学习来源:日撸 Java 三百行(41-50天,查找与排序))_闵帆的博客-优快云博客
46.快速排序
1.平均时间复杂度为O(nlogn), 但最坏情况还是 O(n^2)
2.Pivot 应该选 (该子序列的) 最后一个元素.
3.递归算法, 每次只能确定 pivot 的位置.
4.判断条件 && (tempLeft < tempRight) 不能少.
5.(data[tempRight].key >= tempPivot) 不能写成 >, 否则出现两个相同 key 时可能出错.
public void quickSortRecursive(int paraStart, int paraEnd) {
// Nothing to sort.
if (paraStart >= paraEnd) {
return;
} // Of if
int tempPivot = data[paraEnd].key;
DataNode tempNodeForSwap;
int tempLeft = paraStart;
int tempRight = paraEnd - 1;
// Find the position for the pivot.
// At the same time move smaller elements to the left and bigger one to the
// right.
while (true) {
while ((data[tempLeft].key < tempPivot) && (tempLeft < tempRight)) {
tempLeft++;
} // Of while
while ((data[tempRight].key >= tempPivot) && (tempLeft < tempRight)) {
tempRight--;
} // Of while
if (tempLeft < tempRight) {
// Swap.
System.out.println("Swapping " + tempLeft + " and " + tempRight);
tempNodeForSwap = data[tempLeft];
data[tempLeft] = data[tempRight];
data[tempRight] = tempNodeForSwap;
} else {
break;
} // Of if
} // Of while
// Swap
if (data[tempLeft].key > tempPivot) {
tempNodeForSwap = data[paraEnd];
data[paraEnd] = data[tempLeft];
data[tempLeft] = tempNodeForSwap;
} else {
tempLeft++;
} // Of if
System.out.print("From " + paraStart + " to " + paraEnd + ": ");
System.out.println(this);
quickSortRecursive(paraStart, tempLeft - 1);
quickSortRecursive(tempLeft + 1, paraEnd);
}// Of quickSortRecursive
/**
*********************
* Quick sort.
*********************
*/
public void quickSort() {
quickSortRecursive(0, length - 1);
}// Of quickSort
/**
*********************
* Test the method.
*********************
*/
public static void quickSortTest() {
int[] tempUnsortedKeys = { 1, 3, 12, 10, 5, 7, 9 };
String[] tempContents = { "if", "then", "else", "switch", "case", "for", "while" };
DataArray tempDataArray = new DataArray(tempUnsortedKeys, tempContents);
System.out.println(tempDataArray);
tempDataArray.quickSort();
System.out.println("Result\r\n" + tempDataArray);
}// Of quickSortTest
运行截图:

47.选择排序
1.与插入排序不同, 先做最麻烦的, 要进行 n − 1 次比较才能获得最小的数据.
2.数据一旦被选择并确定位置, 就不再改变.
3.做为一种简单算法, 其时间复杂度为 O ( n 2 )
4.只需要两个额外的空间来存放最小数据的引用与下标, 因此空间复杂度为 O(1).
public void selectionSort() {
DataNode tempNode;
int tempIndexForSmallest;
for (int i = 0; i < length - 1; i++) {
// Initialize.
tempNode = data[i];
tempIndexForSmallest = i;
for (int j = i + 1; j < length; j++) {
if (data[j].key < tempNode.key) {
tempNode = data[j];
tempIndexForSmallest = j;
} // Of if
} // Of for j
// Change the selected one with the current one.
data[tempIndexForSmallest] = data[i];
data[i] = tempNode;
} // Of for i
}// Of selectionSort
/**
*********************
* Test the method.
*********************
*/
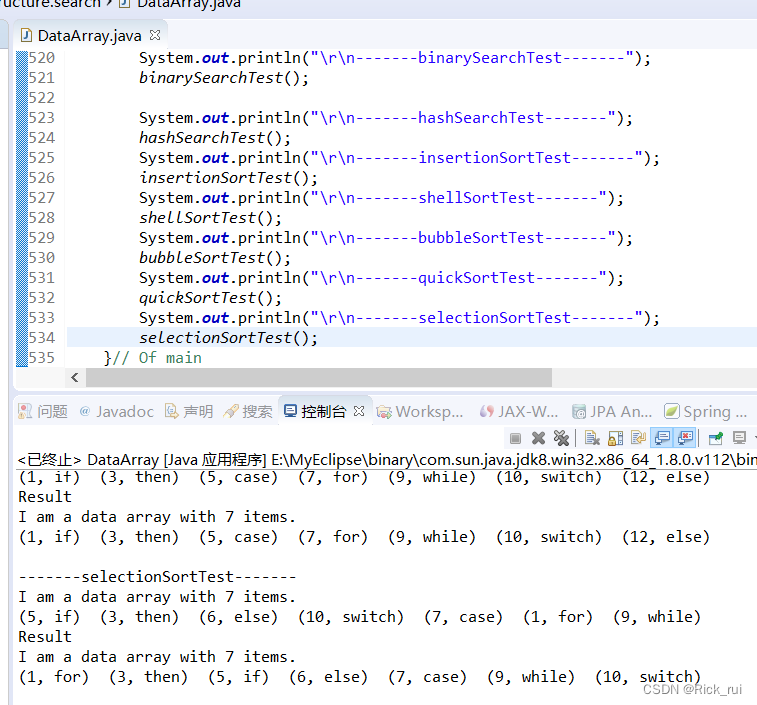
public static void selectionSortTest() {
int[] tempUnsortedKeys = { 5, 3, 6, 10, 7, 1, 9 };
String[] tempContents = { "if", "then", "else", "switch", "case", "for", "while" };
DataArray tempDataArray = new DataArray(tempUnsortedKeys, tempContents);
System.out.println(tempDataArray);
tempDataArray.selectionSort();
System.out.println("Result\r\n" + tempDataArray);
}// Of selectionSortTest
运行截图:
48. 堆排序
1.堆排序可能是排序算法中最难的. 用到了二叉树.
2.建初始堆比较费劲.
3.调整堆的时间复杂度为O(logn), 所以总体时间复杂度只有 O(nlogn).
4.空间复杂度只有O(1).
public void heapSort() {
DataNode tempNode;
// Step 1. Construct the initial heap.
for (int i = length / 2 - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
adjustHeap(i, length);
} // Of for i
System.out.println("The initial heap: " + this + "\r\n");
// Step 2. Swap and reconstruct.
for (int i = length - 1; i > 0; i--) {
tempNode = data[0];
data[0] = data[i];
data[i] = tempNode;
adjustHeap(0, i);
System.out.println("Round " + (length - i) + ": " + this);
} // Of for i
}// Of heapSort
/**
*********************
* Adjust the heap.
*
* @param paraStart The start of the index.
* @param paraLength The length of the adjusted sequence.
*********************
*/
public void adjustHeap(int paraStart, int paraLength) {
DataNode tempNode = data[paraStart];
int tempParent = paraStart;
int tempKey = data[paraStart].key;
for (int tempChild = paraStart * 2 + 1; tempChild < paraLength; tempChild = tempChild * 2 + 1) {
// The right child is bigger.
if (tempChild + 1 < paraLength) {
if (data[tempChild].key < data[tempChild + 1].key) {
tempChild++;
} // Of if
} // Of if
System.out.println("The parent position is " + tempParent + " and the child is " + tempChild);
if (tempKey < data[tempChild].key) {
// The child is bigger.
data[tempParent] = data[tempChild];
System.out.println("Move " + data[tempChild].key + " to position " + tempParent);
tempParent = tempChild;
} else {
break;
} // Of if
} // Of for tempChild
data[tempParent] = tempNode;
System.out.println("Adjust " + paraStart + " to " + paraLength + ": " + this);
}// Of adjustHeap
/**
*********************
* Test the method.
*********************
*/
public static void heapSortTest() {
int[] tempUnsortedKeys = { 5, 3, 6, 10, 7, 1, 9 };
String[] tempContents = { "if", "then", "else", "switch", "case", "for", "while" };
DataArray tempDataArray = new DataArray(tempUnsortedKeys, tempContents);
System.out.println(tempDataArray);
tempDataArray.heapSort();
System.out.println("Result\r\n" + tempDataArray);
}// Of heapSortTest
运行截图: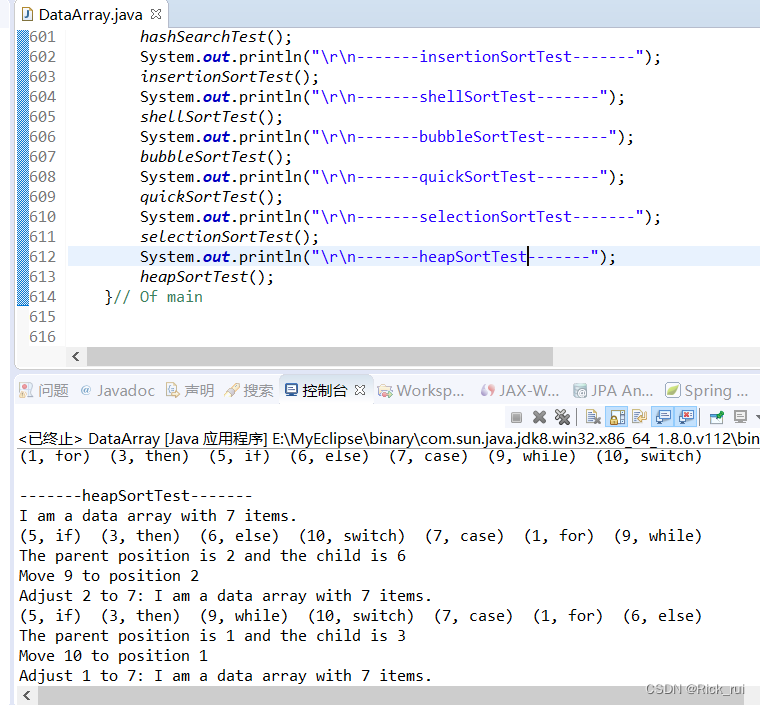
49.归并排序
1.nlogn 轮, 每轮O(n) 次拷贝. 因此时间复杂度O(nlogn).
2.空间复杂度为 O(n). 只需要一行辅助空间.
3.全都是在拷贝引用, 而不是数据本身. 这是 Java 的特性.
4.里面的两重循环总共只有O(n). 这里是分成了若干个小组.
5.归并两个有序小组的时候, 用了三个并列的循环.
6.涉及分组后尾巴的各种情况, 所以需要相应的 if 语句.
public void mergeSort() {
// Step 1. Allocate space.
int tempRow; // The current row
int tempGroups; // Number of groups
int tempActualRow; // Only 0 or 1
int tempNextRow = 0;
int tempGroupNumber;
int tempFirstStart, tempSecondStart, tempSecondEnd;
int tempFirstIndex, tempSecondIndex;
int tempNumCopied;
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
System.out.print(data[i]);
} // Of for i
System.out.println();
DataNode[][] tempMatrix = new DataNode[2][length];
// Step 2. Copy data.
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
tempMatrix[0][i] = data[i];
} // Of for i
// Step 3. Merge. log n rounds
tempRow = -1;
for (int tempSize = 1; tempSize <= length; tempSize *= 2) {
// Reuse the space of the two rows.
tempRow++;
System.out.println("Current row = " + tempRow);
tempActualRow = tempRow % 2;
tempNextRow = (tempRow + 1) % 2;
tempGroups = length / (tempSize * 2);
if (length % (tempSize * 2) != 0) {
tempGroups++;
} // Of if
System.out.println("tempSize = " + tempSize + ", numGroups = " + tempGroups);
for (tempGroupNumber = 0; tempGroupNumber < tempGroups; tempGroupNumber++) {
tempFirstStart = tempGroupNumber * tempSize * 2;
tempSecondStart = tempGroupNumber * tempSize * 2 + tempSize;
if (tempSecondStart > length - 1) {
// Copy the first part.
for (int i = tempFirstStart; i < length; i++) {
tempMatrix[tempNextRow][i] = tempMatrix[tempActualRow][i];
} // Of for i
continue;
} // Of if
tempSecondEnd = tempGroupNumber * tempSize * 2 + tempSize * 2 - 1;
if (tempSecondEnd > length - 1) {
tempSecondEnd = length - 1;
} // Of if
System.out
.println("Trying to merge [" + tempFirstStart + ", " + (tempSecondStart - 1)
+ "] with [" + tempSecondStart + ", " + tempSecondEnd + "]");
tempFirstIndex = tempFirstStart;
tempSecondIndex = tempSecondStart;
tempNumCopied = 0;
while ((tempFirstIndex <= tempSecondStart - 1)
&& (tempSecondIndex <= tempSecondEnd)) {
if (tempMatrix[tempActualRow][tempFirstIndex].key <= tempMatrix[tempActualRow][tempSecondIndex].key) {
tempMatrix[tempNextRow][tempFirstStart
+ tempNumCopied] = tempMatrix[tempActualRow][tempFirstIndex];
tempFirstIndex++;
System.out.println("copying " + tempMatrix[tempActualRow][tempFirstIndex]);
} else {
tempMatrix[tempNextRow][tempFirstStart
+ tempNumCopied] = tempMatrix[tempActualRow][tempSecondIndex];
System.out.println("copying " + tempMatrix[tempActualRow][tempSecondIndex]);
tempSecondIndex++;
} // Of if
tempNumCopied++;
} // Of while
while (tempFirstIndex <= tempSecondStart - 1) {
tempMatrix[tempNextRow][tempFirstStart
+ tempNumCopied] = tempMatrix[tempActualRow][tempFirstIndex];
tempFirstIndex++;
tempNumCopied++;
} // Of while
while (tempSecondIndex <= tempSecondEnd) {
tempMatrix[tempNextRow][tempFirstStart
+ tempNumCopied] = tempMatrix[tempActualRow][tempSecondIndex];
tempSecondIndex++;
tempNumCopied++;
} // Of while
} // Of for groupNumber
System.out.println("Round " + tempRow);
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
System.out.print(tempMatrix[tempNextRow][i] + " ");
} // Of for j
System.out.println();
} // Of for tempStepSize
data = tempMatrix[tempNextRow];
}// Of mergeSort
/**
*********************
* Test the method.
*********************
*/
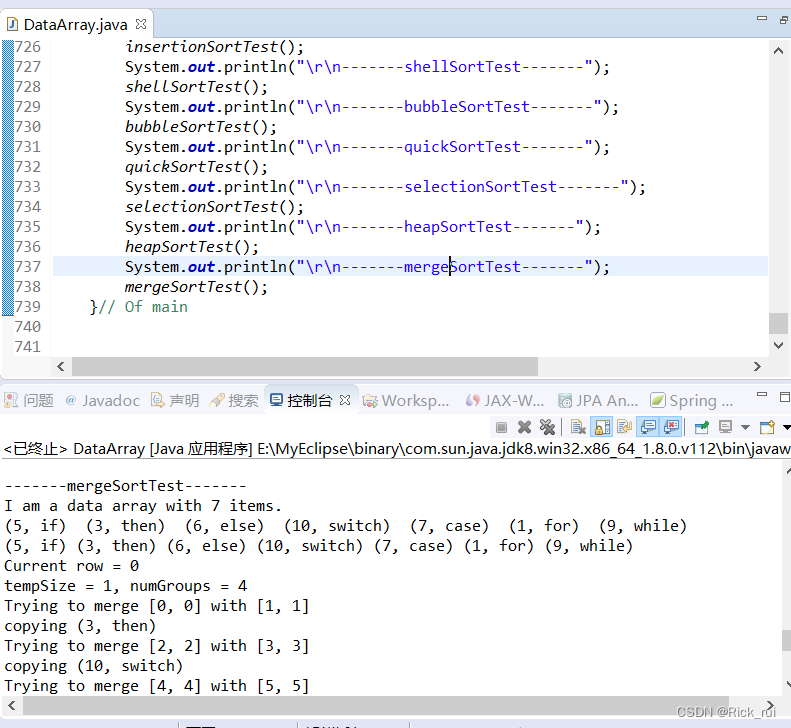
public static void mergeSortTest() {
int[] tempUnsortedKeys = { 5, 3, 6, 10, 7, 1, 9 };
String[] tempContents = { "if", "then", "else", "switch", "case", "for", "while" };
DataArray tempDataArray = new DataArray(tempUnsortedKeys, tempContents);
System.out.println(tempDataArray);
tempDataArray.mergeSort();
System.out.println(tempDataArray);
}// Of mergeSortTest
运行截图:





 本文详细介绍了Java实现的四种经典排序算法:快速排序、选择排序、堆排序和归并排序。快速排序平均时间复杂度为O(nlogn),选择排序每次选取最小元素,堆排序利用二叉树特性,归并排序通过分治策略实现。每个排序算法的实现细节、特点和时间复杂度都进行了说明,并附有测试用例和运行截图。
本文详细介绍了Java实现的四种经典排序算法:快速排序、选择排序、堆排序和归并排序。快速排序平均时间复杂度为O(nlogn),选择排序每次选取最小元素,堆排序利用二叉树特性,归并排序通过分治策略实现。每个排序算法的实现细节、特点和时间复杂度都进行了说明,并附有测试用例和运行截图。
















 8万+
8万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








