C. Mashmokh and Numbers
time limit per test
1 second
memory limit per test
256 megabytes
input
standard input
output
standard output
It's holiday. Mashmokh and his boss, Bimokh, are playing a game invented by Mashmokh.
In this game Mashmokh writes sequence of n distinct integers on the board. Then Bimokh makes several (possibly zero) moves. On the first move he removes the first and the second integer from from the board, on the second move he removes the first and the second integer of the remaining sequence from the board, and so on. Bimokh stops when the board contains less than two numbers. When Bimokh removes numbers x and y from the board, he gets gcd(x, y) points. At the beginning of the game Bimokh has zero points.
Mashmokh wants to win in the game. For this reason he wants his boss to get exactly k points in total. But the guy doesn't know how choose the initial sequence in the right way.
Please, help him. Find n distinct integers a1, a2, ..., an such that his boss will score exactly k points. Also Mashmokh can't memorize too huge numbers. Therefore each of these integers must be at most 109.
Input
The first line of input contains two space-separated integers n, k (1 ≤ n ≤ 105; 0 ≤ k ≤ 108).
Output
If such sequence doesn't exist output -1 otherwise output n distinct space-separated integers a1, a2, ..., an (1 ≤ ai ≤ 109).
Examples
input
Copy
5 2
output
Copy
1 2 3 4 5
input
Copy
5 3
output
Copy
2 4 3 7 1
input
Copy
7 2
output
Copy
-1
Note
gcd(x, y) is greatest common divisor of x and y.
#include<cstdio>
#include<algorithm>
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
//inline int gcd(int a,int b)
//{
// return b>0 ? gcd(b,a%b):a;
//}
int n,m,k;
inline int gcd(int a,int b)
{
while(b^=a^=b^=a%=b);
return a;
}
//长度为n那么总共可以搜索n/2次
//如果k=n/2,那么输出n个连续的数
//如果k>n/2,先凑两个gcd(a,b)=k-(n-2)/2,接下来输出n-2个连续数
int main(){
cin>>n>>k;
int t=n/2;
if(t>k || (k!=0 && t==0))//组数>k或(k不为0,但是0组)
{
cout<<"-1"<<endl;
}
else if(t==k)
{//组=k那么只能是所有组为连续数
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
cout<<i<<" ";
cout<<endl;
}
else
{
//int c=k-t+1;
int c=k-(n-2)/2;
cout<<c<<" "<<c*2<<" ";
int zu=2;//现在有的个数
for(int i=c*2+1;;i++)
{
if(zu==n)
break;
cout<<i<<" ";
zu++;
}
cout<<endl;
}
return 0;
}
D. Mashmokh and ACM
time limit per test
1 second
memory limit per test
256 megabytes
input
standard input
output
standard output
Mashmokh's boss, Bimokh, didn't like Mashmokh. So he fired him. Mashmokh decided to go to university and participate in ACM instead of finding a new job. He wants to become a member of Bamokh's team. In order to join he was given some programming tasks and one week to solve them. Mashmokh is not a very experienced programmer. Actually he is not a programmer at all. So he wasn't able to solve them. That's why he asked you to help him with these tasks. One of these tasks is the following.
A sequence of l integers b1, b2, ..., bl (1 ≤ b1 ≤ b2 ≤ ... ≤ bl ≤ n) is called good if each number divides (without a remainder) by the next number in the sequence. More formally
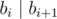
for all i (1 ≤ i ≤ l - 1).
Given n and k find the number of good sequences of length k. As the answer can be rather large print it modulo 1000000007 (109 + 7).
Input
The first line of input contains two space-separated integers n, k (1 ≤ n, k ≤ 2000).
Output
Output a single integer — the number of good sequences of length k modulo 1000000007 (109 + 7).
Examples
input
Copy
3 2
output
Copy
5
input
Copy
6 4
output
Copy
39
input
Copy
2 1
output
Copy
2
Note
In the first sample the good sequences are: [1, 1], [2, 2], [3, 3], [1, 2], [1, 3].
#include<stdio.h>
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#define N 100010
#include<cstring>
#define M 2010
#define mod 1000000007
using namespace std;
int d[M][M];//前i个数、j为结尾
//因为j结尾是j能整除前面那个数推导而来的
int main()
{
int n,m;
cin>>n>>m;
memset(d,0,sizeof d);
d[0][1]=1;
for(int i=0;i<=m;i++)//dp[i]为i个数
{
for(int j=1;j<=n;j++)
{
for(int k=j;k<=n;k+=j)
{
d[i+1][k]=(d[i+1][k]+d[i][j])%mod;
}
}
}
int ans=0;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
ans=(ans+d[m][i])%mod;
cout<<ans<<endl;
return 0;
}





 这篇博客探讨了两个与数学和编程竞赛相关的问题。第一个问题是Mashmokh和Bimokh之间的游戏,目标是找出一组整数序列,使得在特定的游戏规则下,Bimokh能够获得特定分数。第二个问题是关于找到满足特定条件的好序列的数量。博客提供了相应的算法解决方案,并附带了示例输入和输出。
这篇博客探讨了两个与数学和编程竞赛相关的问题。第一个问题是Mashmokh和Bimokh之间的游戏,目标是找出一组整数序列,使得在特定的游戏规则下,Bimokh能够获得特定分数。第二个问题是关于找到满足特定条件的好序列的数量。博客提供了相应的算法解决方案,并附带了示例输入和输出。
















 1355
1355

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








