论文网址:Toward Generalizing Visual Brain Decoding to Unseen Subjects | OpenReview
论文代码:https://github.com/Xiangtaokong/TGBD}{https://github.com/Xiangtaokong/TGBD
英文是纯手打的!论文原文的summarizing and paraphrasing。可能会出现难以避免的拼写错误和语法错误,若有发现欢迎评论指正!文章偏向于笔记,谨慎食用
目录
2.4.3. Generalization performance vs. subject similarity
2.5.2. Main results on generalization performance
2.5.3. The generalization performance with different backbones
2.5.4. generalization vs. subject similarity
2.5.5. Experimental results on the NSD dataset
2.6. Discussion: the Source of Generalization Ability
1. 心得
(1)样本很多工作量很大
2. 论文逐段精读
2.1. Abstract
①Challenge of fMRI decoding: generalization to unseen subjects
②Solution: extensive training on large dataset(作者还是觉得所有人应该一起训练泛化性才强
2.2. Introduction
①Limitations: subject specific models and scarce training data
②The authors batch process brain activity by uniformly upsampling voxels and CLIP encoding
2.3. Related Work
①Lists a) fMRI decoding models for image reconstruction; b) cross-subject training and fine-tune model; c) feature alignment
2.4. Methods
2.4.1. Dataset consolidation
①Due to limited subject in image-watching tasks, they utilize larger number of subjects in task of watching moive
②Commonly used fMRI decoding datasets:
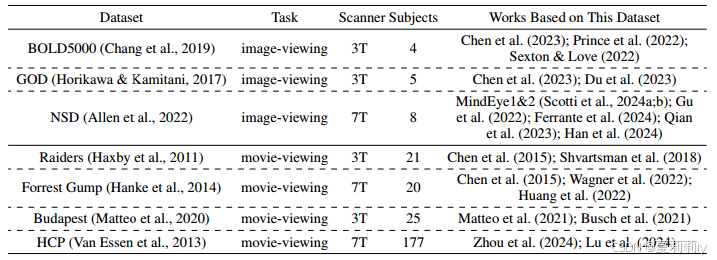
they utilize HCP with 177 subjects and 3127 stimuli frame for each(但作者也说这个是视听的,感觉有弊端?有音频的图像帧和直接看图片的脑信号不一定一样吧,也有在处理语言)
③Activity capturing:

- stimuli selection: the last frame of each second.
- original response voxel:
- response: for 4-second hemodynamic delay
2.4.2. Learning paradigm
①NSD general.nii:
②Pipeline of model:
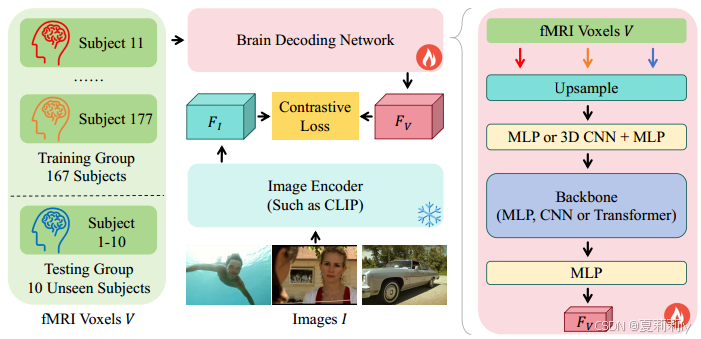
where image encoder is CLIP-ViT-L/14
③Constrastive loss:
where and
are embeddings of the
-th image and fMRI voxel,
denotes temperature parameter,
denotes the cosine similarity between
and
:
④Brain decoding network: MLP
2.4.3. Generalization performance vs. subject similarity
①Calculate the embedding similarity to obtain the top ten given subjects that are most similar to the unseen subject:
2.5. Experiments
2.5.1. Implementation details
①Optimizer: AdamW with β1=0.9,β2=0.999
②Batch size: 300
③Learning strategy: OneCycleLR with max learning rate 1e-4
④Data split: the same 100 frames for test (1-10 subject each) and other ((177-10)*3127-100) for training (all other subject) on HCP.
2.5.2. Main results on generalization performance
①Results on HCP:
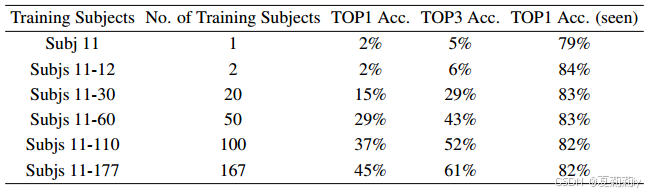
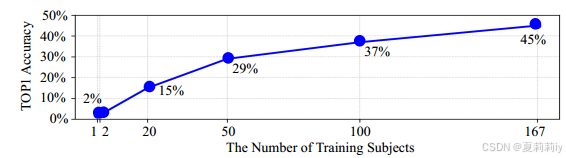
②Accuracy curve with increasing training samples:
2.5.3. The generalization performance with different backbones
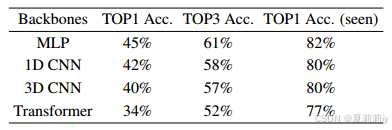
①Backbone ablation:
2.5.4. generalization vs. subject similarity
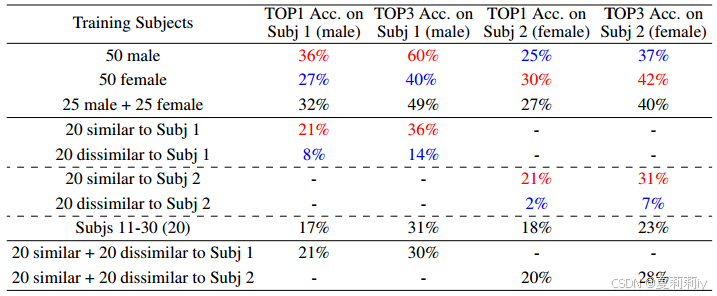
①Due to sex bias, they seperately test subjects with different sex:
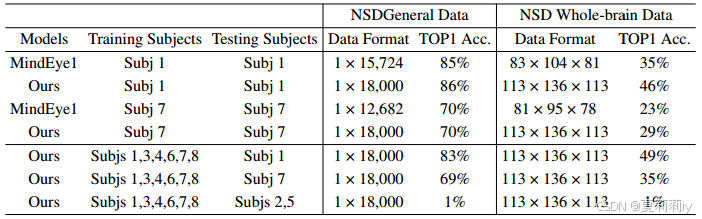
2.5.5. Experimental results on the NSD dataset
①Training on NSD dataset:
2.6. Discussion: the Source of Generalization Ability
论证了很多样本的好处
2.7. Conclusion
~

























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








