-
先用Colab Notebook在线试试吧
下述所有示例都可用Google colab Notebooks执行:
-
基础用法:训练、保存、载入
在下述案例,我们会在Lunar Lander(登月飞行器)环境训练、保存并载入一个DQN模型

LunarLander需要box2d这个Python包。可以先apt install swig再pip install box2d box2d-kengz实现安装
每次调用,
load函数会从头重建模型,这个过程可能较慢。如果你用不同参数数据集评估同一模型,可以考虑用load_parameters来替代。
import gym
from stable_baselines import DQN
# Create environment
env = gym.make('LunarLander-v2')
# Instantiate the agent
model = DQN('MlpPolicy', env, learning_rate=1e-3, prioritized_replay=True, verbose=1)
# Train the agent
model.learn(total_timesteps=int(2e5))
# Save the agent
model.save("dqn_lunar")
del model # delete trained model to demonstrate loading
# Load the trained agent
model = DQN.load("dqn_lunar")
# Enjoy trained agent
obs = env.reset()
for i in range(1000):
action, _states = model.predict(obs)
obs, rewards, dones, info = env.step(action)
env.render()
import gym
import numpy as np
from stable_baselines.common.policies import MlpPolicy
from stable_baselines.common.vec_env import SubprocVecEnv
from stable_baselines.common import set_global_seeds
from stable_baselines import ACKTR
def make_env(env_id, rank, seed=0):
"""
Utility function for multiprocessed env.
:param env_id: (str) the environment ID
:param num_env: (int) the number of environments you wish to have in subprocesses
:param seed: (int) the inital seed for RNG
:param rank: (int) index of the subprocess
"""
def _init():
env = gym.make(env_id)
env.seed(seed + rank)
return env
set_global_seeds(seed)
return _init
env_id = "CartPole-v1"
num_cpu = 4 # Number of processes to use
# Create the vectorized environment
env = SubprocVecEnv([make_env(env_id, i) for i in range(num_cpu)])
model = ACKTR(MlpPolicy, env, verbose=1)
model.learn(total_timesteps=25000)
obs = env.reset()
for _ in range(1000):
action, _states = model.predict(obs)
obs, rewards, dones, info = env.step(action)
env.render()
-
使用Callback:监控训练
你可以定义一个在agent内部调用的回调函数。有助于监控训练,比如在Tensorboard(或Visdom)中呈现实时学习曲线或保存最佳agent。如果你的回调函数返回False,说明训练异常退出。
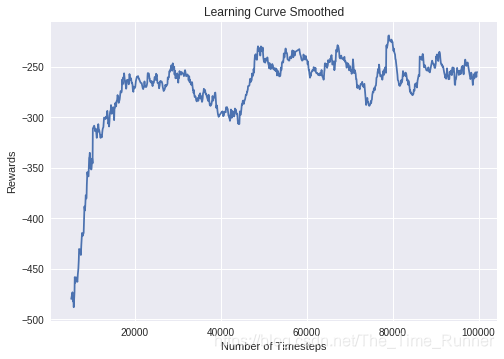
LunarLanderContinuous环境中DDPG的学习曲线
import os
import gym
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from stable_baselines.ddpg.policies import LnMlpPolicy
from stable_baselines.bench import Monitor
from stable_baselines.results_plotter import load_results, ts2xy
from stable_baselines import DDPG
from stable_baselines.ddpg import AdaptiveParamNoiseSpec
best_mean_reward, n_steps = -np.inf, 0
def callback(_locals, _globals):
"""
Callback called at each step (for DQN an others) or after n steps (see ACER or PPO2)
:param _locals: (dict)
:param _globals: (dict)
"""
global n_steps, best_mean_reward
# Print stats every 1000 calls
if (n_steps + 1) % 1000 == 0:
# Evaluate policy training performance
x, y = ts2xy(load_results(log_dir), 'timesteps')
if len(x) > 0:
mean_reward = np.mean(y[-100:])
print(x[-1], 'timesteps')
print("Best mean reward: {:.2f} - Last mean reward per episode: {:.2f}".format(best_mean_reward, mean_reward))
# New best model, you could save the agent here
if mean_reward > best_mean_reward:
best_mean_reward = mean_reward
# Example for saving best model
print("Saving new best model")
_locals['self'].save(log_dir + 'best_model.pkl')
n_steps += 1
return True
# Create log dir
log_dir = "/tmp/gym/"
os.makedirs(log_dir, exist_ok=True)
# Create and wrap the environment
env = gym.make('LunarLanderContinuous-v2')
env = Monitor(env, log_dir, allow_early_resets=True)
# Add some param noise for exploration
param_noise = AdaptiveParamNoiseSpec(initial_stddev=0.1, desired_action_stddev=0.1)
# Because we use parameter noise, we should use a MlpPolicy with layer normalization
model = DDPG(LnMlpPolicy, env, param_noise=param_noise, verbose=0)
# Train the agent
model.learn(total_timesteps=int(1e5), callback=callback)
在Breakout训练好的A2C智体
Pong环境
幸好有make_atari_env帮助函数可以简化Atari游戏RL智体的训练。此函数可为你完成所有预处理和多重处理。
from stable_baselines.common.cmd_util import make_atari_env
from stable_baselines.common.vec_env import VecFrameStack
from stable_baselines import ACER
# There already exists an environment generator
# that will make and wrap atari environments correctly.
# Here we are also multiprocessing training (num_env=4 => 4 processes)
env = make_atari_env('PongNoFrameskip-v4', num_env=4, seed=0)
# Frame-stacking with 4 frames
env = VecFrameStack(env, n_stack=4)
model = ACER('CnnPolicy', env, verbose=1)
model.learn(total_timesteps=25000)
obs = env.reset()
while True:
action, _states = model.predict(obs)
obs, rewards, dones, info = env.step(action)
env.render()
-
Mujoco:标准化输入特征
标准化输入特征对于RL智体的成功训练非常重要(默认情况,图像是缩放的而不是其他输入类型),比如在 Mujoco训练的时候。为此存在一个包装器,用于计算输入特征的运算均值和标准差(对奖励也可如此计算)。
我们无法为此例提供一个notebook,因为Mujoco是一个专有引擎,需要一份许可证
import gym from stable_baselines.common.policies import MlpPolicy from stable_baselines.common.vec_env import DummyVecEnv, VecNormalize from stable_baselines import PPO2 env = DummyVecEnv([lambda: gym.make("Reacher-v2")]) # Automatically normalize the input features env = VecNormalize(env, norm_obs=True, norm_reward=False, clip_obs=10.) model = PPO2(MlpPolicy, env) model.learn(total_timesteps=2000) # Don't forget to save the running average when saving the agent log_dir = "/tmp/" model.save(log_dir + "ppo_reacher") env.save_running_average(log_dir) -
自定义策略网络
Stable baselines为图像(CNN策略)和其他输入类型(Mlp策略)提供默认策略网络。然而,你也可简单地定义一个自定义策略网络架构。(具体见自定义策略部分):
import gym from stable_baselines.common.policies import FeedForwardPolicy from stable_baselines.common.vec_env import DummyVecEnv from stable_baselines import A2C # Custom MLP policy of three layers of size 128 each class CustomPolicy(FeedForwardPolicy): def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs): super(CustomPolicy, self).__init__(*args, **kwargs, net_arch=[dict(pi=[128, 128, 128], vf=[128, 128, 128])], feature_extraction="mlp") model = A2C(CustomPolicy, 'LunarLander-v2', verbose=1) # Train the agent model.learn(total_timesteps=100000) -
获取并调整模型参数
load_parameters和get_parameters函数用字典将变量名映射到Numpy数组,可通过他们获取模型参数。当你评估大量相同网络结构模型、可视化不同网络层、手动调参时,这些函数很有用。
你可以用
get_parameter_list实现访问原始Tensorflow变量。下述案例演示了读取参数、调参、通过实现解决CartPole-v1环境的演化策略来载入他们。通过对模型进行A2C策略梯度更新可获得参数的初始估计。
import gym import numpy as np from stable_baselines.common.policies import MlpPolicy from stable_baselines.common.vec_env import DummyVecEnv from stable_baselines import A2C def mutate(params): """Mutate parameters by adding normal noise to them""" return dict((name, param + np.random.normal(size=param.shape)) for name, param in params.items()) def evaluate(env, model): """Return mean fitness (sum of episodic rewards) for given model""" episode_rewards = [] for _ in range(10): reward_sum = 0 done = False obs = env.reset() while not done: action, _states = model.predict(obs) obs, reward, done, info = env.step(action) reward_sum += reward episode_rewards.append(reward_sum) return np.mean(episode_rewards) # Create env env = gym.make('CartPole-v1') env = DummyVecEnv([lambda: env]) # Create policy with a small network model = A2C(MlpPolicy, env, ent_coef=0.0, learning_rate=0.1, policy_kwargs={'net_arch': [8, ]}) # Use traditional actor-critic policy gradient updates to # find good initial parameters model.learn(total_timesteps=5000) # Get the parameters as the starting point for ES mean_params = model.get_parameters() # Include only variables with "/pi/" (policy) or "/shared" (shared layers) # in their name: Only these ones affect the action. mean_params = dict((key, value) for key, value in mean_params.items() if ("/pi/" in key or "/shared" in key)) for iteration in range(10): # Create population of candidates and evaluate them population = [] for population_i in range(100): candidate = mutate(mean_params) # Load new policy parameters to agent. # Tell function that it should only update parameters # we give it (policy parameters) model.load_parameters(candidate, exact_match=False) fitness = evaluate(env, model) population.append((candidate, fitness)) # Take top 10% and use average over their parameters as next mean parameter top_candidates = sorted(population, key=lambda x: x[1], reverse=True)[:10] mean_params = dict( (name, np.stack([top_candidate[0][name] for top_candidate in top_candidates]).mean(0)) for name in mean_params.keys() ) mean_fitness = sum(top_candidate[1] for top_candidate in top_candidates) / 10.0 print("Iteration {:<3} Mean top fitness: {:.2f}".format(iteration, mean_fitness)) -
迭代策略
这个示例展示如何训练并测试一个递归策略。
迭代策略的一个当前限制是,你必须用与训练时相同数量的环境进行测试。
from stable_baselines import PPO2 # For recurrent policies, with PPO2, the number of environments run in parallel # should be a multiple of nminibatches. model = PPO2('MlpLstmPolicy', 'CartPole-v1', nminibatches=1, verbose=1) model.learn(50000) # Retrieve the env env = model.get_env() obs = env.reset() # Passing state=None to the predict function means # it is the initial state state = None # When using VecEnv, done is a vector done = [False for _ in range(env.num_envs)] for _ in range(1000): # We need to pass the previous state and a mask for recurrent policies # to reset lstm state when a new episode begin action, state = model.predict(obs, state=state, mask=done) obs, reward , done, _ = env.step(action) # Note: with VecEnv, env.reset() is automatically called # Show the env env.render() -
事后经验回放(HER)
在此例,我们用 @eleurent提供的Highway-Env。
parking环境是一个以目标为环境的连续控制任务,车辆必须停在划定范围内。
下述超参数是上述环境下的优化
import gym
import highway_env
import numpy as np
from stable_baselines import HER, SAC, DDPG, TD3
from stable_baselines.ddpg import NormalActionNoise
env = gym.make("parking-v0")
# Create 4 artificial transitions per real transition
n_sampled_goal = 4
# SAC hyperparams:
model = HER('MlpPolicy', env, SAC, n_sampled_goal=n_sampled_goal,
goal_selection_strategy='future',
verbose=1, buffer_size=int(1e6),
learning_rate=1e-3,
gamma=0.95, batch_size=256,
policy_kwargs=dict(layers=[256, 256, 256]))
# DDPG Hyperparams:
# NOTE: it works even without action noise
# n_actions = env.action_space.shape[0]
# noise_std = 0.2
# action_noise = NormalActionNoise(mean=np.zeros(n_actions), sigma=noise_std * np.ones(n_actions))
# model = HER('MlpPolicy', env, DDPG, n_sampled_goal=n_sampled_goal,
# goal_selection_strategy='future',
# verbose=1, buffer_size=int(1e6),
# actor_lr=1e-3, critic_lr=1e-3, action_noise=action_noise,
# gamma=0.95, batch_size=256,
# policy_kwargs=dict(layers=[256, 256, 256]))
model.learn(int(2e5))
model.save('her_sac_highway')
# Load saved model
model = HER.load('her_sac_highway', env=env)
obs = env.reset()
# Evaluate the agent
episode_reward = 0
for _ in range(100):
action, _ = model.predict(obs)
obs, reward, done, info = env.step(action)
env.render()
episode_reward += reward
if done or info.get('is_success', False):
print("Reward:", episode_reward, "Success?", info.get('is_success', False))
episode_reward = 0.0
obs = env.reset()
-
持续学习
你还可以从一个环境的学习转移到另一个以实现连续学习(
PPO2先在DemonAttack-v0学习,然后转到SpaceInvaders-v0):from stable_baselines.common.cmd_util import make_atari_env from stable_baselines import PPO2 # There already exists an environment generator # that will make and wrap atari environments correctly env = make_atari_env('DemonAttackNoFrameskip-v4', num_env=8, seed=0) model = PPO2('CnnPolicy', env, verbose=1) model.learn(total_timesteps=10000) obs = env.reset() for i in range(1000): action, _states = model.predict(obs) obs, rewards, dones, info = env.step(action) env.render() # The number of environments must be identical when changing environments env = make_atari_env('SpaceInvadersNoFrameskip-v4', num_env=8, seed=0) # change env model.set_env(env) model.learn(total_timesteps=10000) obs = env.reset() while True: action, _states = model.predict(obs) obs, rewards, dones, info = env.step(action) env.render() -
记录视频
记录mp4格式视频(此处使用随机智体)。
本例要求安装
ffmpeg或avconvimport gym from stable_baselines.common.vec_env import VecVideoRecorder, DummyVecEnv env_id = 'CartPole-v1' video_folder = 'logs/videos/' video_length = 100 env = DummyVecEnv([lambda: gym.make(env_id)]) obs = env.reset() # Record the video starting at the first step env = VecVideoRecorder(env, video_folder, record_video_trigger=lambda x: x == 0, video_length=video_length, name_prefix="random-agent-{}".format(env_id)) env.reset() for _ in range(video_length + 1): action = [env.action_space.sample()] obs, _, _, _ = env.step(action) env.close() -
好处:制作训练好智体的GIF图片
import imageio import numpy as np from stable_baselines.common.policies import MlpPolicy from stable_baselines import A2C model = A2C(MlpPolicy, "LunarLander-v2").learn(100000) images = [] obs = model.env.reset() img = model.env.render(mode='rgb_array') for i in range(350): images.append(img) action, _ = model.predict(obs) obs, _, _ ,_ = model.env.step(action) img = model.env.render(mode='rgb_array') imageio.mimsave('lander_a2c.gif', [np.array(img[0]) for i, img in enumerate(images) if i%2 == 0], fps=29)





 本文档介绍了Stable Baselines框架的使用,包括在Lunar Lander环境中的DQN模型训练、保存与加载,利用多重处理提升效率,监控训练过程,以及在Atari游戏和Mujoco环境中的应用。同时,还讨论了自定义策略网络、事后经验回放(HER)和连续学习的概念,并提供了相应的Google Colab Notebook示例。
本文档介绍了Stable Baselines框架的使用,包括在Lunar Lander环境中的DQN模型训练、保存与加载,利用多重处理提升效率,监控训练过程,以及在Atari游戏和Mujoco环境中的应用。同时,还讨论了自定义策略网络、事后经验回放(HER)和连续学习的概念,并提供了相应的Google Colab Notebook示例。

















 809
809










