矩阵基础
在大部分情况下只需要知道一维矩阵和二维矩阵就行了,更高维的操作叫张量在Tensor类中。
一维矩阵类:
Eigen::RowVectorXcd
二维矩阵类:
Eigen::MatrixXcd
综合举例:
int main()
{
Eigen::MatrixXd matrix(1, 3);
Eigen::RowVectorXd vector(3);
vector << 2, 3, 4;
matrix << 1, 2, 3;
std::cout << "1*3 matrix: " << matrix << std::endl;
std::cout << "1*3 vector: " << vector << std::endl;
return 0;
}
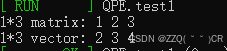
在本质上Eigen::MatrixXd matrix(1, 3);和 Eigen::RowVectorXd vector(3)实际上时一个类型,一模一样。
一维矩阵和二维矩阵之间的转换
reshaped<RowMajor>(); RowMajor是为了以行为主变化,不加默认是以列为主,reshaped参数为空时默认是reshape为以一行或一列。
实例:
#include <iostream>
#include <Eigen/Dense>
#include <time.h>
#include <ccomplex>
int main()
{
Eigen::MatrixXcd matrix(3,3);
matrix << std::complex<double>(0.5, 0.5), std::complex<double>(1,-0.5), 3,
1, 5, 6,
7, 8, 9;
Eigen::RowVectorXd rowVector = imag.reshaped<RowMajor>();
std::cout << "Row vector: " << rowVector << std::endl;
return 0;
}
矩阵赋值
<< 、 =
举例
#include <iostream>
#include <Eigen/Dense>
#include <time.h>
#include <ccomplex>
int main()
{
Eigen::MatrixXcd matrix(3,3);
// 第一种赋值
matrix << std::complex<double>(0.5, 0.5), std::complex<double>(1,-0.5), 3,
1, 5, 6,
7, 8, 9;
// 第二种赋值
for(int i=0;i<9;i++)
{
matrix(i/3,i%3) = i;
}
std::cout << "Row vector: " << rowVector << std::endl;
return 0;
}
二维取值:MatrixXcd(row,col)
一维取值:RowVectorXcd(col)
矩阵操作:
* 矩阵形状变换:
1.resize()
2.conservativeResize();
3.reshape();
* 转置:
transpose();
* 共轭:
conjugate()
* :共轭转置:
adjoint()
* :矩阵的逆:
inverse()
* 拼接矩阵
int main()
{
Eigen::MatrixXd matrix(1, 3);
Eigen::RowVectorXd vector(3);
vector << 4, 5, 6;
matrix << 1, 2, 3;
std::cout << "1*3 matrix: " << matrix << std::endl;
std::cout << "1*3 vector: " << vector << std::endl;
Eigen::MatrixXd matrix2(1, matrix.size() + vector.size());
matrix2 << matrix, vector;
std::cout << "1*6 matrix: " << matrix2 << std::endl;
return true;
}
结果:
* 矩阵求和
全部矩阵的值求和:sum();
每行求和 matrix.rowwise().sum();
每列求和 matrix.colwise().sum();
举例:
int main()
{
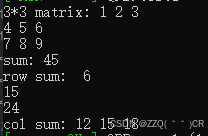
Eigen::MatrixXd matrix(3, 3);
matrix << 1, 2, 3,
4,5,6,
7,8,9;
std::cout << "3*3 matrix: " << matrix << std::endl;
double sum = matrix.sum();
auto a = matrix.rowwise().sum();
auto b = matrix.colwise().sum();
std::cout << "sum: " << sum << std::endl;
std::cout << "row sum: " << a << std::endl;
std::cout << "col sum: " << b << std::endl;
return true;
}
运行结果:
* 矩阵切片
block();
示例:
int main()
{
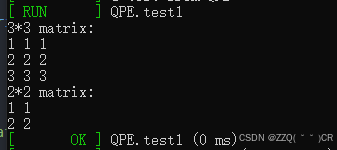
Eigen::MatrixXd matrix(3, 3);
matrix << 1, 1, 1,
2,2,2,
3,3,3;
std::cout << "3*3 matrix:\n" << matrix << std::endl;
matrix = matrix.block(0, 0, 2, 2);
std::cout << "2*2 matrix: \n" << matrix << std::endl;
return true;
}
运行结果:
矩阵算术运算:
乘除法
可以与数字相乘除,与矩阵相乘除。直接使用符号* /
int main()
{
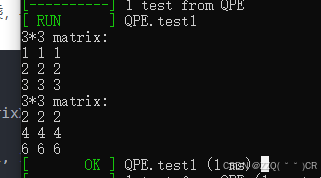
Eigen::MatrixXd matrix(3, 3);
matrix << 1, 1, 1,
2,2,2,
3,3,3;
std::cout << "3*3 matrix:\n" << matrix << std::endl;
matrix = matrix*2;
std::cout << "3*3 matrix: \n" << matrix << std::endl;
return true;
}
运行结果:
加减法
相同行列的矩阵之间可以执行加减法,直接使用符号+ -。
复数矩阵额外的操作:
* 取实部:
MatrixXd = MatrixXcd.real();
MatrixXd imag = matrix.real();//用double矩阵接收返回的矩阵。
* 取虚部:
MatrixXd = MatrixXcd.imag();
MatrixXd imag = matrix.imag();//用double矩阵接收返回的矩阵。
* 复数矩阵初始化:
方式1 使用c++的complex
// 创建一个2x2的复数矩阵
Eigen::MatrixXcd m(2,2);
m << std::complex<double>(1, 2), std::complex<double>(3, 4),
std::complex<double>(5, 6), std::complex<double>(7, 8);
方式2 使用eigen库的i表示复数,如果报错可以自己重写“”实现I。
std::complex<double> operator""I(long double _Val) {
return std::complex<double>(0.0, static_cast<double>(_Val));
}
std::complex<double> operator""I(unsigned long long _Val) {
return std::complex<double>(0.0, static_cast<double>(_Val));
}
Eigen::MatrixXcd matrix(3,3);
matrix << std::complex<double>(0.5, 0.5), std::complex<double>(1,-0.5), 3,
2i, -0.5i, 6,
7, 8, 9;
重载运算符+来方便快捷定义复数:
// 重载 + 运算符,使 int 和 std::complex<double> 可以相加
std::complex<double> operator+(const std::complex<double>& lhs, int rhs) {
return std::complex<double>(lhs.real()+rhs, lhs.imag());
}
std::complex<double> operator+(int rhs, const std::complex<double>& lhs) {
return std::complex<double>(lhs.real() + rhs, lhs.imag());
}
综合两个重写可以更方便的表示复数,举例:
Eigen::MatrixXcd matrix(3,3);
matrix << std::complex<double>(0.5, 0.5), std::complex<double>(1,-0.5), 3,
1+2I, 5, 6,
7, 8, 9;
RowVectorXcd residuals(matrix.size());
MatrixXd imag = matrix.imag();
std::cout << "imag: " << imag << std::endl;
常见报错:
1.在赋值或者初始化时,矩阵的元素数量和给定的元素数量不一致,或者尺寸不一样。
2. 二维矩阵错误的使用了一维矩阵的操作,例如resize(5)只能被一维矩阵使用,二维矩阵要改为resize(1,5)
结语
有不懂的可以在评论区里问,后续遇到更多操作会继续补充。




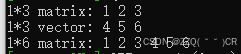
















 1213
1213

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








