
论文代码:https://github.com/iMoonLab/HGST
英文是纯手打的!论文原文的summarizing and paraphrasing。可能会出现难以避免的拼写错误和语法错误,若有发现欢迎评论指正!文章偏向于笔记,谨慎食用
目录
2.3.1. Self-supervised learning
2.3.3. Hypergraph neural networks
2.4.2. High-order semantic-aware SSL
2.4.3. High-order topology-aware SSL
2.4.4. Brain disease diagnosis
2.5.1. Datasets and preprocessing
2.5.4. Experimental results on ADHD and MDD datasets
1. 心得
(1)thu/imoon真的猛猛发超图啊,让我膜拜一下新进展
(2)2026!(误)的REST-meta-MDD和ADHD-200数据集上还是性能不咋样!(好心审稿人能不能补药再diss我70+ACC差了啊
(3)后知后觉,我以前一直以为我不喜欢写项目书orPPT,但其实我私底下很喜欢做笔记和画图...实际上是不喜欢老师一张图改一个月吧(并不是因为画的不好,而是计划有变之类的
2. 论文逐段精读
2.1. Abstract
①Limitations: exisitng models can not capture the high order topological/semantic feature
②So they proposed HyperGraph-based Semantic and Topological self-supervised learning (HGST) method to capture complex interactions
2.2. Introduction
①没说什么特别的,就是很正常的intro
2.3. Related works
2.3.1. Self-supervised learning
①Though SSL brings stronger performance on scarse data, current works only focus on
2.3.2. Graph neural network
①Existing GNNs relys on simple graph structure
2.3.3. Hypergraph neural networks
①Most of HGNNs are verified on single dataset
2.4. Methods
2.4.1. The framework of HGST
①The schematic of HGST:
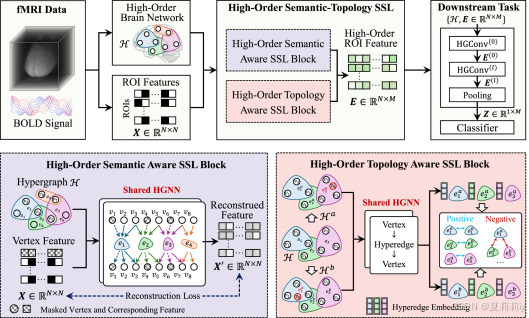
2.4.2. High-order semantic-aware SSL
①The hyperedge set is constructed by Lasso
(1)Node feature masking and encoding
①Hyper graph is represented by , where
denotes brain region set and
is hyper edge set.
②The subset is marked by
, so the node feature matrix can be noted by:
where
③The hypergraph encoder processes node feature matrix and hyperedge index to high order semantic embedding :
(2)Semantic reconstruction decoding
①To avoid over smooth, they define token for node subset
:
where
②The embedding needs decoding:
(3)Loss function design
①Reonstruction loss:
2.4.3. High-order topology-aware SSL
(1)Topology augmentation and encoding
①“具体来说,对于每个超边,其中的每个节点都会被随机保留或丢弃,概率为,从而产生新的超边子集。随后,计算此子集与原始超边之间的差集,以形成增强的超边。为避免产生重复的超边(即具有相同节点组合的冗余超边),我们向这些冗余超边随机添加顶点以确保它们的唯一性。”
②They generate 2 enhanced hypergraph and
with the same number of hyperedge
(2)Structural distance measurement
①Brain network hypergraph can be represented by , where
and
are probability measures,
is relationship between brain regions and functional connections
②Regularize the distribution of hypergraph:
③The structural distance between corresponding hyperedges:
where is a coupling function between the node distributions
(3)Topology-aware contrastive learning
①Similarity weight of hyperedges:
where denotes hyperparameters
②Contrastive loss of edge pairs:
where denotes the temperature parameter controlling the sparsity of the contrastive learning distribution
2.4.4. Brain disease diagnosis
①Total loss:
②Readout and classification:
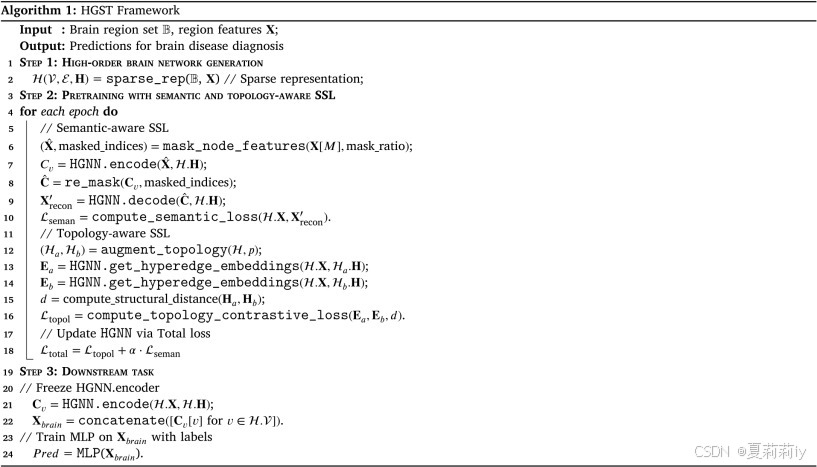
③Algorithm of HGST:
2.5. Experiments
2.5.1. Datasets and preprocessing
①Datasets: ADHD-200 with 362 ADHD and 585 NC and REST-meta-MDD with 1300 MD and 1128 NC
2.5.2. Compared methods
①不赘述
2.5.3. Implement details
①Hidden dim of hypergraph: 512
②Learning rate in pre-training stage: 0.001
③Max epoch number: 150
④Optimizer: Adam
⑤Mask rate: 0.5
⑥Data enhancement parameter: 0.5
⑦The hyperedge construction parameter of sparse representation: 0.2
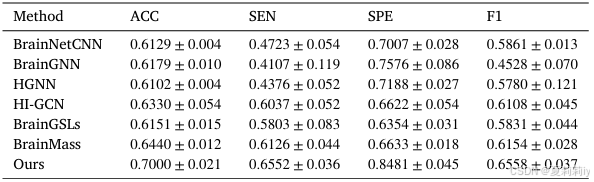
2.5.4. Experimental results on ADHD and MDD datasets
①Performance on ADHD:
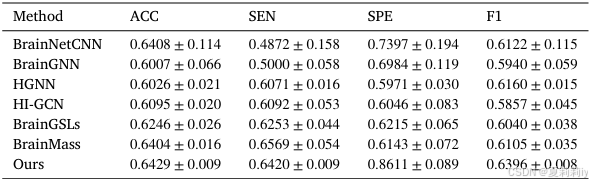
②Performance on MDD:
2.5.5. Ablation study
①Module ablation on ADHD-200:
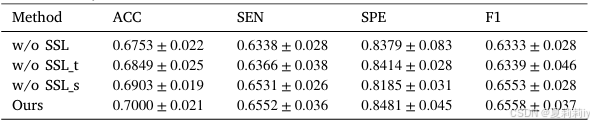
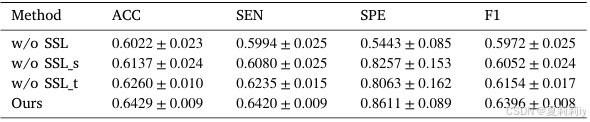
②Module ablation on MDD:
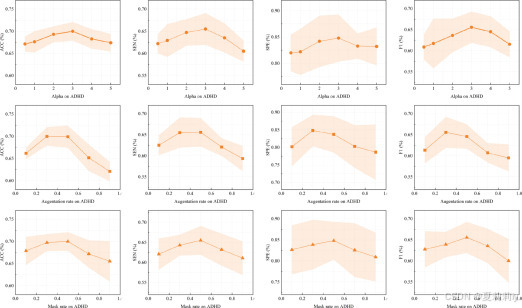
2.5.6. Sensitivity analysis
①Sensitivity of hyper-parameters:
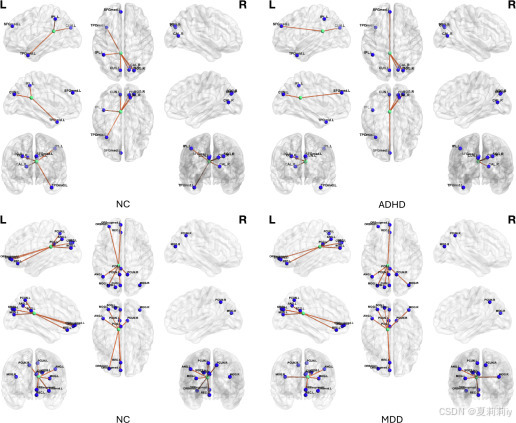
2.5.7. Interpretable study
①Significant connections:
2.6. Conclusion
~

























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








