作者:来自 Elastic Jeffrey Rengifo
学习如何创建一个私有、离线的本地 RAG 个人知识助手,使用 e5-small 进行 embeddings,并在 Elasticsearch 中使用 dolphin3.0-qwen2.5-0.5b 进行 completions,以总结会议和内部报告。
Agent Builder 现已以技术预览版提供。通过 Elastic Cloud Trial 开始使用,并在此查看 Agent Builder 的文档。
使用完全运行在一台中端笔记本上的组件,可以在本地构建一个 Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) 系统。Elasticsearch 提供向量数据库基础设施,而 LocalAI 让你无需强大的 GPU 或外部服务,就能轻松运行小型、高效的语言模型。结合这些工具,我们可以实现对公司或个人数据的私有、快速、离线访问。
目标是构建一个完整的 RAG 系统:在本地使用 Embeddings 进行检索,并使用 LLM 生成答案,同时尽量少用资源,不影响延迟和答案质量。
前置条件
- Docker
- Python 3.10+
使用场景:个人知识助手
目标是通过一个简单的助手,从本地文件中解锁洞察。在这个示例中,我们将重点关注一个 CRM 迁移项目的内部文档,其中包括会议记录、进度报告和规划笔记。所有内容都将在同一台机器上运行;Elasticsearch 负责存储和语义搜索,而本地 LLM 会基于检索到的文档生成答案和摘要。
为什么要在本地这样做?
选择在本地并使用这一组工具有多个优势,例如:
- 隐私:由于你使用的是本地 LLM,你可以完全控制传递给它的信息。虽然一些基于云的 LLM 提供禁用跟踪或数据保留的企业级方案,但这并不能保证适用于所有提供商或所有套餐。
- 灵活性:像 LocalAI 这样的工具提供了多种模型,并且可以根据需要轻松替换模型,无论是评估新模型、运行测试、处理与安全相关的更新,还是在不同任务类型之间切换模型。另一方面,将 Elasticsearch 用作向量数据库,可以与许多第三方 embedding 模型集成。
- 成本:通过这种方式,你不需要为 embeddings 或 LLM 的使用支付任何基于云的服务费用,因此更加经济。
- 不依赖互联网:本地方案的另一个优势是你可以完全离线工作,这也使其适用于隔离或 air-gaped 环境,在这些环境中,由于严格的安全或合规要求,网络访问被有意限制。
- 速度:根据所选模型和你的硬件条件,这种方式在某些情况下可能比 Web 服务更快。
设置核心组件:最小化的 Elasticsearch 实例
为了在本地安装 Elasticsearch,我们将使用 start-local,它通过底层使用 Docker,让你只需一条命令即可安装 Elasticsearch。
由于我们不会使用 Kibana,我们将只安装 Elasticsearch,并使用 --esonly 参数:
curl -fsSL https://elastic.co/start-local | sh -s -- --esonlycurl -fsSL https://elastic.co/start-local | sh -s -- --esonly如果一切顺利,你将看到类似这样的消息:
🎉 Congrats, Elasticsearch is installed and running in Docker!
🔌 Elasticsearch API endpoint: http://localhost:9200
🔑 API key: MDk0NVRwa0IxRGRjVmVKSGl2ZFc6dUFaNkZTUHVXRzEzVjdrejQzSUNxZw==注意:如果你忘记了你的凭据,可以在 …/elastic-start-local/.env 中找到它们。
你可以使用 docker ps 命令来检查 Elasticsearch 实例是否正在运行。
docker ps响应:
CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES
061fbfbb67bb docker.elastic.co/elasticsearch/elasticsearch:9.1.3-arm64 "/bin/tini -- /usr/l…" 11 minutes ago Up 11 minutes (healthy) 127.0.0.1:9200->9200/tcp, 9300/tcp es-local-dev对于这个 Elasticsearch 实例,我们可以发送请求,例如:
curl -X GET "http://localhost:9200/" \
-H "Authorization: ApiKey MDk0NVRwa0IxRGRjVmVKSGl2ZFc6dUFaNkZTUHVXRzEzVjdrejQzSUNxZw=="响应:
{
"name" : "061fbfbb67bb",
"cluster_name" : "docker-cluster",
"cluster_uuid" : "IC_VY7cyQw6F_wJbH5Ik3A",
"version" : {
"number" : "9.1.3",
"build_flavor" : "default",
"build_type" : "docker",
"build_hash" : "0c781091a2f57de895a73a1391ff8426c0153c8d",
"build_date" : "2025-08-24T22:05:04.526302670Z",
"build_snapshot" : false,
"lucene_version" : "10.2.2",
"minimum_wire_compatibility_version" : "8.19.0",
"minimum_index_compatibility_version" : "8.0.0"
},
"tagline" : "You Know, for Search"
}这个本地实例将存储我们的 CRM 迁移笔记和报告,以便以后进行语义搜索。
添加 AI:选择合适的本地模型
现在我们将选择两个模型来实现功能:
- Embeddings 模型:用于 embeddings,我们将使用多语言模型 multilingual-e5-small。它在 Elasticsearch 中预先配置可用,但在使用前需要部署。
- Completion 模型:用于聊天、生成响应以及与数据交互,我们需要选择一个在大小和性能之间有最佳平衡的模型。为此,我准备了下面的表格,对一些小型模型进行了比较:
| Model | Parameters | Size in memory (Approx) |
|---|---|---|
| llama-smoltalk-3.2-1b-instruct | 1B | 500 MB |
| dolphin3.0-qwen2.5-0.5b | 0.5B | 200 MB |
| fastllama-3.2-1b-instruct | 1B | 550 MB |
| smollm2-1.7b-instruct | 1.7B | 1.0 GB |
最终决策取决于你的需求和你的机器。在这个示例中,我们将使用 dolphin3.0-qwen2.5-0.5b 模型,因为它在 RAG 系统中具有强大的能力,并且在表格中提供了最佳的大小与参数比率。其他选项在此用例中也能良好工作,但考虑到其大小,dolphin3.0-qwen2.5-0.5b 是我们的选择。
CPU 和内存使用的平衡很重要,因为我们的助手需要在中端笔记本资源下,以合理的时间总结会议和报告。
为了下载 dolphin3.0-qwen2.5-0.5b,我们将使用 LocalAI,这是一个易于在本地运行模型的解决方案。你可以在机器上安装 LocalAI,但我们将使用 Docker 来隔离 LocalAI 服务和模型。按照以下说明安装官方 LocalAI Docker 镜像。
LocalAI REST API
LocalAI 的主要功能之一是能够通过 HTTP 请求以 OpenAI API 兼容格式提供模型服务。这个功能在后续步骤中会非常有用。
LocalAI 服务将在 8080 端口可访问,我们将在这里发送 HTTP 请求。让我们发送一个请求来下载 dolphin3.0-qwen2.5-0.5b 模型:
curl -X POST http://localhost:8080/models/apply \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{"id": "dolphin3.0-qwen2.5-0.5b"}'
# Response:
{"uuid":"d5212e97-bf1d-11f0-ba2a-22b2311545e6","status":"http://localhost:8080/models/jobs/d5212e97-bf1d-11f0-ba2a-22b2311545e6"}% 我们可以使用上一步生成的 ID 来检查下载状态:
curl -s http://localhost:8080/models/jobs/d5212e97-bf1d-11f0-ba2a-22b2311545e6
# Response:
{
"deletion": false,
"file_name": "/models/dolphin-3.0-qwen2.5-0.5b-instruct.Q4_K_M.gguf.partial",
"error": null,
"processed": false,
"message": "processing",
"progress": 9.860515383462856,
"file_size": "391.2 MiB",
"downloaded_size": "37.2 MiB",
"gallery_element_name": ""
}progress 字段表示当前下载的百分比;我们需要等待它完成。一旦完成,我们可以创建一个测试以确保一切正常运行:
curl -X POST http://localhost:8080/v1/chat/completions \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{
"model": "dolphin3.0-qwen2.5-0.5b",
"messages": [
{
"role": "user",
"content": "Why is the sky blue?"
}
],
"stream": false
}在这里查看 LLM 结果。
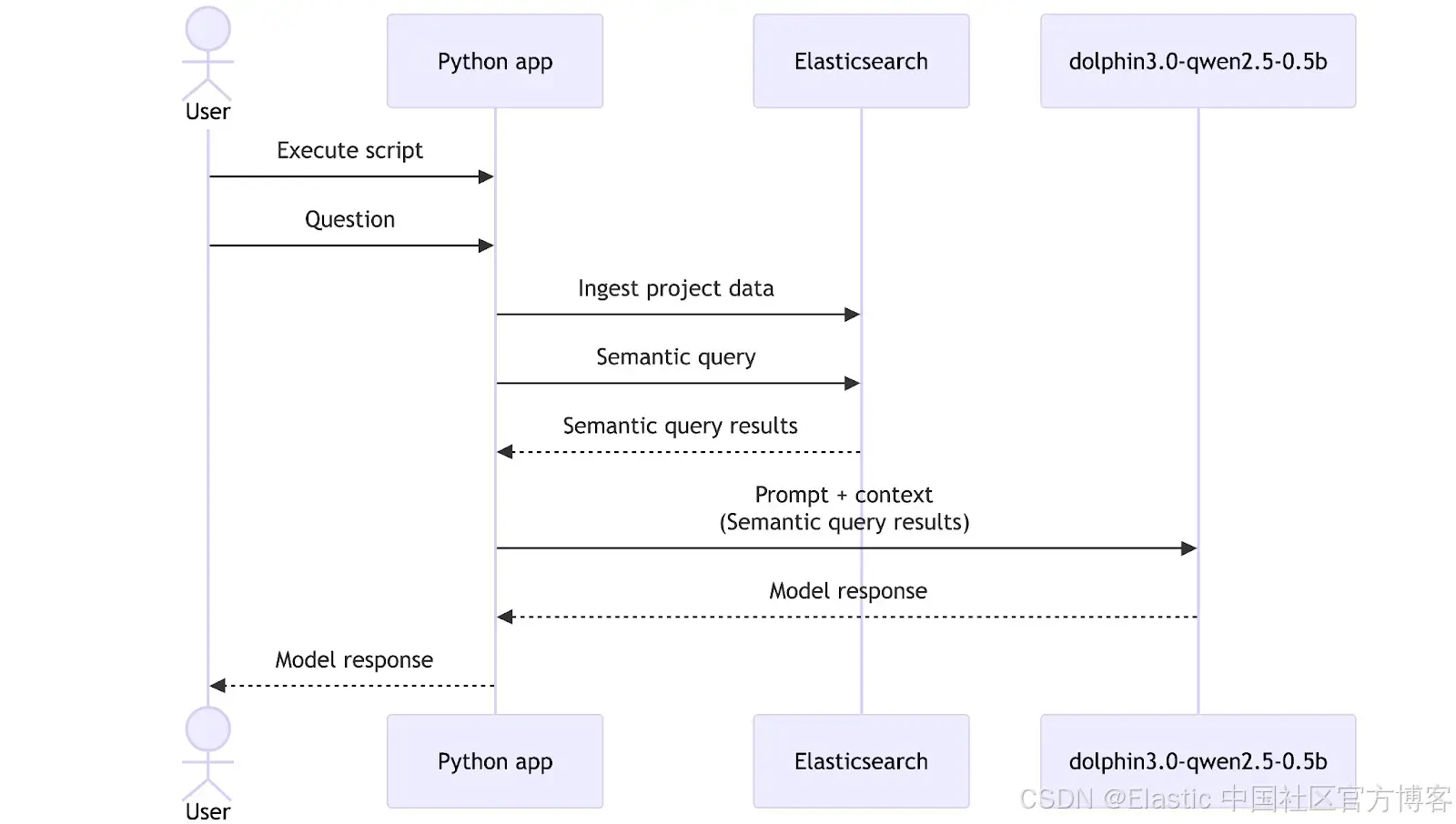
展示工作流程:从项目数据到答案
现在我们有了一个 embeddings 模型和一个通用 LLM 模型,是时候将它们与 Elasticsearch 结合起来,构建一个可以帮助我们探索数据的工具。在本次演练中,我们准备了一个包含相关数据的文件夹,用于我们的模拟 CRM 迁移项目,包括报告和会议记录。在实际应用中,这个数据摄取步骤通常会通过部署管道或后台进程自动完成,但这里为了简单起见,我们将手动触发它。
数据概览
整个数据集可在这个 GitHub 仓库中访问。
/CRM migration data
|__
|-- meeting_QA-team_wednesday.txt
|-- meeting_development-team_monday.txt
|-- meeting_management-sync_friday.txt
|-- report_QA-team.txt
为了展示效果,让我们测试几个示例:
meeting_development-team_monday.txt:
MEETING TRANSCRIPT - DEVELOPMENT TEAM
Date: Monday, September 16, 2025
Time: 09:00 AM - 10:15 AM
Participants: Alice (Tech Lead), John (Senior Developer), Sarah (Backend Developer), Mike (DevOps Engineer)
[09:02] Alice:Let's review the search API deployed last week. Any issues?
[09:03] Sarah:API works but performance degrades with 1,000+ queries per minute. Response times jump from 200ms to 3 seconds.
...WEEKLY REPORT - DEVELOPMENT TEAM
Week of September 16-20, 2025
Prepared by: Alice Thompson, Tech Lead
=== EXECUTIVE SUMMARY ===
Development team completed critical infrastructure components but identified performance bottlenecks requiring attention before production deployment.
=== KEY ACCOMPLISHMENTS ===
- Database schema and indexes completed for CRM
...Elasticsearch 设置
现在我们需要在 Elasticsearch 中创建一个数据结构和推理端点,以存储和生成数据的 embeddings。
首先,让我们使用 .multilingual-e5-small 模型创建一个推理端点:
def setup_inference_endpoint():
inference_id = "e5-small-model"
try:
es_client.inference.put(
inference_id=inference_id,
task_type="text_embedding",
body={
"service": "elasticsearch",
"service_settings": {
"num_allocations": 1,
"num_threads": 1,
"model_id": ".multilingual-e5-small",
},
},
)
print(f"✅ Inference endpoint '{inference_id}' created successfully")
except Exception as e:
print(f"❌ Error creating inference endpoint: {str(e)}")响应应该是这样的:
{"inference_id":"e5-small-model","task_type":"text_embedding","service":"elasticsearch","service_settings":{"num_allocations":1,"num_threads":1,"model_id":".multilingual-e5-small"},"chunking_settings":{"strategy":"sentence","max_chunk_size":250,"sentence_overlap":1}}这将在摄取和查询时自动下载模型并为我们的 embeddings 创建推理端点。如果你需要在隔离环境中安装 embeddings 模型,可以按照这些说明操作。
现在,让我们为数据创建 mappings。我们将创建 3 个字段:file_title 用于存储文件名,file_content 用于存储每个文档的内容,semantic 用于存储两个字段(file_title 和 file_content)的 embeddings 和纯文本内容:
def setup_index():
try:
if es_client.indices.exists(index=INDEX_NAME):
print(f"✅ Index '{INDEX_NAME}' already exists")
return False
print(f"Creating index '{INDEX_NAME}'...")
es_client.indices.create(
index=INDEX_NAME,
body={
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"file_title": {"type": "text", "copy_to": "semantic_field"},
"file_content": {"type": "text", "copy_to": "semantic_field"},
"semantic_field": {
"type": "semantic_text",
"inference_id": "e5-small-model",
},
}
}
},
)
print(f"Index '{INDEX_NAME}' created successfully")
return True
except Exception as e:
print(f"Error creating index: {str(e)}")
exit(1)Elasticsearch 响应:
{"acknowledged":true,"shards_acknowledged":true,"index":"team-data"}通过这种设置,CRM 迁移项目中的每个文件都会被索引,并且可以被搜索。
Python 脚本
为了将 Elasticsearch、数据和 LLM 集中管理,我们将创建一个简单的 Python 脚本,用于摄取数据、向 Elasticsearch 发起搜索请求,并向 LLM 发送提示。这个方法允许我们自定义工作流程、修改提示和模型,并实现流程自动化。
让我们创建一个 venv 环境来处理执行脚本所需的依赖:
python -m venv venv && source venv/bin/activate现在我们需要安装 elasticsearch 依赖,以便与本地运行的 Elasticsearch 实例进行交互,同时使用 requests 处理 HTTP 请求:
pip install elasticsearch requests openai安装完成后,创建一个名为 script.py 的 Python 文件,开始编写脚本:
import os
import time
from elasticsearch import Elasticsearch, helpers
from openai import OpenAI
ES_URL = "http://localhost:9200"
ES_API_KEY = "NDdDQWM1b0JPSDBFTV9JQzA0WVo6eHFXcWFJQmFYNzBwS1RjUllpRUNHZw=="
INDEX_NAME = "team-data"
LOCAL_AI_URL = "http://localhost:8080/v1"
DATASET_FOLDER = "./Dataset"
es_client = Elasticsearch(ES_URL, api_key=ES_API_KEY)
ai_client = OpenAI(base_url=LOCAL_AI_URL, api_key="sk-x") # The API key needs to have a value to work 在上面的代码中,我们导入了必要的包,设置了一些相关变量,并实例化了 Elasticsearch Python 客户端和 OpenAI 客户端来处理 AI 请求。无需真实的 OpenAI API key,就可以运行;你可以随意填入任何值。
使用 bulk API,我们创建了两个方法,将数据直接从文件夹摄取到 Elasticsearch:index_documents 和 load_documents。要执行语义查询,我们将使用 semantic_search 方法:
def load_documents(dataset_folder, index_name):
for filename in os.listdir(dataset_folder):
if filename.endswith(".txt"):
filepath = os.path.join(dataset_folder, filename)
with open(filepath, "r", encoding="utf-8") as file: # UTF-8 encoding ensures proper handling of special characters and international text
content = file.read()
yield {
"_index": index_name,
"_source": {"file_title": filename, "file_content": content},
}
def index_documents():
try:
if es_client.indices.exists(index=INDEX_NAME) is False:
print(f"❌ Error: Index '{INDEX_NAME}' does not exist. ")
exit(1)
success, _ = helpers.bulk(es_client, load_documents(DATASET_FOLDER, INDEX_NAME))
print(f"✅ Indexed {success} documents successfully")
return success
except Exception as e:
print(f"❌ Error indexing documents: {str(e)}")
exit(1)
def semantic_search(query, size=3):
start_time = time.time()
search_body = {
"query": {"semantic": {"field": "semantic_field", "query": query}},
"size": size,
}
response = es_client.search(index=INDEX_NAME, body=search_body)
search_latency = (time.time() - start_time) * 1000 # ms
return response["hits"]["hits"], search_latencyquery_local_ai 函数负责处理对 LocalAI 模型的请求。
def query_local_ai(prompt, model):
start_time = time.time()
try:
response = ai_client.chat.completions.create(
model=model,
messages=[{"role": "user", "content": prompt}],
)
ai_latency = (time.time() - start_time) * 1000 # ms
# Extract response text
response_text = response.choices[0].message.content
# Calculate tokens per second if usage info is available
tokens_per_second = 0
if hasattr(response, "usage") and response.usage:
total_tokens = response.usage.completion_tokens
if ai_latency > 0:
tokens_per_second = (total_tokens / ai_latency) * 1000 # tokens/second
return response_text, ai_latency, tokens_per_second
except Exception as e:
ai_latency = (time.time() - start_time) * 1000
return f"Error: {str(e)}", ai_latency, 0我们将把从 Elasticsearch 检索到的数据和提示一起传递给 query_local_ai 函数:
if __name__ == "__main__":
print("🚀 Setting up infrastructure...")
# Setup inference endpoint and index
setup_inference_endpoint()
is_created = setup_index()
if is_created: # Index was just created, need to index documents
print("\n📥 Indexing documents...")
success = index_documents()
if success == 0: # if indexing failed, exit
print("❌ Documents indexing failed. Exiting.")
exit(1)
time.sleep(1) # Wait for indexing to complete
query = "Can you summarize the performance issues in the API?"
print(f"🔍 Search: '{query}'")
search_results, search_latency = semantic_search(query)
context = ""
citations = []
for idx, hit in enumerate(search_results, 1):
source = hit["_source"]
context += f"[{idx}] File: {source['file_title']}\n"
context += f"Content: {source['file_content']}\n\n"
citations.append(f"[{idx}] {source['file_title']}")
prompt = f"""Based on the following documents, answer the user's question.
You MUST cite your sources using the format [1], [2], etc. when referencing information from the documents.
Documents:
{context}
User Question: {query}
"""
ai_model = "dolphin3.0-qwen2.5-0.5b"
print(f"🤖 Asking to model: {ai_model}")
response, ai_latency, tokens_per_second = query_local_ai(prompt, ai_model)
print(f"\n💡 Question: {query}\n📝 Answer: {response}")
for citation in citations:
print(f" {citation}")
print(f"\n🔍 Search Latency: {search_latency:.0f}ms")
print(f"🤖 AI Latency: {ai_latency:.0f}ms | {tokens_per_second:.1f} tokens/s")最后,我们可以看到完整的脚本工作流程:首先,使用 index_documents 摄取文档;然后,使用 semantic_search 检索 Elasticsearch 数据;接着,将这些结果发送给 dolphin3.0-qwen2.5-0.5b 模型,通过调用 query_local_ai 函数生成符合我们要求的 LLM 响应(包括引用生成)。脚本末尾会测量并打印延迟和每秒处理的 token 数。在此工作流程中,查询 “Can you summarize the performance issues in the API?” 作为用户的自然语言请求,引导搜索和最终的 LLM 响应。
运行以下命令以执行脚本:
python script.py响应:
📝 Answer:
The performance issues in the API can be summarized as follows:
1. **Search API degrades with 1,000+ queries per minute**: The search API has degraded, with performance degrades to a time of 3 seconds compared to the target of 200ms.
2. **Complex queries are slow and no caching layer**: Complex queries take longer to execute as expected.
3. **CPU limits during spikes**: The CPU usage is at 100% at the peak hour and limits to 70% at the peak hour.
📚 Citations:
[1] report_development-team.txt
[2] meeting_development-team_monday.txt
[3] meeting_management-sync_friday.txt在这里查看完整答案。
模型的回答令人满意:它以简明的方式突出关键性能问题,并正确指出潜在原因,为进一步诊断提供了坚实的基础。
延迟
如上面应用结果所示,我们的延迟如下:
📥 Indexing documents...
🔍 Search: 'Can you summarize the performance issues in the API?'
🤖 Asking to model...
...
🔍 Search Latency: 14ms
🤖 AI Latency: 16044ms | 9.5 tokens/s将所有时间加总后,我们可以看到整个流程获取响应共耗时 17 秒,生成速度为每秒 9.5 个 token。
硬件使用情况
最后一步是分析整个环境的资源消耗。我们根据下图所示的 Docker 环境配置进行描述:
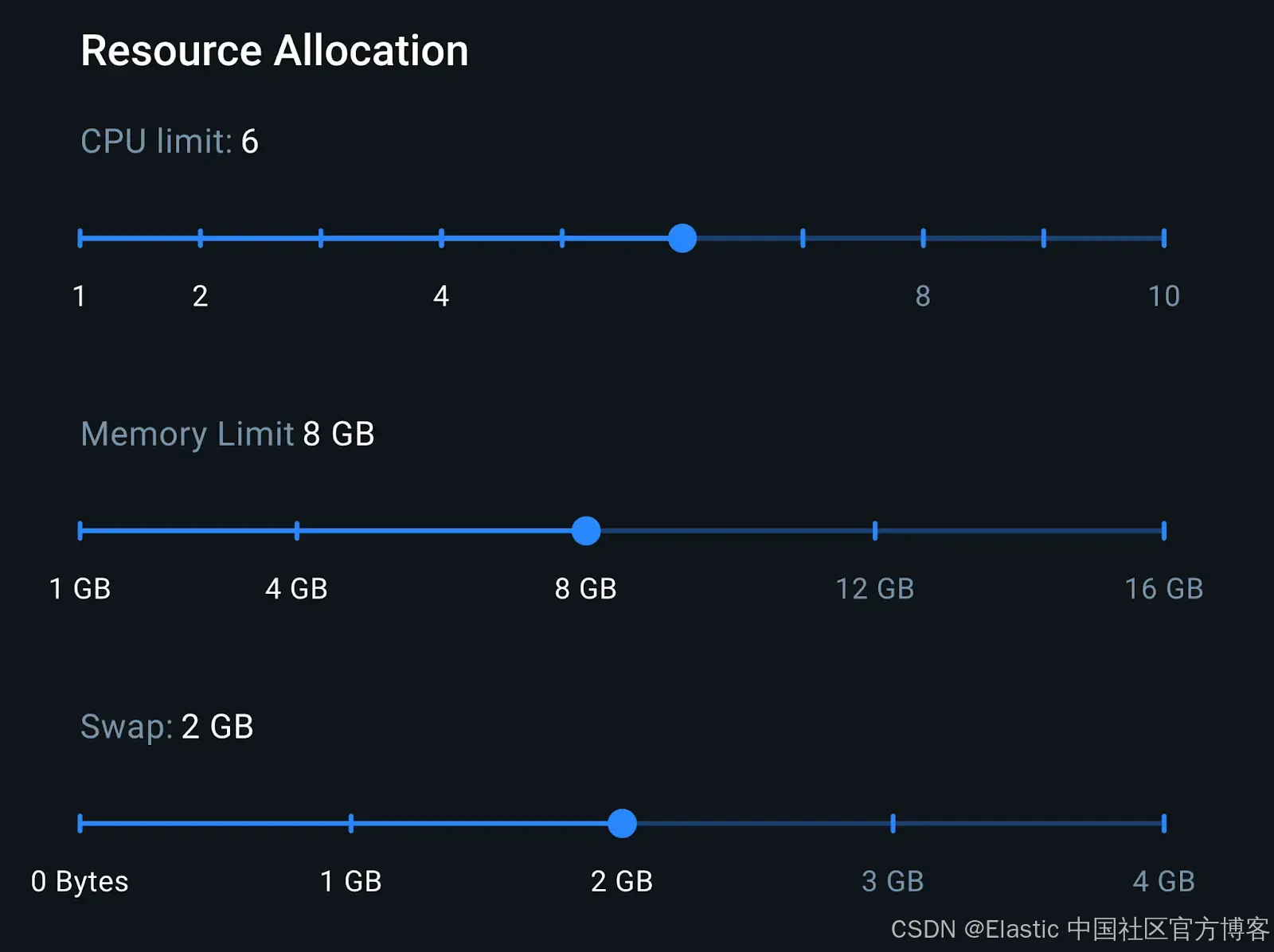
在 8GB 内存下,我们有足够的内存来运行 LocalAI 容器和 Elasticsearch 容器。这个配置代表了一台中端笔记本的设置,有助于我们更好地估算实际推理性能。
资源消耗
使用 Docker Live Charts 扩展,我们可以看到两个容器在生成响应时的资源消耗:
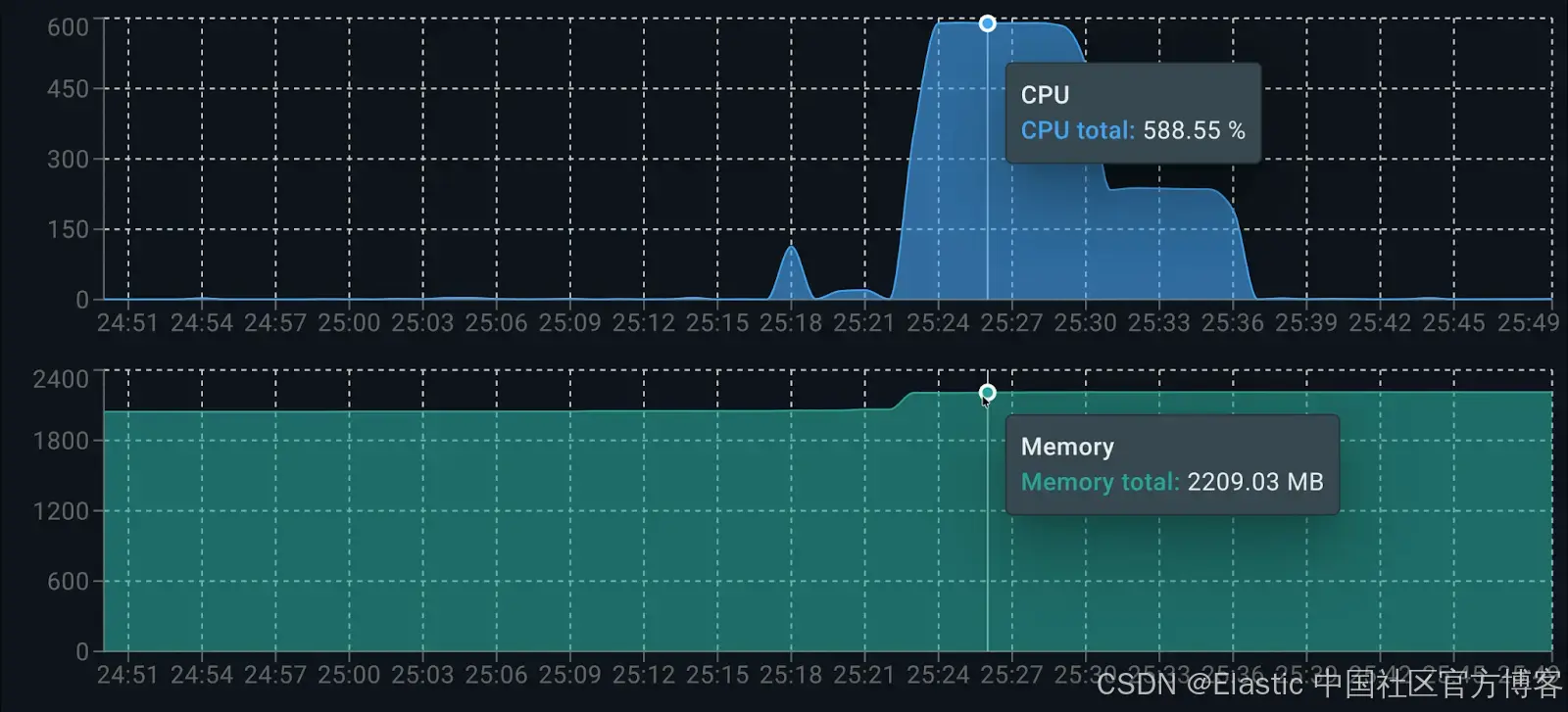
各容器的资源消耗如下:
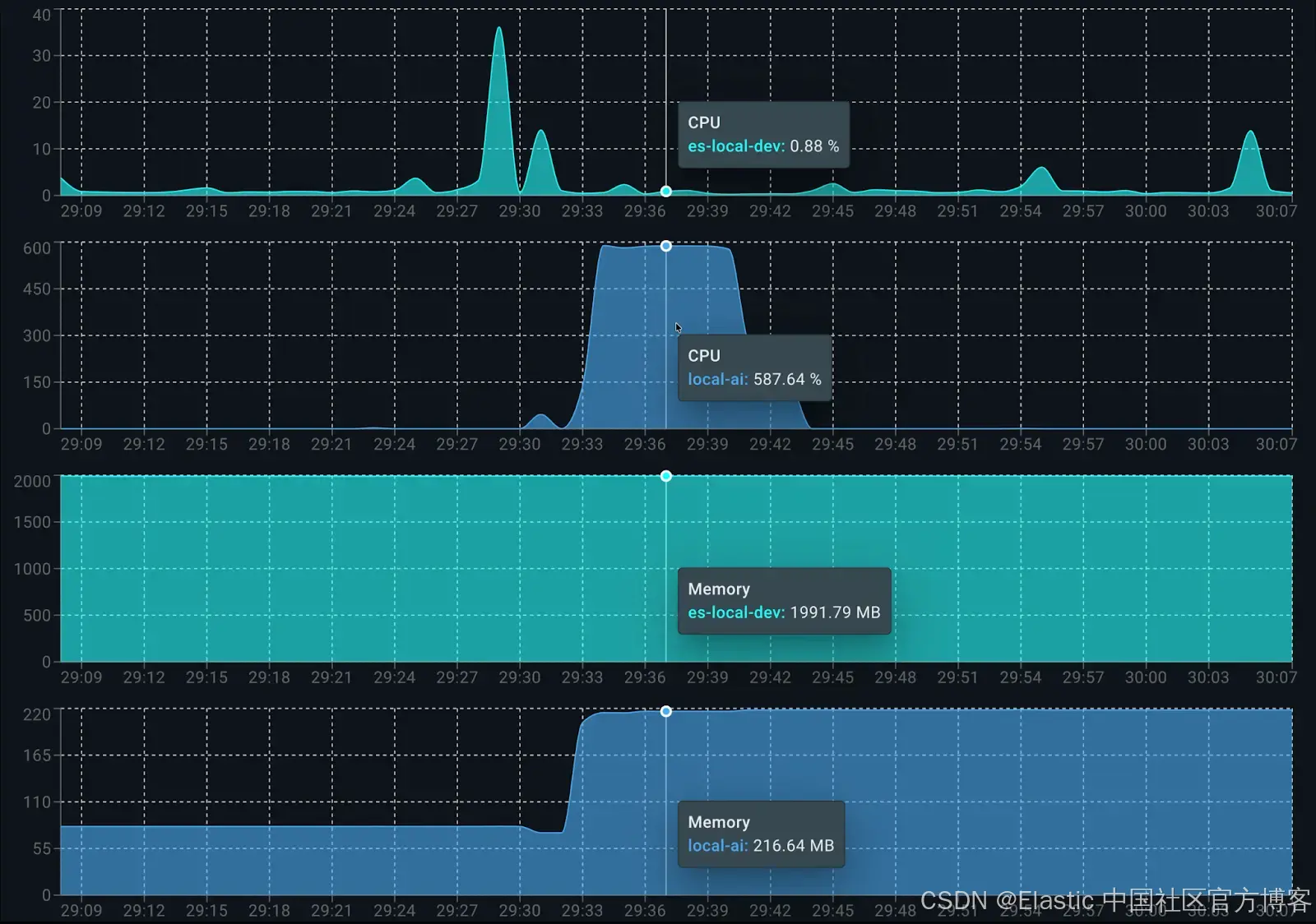
在运行时,Elasticsearch 用于数据索引约占 0.5 个核心。LocalAI 方面,dolphin3.0-qwen2.5-0.5b 在生成答案时占用 6 个可用核心的 100%。在内存消耗方面,总共约使用 2.2GB:Elasticsearch 占 1.9GB,LocalAI(客户端和模型)占 200MB。
资源需求更高的替代模型:smollm2-1.7b-instruct
为了展示这种方法的灵活性,我们可以通过在代码中将变量 ai_model 切换为 ai_model = "smollm2-1.7b-instruct" 来更换模型。由于该模型参数量更大,需要显著更多内存,这会影响每秒 token 生成率,并在生成响应时增加整体延迟。
🤖 Asking to model: smollm2-1.7b-instruct
💡 Question: Can you summarize the performance issues in the API?
📝 Answer: The development team identified two key technical challenges for the API:
1. The search API degrades at 1,000+ queries per minute, causing average execution times to jump from 200ms to 3 seconds.
2. The root cause is complex database queries without a caching layer, leading to poor query performance.
📚 Citations:
[1] report_development-team.txt
[2] meeting_development-team_monday.txt
[3] meeting_management-sync_friday.txt
🔍 Search Latency: 16ms
🤖 AI Latency: 47561ms | 4.8 tokens/s正如预期,由于模型较大,smollm2-1.7b-instruct 对同一个问题的每秒 token 生成量较少(4.8),并且生成时间显著增加(大约多 30 秒)。
响应效果良好且详细,与 dolphin3.0-qwen2.5-0.5b 模型生成的答案类似,但生成时间更长,资源消耗更多,该模型大约使用 1 GB 内存。
资源与性能折中模型:llama-smoltalk-3.2-1b-instruct
现在我们通过将 ai_model 更改为 llama-smoltalk-3.2-1b-instruct 再次尝试。
🤖 Asking to model: llama-smoltalk-3.2-1b-instruct
💡 Question: Can you summarize the performance issues in the API?
📝 Answer: Based on the documents, it appears that the main performance issue with the API is related to the search query optimization. The API degrades to around 1,000+ queries per minute (QP/min) when there are 12 of 18 API endpoints integrated with authentication. This issue is caused by complex queries without a caching layer, leading to performance degrades and slow response times.
However, there is also a smaller issue with the "Search" API, where it degrades to around 3+ seconds after 1.2 seconds execution time. This is likely due to multi-filter searches and the need for a caching layer to improve performance.
To address these issues, the team is working on implementing a caching layer (Sarah) and optimizing bool queries and adding calculated index fields (John) to improve query efficiency. They are also working on setting up auto-scaling for the database (Mike) to ensure that it can handle increased traffic.
A meeting was held to discuss these issues and a plan for improvement was agreed upon. The team will work together to implement a caching layer and optimize the queries, and the team will work with product team to ensure that the migration is completed on time and does not impact the October migration date.
📚 Citations:
[1] report_development-team.txt
[2] meeting_development-team_monday.txt
[3] meeting_management-sync_friday.txt
🔍 Search Latency: 12ms
🤖 AI Latency: 21019ms | 5.8 tokens/s分析结果可知,llama-smoltalk-3.2-1b-instruct 的响应与其他模型相似,在格式和长度上略有差异。然而,与较轻的模型相比,其代价更高(大约慢 5 秒,每秒少 4 个 token)。它的内存消耗也比 dolphin3.0-qwen2.5-0.5b 高(总共约多 500 MB)。这使它在精确摘要任务上可靠,但在快速或交互式场景中效率较低。
表格比较
为了更清楚地了解模型的资源消耗,我们列出一张比较结果的表格:
| Model | Memory Usage | Latency | Tokens/s |
|---|---|---|---|
| dolphin3.0-qwen2.5-0.5b | ~200 MB | 16,044 ms | 9.5 tokens/s |
| smollm2-1.7b-instruct | ~1 GB | 47,561 ms | 4.8 tokens/s |
| llama-smoltalk-3.2-1b-instruct | ~700 MB | 21,019 ms | 5.8 tokens/s |
结论
结合 e5-small 用于 embeddings 和 dolphin3.0-qwen2.5-0.5b 用于 completions,我们可以在中端笔记本上搭建一个高效且功能完整的 RAG 应用,所有数据都保持私有。正如在延迟部分看到的,使用 dolphin 模型进行的第一次测试中,流程中耗时最长的是 LLM 推理步骤(16 秒),而 Elasticsearch 向量检索非常快(81 毫秒)。
dolphin3.0-qwen2.5-0.5b 是生成答案的最佳 LLM 候选模型。其他模型如 llama-smoltalk-3.2-1b-instruct 确实快速且可靠,但通常是更重的模型。它们需要更多资源,每秒生成的 token 更少,但在响应质量上略有提升。
原文:https://www.elastic.co/search-labs/blog/local-rag-personal-knowlege-assistant-localai-elasticsearch
























 1961
1961

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








