1.Words or Vision: Do Vision-Language Models Have Blind Faith in Text?
Authors:Ailin Deng, Tri Cao, Zhirui Chen, Bryan Hooi
Affiliations: National University of Singapore
https://arxiv.org/abs/2503.02199
论文摘要
Vision-Language Models (VLMs) excel in integrating visual and textual information for vision-centric tasks, but their handling of inconsistencies between modalities is underexplored. We investigate VLMs’ modality preferences when faced with visual data and varied textual inputs in vision-centered settings. By introducing textual variations to four vision-centric tasks and evaluating ten Vision-Language Models (VLMs), we discover a blind faith in text phenomenon: VLMs disproportionately trust textual data over visual data when inconsistencies arise, leading to significant performance drops under corrupted text and raising safety concerns. We analyze factors influencing this text bias, including instruction prompts, language model size, text relevance, token order, and the interplay between visual and textual certainty. While certain factors, such as scaling up the language model size, slightly mitigate text bias, others like token order can exacerbate it due to positional biases inherited from language models. To address this issue, we explore supervised fine-tuning with text augmentation and demonstrate its effectiveness in reducing text bias. Additionally, we provide a theoretical analysis suggesting that the blind faith in text phenomenon may stem from an imbalance of pure text and multi-modal data during training. Our findings highlight the need for balanced training and careful consideration of modality interactions in VLMs to enhance their robustness and reliability in handling multi-modal data inconsistencies.
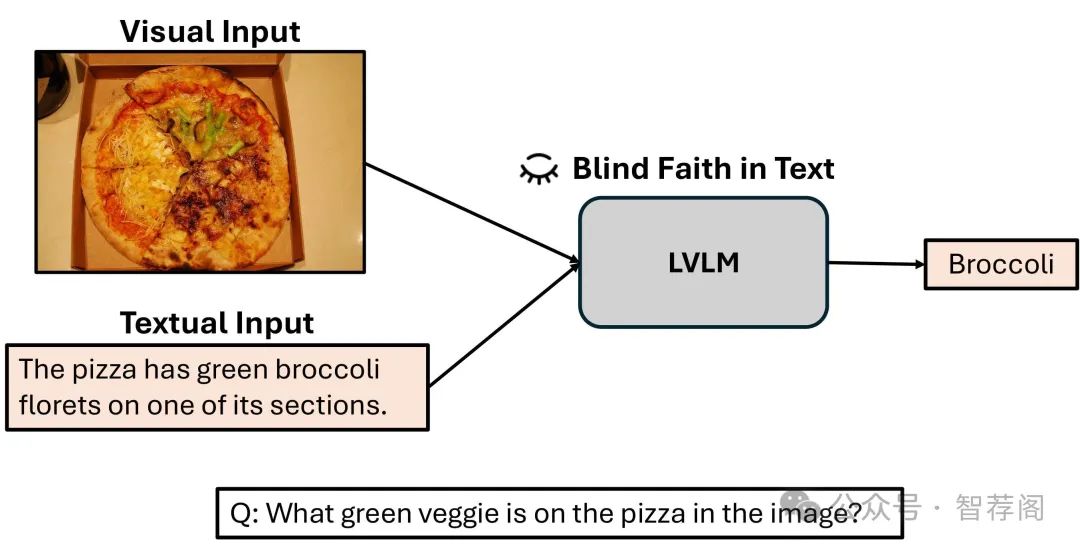
论文简评: 该论文《"盲信文本现象"在视觉语言模型(Vision-Language Models, VLMs)中的表现》深入探讨了视觉语言模型(VLMs)中“文本依赖过度”这一现象,即这些模型过于信任文本数据而忽视图像信息,尤其是在出现矛盾时。作者通过分析十种不同的视觉语言模型(VLMs)在不同任务中的表现,揭示了导致这种文本偏见的因素,并提出了通过监督式微调与文本增强来缓解这一问题的解决方案。研究结果强调了安全性的潜在风险,因为模型在受污染的文本输入下可能会表现出性能下降。论文提供了对视觉语言模型中可能存在的潜在安全漏洞的关注,为未来的研究提供了指导方向。
2.Investigating and Enhancing Vision-Audio Capability in Omnimodal Large Language Models
Authors:Rui Hu, Delai Qiu, Shuyu Wei, Jiaming Zhang, Yining Wang, Shengping Liu, Jitao Sang
Affiliations: Beijing Jiaotong University; Unisound AI Technology Co., Ltd.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2503.00059
论文摘要
Omnimodal Large Language Models (OLLMs) have shown significant progress in integrating vision and text, but still struggle with integrating vision and audio, often exhibiting suboptimal performance when processing audio queries compared to text queries. This disparity is primarily due to insufficient alignment between vision and audio modalities during training, leading to inadequate attention to visual information when using audio queries. To mitigate this issue, we propose a Self-Knowledge Distillation (Self-KD) training method where the vision-text component of the OLLM serves as the teacher and the vision-audio component as the student. This enables the model to process audio in a manner analogous to its text processing. Our experimental results demonstrate that Self-KD is an effective method for enhancing the vision-audio capabilities of OLLMs by learning from the vision-text components, which subsequently improves the interaction between audio and images and results in improved performance on multimodal tasks.

论文简评: 该篇论文针对Omni-modal Large Language Models(OLLMs)处理视觉-音频任务时出现的性能差距进行了深入研究。作者提出了一种名为自知识蒸馏(Self-KD)的方法,旨在通过使用视觉文本组件作为音频图像组件的知识蒸馏教师来增强视觉-音频能力。实验结果表明,自知识蒸馏提高了音频与图像之间的互动性,尽管性能仍然落后于视觉-文本任务。
该论文的关键在于对一个重要问题——如何在Ollms中整合视觉和音频的能力——进行了深入分析,并提出了一个创新性的自知识蒸馏方法。此外,论文还详细描述了实验结果,显示了自知识蒸馏在提高视觉-音频性能方面的效果。因此,该文整体内容丰富且结构清晰,重点突出,对于理解和解决Ollms中的视觉-音频交互问题具有重要意义。
3.Delving into Out-of-Distribution Detection with Medical Vision-Language Models
Authors:Lie Ju, Sijin Zhou, Yukun Zhou, Huimin Lu, Zhuoting Zhu, Pearse A. Keane, Zongyuan Ge
Affiliations: Monash University; Moorfields Eye Hospital; University College London; Airdoc Technology Inc; Southeast University; Melbourne University
https://arxiv.org/abs/2503.01020
论文摘要
Recent advances in medical vision-language models (VLMs) demonstrate impressive performance in image classification tasks, driven by their strong zero-shot generalization capabilities. However, given the high variability and complexity inherent in medical imaging data, the ability of these models to detect out-of-distribution (OOD) data in this domain remains underexplored. In this work, we conduct the first systematic investigation into the OOD detection potential of medical VLMs. We evaluate state-of-the-art VLM-based OOD detection methods across a diverse set of medical VLMs, including both general and domain-specific purposes. To accurately reflect real-world challenges, we introduce a cross-modality evaluation pipeline for benchmarking full-spectrum OOD detection, rigorously assessing model robustness against both semantic shifts and covariate shifts. Furthermore, we propose a novel hierarchical prompt-based method that significantly enhances OOD detection performance. Extensive experiments are conducted to validate the effectiveness of our approach. The codes are available at https://github.com/PyJulie/Medical-VLMs-OOD-Detection.

论文简评: 该篇论文聚焦于对医疗视觉语言模型(VLMs)的脱域检测能力的研究,并提出了一种基于层次提示的高级方法来增强其性能。它评估了各种最先进的脱域检测方法,并引入了一个新的基准测试管道来解决与医学图像中语义和共变分量变化相关的挑战。
论文的核心在于解决了当前医疗VLM在处理脱域任务时面临的困难,特别是在临床应用中的重要性。论文提出的解决方案通过利用结构化的医学意义来进行高层次的提示,从而提高了VLM在脱域检测方面的表现。此外,论文还系统地评估了多种先进的脱域检测方法,这对于研究者们理解不同VLM之间的差异以及如何改进现有方法具有重要意义。
总的来说,这篇论文提供了对医疗VLM脱域检测能力的一次全面而深入的考察,展示了对于这一领域的重要贡献。通过对多种先进方法的比较和分析,论文为未来的研究提供了宝贵的视角和方向。
4.CognitiveDrone: A VLA Model and Evaluation Benchmark for Real-Time Cognitive Task Solving and Reasoning in UAVs
Authors:Artem Lykov, Valerii Serpiva, Muhammad Haris Khan, Oleg Sautenkov, Artyom Myshlyaev, Grik Tadevosyan, Yasheerah Yaqoot, Dzmitry Tsetserukou
Affiliations: Skolkovo Institute of Science and Technology
https://arxiv.org/abs/2503.01378
论文摘要
This paper introduces CognitiveDrone, a novel Vision-Language-Action (VLA) model tailored for complex Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs) tasks that demand advanced cognitive abilities. Trained on a dataset comprising over 8,000 simulated flight trajectories across three key categories-Human Recognition, Symbol Understanding, and Reasoning-the model generates real-time 4D action commands based on first-person visual inputs and textual instructions. To further enhance performance in intricate scenarios, we propose CognitiveDrone-R1, which integrates an additional Vision-Language Model (VLM) reasoning module to simplify task directives prior to high-frequency control. Experimental evaluations using our open-source benchmark, CognitiveDroneBench, reveal that while a racing-oriented model (RaceVLA) achieves an overall success rate of 31.3%, the base CognitiveDrone model reaches 59.6%, and CognitiveDrone-R1 attains a success rate of 77.2%. These results demonstrate improvements of up to 30% in critical cognitive tasks, underscoring the effectiveness of incorporating advanced reasoning capabilities into UAV control systems. Our contributions include the development of a state-of-the-art VLA model for UAV control and the introduction of the first dedicated benchmark for assessing cognitive tasks in drone operations. The complete repository is available at this http URL.

论文简评: 该论文提出了一种名为CognitiveDrone的新框架和评估基准(CognitiveDroneBench),旨在增强无人机(UAV)的认知能力以实时解决复杂的任务。通过使用超过8,000个模拟飞行轨迹的数据集,以及引入CognitiveDroneR1辅助推理模块,研究显示了显著的任务性能改进,特别是在集成辅助推理模块后。研究成果提供了数据支持,证明了引入推理能力的有效性,并提供了一个全面的数据集和一个开源平台,有助于进一步研究无人机认知控制系统。
5.Visual-RFT: Visual Reinforcement Fine-Tuning
Authors:Ziyu Liu, Zeyi Sun, Yuhang Zang, Xiaoyi Dong, Yuhang Cao, Haodong Duan, Dahua Lin, Jiaqi Wang
Affiliations: Shanghai Jiaotong University; Shanghai Artificial Intelligence Laboratory; The Chinese University of Hong Kong
https://arxiv.org/abs/2503.01785
论文摘要
Reinforcement Fine-Tuning (RFT) in Large Reasoning Models like OpenAI o1 learns from feedback on its answers, which is especially useful in applications when fine-tuning data is scarce. Recent open-source work like DeepSeek-R1 demonstrates that reinforcement learning with verifiable reward is one key direction in reproducing o1. While the R1-style model has demonstrated success in language models, its application in multi-modal domains remains under-explored. This work introduces Visual Reinforcement Fine-Tuning (Visual-RFT), which further extends the application areas of RFT on visual tasks. Specifically, Visual-RFT first uses Large Vision-Language Models (LVLMs) to generate multiple responses containing reasoning tokens and final answers for each input, and then uses our proposed visual perception verifiable reward functions to update the model via the policy optimization algorithm such as Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO). We design different verifiable reward functions for different perception tasks, such as the Intersection over Union (IoU) reward for object detection. Experimental results on fine-grained image classification, few-shot object detection, reasoning grounding, as well as open-vocabulary object detection benchmarks show the competitive performance and advanced generalization ability of Visual-RFT compared with Supervised Fine-tuning (SFT). For example, Visual-RFT improves accuracy by 24.3% over the baseline in one-shot fine-grained image classification with around 100 samples. In few-shot object detection, Visual-RFT also exceeds the baseline by 21.9 on COCO’s two-shot setting and 15.4 on LVIS. Our Visual-RFT represents a paradigm shift in fine-tuning LVLMs, offering a data-efficient, reward-driven approach that enhances reasoning and adaptability for domain-specific tasks.
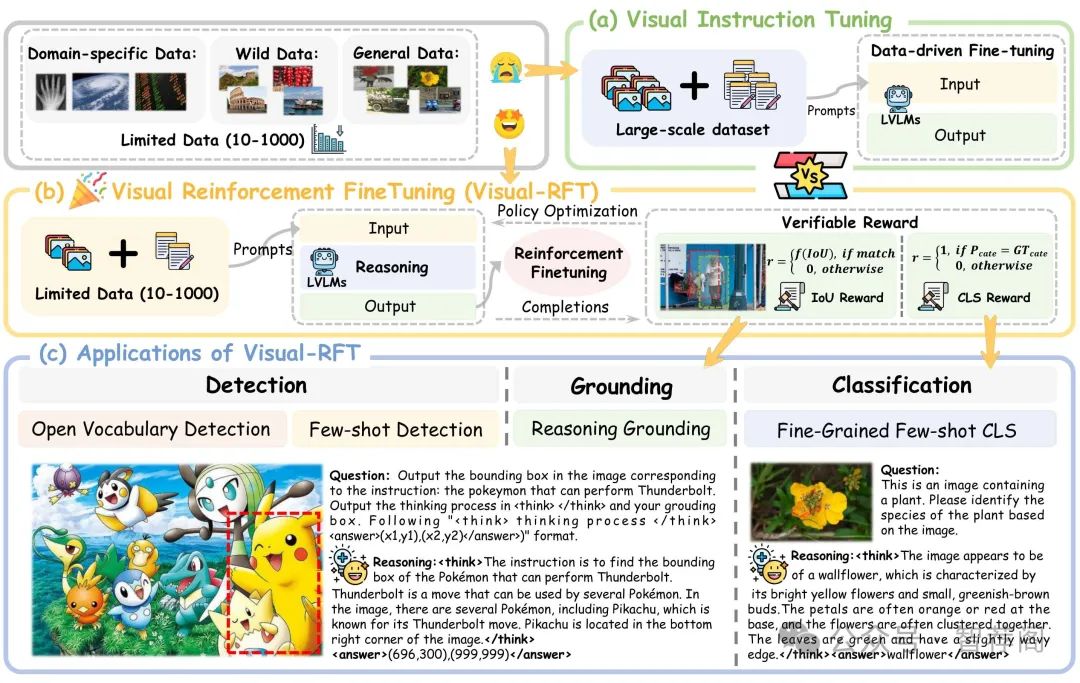
论文简评: 在这篇关于视觉强化强化学习(Visual Reinforcement Fine-Tuning)的研究中,作者提出了一个新颖的方法来扩展强化学习到视觉任务,并使用可验证奖励来增强大型视图语言模型(LVLMs)的表现。该研究声称,在多种视觉感知任务上取得了显著的进步,相比传统的监督式微调(Supervised Fine-Tuning),这种方法显示了其有效性。
论文的核心在于引入一种新的方法——Visual-RFT,旨在利用可验证的奖励来增强大型视觉语言模型的性能。通过实验结果,研究人员证实了这种方法的有效性,尤其是在多个视觉感知任务上的表现。此外,开放源代码和数据集的发布也鼓励了后续的研究者对这项工作进行复制和改进。
综上所述,这篇论文的主要贡献在于提出了一种创新的方法——Visual-RFT,用于增强大型视觉语言模型在视觉任务中的性能,并通过实验结果证明了其有效性。同时,该研究还强调了共享开源资源的重要性,为其他研究者提供了便利。因此,本文可以被视为是视觉领域的一项重要成果,值得进一步深入研究和应用。
如何学习大模型 AI ?
由于新岗位的生产效率,要优于被取代岗位的生产效率,所以实际上整个社会的生产效率是提升的。
但是具体到个人,只能说是:
“最先掌握AI的人,将会比较晚掌握AI的人有竞争优势”。
这句话,放在计算机、互联网、移动互联网的开局时期,都是一样的道理。
我在一线互联网企业工作十余年里,指导过不少同行后辈。帮助很多人得到了学习和成长。
我意识到有很多经验和知识值得分享给大家,也可以通过我们的能力和经验解答大家在人工智能学习中的很多困惑,所以在工作繁忙的情况下还是坚持各种整理和分享。但苦于知识传播途径有限,很多互联网行业朋友无法获得正确的资料得到学习提升,故此将并将重要的AI大模型资料包括AI大模型入门学习思维导图、精品AI大模型学习书籍手册、视频教程、实战学习等录播视频免费分享出来。

第一阶段(10天):初阶应用
该阶段让大家对大模型 AI有一个最前沿的认识,对大模型 AI 的理解超过 95% 的人,可以在相关讨论时发表高级、不跟风、又接地气的见解,别人只会和 AI 聊天,而你能调教 AI,并能用代码将大模型和业务衔接。
- 大模型 AI 能干什么?
- 大模型是怎样获得「智能」的?
- 用好 AI 的核心心法
- 大模型应用业务架构
- 大模型应用技术架构
- 代码示例:向 GPT-3.5 灌入新知识
- 提示工程的意义和核心思想
- Prompt 典型构成
- 指令调优方法论
- 思维链和思维树
- Prompt 攻击和防范
- …
第二阶段(30天):高阶应用
该阶段我们正式进入大模型 AI 进阶实战学习,学会构造私有知识库,扩展 AI 的能力。快速开发一个完整的基于 agent 对话机器人。掌握功能最强的大模型开发框架,抓住最新的技术进展,适合 Python 和 JavaScript 程序员。
- 为什么要做 RAG
- 搭建一个简单的 ChatPDF
- 检索的基础概念
- 什么是向量表示(Embeddings)
- 向量数据库与向量检索
- 基于向量检索的 RAG
- 搭建 RAG 系统的扩展知识
- 混合检索与 RAG-Fusion 简介
- 向量模型本地部署
- …
第三阶段(30天):模型训练
恭喜你,如果学到这里,你基本可以找到一份大模型 AI相关的工作,自己也能训练 GPT 了!通过微调,训练自己的垂直大模型,能独立训练开源多模态大模型,掌握更多技术方案。
到此为止,大概2个月的时间。你已经成为了一名“AI小子”。那么你还想往下探索吗?
- 为什么要做 RAG
- 什么是模型
- 什么是模型训练
- 求解器 & 损失函数简介
- 小实验2:手写一个简单的神经网络并训练它
- 什么是训练/预训练/微调/轻量化微调
- Transformer结构简介
- 轻量化微调
- 实验数据集的构建
- …
第四阶段(20天):商业闭环
对全球大模型从性能、吞吐量、成本等方面有一定的认知,可以在云端和本地等多种环境下部署大模型,找到适合自己的项目/创业方向,做一名被 AI 武装的产品经理。
- 硬件选型
- 带你了解全球大模型
- 使用国产大模型服务
- 搭建 OpenAI 代理
- 热身:基于阿里云 PAI 部署 Stable Diffusion
- 在本地计算机运行大模型
- 大模型的私有化部署
- 基于 vLLM 部署大模型
- 案例:如何优雅地在阿里云私有部署开源大模型
- 部署一套开源 LLM 项目
- 内容安全
- 互联网信息服务算法备案
- …
学习是一个过程,只要学习就会有挑战。天道酬勤,你越努力,就会成为越优秀的自己。
如果你能在15天内完成所有的任务,那你堪称天才。然而,如果你能完成 60-70% 的内容,你就已经开始具备成为一名大模型 AI 的正确特征了。
这份完整版的大模型 AI 学习资料已经上传优快云,朋友们如果需要可以微信扫描下方优快云官方认证二维码免费领取【保证100%免费】





















 1214
1214

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








