本文开始前要求你得掌握基本python语法和具备一定的深度学习理论,完整源代码在文章末尾
目录
1、下载数据集
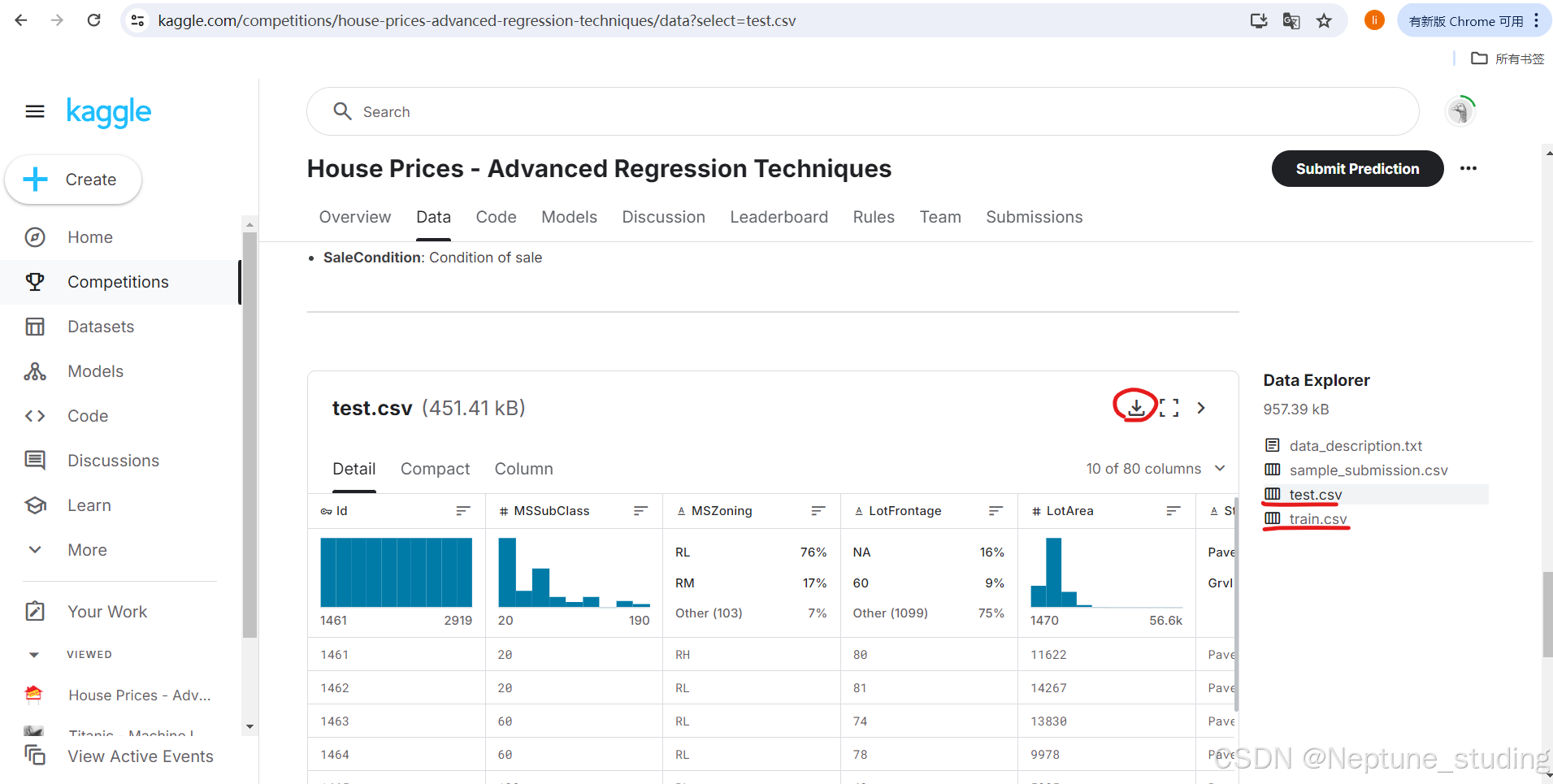
首先大家先注册好kaggle账号,并找到房价预测的比赛,下面的是对应的网址https://www.kaggle.com/competitions/house-prices-advanced-regression-techniques/overview
找到data下的test.csv和train.csv并下载到你project包的data包内
2、数据预处理
先导入必要的一些包
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import torch
from torch import nn
from d2l import torch as d2l先用两个变量接收训练集和测试集,然后再把两个集合的特征提取出来进行操作。主要是将特征归一化,用特征减去均值再除以标准差,得到一个服从正态分布(0,1)的特征集;然后将特征里的缺失值置为0,方便后面计算;最后处理非数值型的特征,调用pandas的get_dummies()方法将其转化为独热编码。
处理完特征之后,就可以转为tensor张量的类型方便后面训练模型,从而得到train_features, train_labels, test_features三个张量
train_data = pd.read_csv('data/train.csv')
test_data = pd.read_csv('data/test.csv')
# print(train_data.iloc[0:4, [0, 1, 2, 3, -3, -2, -1]])
all_features = pd.concat((train_data.iloc[:, 1:-1], test_data.iloc[:, 1, ]))
# 数据预处理
numeric_features = all_features.dtypes[all_features.dtypes != 'object'].index
all_features[numeric_features] = all_features[numeric_features].apply(
lambda x: (x - x.mean()) / (x.std())
)
# 在标准化之后,所有数据都意味着消失,因此我们可以将缺失值na设置为0
all_features[numeric_features] = all_features[numeric_features].fillna(0)
# 处理离散值,比如MSZoning包含值RL和RM,通过调用pandas的方法get_dummies创建MSZoning_RL和MSZoningRM,分别设置为1,0,这个就叫独热编码
all_features = pd.get_dummies(all_features, dummy_na=True)
# print(all_features.shape)
# 将特征转换为张量用于训练,通过values属性可以从pandas格式先转化为numpy,再转化为tensor
n_train = train_data.shape[0] # 行数
train_features = torch.tensor(
all_features[:n_train].values, dtype=torch.float32)
train_labels = torch.tensor(
train_data.SalePrice.values.reshape(-1, 1), dtype=torch.float32)
test_features = torch.tensor(
all_features[n_train:].values, dtype=torch.float32)三、训练模型
训练模型首先要定义loss函数,网络模型,评估模型的函数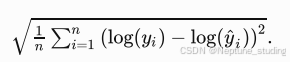
loss = nn.MSELoss()
in_features = train_features.shape[1] # 列数
def get_net():
net = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(in_features, 1)
)
return net
def log_rmse(net, features, labels):
# 将net(features)的输出限制在1和正无穷之间,确保log大于0
clipped_preds = torch.clamp(net(features), 1, float('inf'))
rmse = torch.sqrt(loss(torch.log(clipped_preds), torch.log(labels)))
return rmse.item()接着就是定义训练模型函数,从而计算出训练集和测试集的损失误差,先将训练集的特征和标签分成batch_size大小的几组张量,在定义优化器(此处使用Adam优化器),然后开始训练模型(一共训练num_epochs次),训练过程就是先置梯度为0->forward传递计算loss->反向传播更新权重,每完成一次就将算出来的误差添加到后面,最后返回两个集合的误差。
def train(net, train_features, train_labels, test_features,
test_labels, num_epochs, learning_rate, weight_decay, batch_size):
train_ls, test_ls = [], []
train_iter = d2l.load_array(
(train_features, train_labels), batch_size, is_train=True)
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(
net.parameters(),
lr=learning_rate,
weight_decay=weight_decay)
for epoch in range(num_epochs):
for x, y in train_iter:
optimizer.zero_grad()
l = loss(net(x), y)
l.backward()
optimizer.step()
train_ls.append(log_rmse(net, train_features, train_labels))
if test_labels is not None:
test_ls.append(log_rmse(net, test_features, test_labels))
return train_ls, test_ls四、预测和提交
设置num_epochs=100, lr=5, weight_decay=0, batch_size=64, 先训练然后得到预测值,接着提交预测值,他会生成一个csv文件,在kaggle上点击submit,然后把这个csv文件直接拖拽到kaggle上,
五、完整代码:
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import torch
from torch import nn
from d2l import torch as d2l
train_data = pd.read_csv('data/train.csv')
test_data = pd.read_csv('data/test.csv')
# print(train_data.iloc[0:4, [0, 1, 2, 3, -3, -2, -1]])
all_features = pd.concat((train_data.iloc[:, 1:-1], test_data.iloc[:, 1, ]))
# 数据预处理
numeric_features = all_features.dtypes[all_features.dtypes != 'object'].index
all_features[numeric_features] = all_features[numeric_features].apply(
lambda x: (x - x.mean()) / (x.std())
)
# 在标准化之后,所有数据都意味着消失,因此我们可以将缺失值na设置为0
all_features[numeric_features] = all_features[numeric_features].fillna(0)
# 处理离散值,比如MSZoning包含值RL和RM,通过调用pandas的方法get_dummies创建MSZoning_RL和MSZoningRM,分别设置为1,0,这个就叫独热编码
all_features = pd.get_dummies(all_features, dummy_na=True)
# print(all_features.shape)
# 将特征转换为张量用于训练,通过values属性可以从pandas格式先转化为numpy,再转化为tensor
n_train = train_data.shape[0] # 行数
train_features = torch.tensor(
all_features[:n_train].values, dtype=torch.float32)
train_labels = torch.tensor(
train_data.SalePrice.values.reshape(-1, 1), dtype=torch.float32)
test_features = torch.tensor(
all_features[n_train:].values, dtype=torch.float32)
# 训练过程
loss = nn.MSELoss()
in_features = train_features.shape[1] # 列数
def get_net():
net = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(in_features, 1)
)
return net
def log_rmse(net, features, labels):
# 将net(features)的输出限制在1和正无穷之间,确保log大于0
clipped_preds = torch.clamp(net(features), 1, float('inf'))
rmse = torch.sqrt(loss(torch.log(clipped_preds), torch.log(labels)))
return rmse.item()
def train(net, train_features, train_labels, test_features,
test_labels, num_epochs, learning_rate, weight_decay, batch_size):
train_ls, test_ls = [], []
train_iter = d2l.load_array(
(train_features, train_labels), batch_size, is_train=True)
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(
net.parameters(),
lr=learning_rate,
weight_decay=weight_decay)
for epoch in range(num_epochs):
for x, y in train_iter:
optimizer.zero_grad()
l = loss(net(x), y)
l.backward()
optimizer.step()
train_ls.append(log_rmse(net, train_features, train_labels))
if test_labels is not None:
test_ls.append(log_rmse(net, test_features, test_labels))
return train_ls, test_ls
def train_pred(train_features,test_features,train_labels,test_data,num_epochs,lr,weight_decay,batch_size):
net=get_net()
train_ls,_=train(net,train_features,train_labels,None,None,num_epochs,lr,weight_decay,batch_size)
d2l.plot(np.arange(1,num_epochs+1),[train_ls],
xlabel='epoch',ylabel='log rmse',xlim=[1,num_epochs],yscale='log')
print(f"train log rmse{float(train_ls[-1]):f}")
preds=net(test_features).detach().numpy()
test_data['SalePrice']=pd.Series(preds.reshape(1,-1)[0])
submission=pd.concat([test_data['Id'],test_data['SalePrice']],axis=1)
submission.to_csv('submission.csv',index=False)
num_epochs, lr, weight_decay, batch_size = 100, 5, 0, 64
train_pred(train_features, test_features, train_labels, test_data, num_epochs, lr, weight_decay, batch_size)




















 3312
3312

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








