英文是纯手打的!论文原文的summarizing and paraphrasing。可能会出现难以避免的拼写错误和语法错误,若有发现欢迎评论指正!文章偏向于笔记,谨慎食用
目录
2.3.2. Comparison with existing deep learning based architectures for brain network analysis
2.4.1. Functional connectivity graph creation
2.6.2. Interpretation of brain regions and networks
2.6.3. Experiment with HCP dataset
2.7. Discussion and conclusion
1. 心得
(1)难评,懂得都懂
(2)和我今天喝的茶屿一样。两个一起喷了
2. 论文逐段精读
2.1. Abstract
①They aim to predict intellegence
2.2. Introduction
①Types of intellegence:
| fluid intelligence (FI) | the ability to reason and solve problems in novel situations |
| crystallized intelligence (CI) | the ability to use knowledge and experience to solve problems |
| total intelligence (TI) | a composite measure of overall cognitive ability |
②They proposed Brain ROI-aware Graph Isomorphism Networks (BrainRGIN) for cluster-specific learning
2.3. Theory and related work
2.3.1. Graph neural networks
①For graph with node set
and edge set
, to learn a global graph representation to predict
②Introduced traditional GNNs (not for brains)
2.3.2. Comparison with existing deep learning based architectures for brain network analysis
①Lists relevant GNN research on fMRI
2.4. Proposed architecture
①Overall framework of BrainRGIN:
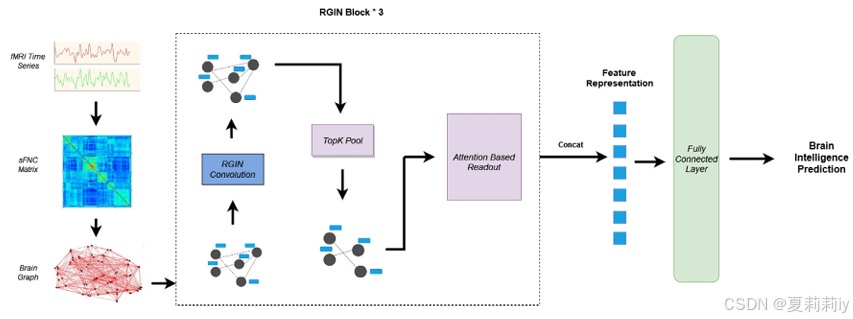
(图画的太简单了,topk不是他提出的,SERO和GARO也不是他提出的)
2.4.1. Functional connectivity graph creation
①"regions selected based on an atlas lead to an FC matrix, while regions generated by independent component analyzes (ICA) lead to an FNC matrix"
②The adjacency matrix is constructed by Pearson correlation:
(1)RGIN convolution
①Message passing in RGIN (combined with RGCN and GIN, the aggregation function of RGCN replaces the function of GIN):
where and
are learnable parameters, and
contains the positional information form
:
where stores the one-hot positional encoding information
但作者觉得
存one hot是稀疏矩阵,其实很占空间,就想优化一下:
其中
,这样直接用可学习参数代替一个矩阵乘上另一个可学习参数。同时把二维的
拆分成集群数个
的基矩阵
。这样可以更新为:
②Forward propagation function of RGIN Convolution:
(2)Pooling layers
①Top k selection:
(3)Readout
①都不是你自己的了干嘛非要又把GARO和SERO详细介绍一遍??没看过的人建议转移去STAGIN原文
(4)Loss functions
①SmoothL1Loss: compared with MSE, SmoothL1Loss is robuster and less sensitive:
②Unit loss for learnable constraining vector:
③Top k loss:
④Total loss:
2.5. Experiments
①Dataset: ABCD
②Data split: 5964 for tr, 1278 for val and 1278 for test
2.5.1. Experimental setup
①Node: 53 by NeuroMark ICA Components
②Node feature: number of pairwise correlations between each other nodes (i.e., 53)
③Pooling rate: 0.38 for FI, 0.46 for CI and 0.78 for TI
④Cluster number: 7 (because of Yeo 7)
⑤Model comparison tool: sergeyplis/polyssifier: run a multitude of classifiers on you data and get an AUC report
2.6. Results
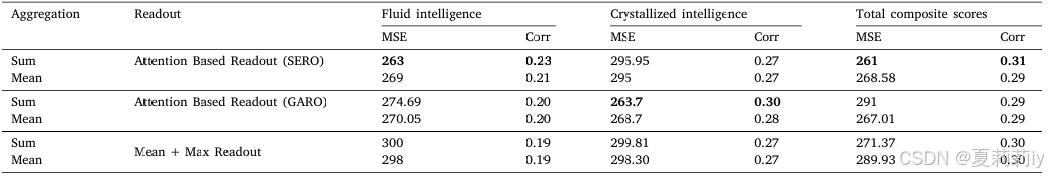
①Readout ablation of BrainRGIN:
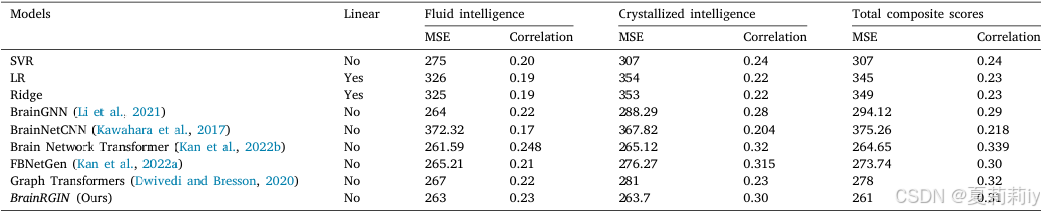
②Comparison table:
2.6.1. Hyperparameter study
①How top k influence performance:
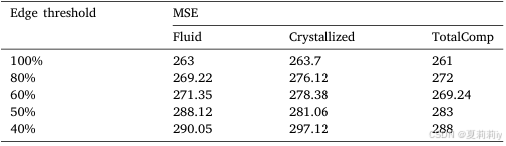
2.6.2. Interpretation of brain regions and networks
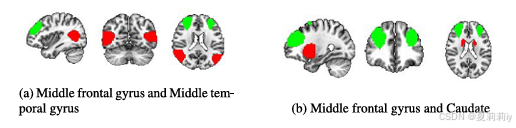
①Top 2 ROI for FI and CI:
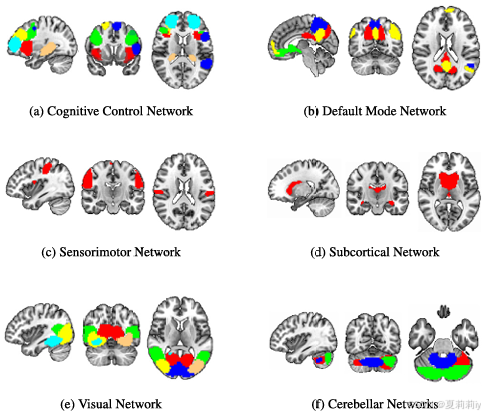
②Top 21 ROI for TI:
2.6.3. Experiment with HCP dataset
(1)HCP dataset
①Dataset: HCP S1200
(2)Hyperparameter settings for HCP
①Using different hyper-parameter in training on HCP dataset
(3)Results from HCP dataset
①Performance:
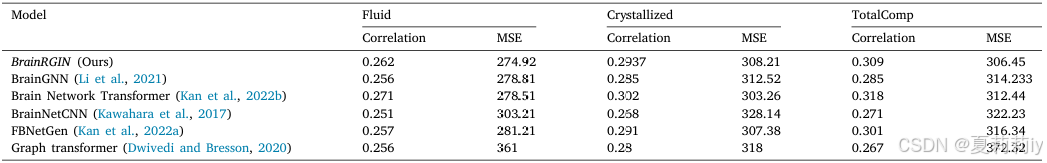
(4)Study of BrainRGIN components
①Module ablation:

2.7. Discussion and conclusion
①还做了t检验,全面啊
②分析了脑区对不同智力的贡献:“对流体智力做出贡献的前两个区域是额中回和颞中回。在结晶智力的背景下,除了额中回外,尾状核起着最显着的贡献。被确定为与总综合分相关的不同大脑区域反映了认知过程的复杂性和分布性,以及 “智力 ”的一般和广泛属性。这些区域覆盖了六个相对独立的大脑网络。”

























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








