学习来源:日撸 Java 三百行(41-50天,查找与排序))_闵帆的博客-优快云博客
41.顺序查找与折半查找
1.顺序查找使用岗哨可以节约一半的时间. 为此, 第 0 个位置不可以放有意义的数据, 即有效数据只有 length - 1 个.
2.顺序查找时间复杂度为 O ( n ) O(n)O(n).
3.折半查找时间复杂度为 O ( log n ) O(\log n)O(logn).
4.书上为简化起见, 只关注键. 这里使用键值对来表示一条完整的数据. 实际应用中可以把 content 改成任何想要的数据类型.
5.102 行是一个空语句. 这里提供了一种更简洁的写法, 可以把 101-103 并作一行 (100行).
6.for 语句这些的花括号, 本意是将一个代码块当一条语句来处理, for 循环里面只有一条语句, 可以将花括号省略掉.
package datastructure.search;
/**
* Data array for searching and sorting algorithms.
*
* @author Rui Chen 1369097405@qq.com.
*/
public class DataArray {
/**
* An inner class for data nodes. The text book usually use an int value to
* represent the data. I would like to use a key-value pair instead.
*/
class DataNode {
/**
* The key.
*/
int key;
/**
* The data content.
*/
String content;
/**
*********************
* The first constructor.
*********************
*/
DataNode(int paraKey, String paraContent) {
key = paraKey;
content = paraContent;
}// Of the second constructor
/**
*********************
* Overrides the method claimed in Object, the superclass of any class.
*********************
*/
public String toString() {
return "(" + key + ", " + content + ") ";
}// Of toString
}// Of class DataNode
/**
* The data array.
*/
DataNode[] data;
/**
* The length of the data array.
*/
int length;
/**
*********************
* The first constructor.
*
* @param paraKeyArray The array of the keys.
* @param paraContentArray The array of contents.
*********************
*/
public DataArray(int[] paraKeyArray, String[] paraContentArray) {
length = paraKeyArray.length;
data = new DataNode[length];
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
data[i] = new DataNode(paraKeyArray[i], paraContentArray[i]);
} // Of for i
}// Of the first constructor
/**
*********************
* Overrides the method claimed in Object, the superclass of any class.
*********************
*/
public String toString() {
String resultString = "I am a data array with " + length + " items.\r\n";
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
resultString += data[i] + " ";
} // Of for i
return resultString;
}// Of toString
/**
*********************
* Sequential search. Attention: It is assume that the index 0 is NOT used.
*
* @param paraKey The given key.
* @return The content of the key.
*********************
*/
public String sequentialSearch(int paraKey) {
data[0].key = paraKey;
int i;
// Note that we do not judge i >= 0 since data[0].key = paraKey.
// In this way the runtime is saved about 1/2.
// This for statement is equivalent to
//for (i = length - 1; data[i].key != paraKey; i--);
for (i = length - 1; data[i].key != paraKey; i--) {
;
}//Of for i
return data[i].content;
}// Of sequentialSearch
/**
*********************
* Test the method.
*********************
*/
public static void sequentialSearchTest() {
int[] tempUnsortedKeys = { -1, 5, 3, 6, 10, 7, 1, 9 };
String[] tempContents = { "null", "if", "then", "else", "switch", "case", "for", "while" };
DataArray tempDataArray = new DataArray(tempUnsortedKeys, tempContents);
System.out.println(tempDataArray);
System.out.println("Search result of 10 is: " + tempDataArray.sequentialSearch(10));
System.out.println("Search result of 5 is: " + tempDataArray.sequentialSearch(5));
System.out.println("Search result of 4 is: " + tempDataArray.sequentialSearch(4));
}// Of sequentialSearchTest
/**
*********************
* Binary search. Attention: It is assume that keys are sorted in ascending
* order.
*
* @param paraKey The given key.
* @return The content of the key.
*********************
*/
public String binarySearch(int paraKey) {
int tempLeft = 0;
int tempRight = length - 1;
int tempMiddle = (tempLeft + tempRight) / 2;
while (tempLeft <= tempRight) {
tempMiddle = (tempLeft + tempRight) / 2;
if (data[tempMiddle].key == paraKey) {
return data[tempMiddle].content;
} else if (data[tempMiddle].key <= paraKey) {
tempLeft = tempMiddle + 1;
} else {
tempRight = tempMiddle - 1;
}
} // Of while
// Not found.
return "null";
}// Of binarySearch
/**
*********************
* Test the method.
*********************
*/
public static void binarySearchTest() {
int[] tempSortedKeys = { 1, 3, 5, 6, 7, 9, 10 };
String[] tempContents = { "if", "then", "else", "switch", "case", "for", "while" };
DataArray tempDataArray = new DataArray(tempSortedKeys, tempContents);
System.out.println(tempDataArray);
System.out.println("Search result of 10 is: " + tempDataArray.binarySearch(10));
System.out.println("Search result of 5 is: " + tempDataArray.binarySearch(5));
System.out.println("Search result of 4 is: " + tempDataArray.binarySearch(4));
}// Of binarySearchTest
/**
*********************
* The entrance of the program.
*
* @param args Not used now.
*********************
*/
public static void main(String args[]) {
System.out.println("\r\n-------sequentialSearchTest-------");
sequentialSearchTest();
System.out.println("\r\n-------binarySearchTest-------");
binarySearchTest();
}// Of main
}// Of class DataArray
运行截图:
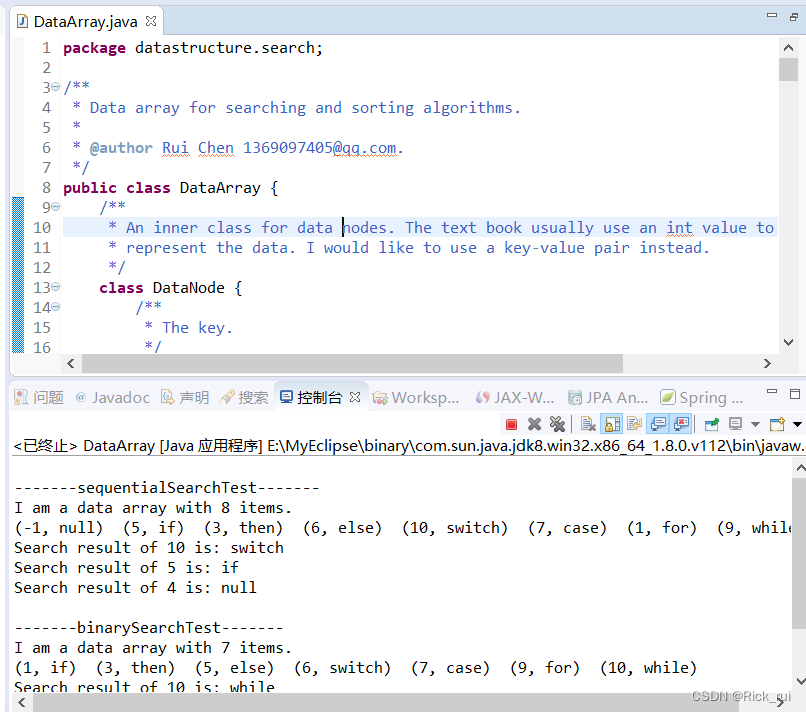
42. 哈希表
1.神奇、实用、粗暴的方法. 空间换时间.
2.保证空间足够.
3.在构造方法中装入数据. 自己可以写代码增加数据.
4.使用 (最简单的) 除数取余法获得数据存放地址 (下标).
5.使用 (最简单的) 顺移位置法解决冲突.
6.搜索的时间复杂度仅与冲突概率相关, 间接地就与装填因子相关. 如果空间很多, 可以看出时间复杂度为 O ( 1 ) O(1)O(1).
public DataArray(int[] paraKeyArray, String[] paraContentArray, int paraLength) {
// Step 1. Initialize.
length = paraLength;
data = new DataNode[length];
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
data[i] = null;
} // Of for i
// Step 2. Fill the data.
int tempPosition;
for (int i = 0; i < paraKeyArray.length; i++) {
// Hash.
tempPosition = paraKeyArray[i] % paraLength;
// Find an empty position
while (data[tempPosition] != null) {
tempPosition = (tempPosition + 1) % paraLength;
System.out.println("Collision, move forward for key " + paraKeyArray[i]);
} // Of while
data[tempPosition] = new DataNode(paraKeyArray[i], paraContentArray[i]);
} // Of for i
}// Of the second constructor
/**
*********************
* Hash search.
*
* @param paraKey The given key.
* @return The content of the key.
*********************
*/
public String hashSearch(int paraKey) {
int tempPosition = paraKey % length;
while (data[tempPosition] != null) {
if (data[tempPosition].key == paraKey) {
return data[tempPosition].content;
} // Of if
System.out.println("Not this one for " + paraKey);
tempPosition = (tempPosition + 1) % length;
} // Of while
return "null";
}// Of hashSearch
/**
*********************
* Test the method.
*********************
*/
public static void hashSearchTest() {
int[] tempUnsortedKeys = { 16, 33, 38, 69, 57, 95, 86 };
String[] tempContents = { "if", "then", "else", "switch", "case", "for", "while" };
DataArray tempDataArray = new DataArray(tempUnsortedKeys, tempContents, 19);
System.out.println(tempDataArray);
System.out.println("Search result of 95 is: " + tempDataArray.hashSearch(95));
System.out.println("Search result of 38 is: " + tempDataArray.hashSearch(38));
System.out.println("Search result of 57 is: " + tempDataArray.hashSearch(57));
System.out.println("Search result of 4 is: " + tempDataArray.hashSearch(4));
}// Of hashSearchTest
/**
*********************
* The entrance of the program.
*
* @param args Not used now.
*********************
*/
public static void main(String args[]) {
System.out.println("\r\n-------sequentialSearchTest-------");
sequentialSearchTest();
System.out.println("\r\n-------binarySearchTest-------");
binarySearchTest();
System.out.println("\r\n-------hashSearchTest-------");
hashSearchTest();
}// Of main
运行截图:
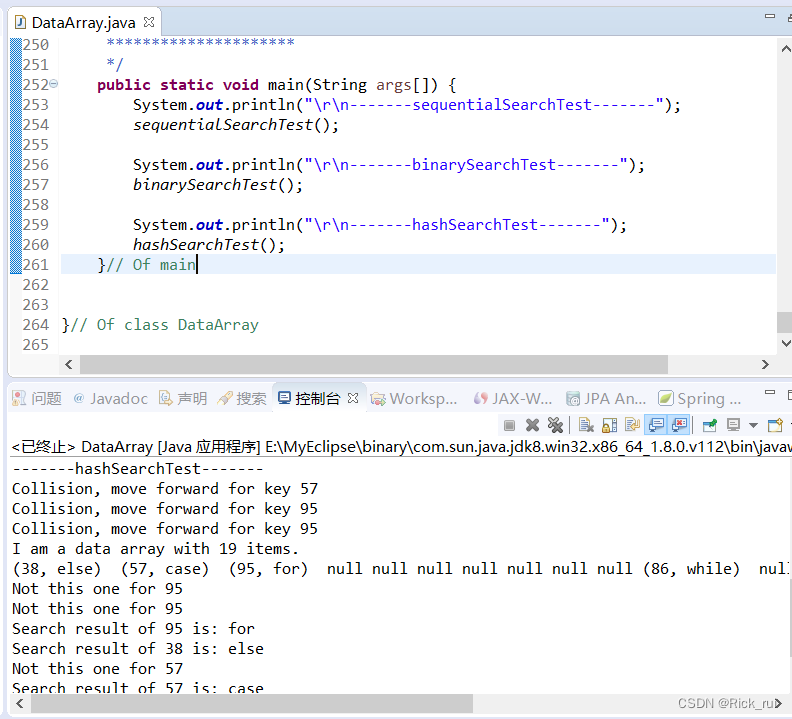
43.插入排序
1.插入排序是简单直接的排序方式之一. 代码非常短.
2.每次保证前 i 个数据是有序的.
3.先做简单的事情 (第 1 轮最多有 1 次移动), 再做麻烦的事情 (最后一轮最多有 n − 1 n - 1n−1 次移动).
4.下标 0 的数据为岗哨, 与 41 天内容同理. 比其它排序方式多用一个空间.
5.又见 this.
6.tempNode 只分配了引用 (指针) 的空间, 并未 new.
public void insertionSort() {
DataNode tempNode;
int j;
for (int i = 2; i < length; i++) {
tempNode = data[i];
//Find the position to insert.
//At the same time, move other nodes.
for (j = i - 1; data[j].key > tempNode.key; j--) {
data[j + 1] = data[j];
} // Of for j
//Insert.
data[j + 1] = tempNode;
System.out.println("Round " + (i - 1));
System.out.println(this);
} // Of for i
}// Of insertionSort
/**
*********************
* Test the method.
*********************
*/
public static void insertionSortTest() {
int[] tempUnsortedKeys = { -100, 5, 3, 6, 10, 7, 1, 9 };
String[] tempContents = { "null", "if", "then", "else", "switch", "case", "for", "while" };
DataArray tempDataArray = new DataArray(tempUnsortedKeys, tempContents);
System.out.println(tempDataArray);
tempDataArray.insertionSort();
System.out.println("Result\r\n" + tempDataArray);
}// Of insertionSortTest
运行截图:
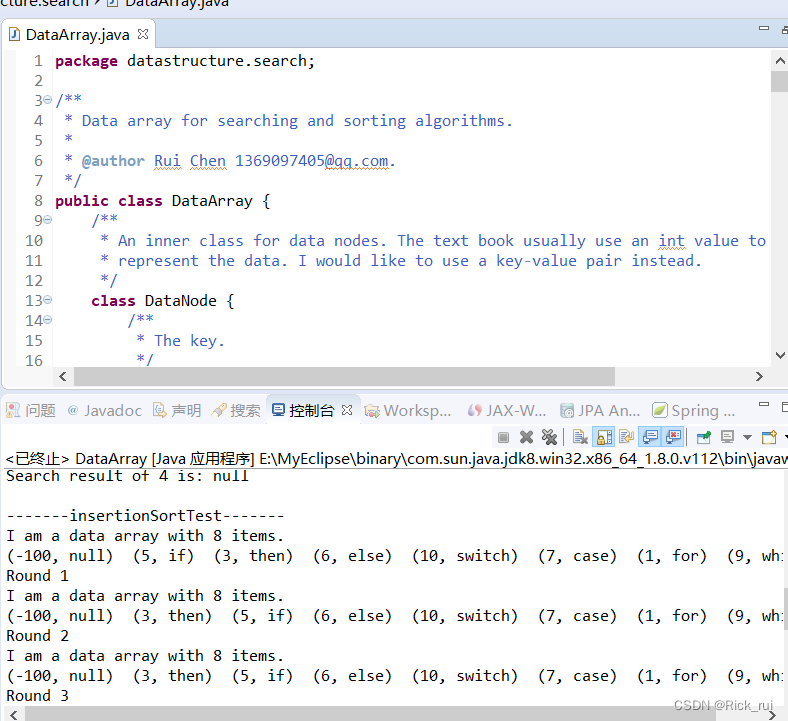
44.希尔排序
1.多达 4 重循环, 但时间复杂度只有 O ( n 2 ) ,多次排序反正减少了平均排序时间. 神奇的脑回路.
2.岗哨的个数与最初的步长相关, 我们的程序中为 5. 简便起见我就没用了.
3.可以改变 tempJumpArray.
public void shellSort() {
DataNode tempNode;
int[] tempJumpArray = { 5, 3, 1 };
int tempJump;
int p;
for (int i = 0; i < tempJumpArray.length; i++) {
tempJump = tempJumpArray[i];
for (int j = 0; j < tempJump; j++) {
for (int k = j + tempJump; k < length; k += tempJump) {
tempNode = data[k];
// Find the position to insert.
// At the same time, move other nodes.
for (p = k - tempJump; p >= 0; p -= tempJump) {
if (data[p].key > tempNode.key) {
data[p + tempJump] = data[p];
} else {
break;
} // Of if
} // Of for p
// Insert.
data[p + tempJump] = tempNode;
} // Of for k
} // Of for j
System.out.println("Round " + i);
System.out.println(this);
} // Of for i
}// Of shellSort
/**
*********************
* Test the method.
*********************
*/
public static void shellSortTest() {
int[] tempUnsortedKeys = { 5, 3, 6, 10, 7, 1, 9, 12, 8, 4 };
String[] tempContents = { "if", "then", "else", "switch", "case", "for", "while", "throw", "until", "do" };
DataArray tempDataArray = new DataArray(tempUnsortedKeys, tempContents);
System.out.println(tempDataArray);
tempDataArray.shellSort();
System.out.println("Result\r\n" + tempDataArray);
}// Of shellSortTest
运行截图: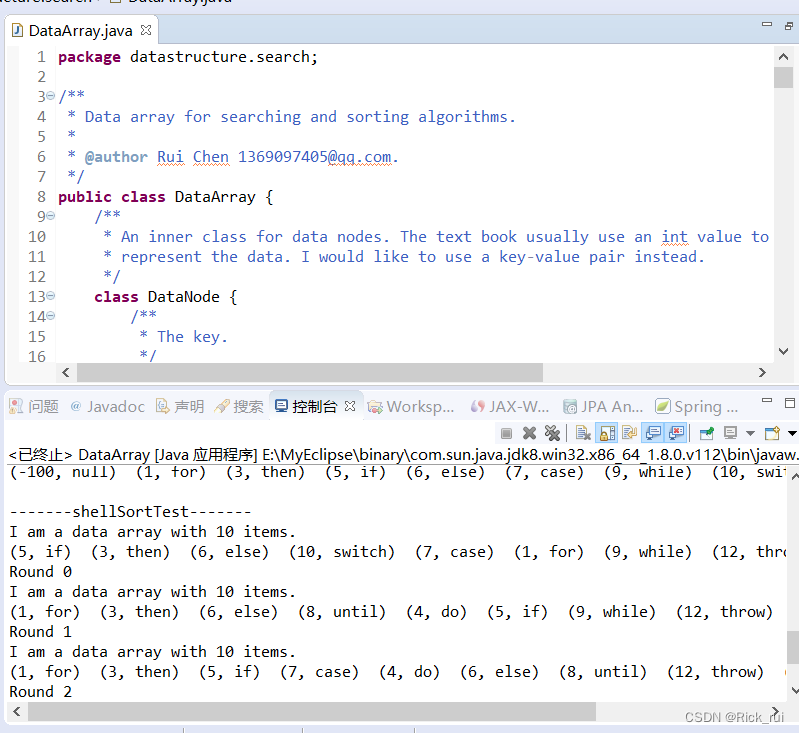
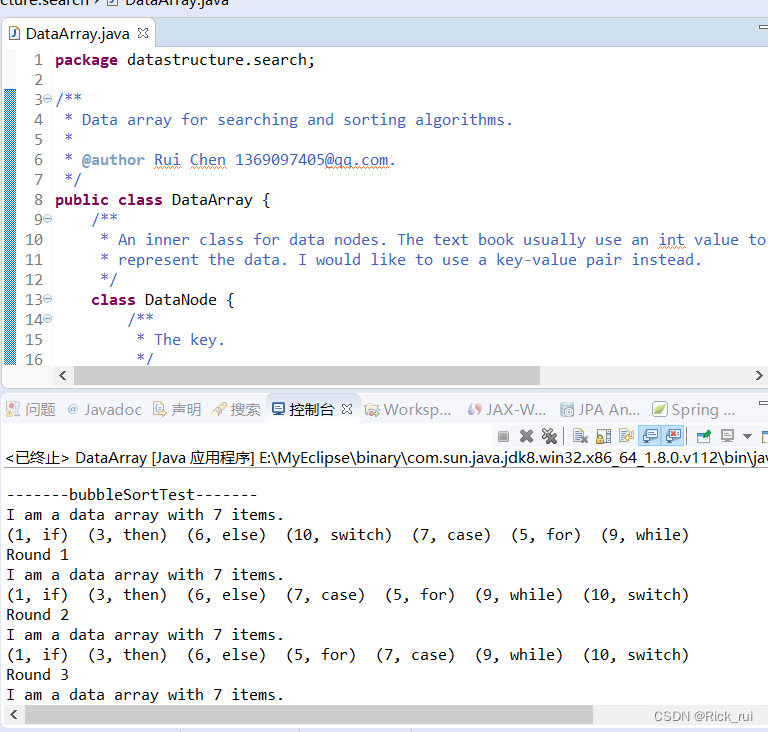
45.冒泡排序
1.每次确定当前最大值, 也就是确定一个位置的数据.
2.仅交换相邻数据.
3.如果某一趟没有交换, 就表示数据已经有序 (早熟, premature), 可以提前结束了.
public void bubbleSort() {
boolean tempSwapped;
DataNode tempNode;
for (int i = length - 1; i > 1; i--) {
tempSwapped = false;
for (int j = 0; j < i; j++) {
if (data[j].key > data[j + 1].key) {
// Swap.
tempNode = data[j + 1];
data[j + 1] = data[j];
data[j] = tempNode;
tempSwapped = true;
} // Of if
} // Of for j
// No swap in this round. The data are already sorted.
if (!tempSwapped) {
System.out.println("Premature");
break;
} // Of if
System.out.println("Round " + (length - i));
System.out.println(this);
} // Of for i
}// Of bubbleSort
/**
*********************
* Test the method.
*********************
*/
public static void bubbleSortTest() {
int[] tempUnsortedKeys = { 1, 3, 6, 10, 7, 5, 9 };
String[] tempContents = { "if", "then", "else", "switch", "case", "for", "while" };
DataArray tempDataArray = new DataArray(tempUnsortedKeys, tempContents);
System.out.println(tempDataArray);
tempDataArray.bubbleSort();
System.out.println("Result\r\n" + tempDataArray);
}// Of bubbleSortTest
运行截图:





















 2万+
2万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








