本文是对GMSD图像质量评价指标的代码解读,原文解读请看GMSD文章讲解。
本文的代码来源于IQA-Pytorch工程。
1、原文概要
现有 FR-IQA 模型(如 FSIM)虽精度高,但计算复杂;部分模型(如 SSIM)虽然计算简单,但精度不够。作者想要提出兼具高预测精度和高计算效率的 FR-IQA 模型。实现该指标可以分为2个步骤:
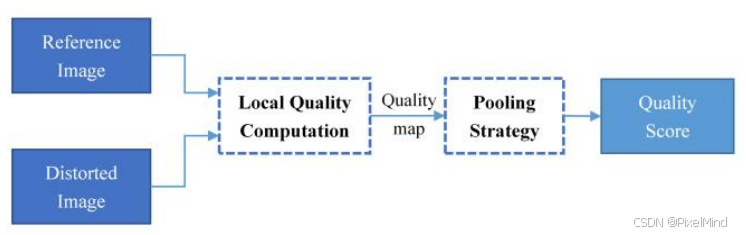
-
Local Quality Computation:用于描述局部区域的质量,使用用 3×3 Prewitt 滤波器来进行提取,公式如下所示。 h x = [ 1 / 3 0 − 1 / 3 1 / 3 0 − 1 / 3 1 / 3 0 − 1 / 3 ] , h y = [ 1 / 3 1 / 3 1 / 3 0 0 0 − 1 / 3 − 1 / 3 − 1 / 3 ] \mathbf{h}_x = \begin{bmatrix} 1/3 & 0 & -1/3 \\ 1/3 & 0 & -1/3 \\ 1/3 & 0 & -1/3 \end{bmatrix}, \quad \mathbf{h}_y = \begin{bmatrix} 1/3 & 1/3 & 1/3 \\ 0 & 0 & 0 \\ -1/3 & -1/3 & -1/3 \end{bmatrix} hx= 1/31/31/3000−1/3−1/3−1/3 ,hy= 1/30−1/31/30−1/31/30−1/3 提取完x和y方向的梯度后,使用以下公式,获取梯度幅值。 m r ( i ) = ( r ⊗ h x ) 2 ( i ) + ( r ⊗ h y ) 2 ( i ) m d ( i ) = ( d ⊗ h x ) 2 ( i ) + ( d ⊗ h y ) 2 ( i ) \mathbf{m}_r(i) = \sqrt{( \mathbf{r} \otimes \mathbf{h}_x )^2 (i) + ( \mathbf{r} \otimes \mathbf{h}_y )^2 (i)} \\ \mathbf{m}_d(i) = \sqrt{( \mathbf{d} \otimes \mathbf{h}_x )^2 (i) + ( \mathbf{d} \otimes \mathbf{h}_y )^2 (i)} mr(i)=(r⊗hx)2(i)+(r⊗hy)2(i)md(i)=(d⊗hx)2(i)+(d⊗hy)2(i) m r \text{m}_{\text r} mr与 m d \text{m}_{\text d} md分别是参考图和退化图的梯度幅值。最后再计算相似度就可以得到局部的质量估计了。 G M S ( i ) = 2 m r ( i ) m d ( i ) + c m r 2 ( i ) + m d 2 ( i ) + c GMS(i) = \frac{2\mathbf{m}_r(i)\mathbf{m}_d(i) + c}{\mathbf{m}_r^2(i) + \mathbf{m}_d^2(i) + c} GMS(i)=mr2(i)+md2(i)+c2mr(i)md(i)+c其中 c c c是一个用于稳定数值的常数。
-
Pooling Strategy:使用radient Magnitude Similarity Deviation (GMSD)方法来进行池化提取全局图像质量分数。计算过程中会使用到Gradient Magnitude Similarity Mean (GMSM),两者的公式表示如下: G M S M = 1 N ∑ i = 1 N G M S ( i ) GMSM = \frac{1}{N} \sum_{i=1}^{N} GMS(i) GMSM=N1i=1∑NGMS(i) G M S D = 1 N ∑ i = 1 N ( G M S ( i ) − G M S M ) 2 GMSD = \sqrt{\frac{1}{N} \sum_{i=1}^{N} \big(GMS(i) - GMSM\big)^2} GMSD=N1i=1∑N(GMS(i)−GMSM)2作者这里还给出了GMSD相较GMSM的优势,比如说下图:

其中(a) 原始图像 “Fishing”、其受高斯噪声污染的版本(DMOS = 0.4403;GMSM = 0.8853;GMSD = 0.1420 )以及它们的梯度相似图。(b) 原始图像 “Flower”、其模糊版本(DMOS = 0.7785;GMSM = 0.8745;GMSD = 0.1946 )以及它们的梯度相似图。基于人类主观 DMOS,图像 “Fishing” 的质量比图像 “Flower” 高得多,然而二者的GMSM指标接近,而GMSD指标可以有明显差距,因此使用GMSD可以更有效的区分开一些质量分数不一样的数据。
2、代码结构
代码实现位于pyiqa/archs/gmsd_arch.py中:

3 、核心代码模块
GMSD 类
这个类实现了整体的参数传入与函数调用。
@ARCH_REGISTRY.register()
class GMSD(nn.Module):
r"""Gradient Magnitude Similarity Deviation Metric.
Args:
- channels: Number of channels.
- test_y_channel: bool, whether to use y channel on ycbcr.
Reference:
Xue, Wufeng, Lei Zhang, Xuanqin Mou, and Alan C. Bovik.
"Gradient magnitude similarity deviation: A highly efficient
perceptual image quality index." IEEE Transactions on Image
Processing 23, no. 2 (2013): 684-695.
"""
def __init__(self, channels: int = 3, test_y_channel: bool = True) -> None:
super(GMSD, self).__init__()
self.channels = channels
self.test_y_channel = test_y_channel
def forward(self, x: torch.Tensor, y: torch.Tensor) -> torch.Tensor:
r"""Args:
x: A distortion tensor. Shape :math:`(N, C, H, W)`.
y: A reference tensor. Shape :math:`(N, C, H, W)`.
Order of input is important.
"""
assert x.shape == y.shape, (
f'Input and reference images should have the same shape, but got {x.shape} and {y.shape}'
)
score = gmsd(x, y, channels=self.channels, test_y_channel=self.test_y_channel)
return score
参数包含2个,一个是输入通道的大小,另一个是是否只使用Y通道进行评价,然后调用gmsd函数得到结果。
gmsd 函数
实际计算的代码。
def gmsd(
x: torch.Tensor,
y: torch.Tensor,
T: int = 170,
channels: int = 3,
test_y_channel: bool = True,
) -> torch.Tensor:
r"""GMSD metric.
Args:
- x: A distortion tensor. Shape :math:`(N, C, H, W)`.
- y: A reference tensor. Shape :math:`(N, C, H, W)`.
- T: A positive constant that supplies numerical stability.
- channels: Number of channels.
- test_y_channel: bool, whether to use y channel on ycbcr.
"""
if test_y_channel:
x = to_y_channel(x, 255)
y = to_y_channel(y, 255)
channels = 1
else:
x = x * 255.0
y = y * 255.0
dx = (
(torch.Tensor([[1, 0, -1], [1, 0, -1], [1, 0, -1]]) / 3.0)
.unsqueeze(0)
.unsqueeze(0)
.repeat(channels, 1, 1, 1)
.to(x)
)
dy = (
(torch.Tensor([[1, 1, 1], [0, 0, 0], [-1, -1, -1]]) / 3.0)
.unsqueeze(0)
.unsqueeze(0)
.repeat(channels, 1, 1, 1)
.to(x)
)
aveKernel = torch.ones(channels, 1, 2, 2).to(x) / 4.0
Y1 = F.conv2d(x, aveKernel, stride=2, padding=0, groups=channels)
Y2 = F.conv2d(y, aveKernel, stride=2, padding=0, groups=channels)
IxY1 = F.conv2d(Y1, dx, stride=1, padding=1, groups=channels)
IyY1 = F.conv2d(Y1, dy, stride=1, padding=1, groups=channels)
gradientMap1 = torch.sqrt(IxY1**2 + IyY1**2 + 1e-12)
IxY2 = F.conv2d(Y2, dx, stride=1, padding=1, groups=channels)
IyY2 = F.conv2d(Y2, dy, stride=1, padding=1, groups=channels)
gradientMap2 = torch.sqrt(IxY2**2 + IyY2**2 + 1e-12)
quality_map = (2 * gradientMap1 * gradientMap2 + T) / (
gradientMap1**2 + gradientMap2**2 + T
)
score = torch.std(quality_map.view(quality_map.shape[0], -1), dim=1)
return score
流程如下:
- 首先定义了dx和dy,两个方向的Prewitt 滤波器,然后使用一个2x2的均值滤波对两幅输入图像处理得到Y1和Y2,这个步骤提取了低频同时也减小了计算量。
- 使用dx和dy两个滤波器对Y1进行处理得到IxY1和IyY1,接着计算强度得到gradientMap1,同样的得到gradientMap2。
- 计算gradientMap1和gradientMap2的相关系数,得到局部质量图quality_map。
- 使用GMSD标准池对quality_map处理得到全局质量分数gmsd。
通过以上计算步骤可以得到两个结论:
- gmsd跟实际我们认知的质量分数是成反比,方差越大意味着相关系数变化越大,则越不相似。
- gmsd的范围是无界的,不像一些质量评价指标存在明显的范围。
3、总结
代码实现核心的部分讲解完毕,GMSD作为一个传统的轻量化全参考IQA指标,可以在一些性能比较差的设备上进行部署来对数据做一个初步的评估,例如压缩任务。
感谢阅读,欢迎留言或私信,一起探讨和交流。
如果对你有帮助的话,也希望可以给博主点一个关注,感谢。























 2022
2022

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








