开发环境配置
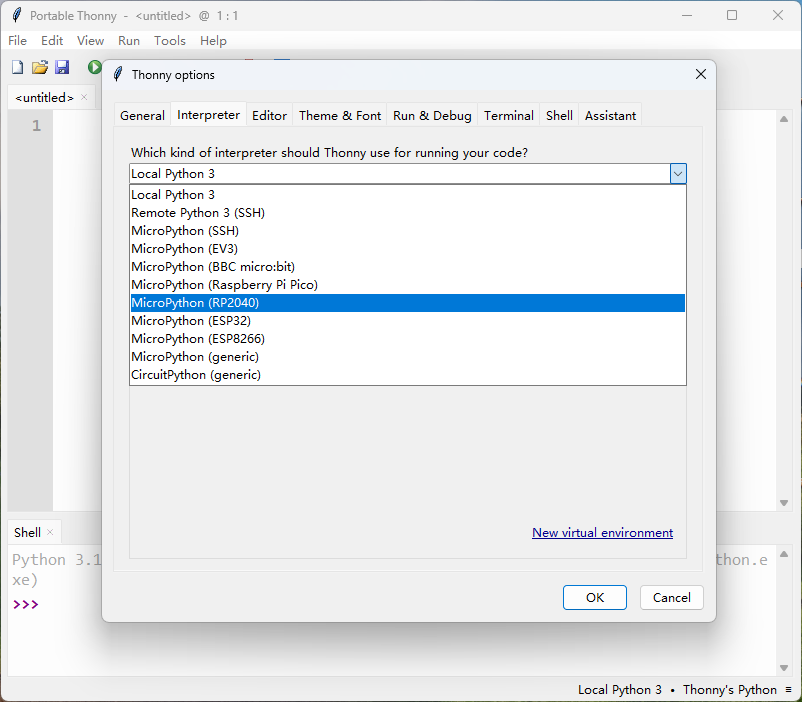
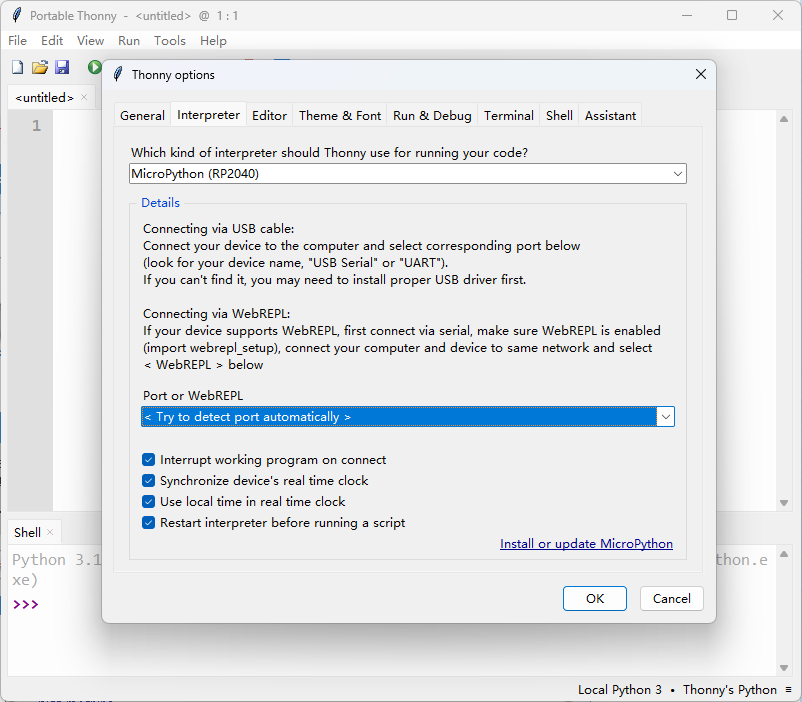
GPIO点灯
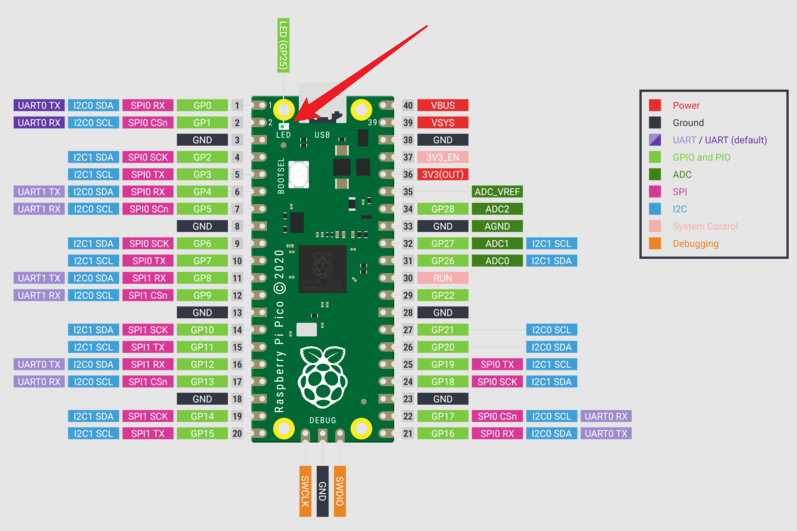
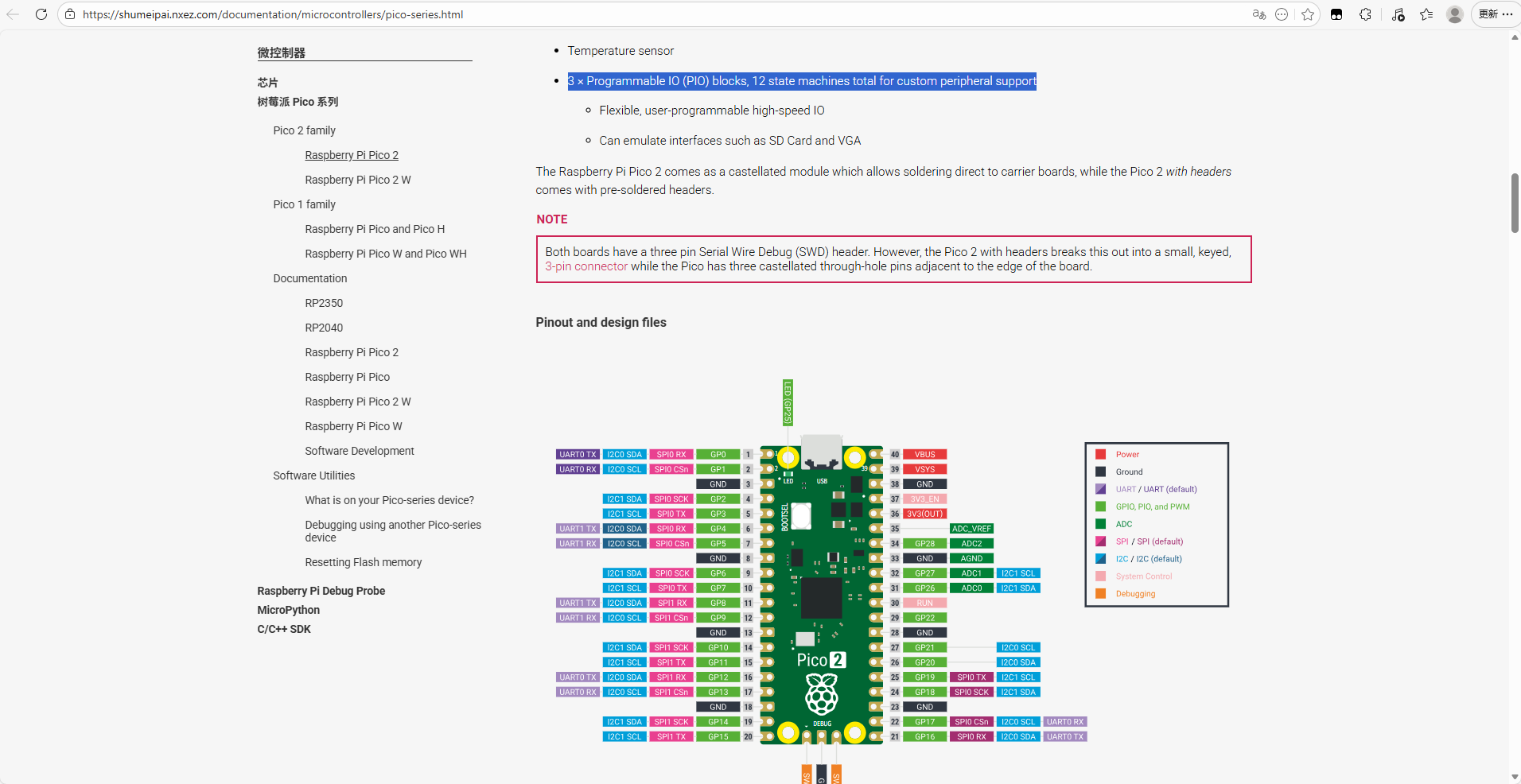
- RP2 快速参考中给出了灯的位置:
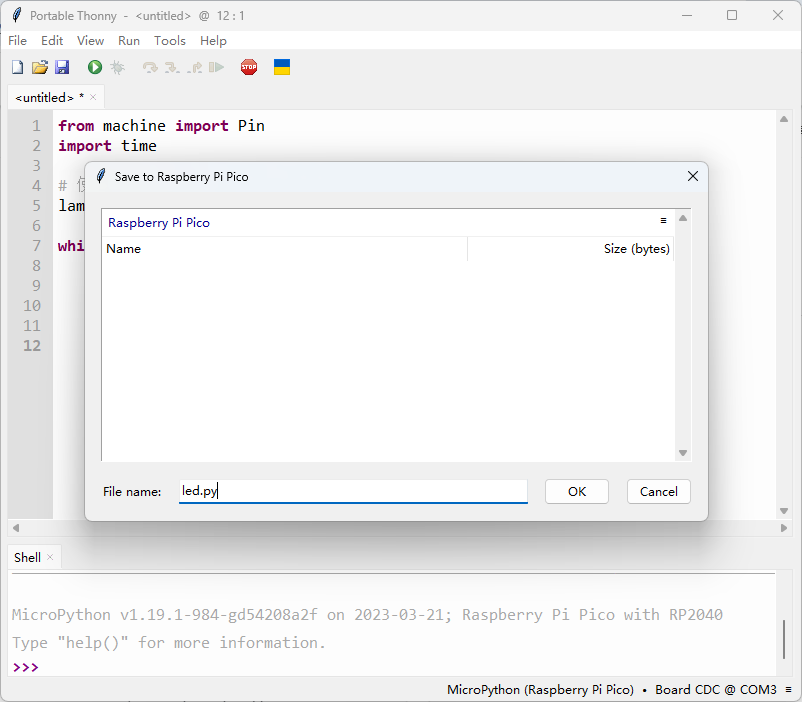
- 需要先改变当前的解释器(右下角),然后将pyton代码保存到单片机上去:
- 程序如下:
from machine import Pin
import time
lamp = Pin(25, Pin.OUT)
while True:
lamp.value(1) # 开灯
time.sleep(1)
lamp.value(0) # 关灯
time.sleep(1)
- 点击运行即可:
PIO点灯
- Python 直接控制 GPIO,延时靠 time.sleep()不精确.如果 Python 在做别的事,就会卡顿,不能做高速或严格时序信号。
- 通过可编程IO(Programmable Input/Output),开发人员可以自定义IO端口的功能和行为,可以实现高精度的输入和输出控制。官方给出了PIO形式的电灯程序( For protocols where there is no hardware support, or where there is a requirement of custom I/O behaviour, Programmable Input Output (PIO) comes into play. )
# Example using PIO to blink an LED and raise an IRQ at 1Hz.
import time
from machine import Pin
import rp2
@rp2.asm_pio(set_init=rp2.PIO.OUT_LOW)
def blink_1hz():
# Cycles: 1 + 1 + 6 + 32 * (30 + 1) = 1000
irq(rel(0))
set(pins, 1)
set(x, 31) [5]
label("delay_high")
nop() [29]
jmp(x_dec, "delay_high")
# Cycles: 1 + 7 + 32 * (30 + 1) = 1000
set(pins, 0)
set(x, 31) [6]
label("delay_low")
nop() [29]
jmp(x_dec, "delay_low")
# Create the StateMachine with the blink_1hz program, outputting on Pin(25).
sm = rp2.StateMachine(0, blink_1hz, freq=2000, set_base=Pin(25))
# Set the IRQ handler to print the millisecond timestamp.
sm.irq(lambda p: print(time.ticks_ms()))
# Start the StateMachine.
sm.active(1)
- 完整周期 = 2000 cycles → 1Hz 严格精准





















 1907
1907

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








