Description
A histogram is a polygon composed of a sequence of rectangles aligned at a common base line. The rectangles have equal widths but may have different heights. For example, the figure on the left shows the histogram that consists of rectangles with the heights
2, 1, 4, 5, 1, 3, 3, measured in units where 1 is the width of the rectangles:
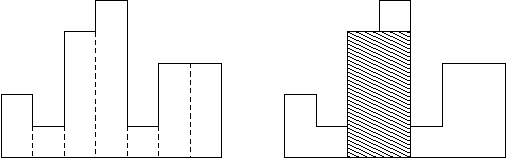
Usually, histograms are used to represent discrete distributions, e.g., the frequencies of characters in texts. Note that the order of the rectangles, i.e., their heights, is important. Calculate the area of the largest rectangle in a histogram that is aligned at the common base line, too. The figure on the right shows the largest aligned rectangle for the depicted histogram.

Usually, histograms are used to represent discrete distributions, e.g., the frequencies of characters in texts. Note that the order of the rectangles, i.e., their heights, is important. Calculate the area of the largest rectangle in a histogram that is aligned at the common base line, too. The figure on the right shows the largest aligned rectangle for the depicted histogram.
题意是求连续的最大矩形的面积
可以假设每一点的高度都是最小的,然后分别向左向右找到最后一个满足使它高度仍然是最小的位置,分别记录下来
每次搜寻都可以利用前面已搜索的结果减少重复搜索
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#define MAX_N 100005
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int n;
while(~scanf("%d",&n)&&n)
{
int a[MAX_N];
int l[MAX_N],r[MAX_N];//每一点对应的左右可到的远的位置
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
scanf("%d",&a[i]);
l[0]=0,l[n+1]=0;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
int k=i-1;
if(a[i]<=a[k])
{
while(k>0&&a[i]<=a[k]) k=l[k]-1; //利用前面已找到的最远位置
}
l[i]=k+1;
}
for(int i=n;i>=1;i--)
{
int k=i+1;
if(a[i]<=a[k])
{
while(k<n+1&&a[i]<=a[k]) k=r[k]+1;
}
r[i]=k-1;
}
long long maxn=-1;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
long long s=(long long)(r[i]-l[i]+1)*a[i];
if(s>maxn) maxn=s;
}
printf("%lld\n",maxn);
}
return 0;
}





 本文介绍了一种高效算法,用于解决寻找直方图中最大矩形面积的问题。该算法通过预处理每个矩形向左右可扩展的最大范围来避免重复计算,从而显著提高效率。
本文介绍了一种高效算法,用于解决寻找直方图中最大矩形面积的问题。该算法通过预处理每个矩形向左右可扩展的最大范围来避免重复计算,从而显著提高效率。
















 4201
4201

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








