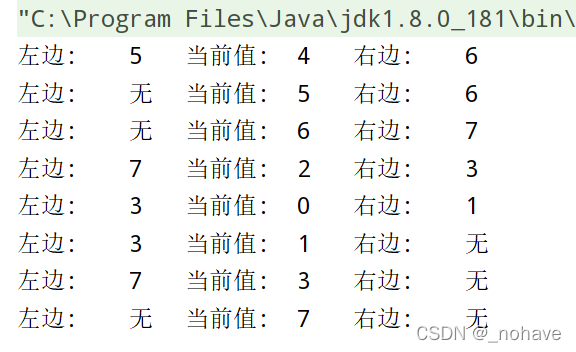
- 数据: {5 4 6 7 2 3 0 1}
- 如4左边最大值5右边最大值是6
- 描述:
- 找出数组中任意位置上,左右两边比它大的数字,左右没有输出 " 无 ", 否则就打印.操作时利用栈结构实现,索引从0开始,如果栈为空直接push,不为空比对栈顶数据和要push的值,如果栈顶的小于要压入的数据,那么就弹出,一直弹出到遇到比它大的栈顶元素停止,接着push就行.需要注意的是,在push过程中由于要将遇到的小的栈内元素弹出,弹出时是需要打印信息的,因为弹出行为就是找到两边大元素的时机.
- 原则: 弹出时,将要压入栈的大的数据就是此时弹出元素的右边最大值,弹出之前压在其下的值就是它左边比它大的值,如果它已经是栈底就代表左边没有比它大的元素. (push时如果栈顶元素比它大直接push,否则就弹栈,如上所述).
- 当数组遍历完毕,压栈操作与部分弹栈操作已经进行,但是栈里面还有数据,此时栈内的元素小的依旧压在大的数据之上,现在的栈顶元素,就是最后入栈的数据,所以它没有右边最大值,而它的左边最大值就是它下面的元素.如果下面没有说明它也没有左边最大值.
public class MonotonyStack {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//数组不存在重复值
int[] arr = {5, 4, 6, 7, 2, 3, 0, 1};
maxOfTwoSide(arr,0);
}
//打印所有位置左右比它大的数据
public static void maxOfTwoSide(int[] arr,int next){
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>();
while(next < arr.length){
if(stack.isEmpty()){
stack.push(next);
}else{
while (!stack.isEmpty()){
if(arr[stack.peek()] < arr[next]){
int cur = stack.pop();
int pre = -1;
if(!stack.isEmpty()){
pre = stack.peek();
}
if(pre == -1){
System.out.println("左边:\t无" + "\t当前值:\t" + arr[cur] + "\t右边:\t" + arr[next]);
}else{
System.out.println("左边:\t" + arr[pre] + "\t当前值:\t" + arr[cur] + "\t右边:\t" + arr[next]);
}
}else{
stack.push(next);
break;
}
}
if(stack.isEmpty()){
stack.push(next);
}
}
next ++;
}
while (!stack.isEmpty()){
if(stack.size() > 1){
int cur = stack.pop();
System.out.println("左边:\t" + arr[stack.peek()] + "\t当前值:\t" + arr[cur] + "\t右边:\t无");
}else{
int cur = stack.pop();
System.out.println("左边:\t无" + "\t当前值:\t" + arr[cur] + "\t右边:\t无");
}
}
}
}
以数组 {5 4 6 7 2 3 0 1} 为例,测试结果如下: 左边 右边 分别代表 "左/右边最大值"
左神算法学习




 该博客介绍了如何利用单调栈解决数组中每个元素左右最大值的问题。通过比较栈顶元素和即将压入的值,确定何时弹出栈顶元素并打印相关信息。遍历数组后,栈内元素的处理方式也得到了详细阐述。
该博客介绍了如何利用单调栈解决数组中每个元素左右最大值的问题。通过比较栈顶元素和即将压入的值,确定何时弹出栈顶元素并打印相关信息。遍历数组后,栈内元素的处理方式也得到了详细阐述。
















 7万+
7万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








