学习来源:日撸 Java 三百行(31-40天,图))_闵帆的博客-优快云博客
36.邻连表
1.相当于图的压缩存储. 每一行数据用一个单链表存储.
2.重写了广度优先遍历. 可以发现, 使用队列的机制不变. 仅仅是把其中的 for 循环换成了 while, 避免检查不存在的边. 如果图很稀疏的话, 可以降低时间复杂度.
package datastructure.graph;
import datastructure.queue.CircleObjectQueue;
/**
* Adjacency list for directed graph.
*
* @author Rui Chen 1369097405@qq.com.
*/
public class AdjacencyList {
/**
* An inner class for adjacent node.
*/
class AdjacencyNode {
/**
* The column index.
*/
int column;
/**
* The next adjacent node.
*/
AdjacencyNode next;
/**
*********************
* The first constructor.
*
* @param paraColumn
* The column.
*********************
*/
public AdjacencyNode(int paraColumn) {
column = paraColumn;
next = null;
}// Of AdjacencyNode
}// Of class AdjacencyNode
/**
* The number of nodes. This member variable may be redundant since it is
* always equal to headers.length.
*/
int numNodes;
/**
* The headers for each row.
*/
AdjacencyNode[] headers;
/**
*********************
* The first constructor.
*
* @param paraMatrix
* The the matrix indicating the graph.
*********************
*/
public AdjacencyList(int[][] paraMatrix) {
numNodes = paraMatrix.length;
// Step 1. Initialize. The data in the headers are not meaningful.
AdjacencyNode tempPreviousNode, tempNode;
headers = new AdjacencyNode[numNodes];
for (int i = 0; i < numNodes; i++) {
headers[i] = new AdjacencyNode(-1);
tempPreviousNode = headers[i];
for (int j = 0; j < numNodes; j++) {
if (paraMatrix[i][j] == 0) {
continue;
} // Of if
// Create a new node.
tempNode = new AdjacencyNode(j);
// Link.
tempPreviousNode.next = tempNode;
tempPreviousNode = tempNode;
} // Of for j
} // Of for i
}// Of class AdjacentTable
/**
*********************
* Overrides the method claimed in Object, the superclass of any class.
*********************
*/
public String toString() {
String resultString = "";
AdjacencyNode tempNode;
for (int i = 0; i < numNodes; i++) {
tempNode = headers[i].next;
while (tempNode != null) {
resultString += " (" + i + ", " + tempNode.column + ")";
tempNode = tempNode.next;
} // Of while
resultString += "\r\n";
} // Of for i
return resultString;
}// Of toString
/**
*********************
* Breadth first traversal.
*
* @param paraStartIndex
* The start index.
* @return The sequence of the visit.
*********************
*/
public String breadthFirstTraversal(int paraStartIndex) {
CircleObjectQueue tempQueue = new CircleObjectQueue();
String resultString = "";
boolean[] tempVisitedArray = new boolean[numNodes];
tempVisitedArray[paraStartIndex] = true;
// Initialize the queue.
// Visit before enqueue.
tempVisitedArray[paraStartIndex] = true;
resultString += paraStartIndex;
tempQueue.enqueue(new Integer(paraStartIndex));
// Now visit the rest of the graph.
int tempIndex;
Integer tempInteger = (Integer) tempQueue.dequeue();
AdjacencyNode tempNode;
while (tempInteger != null) {
tempIndex = tempInteger.intValue();
// Enqueue all its unvisited neighbors. The neighbors are linked
// already.
tempNode = headers[tempIndex].next;
while (tempNode != null) {
if (!tempVisitedArray[tempNode.column]) {
// Visit before enqueue.
tempVisitedArray[tempNode.column] = true;
resultString += tempNode.column;
tempQueue.enqueue(new Integer(tempNode.column));
} // Of if
tempNode = tempNode.next;
} // Of for i
// Take out one from the head.
tempInteger = (Integer) tempQueue.dequeue();
} // Of while
return resultString;
}// Of breadthFirstTraversal
/**
*********************
* Unit test for breadthFirstTraversal. The same as the one in class Graph.
*********************
*/
public static void breadthFirstTraversalTest() {
// Test an undirected graph.
int[][] tempMatrix = { { 0, 1, 1, 0 }, { 1, 0, 0, 1 }, { 1, 0, 0, 1 }, { 0, 1, 1, 0 } };
Graph tempGraph = new Graph(tempMatrix);
System.out.println(tempGraph);
AdjacencyList tempAdjList = new AdjacencyList(tempMatrix);
String tempSequence = "";
try {
tempSequence = tempAdjList.breadthFirstTraversal(2);
} catch (Exception ee) {
System.out.println(ee);
} // Of try.
System.out.println("The breadth first order of visit: " + tempSequence);
}// Of breadthFirstTraversalTest
/**
*********************
* The entrance of the program.
*
* @param args
* Not used now.
*********************
*/
public static void main(String args[]) {
int[][] tempMatrix = { { 0, 1, 0 }, { 1, 0, 1 }, { 0, 1, 0 } };
AdjacencyList tempTable = new AdjacencyList(tempMatrix);
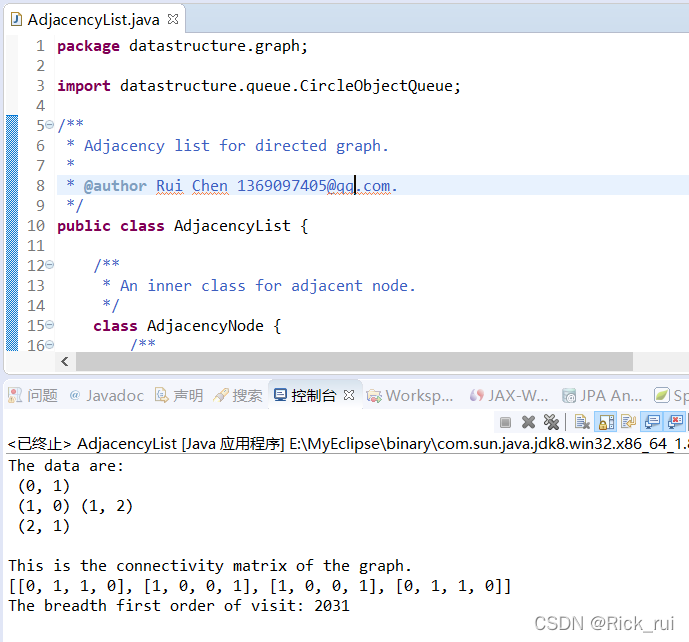
System.out.println("The data are:\r\n" + tempTable);
breadthFirstTraversalTest();
}// Of main
}// Of class AdjacencyList
运行截图:
37.十字链表
比邻接表难一点点, 毕竟多一个指针域.
为控制代码量, 只做了建表和 toString.
package datastructure.graph;
/**
* Orthogonal List for directed graph.
*
* @author Rui Chen 1369097405@qq.com.
*/
public class OrthogonalList {
/**
* An inner class for adjacent node.
*/
class OrthogonalNode {
/**
* The row index.
*/
int row;
/**
* The column index.
*/
int column;
/**
* The next out node.
*/
OrthogonalNode nextOut;
/**
* The next in node.
*/
OrthogonalNode nextIn;
/**
*********************
* The first constructor.
*
* @param paraRow The row.
* @param paraColumn The column.
*********************
*/
public OrthogonalNode(int paraRow, int paraColumn) {
row = paraRow;
column = paraColumn;
nextOut = null;
nextIn = null;
}// Of OrthogonalNode
}// Of class OrthogonalNode
/**
* The number of nodes. This member variable may be redundant since it is always
* equal to headers.length.
*/
int numNodes;
/**
* The headers for each row.
*/
OrthogonalNode[] headers;
/**
*********************
* The first constructor.
*
* @param paraMatrix The matrix indicating the graph.
*********************
*/
public OrthogonalList(int[][] paraMatrix) {
numNodes = paraMatrix.length;
// Step 1. Initialize. The data in the headers are not meaningful.
OrthogonalNode tempPreviousNode, tempNode;
headers = new OrthogonalNode[numNodes];
// Step 2. Link to its out nodes.
for (int i = 0; i < numNodes; i++) {
headers[i] = new OrthogonalNode(i, -1);
tempPreviousNode = headers[i];
for (int j = 0; j < numNodes; j++) {
if (paraMatrix[i][j] == 0) {
continue;
} // Of if
// Create a new node.
tempNode = new OrthogonalNode(i, j);
// Link.
tempPreviousNode.nextOut = tempNode;
tempPreviousNode = tempNode;
} // Of for j
} // Of for i
// Step 3. Link to its in nodes. This step is harder.
OrthogonalNode[] tempColumnNodes = new OrthogonalNode[numNodes];
for (int i = 0; i < numNodes; i++) {
tempColumnNodes[i] = headers[i];
} // Of for i
for (int i = 0; i < numNodes; i++) {
tempNode = headers[i].nextOut;
while (tempNode != null) {
tempColumnNodes[tempNode.column].nextIn = tempNode;
tempColumnNodes[tempNode.column] = tempNode;
tempNode = tempNode.nextOut;
} // Of while
} // Of for i
}// Of the constructor
/**
*********************
* Overrides the method claimed in Object, the superclass of any class.
*********************
*/
public String toString() {
String resultString = "Out arcs: ";
OrthogonalNode tempNode;
for (int i = 0; i < numNodes; i++) {
tempNode = headers[i].nextOut;
while (tempNode != null) {
resultString += " (" + tempNode.row + ", " + tempNode.column + ")";
tempNode = tempNode.nextOut;
} // Of while
resultString += "\r\n";
} // Of for i
resultString += "\r\nIn arcs: ";
for (int i = 0; i < numNodes; i++) {
tempNode = headers[i].nextIn;
while (tempNode != null) {
resultString += " (" + tempNode.row + ", " + tempNode.column + ")";
tempNode = tempNode.nextIn;
} // Of while
resultString += "\r\n";
} // Of for i
return resultString;
}// Of toString
/**
*********************
* The entrance of the program.
*
* @param args Not used now.
*********************
*/
public static void main(String args[]) {
int[][] tempMatrix = { { 0, 1, 0, 0 }, { 0, 0, 0, 1 }, { 1, 0, 0, 0 }, { 0, 1, 1, 0 } };
OrthogonalList tempList = new OrthogonalList(tempMatrix);
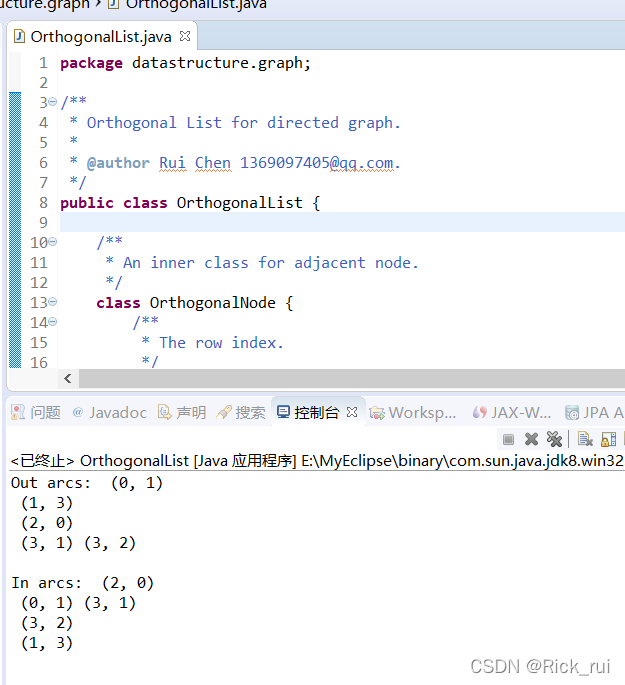
System.out.println("The data are:\r\n" + tempList);
}// Of main
}// Of class OrthogonalList
运行截图:
38.Dijkstra 算法与 Prim 算法
1.又需要画个几个图, 换几个例子.
2.Dijkstra 算法需要有向图, Prim 算法需要无向图. 代码中也需要更换后者.
3.两个算法的结构相同. 不同之处是比较距离的时候, 是用累计的 (Dijkstra) 还是当前边的 (Prim). 建议先写 Dijkstra, 然后拷贝、修改变成 Prim. 到这个阶段, 应该已经具备这样的能力.
package datastructure.graph;
import java.util.Arrays;
import matrix.IntMatrix;
/**
* Weighted graphs are called nets.
*
* @author Rui Chen 1369097405@qq.com.
*/
public class Net {
/**
* The maximal distance. Do not use Integer.MAX_VALUE.
*/
public static final int MAX_DISTANCE = 10000;
/**
* The number of nodes.
*/
int numNodes;
/**
* The weight matrix. We use int to represent weight for simplicity.
*/
IntMatrix weightMatrix;
/**
*********************
* The first constructor.
*
* @param paraNumNodes
* The number of nodes in the graph.
*********************
*/
public Net(int paraNumNodes) {
numNodes = paraNumNodes;
weightMatrix = new IntMatrix(numNodes, numNodes);
for (int i = 0; i < numNodes; i++) {
// For better readability, you may need to write fill() in class
// IntMatrix.
Arrays.fill(weightMatrix.getData()[i], MAX_DISTANCE);
} // Of for i
}// Of the first constructor
/**
*********************
* The second constructor.
*
* @param paraMatrix
* The data matrix.
*********************
*/
public Net(int[][] paraMatrix) {
weightMatrix = new IntMatrix(paraMatrix);
numNodes = weightMatrix.getRows();
}// Of the second constructor
/**
*********************
* Overrides the method claimed in Object, the superclass of any class.
*********************
*/
public String toString() {
String resultString = "This is the weight matrix of the graph.\r\n" + weightMatrix;
return resultString;
}// Of toString
/**
*********************
* The Dijkstra algorithm: shortest path from the source to all nodes.
*
* @param paraSource
* The source node.
* @return The distances to all nodes.
*********************
*/
public int[] dijkstra(int paraSource) {
// Step 1. Initialize.
int[] tempDistanceArray = new int[numNodes];
for (int i = 0; i < numNodes; i++) {
tempDistanceArray[i] = weightMatrix.getValue(paraSource, i);
} // Of for i
int[] tempParentArray = new int[numNodes];
Arrays.fill(tempParentArray, paraSource);
// -1 for no parent.
tempParentArray[paraSource] = -1;
// Visited nodes will not be considered further.
boolean[] tempVisitedArray = new boolean[numNodes];
tempVisitedArray[paraSource] = true;
// Step 2. Main loops.
int tempMinDistance;
int tempBestNode = -1;
for (int i = 0; i < numNodes - 1; i++) {
// Step 2.1 Find out the best next node.
tempMinDistance = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
for (int j = 0; j < numNodes; j++) {
// This node is visited.
if (tempVisitedArray[j]) {
continue;
} // Of if
if (tempMinDistance > tempDistanceArray[j]) {
tempMinDistance = tempDistanceArray[j];
tempBestNode = j;
} // Of if
} // Of for j
tempVisitedArray[tempBestNode] = true;
// Step 2.2 Prepare for the next round.
for (int j = 0; j < numNodes; j++) {
// This node is visited.
if (tempVisitedArray[j]) {
continue;
} // Of if
// This node cannot be reached.
if (weightMatrix.getValue(tempBestNode, j) >= MAX_DISTANCE) {
continue;
} // Of if
if (tempDistanceArray[j] > tempDistanceArray[tempBestNode]
+ weightMatrix.getValue(tempBestNode, j)) {
// Change the distance.
tempDistanceArray[j] = tempDistanceArray[tempBestNode]
+ weightMatrix.getValue(tempBestNode, j);
// Change the parent.
tempParentArray[j] = tempBestNode;
} // Of if
} // Of for j
// For test
System.out.println("The distance to each node: " + Arrays.toString(tempDistanceArray));
System.out.println("The parent of each node: " + Arrays.toString(tempParentArray));
} // Of for i
// Step 3. Output for debug.
System.out.println("Finally");
System.out.println("The distance to each node: " + Arrays.toString(tempDistanceArray));
System.out.println("The parent of each node: " + Arrays.toString(tempParentArray));
return tempDistanceArray;
}// Of dijkstra
/**
*********************
* The minimal spanning tree.
*
* @return The total cost of the tree.
*********************
*/
public int prim() {
// Step 1. Initialize.
// Any node can be the source.
int tempSource = 0;
int[] tempDistanceArray = new int[numNodes];
for (int i = 0; i < numNodes; i++) {
tempDistanceArray[i] = weightMatrix.getValue(tempSource, i);
} // Of for i
int[] tempParentArray = new int[numNodes];
Arrays.fill(tempParentArray, tempSource);
// -1 for no parent.
tempParentArray[tempSource] = -1;
// Visited nodes will not be considered further.
boolean[] tempVisitedArray = new boolean[numNodes];
tempVisitedArray[tempSource] = true;
// Step 2. Main loops.
int tempMinDistance;
int tempBestNode = -1;
for (int i = 0; i < numNodes - 1; i++) {
// Step 2.1 Find out the best next node.
tempMinDistance = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
for (int j = 0; j < numNodes; j++) {
// This node is visited.
if (tempVisitedArray[j]) {
continue;
} // Of if
if (tempMinDistance > tempDistanceArray[j]) {
tempMinDistance = tempDistanceArray[j];
tempBestNode = j;
} // Of if
} // Of for j
tempVisitedArray[tempBestNode] = true;
// Step 2.2 Prepare for the next round.
for (int j = 0; j < numNodes; j++) {
// This node is visited.
if (tempVisitedArray[j]) {
continue;
} // Of if
// This node cannot be reached.
if (weightMatrix.getValue(tempBestNode, j) >= MAX_DISTANCE) {
continue;
} // Of if
// Attention: the difference from the Dijkstra algorithm.
if (tempDistanceArray[j] > weightMatrix.getValue(tempBestNode, j)) {
// Change the distance.
tempDistanceArray[j] = weightMatrix.getValue(tempBestNode, j);
// Change the parent.
tempParentArray[j] = tempBestNode;
} // Of if
} // Of for j
// For test
System.out.println(
"The selected distance for each node: " + Arrays.toString(tempDistanceArray));
System.out.println("The parent of each node: " + Arrays.toString(tempParentArray));
} // Of for i
int resultCost = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < numNodes; i++) {
resultCost += tempDistanceArray[i];
} // Of for i
// Step 3. Output for debug.
System.out.println("Finally");
System.out.println("The parent of each node: " + Arrays.toString(tempParentArray));
System.out.println("The total cost: " + resultCost);
return resultCost;
}// Of prim
/**
*********************
* The entrance of the program.
*
* @param args
* Not used now.
*********************
*/
public static void main(String args[]) {
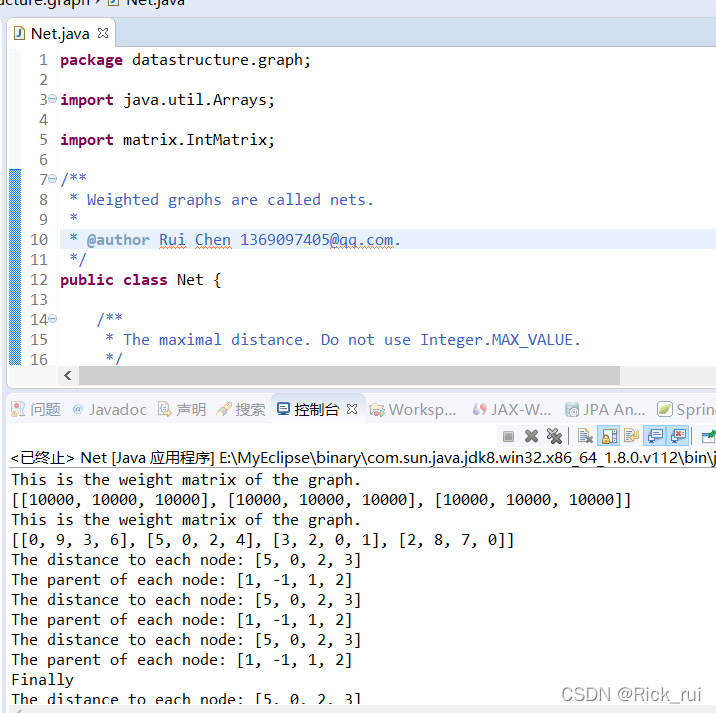
Net tempNet0 = new Net(3);
System.out.println(tempNet0);
int[][] tempMatrix1 = { { 0, 9, 3, 6 }, { 5, 0, 2, 4 }, { 3, 2, 0, 1 }, { 2, 8, 7, 0 } };
Net tempNet1 = new Net(tempMatrix1);
System.out.println(tempNet1);
// Dijkstra
tempNet1.dijkstra(1);
// An undirected net is required.
int[][] tempMatrix2 = { { 0, 7, MAX_DISTANCE, 5, MAX_DISTANCE }, { 7, 0, 8, 9, 7 },
{ MAX_DISTANCE, 8, 0, MAX_DISTANCE, 5 }, { 5, 9, MAX_DISTANCE, 0, 15 },
{ MAX_DISTANCE, 7, 5, 15, 0 } };
Net tempNet2 = new Net(tempMatrix2);
tempNet2.prim();
}// Of main
}// Of class Net
运行截图:
39.关键路径
1.拓扑排序是关键路径的一部分.
2.关键路径长度, 其实是最远路径长度. 然而, 它并非最短路径的对偶问题. 我尝试修改 Dijkstra 算法来解决, 然后发现自己傻了.
3.正向算每个节点的最早开始时间, 逆向算每个节点的最晚开始时间,
public boolean[] criticalPath() {
// One more value to save simple computation.
int tempValue;
// Step 1. The in-degree of each node.
int[] tempInDegrees = new int[numNodes];
for (int i = 0; i < numNodes; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < numNodes; j++) {
if (weightMatrix.getValue(i, j) != -1) {
tempInDegrees[j]++;
} // Of if
} // Of for j
} // Of for i
System.out.println("In-degree of nodes: " + Arrays.toString(tempInDegrees));
// Step 2. Topology sorting.
int[] tempEarliestTimeArray = new int[numNodes];
for (int i = 0; i < numNodes; i++) {
// This node cannot be removed.
if (tempInDegrees[i] > 0) {
continue;
} // Of if
System.out.println("Removing " + i);
for (int j = 0; j < numNodes; j++) {
if (weightMatrix.getValue(i, j) != -1) {
tempValue = tempEarliestTimeArray[i] + weightMatrix.getValue(i, j);
if (tempEarliestTimeArray[j] < tempValue) {
tempEarliestTimeArray[j] = tempValue;
} // Of if
tempInDegrees[j]--;
} // Of if
} // Of for j
} // Of for i
System.out.println("Earlest start time: " + Arrays.toString(tempEarliestTimeArray));
// Step 3. The out-degree of each node.
int[] tempOutDegrees = new int[numNodes];
for (int i = 0; i < numNodes; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < numNodes; j++) {
if (weightMatrix.getValue(i, j) != -1) {
tempOutDegrees[i]++;
} // Of if
} // Of for j
} // Of for i
System.out.println("Out-degree of nodes: " + Arrays.toString(tempOutDegrees));
// Step 4. Reverse topology sorting.
int[] tempLatestTimeArray = new int[numNodes];
for (int i = 0; i < numNodes; i++) {
tempLatestTimeArray[i] = tempEarliestTimeArray[numNodes - 1];
} // Of for i
for (int i = numNodes - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
// This node cannot be removed.
if (tempOutDegrees[i] > 0) {
continue;
} // Of if
System.out.println("Removing " + i);
for (int j = 0; j < numNodes; j++) {
if (weightMatrix.getValue(j, i) != -1) {
tempValue = tempLatestTimeArray[i] - weightMatrix.getValue(j, i);
if (tempLatestTimeArray[j] > tempValue) {
tempLatestTimeArray[j] = tempValue;
} // Of if
tempOutDegrees[j]--;
System.out.println("The out-degree of " + j + " decreases by 1.");
} // Of if
} // Of for j
} // Of for i
System.out.println("Latest start time: " + Arrays.toString(tempLatestTimeArray));
boolean[] resultCriticalArray = new boolean[numNodes];
for (int i = 0; i < numNodes; i++) {
if (tempEarliestTimeArray[i] == tempLatestTimeArray[i]) {
resultCriticalArray[i] = true;
} // Of if
} // Of for i
System.out.println("Critical array: " + Arrays.toString(resultCriticalArray));
System.out.print("Critical nodes: ");
for (int i = 0; i < numNodes; i++) {
if (resultCriticalArray[i]) {
System.out.print(" " + i);
} // Of if
} // Of for i
System.out.println();
return resultCriticalArray;
}// Of criticalPath
/**
*********************
* The entrance of the program.
*
* @param args
* Not used now.
*********************
*/
public static void main(String args[]) {
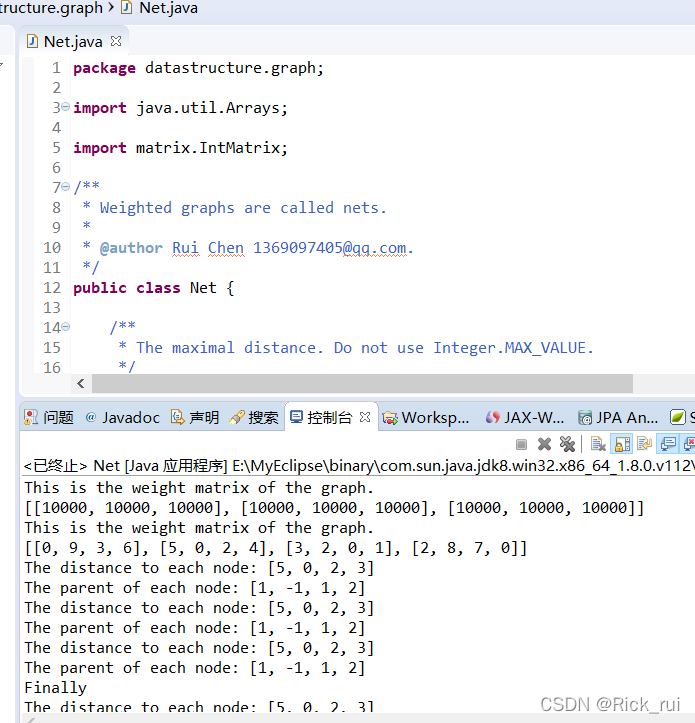
Net tempNet0 = new Net(3);
System.out.println(tempNet0);
int[][] tempMatrix1 = { { 0, 9, 3, 6 }, { 5, 0, 2, 4 }, { 3, 2, 0, 1 }, { 2, 8, 7, 0 } };
Net tempNet1 = new Net(tempMatrix1);
System.out.println(tempNet1);
// Dijkstra
tempNet1.dijkstra(1);
// An undirected net is required.
int[][] tempMatrix2 = { { 0, 7, MAX_DISTANCE, 5, MAX_DISTANCE }, { 7, 0, 8, 9, 7 },
{ MAX_DISTANCE, 8, 0, MAX_DISTANCE, 5 }, { 5, 9, MAX_DISTANCE, 0, 15, },
{ MAX_DISTANCE, 7, 5, 15, 0 } };
Net tempNet2 = new Net(tempMatrix2);
tempNet2.prim();
// A directed net without loop is required.
// Node cannot reach itself. It is indicated by -1.
int[][] tempMatrix3 = { { -1, 3, 2, -1, -1, -1 }, { -1, -1, -1, 2, 3, -1 },
{ -1, -1, -1, 4, -1, 3 }, { -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, 2 }, { -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, 1 },
{ -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1 } };
Net tempNet3 = new Net(tempMatrix3);
System.out.println("-------critical path");
tempNet3.criticalPath();
}// Of main
运行截图:





 本文介绍了图论中的邻接表和十字链表数据结构,并详细讲解了如何利用它们实现Dijkstra算法求最短路径和Prim算法求最小生成树。通过实例演示了关键路径的计算方法。
本文介绍了图论中的邻接表和十字链表数据结构,并详细讲解了如何利用它们实现Dijkstra算法求最短路径和Prim算法求最小生成树。通过实例演示了关键路径的计算方法。
















 386
386

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








