duis aute irure dolor in reprehenderit in voluptate velit
esse cillum dolore eu fugiat nulla pariatur.
</div>
我们可以使用.contents()方法将上述文本转换成三个格式良好的段落:
$('.container').contents().filter(function() {
return this.nodeType == 3;
})
.wrap('<p></p>')
.end()
.filter('br')
.remove();
此代码首先检索<div class="container">的内容,然后过滤它的文本节点,并且将它被包裹在段落标记内。这是通过测试元素的.nodeType属性。这个DOM属性保存一个数字代码,以显示节点的类型;文本节点使用代码3。再次过滤的内容,这次是<br />元素,这些元素都将被删除。
例子:
Example: 段落内找到所有的文本节点,并将他们包装了一个标记。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<script src="//code.jquery.com/jquery-latest.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<p>Hello <a href="http://ejohn.org/">John</a>, how are you doing?</p>
<script>$("p").contents().filter(function(){ return this.nodeType != 1; }).wrap("<b/>");</script>
</body>
</html>
Demo:

Example: 改变背景颜色的iframe里面的链接。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<script src="//code.jquery.com/jquery-latest.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<iframe src="http://api.jquery.com/" width="80%" height="600" id='frameDemo'></iframe>
<script>$("#frameDemo").contents().find("a").css("background-color","#BADA55");</script>
</body>
</html>
.end()
返回: jQuery
描述: 终止在当前链的最新过滤操作,并返回匹配的元素的以前状态。
大多数 jQueryDOM遍历 方法来操作 jQuery 对象实例,并创建一个新的对象,匹配一个不同的 DOM 元素集合。当发生这种情况时,实际上是新的元素集合被压入到对象内部维护的栈中。每次过滤方法都会被压入栈中。当我们需要返回到前一个状态时,我们可以使用end() 进行出栈操作,来返回栈中的前一个状态。
假设页面上有几个短的列表
<ul class="first">
<li class="foo">list item 1</li>
<li>list item 2</li>
<li class="bar">list item 3</li>
</ul>
<ul class="second">
<li class="foo">list item 1</li>
<li>list item 2</li>
<li class="bar">list item 3</li>
</ul>
end() 方法主要用于 jQuery 的链式属性中。当没有使用链式用法时,我们通常只是调用变量名上的前一个对象,所以我们不需要操作栈。使用 end() 时,我们可以一次性调用所有需要的方法:
$('ul.first').find('.foo').css('background-color', 'red')
.end().find('.bar').css('background-color', 'green');
在上面的代码中,首先在链式用法中只在第一个列表中查找样式为 foo 的项目,并将其背景色变成红色。然后 end() 返回调用 find() 之前的状态。因此,第二次 find() 将只会查找 <ul class="first"> 中的 ‘.bar’,而不是继续在 <li class="foo"> 中进行查找,结果是将匹配到的元素的背景色变成绿色。上述代码的最终结果是,第一个列表中的第 1 和第 3 个列表项的背景色有颜色,而第二个列表中的任何项目都没有背景色。
对于一个长的 jQuery 链式写法,可以使用结构块的写法,让其具有很好的可读性,即:将 end() 方法与其对应的过滤方法写在一个嵌套块中,例如:
$('ul.first').find('.foo')
.css('background-color', 'red')
.end().find('.bar')
.css('background-color', 'green')
.end();
最后的end()是不必要的,我们丢弃紧随其后的jQuery对象。然而,当编写这种形式的代码,end()提供了可视化的对称性和完整性,至少一些开发者的眼中,更具可读性,这样存在一些性能成本,因为它是一个额外的函数调用。
例子:
Example: 选择所有的段落,在其中查找 span 元素,之后再恢复到选择段落的状态。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
p, div { margin:1px; padding:1px; font-weight:bold;
font-size:16px; }
div { color:blue; }
b { color:red; }
</style>
<script src="//code.jquery.com/jquery-latest.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<p>
Hi there <span>how</span> are you <span>doing</span>?
</p>
<p>
This <span>span</span> is one of
several <span>spans</span> in this
<span>sentence</span>.
</p>
<div>
Tags in jQuery object initially: <b></b>
</div>
<div>
Tags in jQuery object after find: <b></b>
</div>
<div>
Tags in jQuery object after end: <b></b>
</div>
<script>
jQuery.fn.showTags = function (n) {
var tags = this.map(function () {
return this.tagName;
})
.get().join(", ");
$("b:eq(" + n + ")").text(tags);
return this;
};
$("p").showTags(0)
.find("span")
.showTags(1)
.css("background", "yellow")
.end()
.showTags(2)
.css("font-style", "italic");
</script>
</body>
</html>
Demo:
 Example: Selects all paragraphs, finds span elements inside these, and reverts the selection back to the paragraphs.
Example: Selects all paragraphs, finds span elements inside these, and reverts the selection back to the paragraphs.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>p { margin:10px; padding:10px; }</style>
<script src="//code.jquery.com/jquery-latest.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
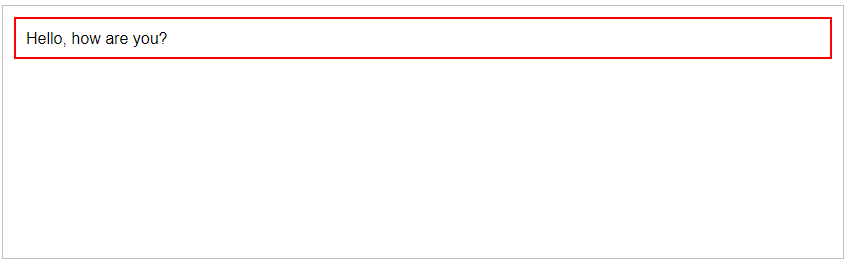
<p><span>Hello</span>, how are you?</p>
<script>$("p").find("span").end().css("border", "2px red solid");</script>
</body>
</html>
Demo:





 本文深入探讨了jQuery的高级用法,包括.contents()方法用于获取DOM元素的所有子元素,包括文本和注释节点,以及.end()方法如何帮助我们在复杂的jQuery链式调用中回退到前一状态。通过具体示例,读者将学会如何利用这些技巧实现更复杂的DOM操作。
本文深入探讨了jQuery的高级用法,包括.contents()方法用于获取DOM元素的所有子元素,包括文本和注释节点,以及.end()方法如何帮助我们在复杂的jQuery链式调用中回退到前一状态。通过具体示例,读者将学会如何利用这些技巧实现更复杂的DOM操作。
















 1139
1139

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








