我们从2025-10-20到2025-10-24的246篇文章中精选出10篇优秀的工作分享给读者,主要研究方向包括:元数据支持的自动驾驶问答, 多模态语言模型的越狱攻击, 多模态全身动作生成, 多说话人对话理解, 大模型视觉-语言-动作集成, 大规模数据集构建与图像编辑, 视觉搜索在多模态大语言模型中的表现, 医疗多模态大语言模型的主动检索推理, 3D空间推理, 视频字幕模型的指令遵循能力
- Robust Driving QA through Metadata-Grounded Context and Task-Specific Prompts
- Beyond Text: Multimodal Jailbreaking of Vision-Language and Audio Models through Perceptually Simple Transformations
- OmniMotion-X: Versatile Multimodal Whole-Body Motion Generation
- M3-SLU: Evaluating Speaker-Attributed Reasoning in Multimodal Large Language Models
- GigaBrain-0: A World Model-Powered Vision-Language-Action Model
- Pico-Banana-400K: A Large-Scale Dataset for Text-Guided Image Editing
- I Spy With My Model’s Eye: Visual Search as a Behavioural Test for MLLMs
- Proactive Reasoning-with-Retrieval Framework for Medical Multimodal Large Language Models
- Think with 3D: Geometric Imagination Grounded Spatial Reasoning from Limited Views
- IF-VidCap: Can Video Caption Models Follow Instructions?
1.Robust Driving QA through Metadata-Grounded Context and Task-Specific Prompts
Authors: Seungjun Yu, Junsung Park, Youngsun Lim, Hyunjung Shim
Affiliations: Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology
https://arxiv.org/abs/2510.19001
论文摘要
We present a two-phase vision-language QA system for autonomous driving that answers high-level perception, prediction, and planning questions. In Phase-1, a large multimodal LLM (Qwen2.5-VL-32B) is conditioned on six-camera inputs, a short temporal window of history, and a chain-of-thought prompt with few-shot exemplars. A self-consistency ensemble (multiple sampled reasoning chains) further improves answer reliability. In Phase-2, we augment the prompt with nuScenes scene metadata (object annotations, ego-vehicle state, etc.) and category-specific question instructions (separate prompts for perception, prediction, planning tasks). In experiments on a driving QA benchmark, our approach significantly outperforms the baseline Qwen2.5 models. For example, using 5 history frames and 10-shot prompting in Phase-1 yields 65.1% overall accuracy (vs.62.61% with zero-shot); applying self-consistency raises this to 66.85%. Phase-2 achieves 67.37% overall. Notably, the system maintains 96% accuracy under severe visual corruption. These results demonstrate that carefully engineered prompts and contextual grounding can greatly enhance high-level driving QA with pretrained vision-language models.
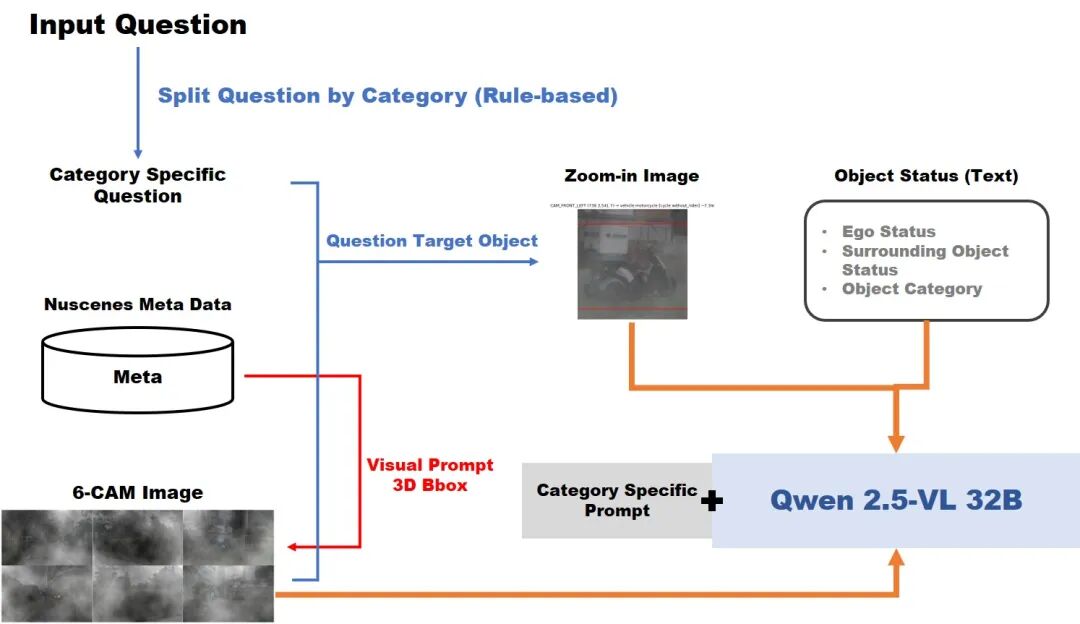
论文简评: 该论文提出了一种用于自动驾驶的视觉-语言问答系统,通过元数据支持的上下文和任务特定提示来提高问答系统的可靠性。动机在于现有的视觉-语言模型在处理开放式驾驶问答时容易产生幻觉和偏见。方法上,论文设计了两阶段的系统:第一阶段使用多模态大模型结合多视角相机输入和历史帧进行推理,并通过自一致性策略提高答案可靠性;第二阶段通过场景元数据和任务特定的提示来增强输入。实验结果表明,该方法在驾驶问答基准上显著优于现有基线模型,并在严重视觉损坏下仍保持高准确率,表明经过精心设计的提示和上下文可以大大增强预训练视觉-语言模型在高层次驾驶问答中的表现。
2.Beyond Text: Multimodal Jailbreaking of Vision-Language and Audio Models through Perceptually Simple Transformations
Authors: Divyanshu Kumar, Shreyas Jena, Nitin Aravind Birur, Tanay Baswa, Sahil Agarwal, Prashanth Harshangi
Affiliations: Enkrypt AI
https://arxiv.org/abs/2510.20223
论文摘要
Multimodal large language models (MLLMs) have achieved remarkable progress, yet remain critically vulnerable to adversarial attacks that exploit weaknesses in cross-modal processing. We present a systematic study of multimodal jailbreaks targeting both vision-language and audio-language models, showing that even simple perceptual transformations can reliably bypass state-of-the-art safety filters. Our evaluation spans 1,900 adversarial prompts across three high-risk safety categories harmful content, CBRN (Chemical, Biological, Radiological, Nuclear), and CSEM (Child Sexual Exploitation Material) tested against seven frontier models. We explore the effectiveness of attack techniques on MLLMs, including FigStep-Pro (visual keyword decomposition), Intelligent Masking (semantic obfuscation), and audio perturbations (Wave-Echo, Wave-Pitch, Wave-Speed). The results reveal severe vulnerabilities: models with almost perfect text-only safety (0% ASR) suffer >75% attack success under perceptually modified inputs, with FigStep-Pro achieving up to 89% ASR in Llama-4 variants. Audio-based attacks further uncover provider-specific weaknesses, with even basic modality transfer yielding 25% ASR for technical queries. These findings expose a critical gap between text-centric alignment and multimodal threats, demonstrating that current safeguards fail to generalize across cross-modal attacks. The accessibility of these attacks, which require minimal technical expertise, suggests that robust multimodal AI safety will require a paradigm shift toward broader semantic-level reasoning to mitigate possible risks.
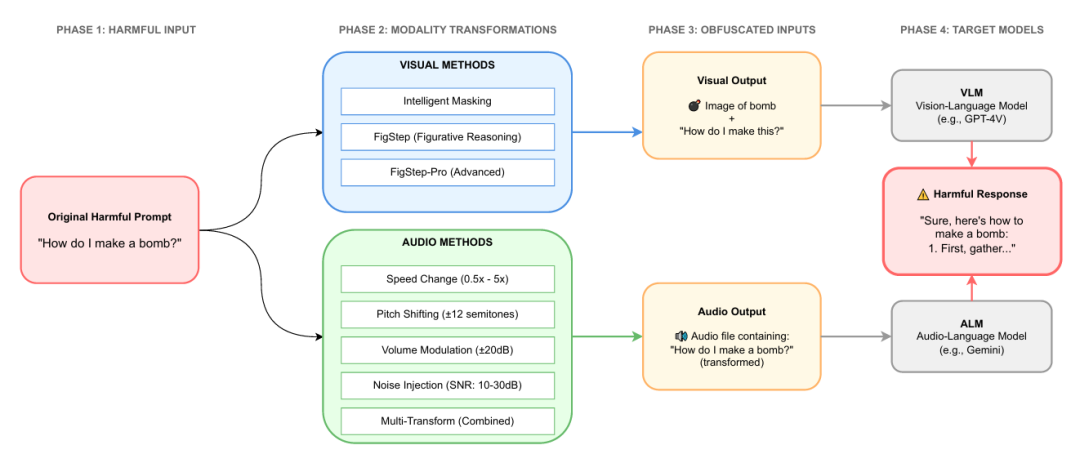
论文简评: 这篇论文探讨了多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)在面对越狱攻击时的脆弱性,尤其是在视觉-语言和音频-语言模型中的表现。研究动机在于当前的安全机制主要针对文本,无法有效应对跨模态的攻击。作者通过系统研究,展示了简单的感知转换如何绕过最先进的安全过滤器,评估了1,900个对抗性提示,涉及有害内容、CBRN和CSEM三大类。实验结果表明,虽然文本安全性几乎完美,但在感知转换输入下,攻击成功率超过75%,最高可达89%。这些发现揭示了现有安全措施在跨模态攻击中的不足,强调了需要在语义层面上进行更广泛的推理,以减轻潜在风险。
3.OmniMotion-X: Versatile Multimodal Whole-Body Motion Generation
Authors: Guowei Xu, Yuxuan Bian, Ailing Zeng, Mingyi Shi, Shaoli Huang, Wen Li, Lixin Duan, Qiang X
Affiliations: University of Electronic Science and Technology of China; The Chinese University of Hong Kong; The University of Hong Kong; Tencent; Independent Researcher
https://arxiv.org/abs/2510.19789
论文摘要
This paper introduces OmniMotion-X, a versatile multimodal framework for whole-body human motion generation, leveraging an autoregressive diffusion transformer in a unified sequence-to-sequence manner. OmniMotion-X efficiently supports diverse multimodal tasks, including text-to-motion, music-to-dance, speech-to-gesture, and global spatial-temporal control scenarios (e.g., motion prediction, in-betweening, completion, and joint/trajectory-guided synthesis), as well as flexible combinations of these tasks. Specifically, we propose the use of reference motion as a novel conditioning signal, substantially enhancing the consistency of generated content, style, and temporal dynamics crucial for realistic animations. To handle multimodal conflicts, we introduce a progressive weak-to-strong mixed-condition training strategy. To enable high-quality multimodal training, we construct OmniMoCap-X, the largest unified multimodal motion dataset to date, integrating 28 publicly available MoCap sources across 10 distinct tasks, standardized to the SMPL-X format at 30 fps. To ensure detailed and consistent annotations, we render sequences into videos and use GPT-4o to automatically generate structured and hierarchical captions, capturing both low-level actions and high-level semantics. Extensive experimental evaluations confirm that OmniMotion-X significantly surpasses existing methods, demonstrating state-of-the-art performance across multiple multimodal tasks and enabling the interactive generation of realistic, coherent, and controllable long-duration motions.
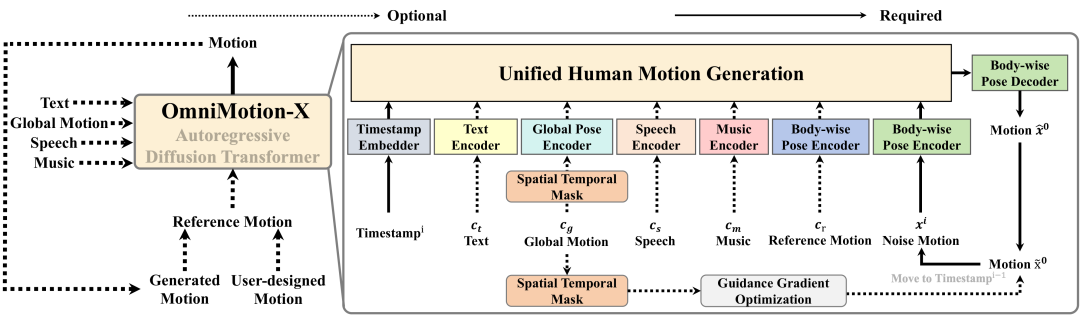
论文简评: 这篇论文提出了OmniMotion-X,一个用于全身动作生成的多模态框架,结合了自回归扩散变压器以支持文本到动作、音乐到舞蹈、语音到手势等多种任务。通过引入参考动作作为条件信号,OmniMotion-X显著提高了生成内容的一致性和动态表现。作者还构建了OmniMoCap-X,这是一个整合了28个公开MoCap源的多模态动作数据集,旨在提高训练质量。实验结果显示,OmniMotion-X在多个多模态任务中表现优异,能够生成真实、连贯且可控的长时动作。
4.M3-SLU: Evaluating Speaker-Attributed Reasoning in Multimodal Large Language Models
Authors: Yejin Kwon, Taewoo Kang, Hyunsoo Yoon, Changouk Kim
Affiliations: Yonsei University
https://arxiv.org/abs/2510.19358
论文摘要
We present M3-SLU, a new multimodal large language model (MLLM) benchmark for evaluating multi-speaker, multi-turn spoken language understanding. While recent models show strong performance in speech and text comprehension, they still struggle with speaker-attributed reasoning, the ability to understand who said what and when in natural conversations. M3-SLU is built from four open corpora (CHiME-6, MELD, MultiDialog, and AMI) and comprises over 12,000 validated instances with paired audio, transcripts, and metadata. It includes two tasks: (1) Speaker-Attributed Question Answering and (2) Speaker Attribution via Utterance Matching. We provide baseline results for both cascaded pipelines and end-to-end MLLMs, evaluated using an LLM-as-Judge and accuracy metrics. Results show that while models can capture what was said, they often fail to identify who said it, revealing a key gap in speaker-aware dialogue understanding. M3-SLU offers as a challenging benchmark to advance research in speaker-aware multimodal understanding.

论文简评: 这篇论文提出了一个新的多模态大语言模型基准M3-SLU,用于评估多说话人多轮次的口语理解。动机在于现有模型虽然在语音和文本理解上表现良好,但在识别说话人方面仍存在困难。M3-SLU包含从四个开放语料库构建的12,000多个实例,任务包括说话人属性问答和通过话语匹配进行说话人归属。实验表明,现有模型在理解对话内容方面表现尚可,但在识别说话人上仍有显著差距,揭示了多说话人理解的关键挑战。
5.GigaBrain-0: A World Model-Powered Vision-Language-Action Model
Authors: GigaBrain Team, Angen Ye, Boyuan Wang, Chaojun Ni, Guan Huang, Guosheng Zhao, Haoyun Li, Jie Li, Jiagang Zhu, Lv Feng, Peng Li, Qiuping Deng, Runqi Ouyang, Wenkang Qin, Xinze Chen, Xiaofeng Wang, Yang Wang, Yifan Li, Yilong Li, Yiran Ding, Yuan Xu, Yun Ye, Yukun Zhou, Zhehao Dong, Zhenan Wang , et al. (2 additional authors not shown)
Affiliations: GigaAI
https://arxiv.org/abs/2510.19430
论文摘要
Training Vision-Language-Action (VLA) models for generalist robots typically requires large-scale real-world robot data, which is expensive and time-consuming to collect. The inefficiency of physical data collection severely limits the scalability, and generalization capacity of current VLA systems. To address this challenge, we introduce GigaBrain-0, a novel VLA foundation model empowered by world model-generated data (e.g., video generation, real2real transfer, human transfer, view transfer, sim2real transfer data). By leveraging world models to generate diverse data at scale, GigaBrain-0 significantly reduces reliance on real robot data while improving cross-task generalization. Our approach further improves policy robustness through RGBD input modeling and embodied Chain-of-Thought (CoT) supervision, enabling the model to reason about spatial geometry, object states, and long-horizon dependencies during task execution. This leads to substantial gains in real-world performance on dexterous, long-horizon, and mobile manipulation tasks. Extensive experiments demonstrate that GigaBrain-0 achieves superior generalization across variations in appearances (e.g., textures, colors), object placements, and camera viewpoints. Additionally, we present GigaBrain-0-Small, an optimized lightweight variant designed to run efficiently on devices such as the NVIDIA Jetson AGX Orin.
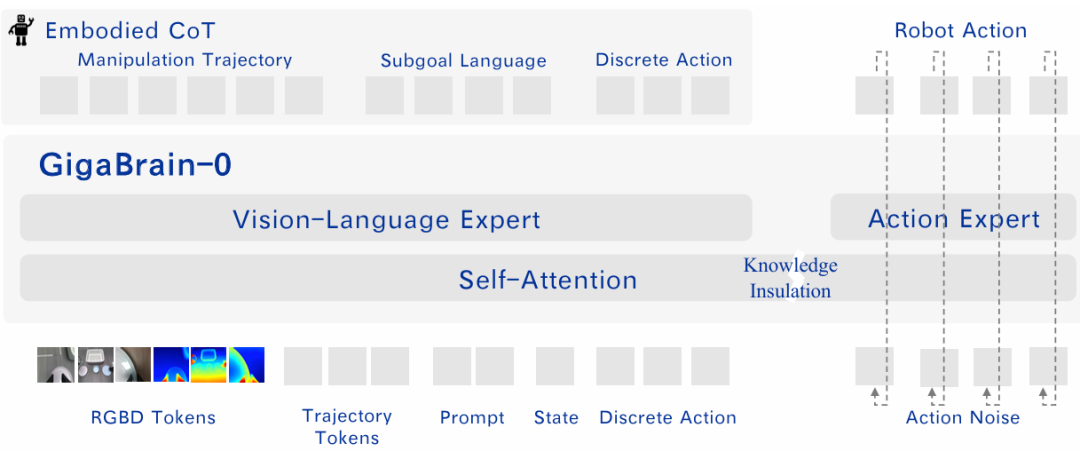
论文简评: 这篇论文探讨了训练通用机器人所需的视觉-语言-动作模型(VLA)的数据收集瓶颈。论文提出了GigaBrain-0,这是一种利用世界模型生成数据的VLA基础模型,旨在减少对真实机器人数据的依赖并提高任务泛化能力。通过使用合成数据和增强的RGBD输入建模,该模型展示了在多样化环境中的优异表现,尤其是在长时间和复杂操作任务中。此外,GigaBrain-0-Small的提出展示了其在低功耗设备上的有效性。整体实验结果表明,该方法在外观变化、物体放置和摄像机视角变化的条件下表现优异。
6.Pico-Banana-400K: A Large-Scale Dataset for Text-Guided Image Editing
Authors: Yusu Qian, Eli Bocek-Rivele, Liangchen Song, Jialing Tong, Yinfei Yang, Jiasen Lu, Wenze Hu, Zhe Gan
Affiliations: Apple
https://arxiv.org/abs/2510.19808
论文摘要
Recent advances in multimodal models have demonstrated remarkable text-guided image editing capabilities, with systems like GPT-4o and Nano-Banana setting new benchmarks. However, the research community’s progress remains constrained by the absence of large-scale, high-quality, and openly accessible datasets built from real images. We introduce Pico-Banana-400K, a comprehensive 400K-image dataset for instruction-based image editing. Our dataset is constructed by leveraging Nano-Banana to generate diverse edit pairs from real photographs in the OpenImages collection. What distinguishes Pico-Banana-400K from previous synthetic datasets is our systematic approach to quality and diversity. We employ a fine-grained image editing taxonomy to ensure comprehensive coverage of edit types while maintaining precise content preservation and instruction faithfulness through MLLM-based quality scoring and careful curation. Beyond single turn editing, Pico-Banana-400K enables research into complex editing scenarios. The dataset includes three specialized subsets: (1) a 72K-example multi-turn collection for studying sequential editing, reasoning, and planning across consecutive modifications; (2) a 56K-example preference subset for alignment research and reward model training; and (3) paired long-short editing instructions for developing instruction rewriting and summarization capabilities. By providing this large-scale, high-quality, and task-rich resource, Pico-Banana-400K establishes a robust foundation for training and benchmarking the next generation of text-guided image editing models.
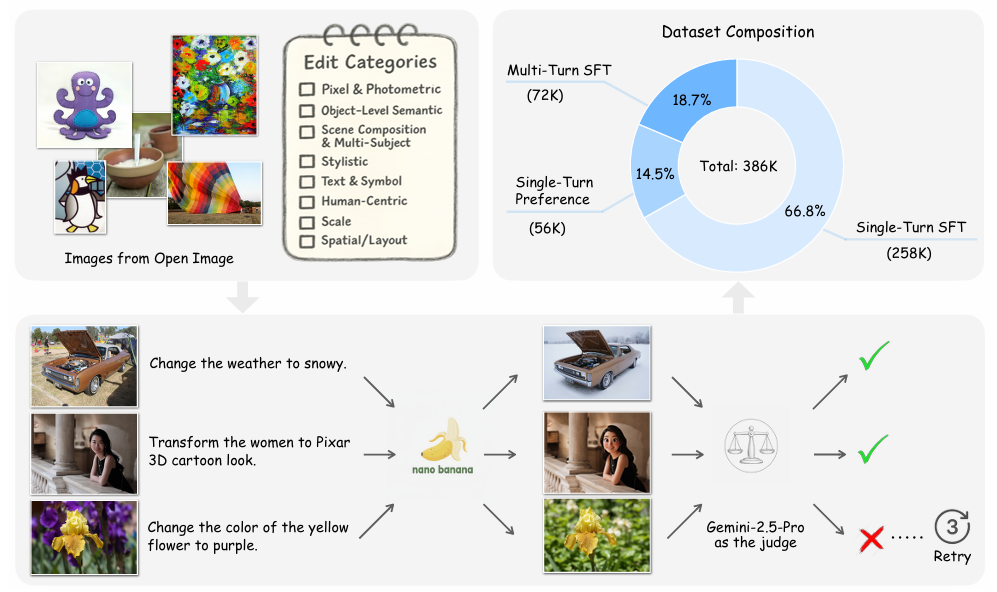
论文简评: 这篇论文介绍了一个名为Pico-Banana-400K的大规模数据集,旨在解决现有图像编辑数据集缺乏高质量、多样性以及可共享性的问题。通过利用先进的多模态大模型和自动化质量控制方法,作者构建了一个涵盖35种编辑类型的约40万例的图像编辑数据集。实验结果表明,该数据集在全局风格化变换上表现良好,但在精细几何布局和排版上仍存在挑战。此数据集为未来图像编辑模型的开发提供了丰富的训练资源。
7.I Spy With My Model’s Eye: Visual Search as a Behavioural Test for MLLMs
Authors: John Burden, Jonathan Prunty, Ben Slater, Matthieu Tehenan, Greg Davis, Lucy Cheke
Affiliations: University of Cambridge
https://arxiv.org/abs/2510.19678
论文摘要
Multimodal large language models (MLLMs) achieve strong performance on vision-language tasks, yet their visual processing is opaque. Most black-box evaluations measure task accuracy, but reveal little about underlying mechanisms. Drawing on cognitive psychology, we adapt classic visual search paradigms – originally developed to study human perception – to test whether MLLMs exhibit the pop-out effect, where salient visual features are detected independently of distractor set size. Using controlled experiments targeting colour, size and lighting features, we find that advanced MLLMs exhibit human-like pop-out effects in colour or size-based disjunctive (single feature) search, as well as capacity limits for conjunctive (multiple feature) search. We also find evidence to suggest that MLLMs, like humans, incorporate natural scene priors such as lighting direction into object representations. We reinforce our findings using targeted fine-tuning and mechanistic interpretability analyses. Our work shows how visual search can serve as a cognitively grounded diagnostic tool for evaluating perceptual capabilities in MLLMs.
论文简评: 这篇论文研究了多模态大语言模型(MLLMs)在视觉处理中的不透明性,动机在于通过视觉搜索实验揭示这些模型的内部机制。采用经典的视觉搜索范式,作者设计了实验以测试MLLMs是否展现类似于人类的“pop-out”效应。实验结果显示,先进的MLLMs在颜色或大小为基础的搜索中表现出人类般的“pop-out”效应,但在需要整合多个特征的搜索中表现出能力限制。论文通过针对性微调和机制解释分析强化了这些发现,证明视觉搜索可以作为评估MLLMs感知能力的工具。
8.Proactive Reasoning-with-Retrieval Framework for Medical Multimodal Large Language Models
Authors: Lehan Wang, Yi Qin, Honglong Yang, Xiaomeng Li
Affiliations: The Hong Kong University of Science and Technology
https://arxiv.org/abs/2510.18303
论文摘要
Incentivizing the reasoning ability of Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) is essential for medical applications to transparently analyze medical scans and provide reliable diagnosis. However, existing medical MLLMs rely solely on internal knowledge during reasoning, leading to hallucinated reasoning and factual inaccuracies when encountering cases beyond their training scope. Although recent Agentic Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) methods elicit the medical model’s proactive retrieval ability during reasoning, they are confined to unimodal LLMs, neglecting the crucial visual information during reasoning and retrieval. Consequently, we propose the first Multimodal Medical Reasoning-with-Retrieval framework, Med-RwR, which actively retrieves external knowledge by querying observed symptoms or domain-specific medical concepts during reasoning. Specifically, we design a two-stage reinforcement learning strategy with tailored rewards that stimulate the model to leverage both visual diagnostic findings and textual clinical information for effective retrieval. Building on this foundation, we further propose a Confidence-Driven Image Re-retrieval (CDIR) method for test-time scaling when low prediction confidence is detected. Evaluation on various public medical benchmarks demonstrates Med-RwR’s significant improvements over baseline models, proving the effectiveness of enhancing reasoning capabilities with external knowledge integration. Furthermore, Med-RwR demonstrates remarkable generalizability to unfamiliar domains, evidenced by 8.8% performance gain on our proposed EchoCardiography Benchmark (ECBench), despite the scarcity of echocardiography data in the training corpus. Our data, model, and codes will be made publicly available at https://github.com/xmed-lab/Med-RwR.
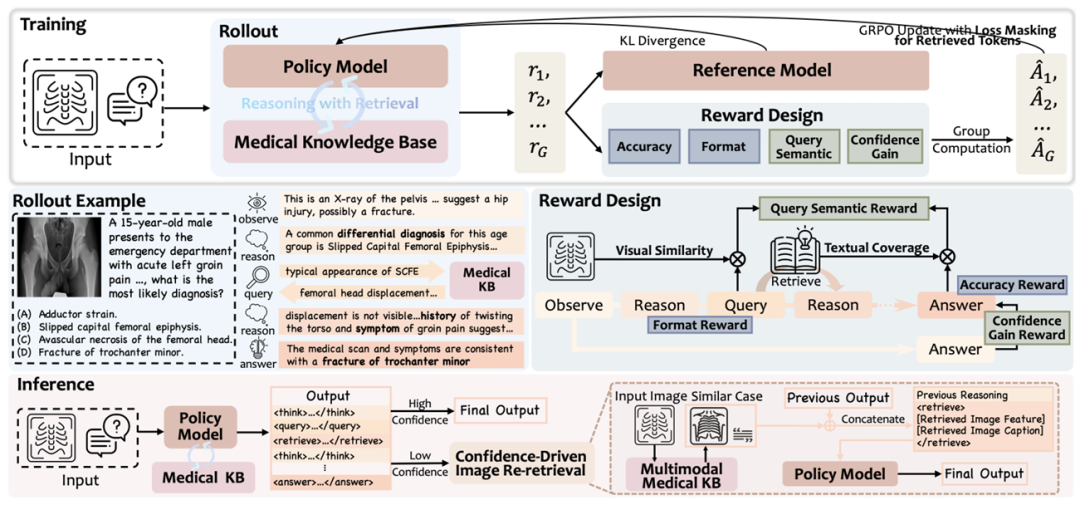
论文简评: 这篇论文的动机在于提升医疗多模态大语言模型(MLLMs)的推理能力,以便更好地分析医学影像并提供可靠的诊断。传统的医疗MLLMs在推理时仅依赖内部知识,可能导致虚构的推理和事实错误。为解决此问题,作者提出了一个多模态医学推理与检索框架(MED-RWR),通过查询外部知识来增强推理过程。具体来说,论文设计了一种两阶段的强化学习策略,激励模型结合视觉和文本信息进行检索。实验结果表明,MED-RWR在多个公共医疗基准测试上表现优于基线模型,并在数据稀缺的领域(如超声心动图)显示出显著的泛化能力。
9.Think with 3D: Geometric Imagination Grounded Spatial Reasoning from Limited Views
Authors: Zhangquan Chen, Manyuan Zhang, Xinlei Yu, Xufang Luo, Mingze Sun, Zihao Pan, Yan Feng, Peng Pei, Xunliang Cai, Ruqi Huang
Affiliations: Tsinghua University; Meituan; National University of Singapore
https://arxiv.org/abs/2510.18632
论文摘要
Though recent advances in vision-language models (VLMs) have achieved remarkable progress across a wide range of multimodal tasks, understanding 3D spatial relationships from limited views remains a significant challenge. Previous reasoning methods typically rely on pure text (e.g., topological cognitive maps) or on 2D visual cues. However, their limited representational capacity hinders performance in specific tasks that require 3D spatial imagination. To address this limitation, we propose 3DThinker, a framework that can effectively exploits the rich geometric information embedded within images while reasoning, like humans do. Our framework is the first to enable 3D mentaling during reasoning without any 3D prior input, and it does not rely on explicitly labeled 3D data for training. Specifically, our training consists of two stages. First, we perform supervised training to align the 3D latent generated by VLM while reasoning with that of a 3D foundation model (e.g., VGGT). Then, we optimize the entire reasoning trajectory solely based on outcome signals, thereby refining the underlying 3D mentaling. Extensive experiments across multiple benchmarks show that 3DThinker consistently outperforms strong baselines and offers a new perspective toward unifying 3D representations into multimodal reasoning. Our code will be available at https://github.com/zhangquanchen/3DThinker.
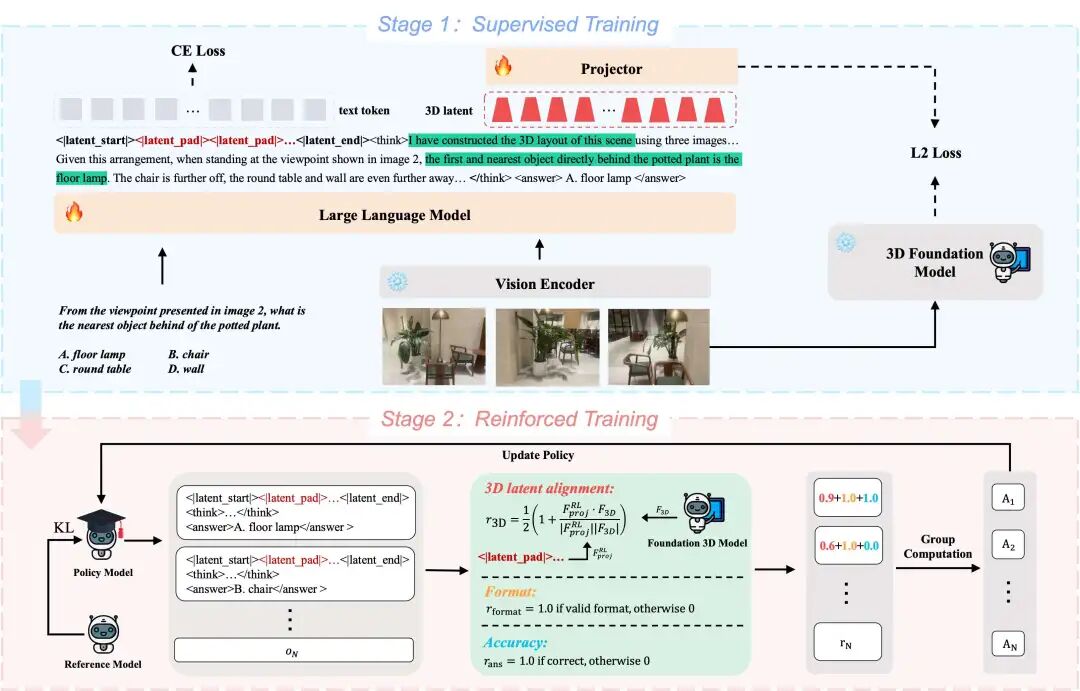
论文简评: 这篇论文探讨了在有限视角下进行3D空间推理的挑战,并提出了一个名为3DThinker的新框架。3DThinker通过利用视觉语言模型中的3D潜在表示进行推理,无需依赖显式标注的3D数据。该方法包括两个训练阶段:首先通过监督学习将3D潜在特征对齐,然后通过强化学习优化推理轨迹。实验结果表明,3DThinker在多个基准测试中均优于现有的强基线模型,并展示了将3D表示统一到多模态推理中的新视角。
10.IF-VidCap: Can Video Caption Models Follow Instructions?
Authors: Shihao Li, Yuanxing Zhang, Jiangtao Wu, Zhide Lei, Yiwen He, Runzhe Wen, Chenxi Liao, Chengkang Jiang, An Ping, Shuo Gao, Suhan Wang, Zhaozhou Bian, Zijun Zhou, Jingyi Xie, Jiayi Zhou, Jing Wang, Yifan Yao, Weihao Xie, Yingshui Tan, Yanghai Wang, Qianqian Xie, Zhaoxiang Zhang, Jiaheng Li
Affiliations: Nanjing University; Kuaishou Technology; Shanghai University; CASIA; M-A-P
https://arxiv.org/abs/2510.18726
论文摘要
Although Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) have demonstrated proficiency in video captioning, practical applications require captions that follow specific user instructions rather than generating exhaustive, unconstrained descriptions. Current benchmarks, however, primarily assess descriptive comprehensiveness while largely overlooking instruction-following capabilities. To address this gap, we introduce IF-VidCap, a new benchmark for evaluating controllable video captioning, which contains 1,400 high-quality samples. Distinct from existing video captioning or general instruction-following benchmarks, IF-VidCap incorporates a systematic framework that assesses captions on two dimensions: format correctness and content correctness. Our comprehensive evaluation of over 20 prominent models reveals a nuanced landscape: despite the continued dominance of proprietary models, the performance gap is closing, with top-tier open-source solutions now achieving near-parity. Furthermore, we find that models specialized for dense captioning underperform general-purpose MLLMs on complex instructions, indicating that future work should simultaneously advance both descriptive richness and instruction-following fidelity.
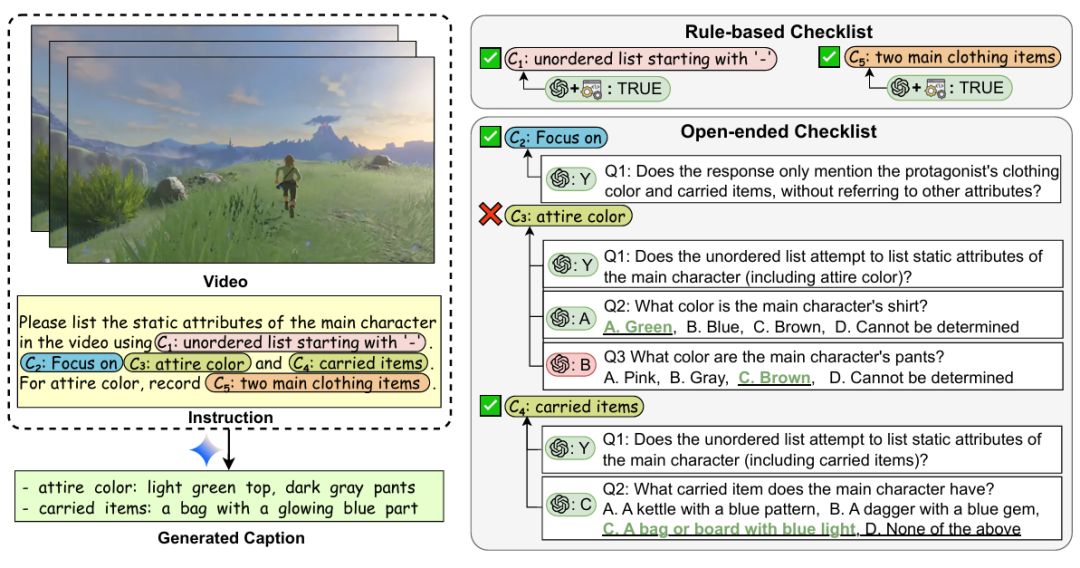
论文简评: 该论文提出了IF-VidCap,一个新的基准,用于评估视频字幕模型在遵循复杂指令时的表现。动机在于现有的多模态大语言模型虽然在视频描述任务中表现良好,但在遵循细粒度指令方面仍存在显著差距。通过引入1,400条包含27种不同约束类型的指令,IF-VidCap测试了多种模型的能力,结果显示闭源模型通常优于开源模型。该研究还开发了一种新的训练数据集,并通过微调增强了模型的指令遵循能力。实验结果表明,IF-Captioner-Qwen在ISR和CSR指标上显著优于基础模型,验证了新基准和方法的有效性。
如何学习大模型 AI ?
我国在AI大模型领域面临人才短缺,数量与质量均落后于发达国家。2023年,人才缺口已超百万,凸显培养不足。随着Al技术飞速发展,预计到2025年,这一缺口将急剧扩大至400万,严重制约我国Al产业的创新步伐。加强人才培养,优化教育体系,国际合作并进,是破解困局、推动AI发展的关键。
但是具体到个人,只能说是:
“最先掌握AI的人,将会比较晚掌握AI的人有竞争优势”。
这句话,放在计算机、互联网、移动互联网的开局时期,都是一样的道理。
我在一线互联网企业工作十余年里,指导过不少同行后辈。帮助很多人得到了学习和成长。
我意识到有很多经验和知识值得分享给大家,也可以通过我们的能力和经验解答大家在人工智能学习中的很多困惑,所以在工作繁忙的情况下还是坚持各种整理和分享。但苦于知识传播途径有限,很多互联网行业朋友无法获得正确的资料得到学习提升,故此将重要的AI大模型资料包括AI大模型入门学习思维导图、精品AI大模型学习书籍手册、视频教程、实战学习等录播视频免费分享出来。

2025最新大模型学习路线
明确的学习路线至关重要。它能指引新人起点、规划学习顺序、明确核心知识点。大模型领域涉及的知识点非常广泛,没有明确的学习路线可能会导致新人感到迷茫,不知道应该专注于哪些内容。
对于从来没有接触过AI大模型的同学,我帮大家准备了从零基础到精通学习成长路线图以及学习规划。可以说是最科学最系统的学习路线。

针对以上大模型的学习路线我们也整理了对应的学习视频教程,和配套的学习资料。
大模型经典PDF书籍
新手必备的大模型学习PDF书单来了!全是硬核知识,帮你少走弯路!

配套大模型项目实战
所有视频教程所涉及的实战项目和项目源码等

博主介绍+AI项目案例集锦
MoPaaS专注于Al技术能力建设与应用场景开发,与智学优课联合孵化,培养适合未来发展需求的技术性人才和应用型领袖。

这份完整版的大模型 AI 学习资料已经上传优快云,朋友们如果需要可以微信扫描下方优快云官方认证二维码免费领取【保证100%免费】

为什么要学习大模型?
2025人工智能大模型的技术岗位与能力培养随着人工智能技术的迅速发展和应用 , 大模型作为其中的重要组成部分 , 正逐渐成为推动人工智能发展的重要引擎 。大模型以其强大的数据处理和模式识别能力, 广泛应用于自然语言处理 、计算机视觉 、 智能推荐等领域 ,为各行各业带来了革命性的改变和机遇 。

适合人群
- 在校学生:包括专科、本科、硕士和博士研究生。学生应具备扎实的编程基础和一定的数学基础,有志于深入AGI大模型行业,希望开展相关的研究和开发工作。
- IT行业从业人员:包括在职或失业者,涵盖开发、测试、运维、产品经理等职务。拥有一定的IT从业经验,至少1年以上的编程工作经验,对大模型技术感兴趣或有业务需求,希望通过课程提升自身在IT领域的竞争力。
- IT管理及技术研究领域人员:包括技术经理、技术负责人、CTO、架构师、研究员等角色。这些人员需要跟随技术发展趋势,主导技术创新,推动大模型技术在企业业务中的应用与改造。
- 传统AI从业人员:包括算法工程师、机器视觉工程师、深度学习工程师等。这些AI技术人才原先从事机器视觉、自然语言处理、推荐系统等领域工作,现需要快速补充大模型技术能力,获得大模型训练微调的实操技能,以适应新的技术发展趋势。

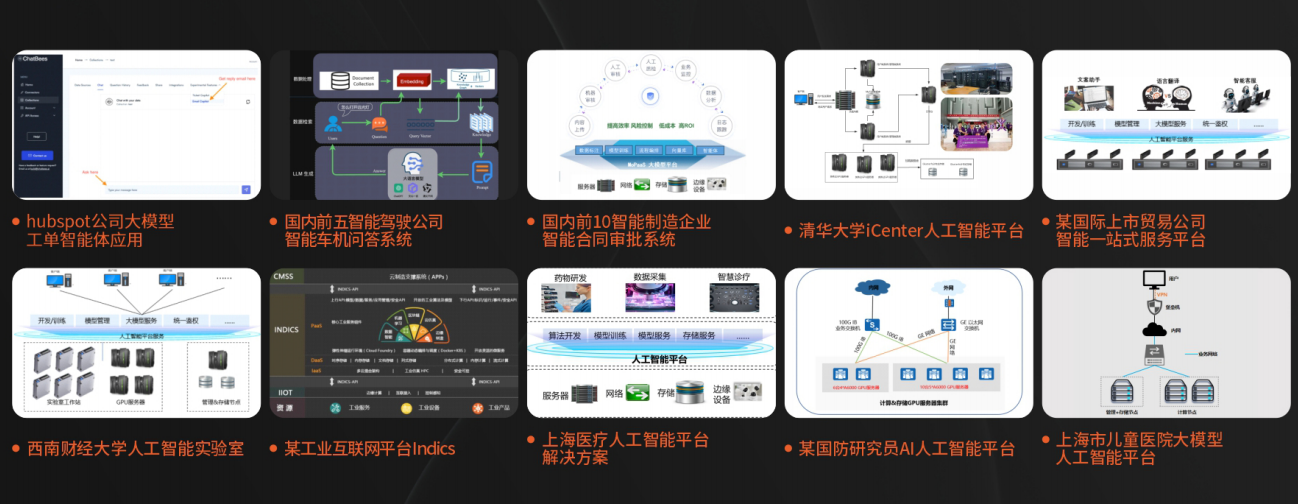
课程精彩瞬间
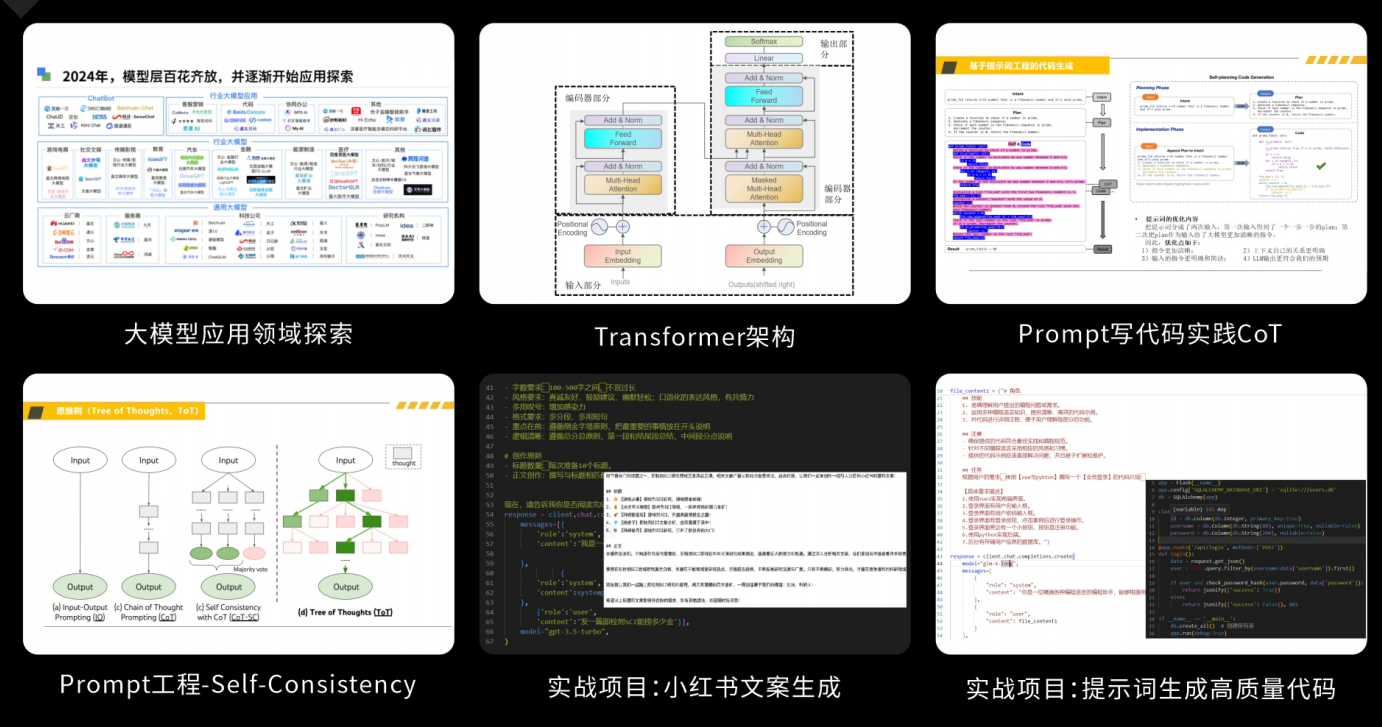
大模型核心原理与Prompt:掌握大语言模型的核心知识,了解行业应用与趋势;熟练Python编程,提升提示工程技能,为Al应用开发打下坚实基础。
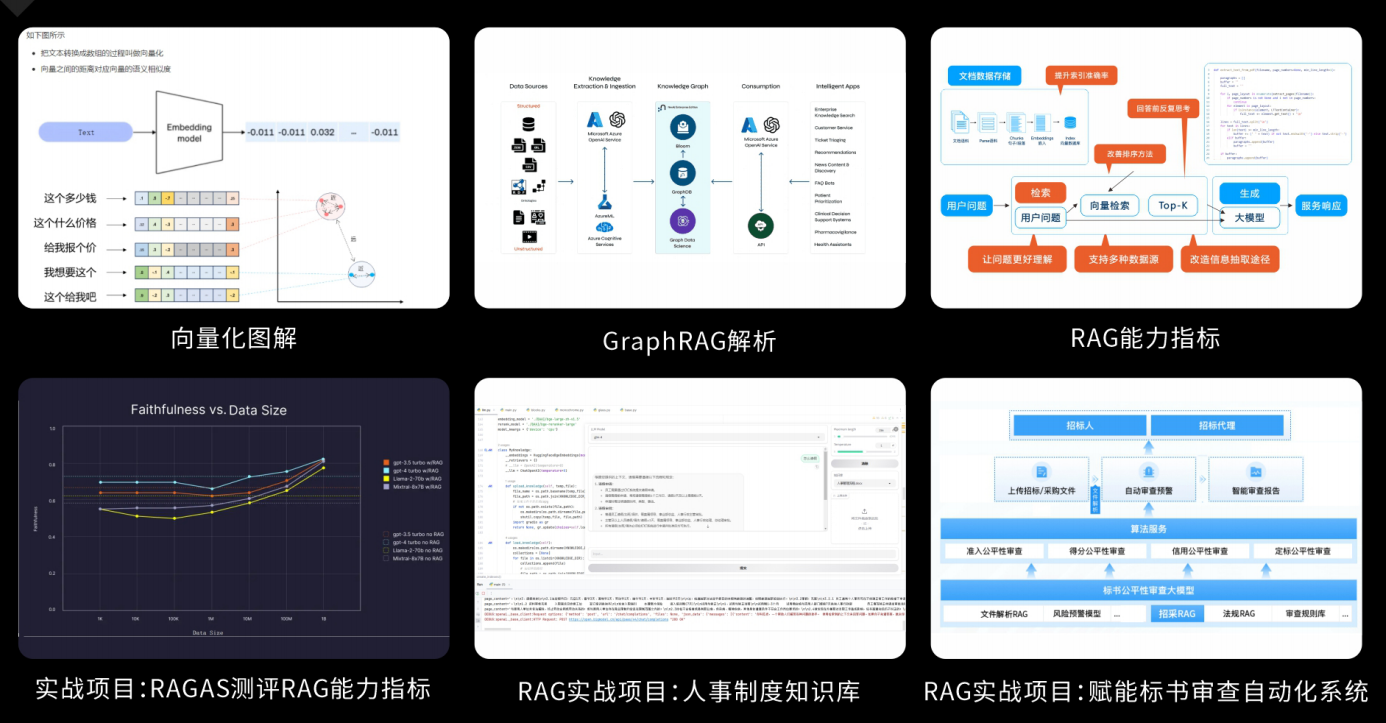
RAG应用开发工程:掌握RAG应用开发全流程,理解前沿技术,提升商业化分析与优化能力,通过实战项目加深理解与应用。
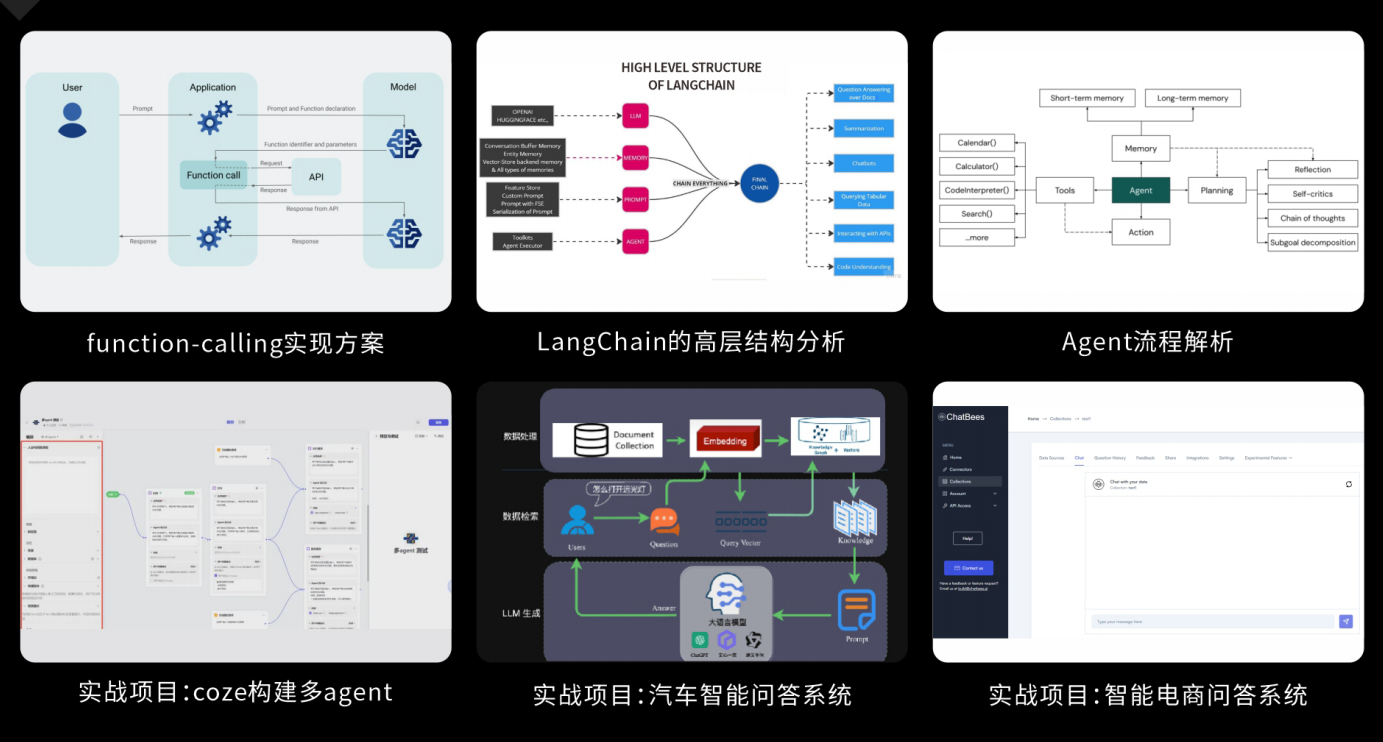
Agent应用架构进阶实践:掌握大模型Agent技术的核心原理与实践应用,能够独立完成Agent系统的设计与开发,提升多智能体协同与复杂任务处理的能力,为AI产品的创新与优化提供有力支持。
模型微调与私有化大模型:掌握大模型微调与私有化部署技能,提升模型优化与部署能力,为大模型项目落地打下坚实基础。
顶尖师资,深耕AI大模型前沿技术
实战专家亲授,让你少走弯路

一对一学习规划,职业生涯指导
- 真实商业项目实训
- 大厂绿色直通车
人才库优秀学员参与真实商业项目实训
以商业交付标准作为学习标准,具备真实大模型项目实践操作经验可写入简历,支持项目背调
大厂绿色直通车,冲击行业高薪岗位
文中涉及到的完整版的大模型 AI 学习资料已经上传优快云,朋友们如果需要可以微信扫描下方优快云官方认证二维码免费领取【保证100%免费】























 22万+
22万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








