神经网络的微积分
学习目标
本课程旨在帮助学员深入理解神经网络中的微积分概念,学习如何计算导数,以及如何利用这些知识来优化神经网络模型。
相关知识点
- 神经网络的微积分
学习内容
通过本课程,学员将能够掌握微积分在神经网络训练过程中的重要性,并学会将其应用于实际的模型优化问题中。学员将学习到导数在神经网络中的作用,链式法则的应用,以及使用梯度下降等优化技术来调整模型参数以减少损失函数值。
1 神经网络的微积分
1.1 导数
微积分在理解和优化神经网络中起着至关重要的作用。它为神经网络模型中使用的训练算法和优化技术提供了数学基础。
导数是微积分中的一个基本概念,在神经网络中被广泛使用。函数的导数表示其在特定点的变化率。
1.1.1 神经网络中的导数
在神经网络的上下文中,导数用于计算损失函数相对于模型参数的梯度。这些梯度表示损失函数相对于每个参数的变化率,允许我们在训练过程中确定参数更新的方向和幅度。
通过计算导数,我们可以执行反向传播,这是训练神经网络的关键算法。反向传播涉及通过网络向后传播梯度,逐层更新参数。这个迭代过程允许网络从训练数据中学习并调整其参数以最小化损失函数。
导数还使我们能够应用链式法则,这是在神经网络中使用的微积分中的另一个重要概念。链式法则允许我们通过将复合函数分解为更小的函数并迭代地应用链式法则来计算复合函数的导数。在神经网络中,“链式规则”用于计算损失函数相对于网络中间层的梯度,从而实现高效的反向传播。
1.2 链式法则
链式法则是微积分中的另一个重要概念,在神经网络中被大量使用。它允许我们通过将复合函数分解为更小的函数并迭代地应用链式法则来计算复合函数的导数。在神经网络中,链式法则用于计算损失函数相对于网络中间层的梯度,从而实现高效的反向传播。
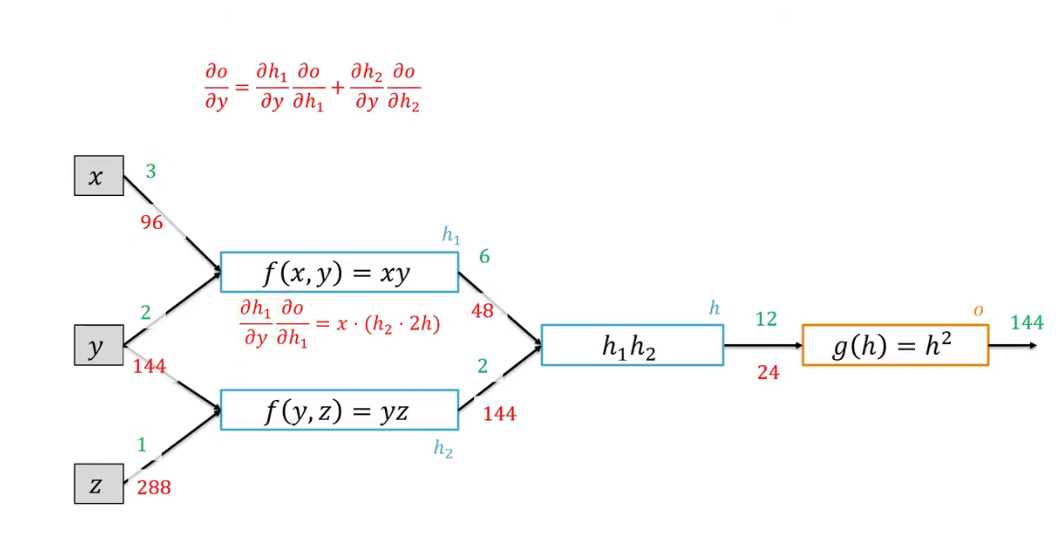
1.3 调优
调优技术(如梯度下降)用于找到模型参数的最优值,使损失函数最小化。微积分提供了必要的工具,通过计算梯度并在最陡下降的方向上更新参数来优化神经网络。
1.3.1 梯度下降
梯度下降是神经网络中常用的一种优化算法,用于找到模型参数的最优值。它依赖于导数的概念来计算损失函数相对于参数的梯度。通过在最陡下降的方向上迭代更新参数,梯度下降旨在最小化损失函数并提高神经网络的性能。
梯度下降有不同的变体,包括批量梯度下降、随机梯度下降和mini-batch梯度下降。在计算效率和收敛速度方面,每个变体都有自己的优势和取舍。
import numpy as np
# Define the gradient function
def gradient(x, y, w, b):
"""
Gradient function:
Calculates the gradients of the loss function with respect to the weight and bias.
Parameters:
- x: numpy array, input data
- y: numpy array, actual output
- w: float, weight
- b: float, bias
Returns:
- float, gradient of weight
- float, gradient of bias
"""
# Calculate the predicted values
y_pred = w * x + b
# Calculate the gradients of the loss function with respect to weight and bias
dw = 2 * np.mean((y_pred - y) * x)
db = 2 * np.mean(y_pred - y)
return dw, db
# Define the gradient descent function
def gradient_descent(x, y, learning_rate, num_iterations):
"""
Gradient Descent function:
Updates the weight and bias using gradient descent.
Parameters:
- x: numpy array, input data
- y: numpy array, actual output
- learning_rate: float, learning rate
- num_iterations: int, number of iterations
Returns:
- float, final weight
- float, final bias
"""
# Initialize the weight and bias
w = 0
b = 0
# Perform gradient descent
for i in range(num_iterations):
# Calculate the gradients
dw, db = gradient(x, y, w, b)
# Update the weight and bias in the opposite direction of the gradient
w -= learning_rate * dw
b -= learning_rate * db
return w, b
# Define the input data
x = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5])
y = np.array([2, 4, 6, 8, 10])
# Set the learning rate and number of iterations
learning_rate = 0.01
num_iterations = 100
# Perform gradient descent
final_w, final_b = gradient_descent(x, y, learning_rate, num_iterations)
# Print the final weight and bias
print("Final Weight:", final_w)
print("Final Bias:", final_b)
扎实地理解微积分对于有效地使用神经网络至关重要。它使学员能够计算导数,应用链式法则,并优化模型参数。通过利用微积分,可以训练和微调神经网络以获得更好的性能和准确性。
 PyTorch神经网络微积分与优化
PyTorch神经网络微积分与优化





















 888
888

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








