F:\pythonProject\gempy-main.venv\Scripts\python.exe F:\pycharm\3d1.py
Setting Backend To: AvailableBackends.numpy
Help on package gempy_viewer:
NAME
gempy_viewer
PACKAGE CONTENTS
API (package)
DEP (package)
_version
core (package)
modules (package)
optional_dependencies
FUNCTIONS
plot_2d(model: gempy.core.data.geo_model.GeoModel, n_axis=None, section_names: list = None, cell_number: Union[int, list[int], str, list[str], NoneType] = None, direction: Union[str, list[str], NoneType] = 'y', series_n: Union[int, List[int]] = 0, legend: bool = True, ve=1, block=None, override_regular_grid=None, kwargs_topography=None, kwargs_lithology=None, kwargs_scalar_field=None, **kwargs) -> gempy_viewer.modules.plot_2d.visualization_2d.Plot2D
Plot 2-D sections of the geomodel.
This function plots cross-sections either based on custom section traces or cell numbers
in the xyz directions. Options are provided to plot lithology blocks, scalar fields, or
rendered surface lines. Input data and topography can be included.
Args:
model (GeoModel): Geomodel object with solutions.
n_axis (Optional[int]): Subplot axis for multiple sections.
section_names (Optional[List[str]]): Names of predefined custom section traces.
cell_number (Optional[Union[int, List[int], str, List[str]]]): Position of the array to plot.
direction (Optional[Union[str, List[str]]]): Cartesian direction to be plotted (xyz).
series_n (Union[int, List[int]]): Number of the scalar field.
legend (bool): If True, plot legend. Defaults to True.
ve (float): Vertical exaggeration. Defaults to 1.
block (Optional[np.ndarray]): Deprecated. Use regular grid instead.
override_regular_grid (Optional[np.ndarray]): Numpy array of the size of model.grid.regular_grid.
If provided, the regular grid will be overridden by this array.
kwargs_topography (Optional[dict]): Additional keyword arguments for topography.
* fill_contour: Fill contour flag.
* hillshade (bool): Calculate and add hillshading using elevation data.
* azdeg (float): Azimuth of sun for hillshade.
- altdeg (float): Altitude in degrees of sun for hillshade.
kwargs_lithology (Optional[dict]): Additional keyword arguments for lithology.
kwargs_scalar_field (Optional[dict]): Additional keyword arguments for scalar field.
Keyword Args:
show_block (bool): If True and the model has been computed, plot cross section of the final model.
show_values (bool): If True and the model has been computed, plot cross section of the value.
show (bool): Call matplotlib show. Defaults to True.
show_data (bool): Show original input data. Defaults to True.
show_results (bool): If False, override show lithology, scalar field, and values. Defaults to True.
show_lith (bool): Show lithological block volumes. Defaults to True.
show_scalar (bool): Show scalar field isolines. Defaults to False.
show_boundaries (bool): Show surface boundaries as lines. Defaults to True.
show_topography (bool): Show topography on plot. Defaults to False.
show_section_traces (bool): Show section traces. Defaults to True.
Returns:
gempy.plot.visualization_2d.Plot2D: Plot2D object.
plot_3d(model: gempy.core.data.geo_model.GeoModel, plotter_type: str = 'basic', active_scalar_field: Optional[str] = None, ve: Optional[float] = None, topography_scalar_type: gempy_viewer.core.scalar_data_type.TopographyDataType = <TopographyDataType.GEOMAP: 2>, kwargs_pyvista_bounds: Optional[dict] = None, kwargs_plot_structured_grid: Optional[dict] = None, kwargs_plot_topography: Optional[dict] = None, kwargs_plot_data: Optional[dict] = None, kwargs_plotter: Optional[dict] = None, kwargs_plot_surfaces: Optional[dict] = None, image: bool = False, show: bool = True, transformed_data: bool = False, **kwargs) -> gempy_viewer.modules.plot_3d.vista.GemPyToVista
Plot 3-D geomodel.
Args:
model (GeoModel): Geomodel object with solutions.
plotter_type (str): Type of plotter to use. Defaults to 'basic'.
active_scalar_field (Optional[str]): Active scalar field for the plot.
ve (Optional[float]): Vertical exaggeration.
topography_scalar_type (TopographyDataType): Type of topography scalar data. Defaults to TopographyDataType.GEOMAP.
kwargs_pyvista_bounds (Optional[dict]): Additional keyword arguments for PyVista bounds.
kwargs_plot_structured_grid (Optional[dict]): Additional keyword arguments for plotting the structured grid.
kwargs_plot_topography (Optional[dict]): Additional keyword arguments for plotting the topography.
kwargs_plot_data (Optional[dict]): Additional keyword arguments for plotting data.
kwargs_plotter (Optional[dict]): Additional keyword arguments for the plotter.
kwargs_plot_surfaces (Optional[dict]): Additional keyword arguments for plotting surfaces.
image (bool): If True, saves the plot as an image. Defaults to False.
show (bool): If True, displays the plot. Defaults to True.
transformed_data (bool): If True, uses transformed data for plotting. Defaults to False.
**kwargs: Additional keyword arguments.
Returns:
GemPyToVista: Object for 3D plotting in GemPy.
plot_section_traces(model: gempy.core.data.geo_model.GeoModel, section_names: list[str] = None)
Plot section traces of section grid in 2-D topview (xy).
plot_stereonet(self, litho=None, planes=True, poles=True, single_plots=False, show_density=False)
plot_topology(regular_grid: gempy.core.data.grid_modules.grid_types.RegularGrid, edges, centroids, direction='y', ax=None, scale=True, label_kwargs=None, edge_kwargs=None)
Plot the topology adjacency graph in 2-D.
Args:
geo_model ([type]): GemPy geomodel instance.
edges (Set[Tuple[int, int]]): Set of topology edges.
centroids (Dict[int, Array[int, 3]]): Dictionary of topology id's and
their centroids.
direction (Union["x", "y", "z", optional): Section direction.
Defaults to "y".
label_kwargs (dict, optional): Keyword arguments for topology labels.
Defaults to None.
edge_kwargs (dict, optional): Keyword arguments for topology edges.
Defaults to None.
DATA
__all__ = ['plot_2d', 'plot_3d', 'plot_section_traces', 'plot_topology...
VERSION
2024.2.0.2
FILE
f:\pythonproject\gempy-main.venv\lib\site-packages\gempy_viewer\__init__.py
Help on package gempy.API in gempy:
NAME
gempy.API - # Initialization API
PACKAGE CONTENTS
_version
compute_API
examples_generator
faults_API
gp2_gp3_compatibility (package)
grid_API
implicit_functions
initialization_API
io_API
map_stack_to_surfaces_API
FUNCTIONS
add_orientations(geo_model: gempy.core.data.geo_model.GeoModel, x: Sequence[float], y: Sequence[float], z: Sequence[float], elements_names: Sequence[str], pole_vector: Optional[Sequence[numpy.ndarray]] = None, orientation: Optional[Sequence[numpy.ndarray]] = None, nugget: Optional[Sequence[float]] = None) -> gempy.core.data.structural_frame.StructuralFrame
Add orientation data to the geological model.
This function adds orientation data to the specified geological elements in the model.
The orientation can be provided directly as pole vectors or as orientation angles (azimuth, dip, polarity).
Optional nugget values can also be specified for each orientation point.
Args:
geo_model (GeoModel): The geological model to which the orientations will be added.
x (Sequence[float]): Sequence of x-coordinates for the orientation points.
y (Sequence[float]): Sequence of y-coordinates for the orientation points.
z (Sequence[float]): Sequence of z-coordinates for the orientation points.
elements_names (Sequence[str]): Sequence of element names corresponding to each orientation point.
pole_vector (Optional[Sequence[np.ndarray]]): Sequence of pole vectors for the orientation points.
orientation (Optional[Sequence[np.ndarray]]): Sequence of orientation angles (azimuth, dip, polarity) for the orientation points.
nugget (Optional[Sequence[float]]): Sequence of nugget values for each orientation point. If not provided,
a default value will be used for all points.
Returns:
StructuralFrame: The updated structural frame of the geological model.
Raises:
ValueError: If neither pole_vector nor orientation is provided, or if the length of the nugget sequence
does not match the lengths of the other input sequences.
add_structural_group(model: gempy.core.data.geo_model.GeoModel, group_index: int, structural_group_name: str, elements: list[gempy.core.data.structural_element.StructuralElement], structural_relation: gempy_engine.core.data.stack_relation_type.StackRelationType, fault_relations: gempy.core.data.structural_group.FaultsRelationSpecialCase = <FaultsRelationSpecialCase.OFFSET_ALL: 3>) -> gempy.core.data.structural_frame.StructuralFrame
add_surface_points(geo_model: gempy.core.data.geo_model.GeoModel, x: Sequence[float], y: Sequence[float], z: Sequence[float], elements_names: Sequence[str], nugget: Optional[Sequence[float]] = None) -> gempy.core.data.structural_frame.StructuralFrame
Add surface points to the geological model.
This function adds surface points to the specified geological elements in the model.
The points are grouped by element names, and optional nugget values can be specified
for each point.
Args:
geo_model (GeoModel): The geological model to which the surface points will be added.
x (Sequence[float]): Sequence of x-coordinates for the surface points.
y (Sequence[float]): Sequence of y-coordinates for the surface points.
z (Sequence[float]): Sequence of z-coordinates for the surface points.
elements_names (Sequence[str]): Sequence of element names corresponding to each surface point.
nugget (Optional[Sequence[float]]): Sequence of nugget values for each surface point. If not provided,
a default value will be used for all points.
Returns:
StructuralFrame: The updated structural frame of the geological model.
Raises:
ValueError: If the length of the nugget sequence does not match the lengths of the other input sequences.
calculate_gravity_gradient(centered_grid: gempy_engine.core.data.centered_grid.CenteredGrid, ugal=True) -> numpy.ndarray
compute_model(gempy_model: gempy.core.data.geo_model.GeoModel, engine_config: Optional[gempy.core.data.gempy_engine_config.GemPyEngineConfig] = None) -> gempy_engine.core.data.solutions.Solutions
Compute the geological model given the provided GemPy model.
Args:
gempy_model (GeoModel): The GemPy model to compute.
engine_config (Optional[GemPyEngineConfig]): Configuration for the computational engine. Defaults to None, in which case a default configuration will be used.
Raises:
ValueError: If the provided backend in the engine_config is not supported.
Returns:
Solutions: The computed geological model.
compute_model_at(gempy_model: gempy.core.data.geo_model.GeoModel, at: numpy.ndarray, engine_config: Optional[gempy.core.data.gempy_engine_config.GemPyEngineConfig] = None) -> numpy.ndarray
Compute the geological model at specific coordinates.
Note: This function sets a custom grid and computes the model so be wary of side effects.
Args:
gempy_model (GeoModel): The GemPy model to compute.
at (np.ndarray): The coordinates at which to compute the model.
engine_config (Optional[GemPyEngineConfig], optional): Configuration for the computational engine. Defaults to None, in which case a default configuration will be used.
Returns:
np.ndarray: The computed geological model at the specified coordinates.
create_data_legacy(*, project_name: str = 'default_project', extent: Union[list, numpy.ndarray] = None, resolution: Union[list, numpy.ndarray] = None, path_i: str = None, path_o: str = None) -> gempy.core.data.geo_model.GeoModel
create_geomodel(*, project_name: str = 'default_project', extent: Union[list, numpy.ndarray] = None, resolution: Union[list, numpy.ndarray] = None, refinement: int = 1, structural_frame: gempy.core.data.structural_frame.StructuralFrame = None, importer_helper: gempy.core.data.importer_helper.ImporterHelper = None) -> gempy.core.data.geo_model.GeoModel
Initializes and returns a GeoModel instance with specified parameters.
Args:
project_name (str, optional): The name of the project. Defaults to 'default_project'.
extent (Union[List, np.ndarray], optional): The 3D extent of the grid. Must be provided if resolution is specified. Defaults to None.
resolution (Union[List, np.ndarray], optional): The resolution of the grid. If None, an octree grid will be initialized. Defaults to None.
refinement (int, optional): The level of refinement for the octree grid. Defaults to 1.
structural_frame (StructuralFrame, optional): The structural frame of the GeoModel. Either this or importer_helper must be provided. Defaults to None.
importer_helper (ImporterHelper, optional): Helper object for importing structural elements. Either this or structural_frame must be provided. Defaults to None.
Returns:
GeoModel: The initialized GeoModel object.
Raises:
ValueError: If neither structural_frame nor importer_helper is provided.
create_orientations_from_surface_points_coords(xyz_coords: numpy.ndarray, subset: Optional[numpy.ndarray] = None, element_name: Optional[str] = 'Generated') -> gempy.core.data.orientations.OrientationsTable
delete_orientations()
delete_surface_points()
generate_example_model(example_model: gempy.core.data.enumerators.ExampleModel, compute_model: bool = True) -> gempy.core.data.geo_model.GeoModel
map_stack_to_surfaces(gempy_model: gempy.core.data.geo_model.GeoModel, mapping_object: Union[dict[str, list[str]], dict[str, tuple]], set_series: bool = True, remove_unused_series=True) -> gempy.core.data.structural_frame.StructuralFrame
Map stack (series) to surfaces by reorganizing elements between groups in a GeoModel's structural frame.
This function reorganizes structural elements (surfaces) based on a mapping object
and updates the structural frame of the GeoModel. It can also create new series
and remove unused ones.
Args:
gempy_model (GeoModel): The GeoModel object whose structural frame is to be modified.
mapping_object (Union[dict[str, list[str]] | dict[str, tuple]]): Dictionary mapping group names to element names.
set_series (bool, optional): If True, creates new series for groups not present in the GeoModel. Defaults to True.
remove_unused_series (bool, optional): If True, removes groups without any elements. Defaults to True.
Returns:
StructuralFrame: The updated StructuralFrame object.
modify_orientations(geo_model: gempy.core.data.geo_model.GeoModel, slice: Union[int, slice, NoneType] = None, **orientation_field: Union[float, numpy.ndarray]) -> gempy.core.data.structural_frame.StructuralFrame
Modifies specified fields of all orientations in the structural frame. The keys of the orientation_field
dictionary should match the field names in the orientations (e.g., "X", "Y", "Z", "G_x", "G_y", "G_z", "nugget").
Args:
geo_model (GeoModel): The GeoModel instance to modify.
slice (Optional[Union[int, slice]]): The slice of orientations to modify. If None, all orientations will be modified.
Keyword Args:
X (Union[float, np.ndarray]): X coordinates of the orientations.
Y (Union[float, np.ndarray]): Y coordinates of the orientations.
Z (Union[float, np.ndarray]): Z coordinates of the orientations.
azimuth (Union[float, np.ndarray]): Azimuth angles of the orientations.
dip (Union[float, np.ndarray]): Dip angles of the orientations.
polarity (Union[float, np.ndarray]): Polarity values of the orientations.
G_x (Union[float, np.ndarray]): X component of the gradient vector.
G_y (Union[float, np.ndarray]): Y component of the gradient vector.
G_z (Union[float, np.ndarray]): Z component of the gradient vector.
nugget (Union[float, np.ndarray]): Nugget value of the orientations.
Returns:
StructuralFrame: The modified structural frame.
modify_surface_points(geo_model: gempy.core.data.geo_model.GeoModel, slice: Union[int, slice, NoneType] = None, elements_names: Optional[Sequence[str]] = None, **surface_points_field: Union[float, numpy.ndarray]) -> gempy.core.data.structural_frame.StructuralFrame
Modifies specified fields of all surface points in the structural frame. The keys of the surface_points_field
dictionary should match the field names in the surface points (e.g., "X", "Y", "Z", "nugget").
Args:
geo_model (GeoModel): The GeoModel instance to modify.
slice (Optional[Union[int, slice]]): The slice of surface points to modify. If None, all surface points will be modified.
Keyword Args:
X (Union[float, np.ndarray]): X coordinates of the surface points.
Y (Union[float, np.ndarray]): Y coordinates of the surface points.
Z (Union[float, np.ndarray]): Z coordinates of the surface points.
nugget (Union[float, np.ndarray]): Nugget value of the surface points.
Returns:
StructuralFrame: The modified structural frame.
remove_element_by_name(model: gempy.core.data.geo_model.GeoModel, element_name: str) -> gempy.core.data.structural_frame.StructuralFrame
remove_structural_group_by_index(model: gempy.core.data.geo_model.GeoModel, group_index: int) -> gempy.core.data.structural_frame.StructuralFrame
remove_structural_group_by_name(model: gempy.core.data.geo_model.GeoModel, group_name: str) -> gempy.core.data.structural_frame.StructuralFrame
set_active_grid(grid: gempy.core.data.grid.Grid, grid_type: list[gempy.core.data.grid.Grid.GridTypes], reset: bool = False)
set_centered_grid(grid: gempy.core.data.grid.Grid, centers: numpy.ndarray, resolution: Sequence[float], radius: Union[float, Sequence[float]])
set_custom_grid(grid: gempy.core.data.grid.Grid, xyz_coord: numpy.ndarray)
set_fault_relation(frame: Union[gempy.core.data.geo_model.GeoModel, gempy.core.data.structural_frame.StructuralFrame], rel_matrix: numpy.ndarray) -> gempy.core.data.structural_frame.StructuralFrame
Sets the fault relations in the structural frame of the GeoModel.
Args:
frame (Union[GeoModel, StructuralFrame]): GeoModel or its StructuralFrame to be modified.
rel_matrix (np.ndarray): Fault relation matrix to be set.
Returns:
StructuralFrame: The updated StructuralFrame object.
set_is_fault(frame: Union[gempy.core.data.geo_model.GeoModel, gempy.core.data.structural_frame.StructuralFrame], fault_groups: Union[list[str], list[gempy.core.data.structural_group.StructuralGroup]], faults_relation_type: gempy.core.data.structural_group.FaultsRelationSpecialCase = <FaultsRelationSpecialCase.OFFSET_FORMATIONS: 1>, change_color: bool = True) -> gempy.core.data.structural_frame.StructuralFrame
Sets given groups as fault in the structural frame of the GeoModel. It can optionally change the color of these groups.
Args:
frame (Union[GeoModel, StructuralFrame]): GeoModel or its StructuralFrame to be modified.
fault_groups (Union[list[str], list[StructuralGroup]]): Groups to be set as faults.
faults_relation_type (FaultsRelationSpecialCase, optional): Faults relation type to be set. Defaults to FaultsRelationSpecialCase.OFFSET_FORMATIONS.
change_color (bool, optional): If True, changes the color of the fault groups. Defaults to True.
Returns:
StructuralFrame: The updated StructuralFrame object.
set_is_finite_fault(self, series_fault=None, toggle: bool = True)
set_section_grid(grid: gempy.core.data.grid.Grid, section_dict: dict)
set_topography_from_arrays(grid: gempy.core.data.grid.Grid, xyz_vertices: numpy.ndarray)
set_topography_from_file(grid: gempy.core.data.grid.Grid, filepath: str, crop_to_extent: Optional[Sequence] = None)
set_topography_from_random(grid: gempy.core.data.grid.Grid, fractal_dimension: float = 2.0, d_z: Optional[Sequence] = None, topography_resolution: Optional[Sequence] = None)
Sets the topography of the grid using a randomly generated topography.
Args:
grid (Grid): The grid object on which to set the topography.
fractal_dimension (float, optional): The fractal dimension of the random topography. Defaults to 2.0.
d_z (Union[Sequence, None], optional): The sequence of elevation increments for the random topography.
If None, a default sequence will be used. Defaults to None.
topography_resolution (Union[Sequence, None], optional): The resolution of the random topography.
If None, the resolution of the grid's regular grid will be used. Defaults to None.
Returns:
The topography object that was set on the grid.
Example:
>>> grid = Grid()
>>> set_topography_from_random(grid, fractal_dimension=1.5, d_z=[0.1, 0.2, 0.3], topography_resolution=[10, 10])
Note:
If topography_resolution is None, the resolution of the grid's regular grid will be used.
If d_z is None, a default sequence of elevation increments will be used.
set_topography_from_subsurface_structured_grid(grid: gempy.core.data.grid.Grid, struct: 'subsurface.StructuredData')
structural_elements_from_borehole_set(borehole_set: 'subsurface.core.geological_formats.BoreholeSet', elements_dict: dict) -> list[gempy.core.data.structural_element.StructuralElement]
Creates a list of StructuralElements from a BoreholeSet.
Args:
borehole_set (subsurface.core.geological_formats.BoreholeSet): The BoreholeSet object containing the boreholes.
elements_dict (dict): A dictionary containing the properties of the structural elements to be created.
Returns:
list[StructuralElement]: A list of StructuralElement objects created from the borehole set.
Raises:
ValueError: If a top lithology ID specified in `elements_dict` is not found in the borehole set.
DATA
__all__ = ['create_data_legacy', 'create_geomodel', 'structural_elemen...
FILE
f:\pythonproject\gempy-main.venv\lib\site-packages\gempy\api\__init__.py
Help on package gempy.core in gempy:
NAME
gempy.core
PACKAGE CONTENTS
color_generator
data (package)
FILE
f:\pythonproject\gempy-main.venv\lib\site-packages\gempy\core\__init__.py
Help on package gempy_engine.API in gempy_engine:
NAME
gempy_engine.API
PACKAGE CONTENTS
_version
dual_contouring (package)
interp_single (package)
model (package)
server (package)
FILE
f:\pythonproject\gempy-main.venv\lib\site-packages\gempy_engine\api\__init__.py
Help on package gempy_engine:
NAME
gempy_engine
PACKAGE CONTENTS
API (package)
_version
config
core (package)
modules (package)
optional_dependencies
plugins (package)
VERSION
2024.2.0
FILE
f:\pythonproject\gempy-main.venv\lib\site-packages\gempy_engine\__init__.py
Process finished with exit code 0
它这个API是如何修改插值的
最新发布
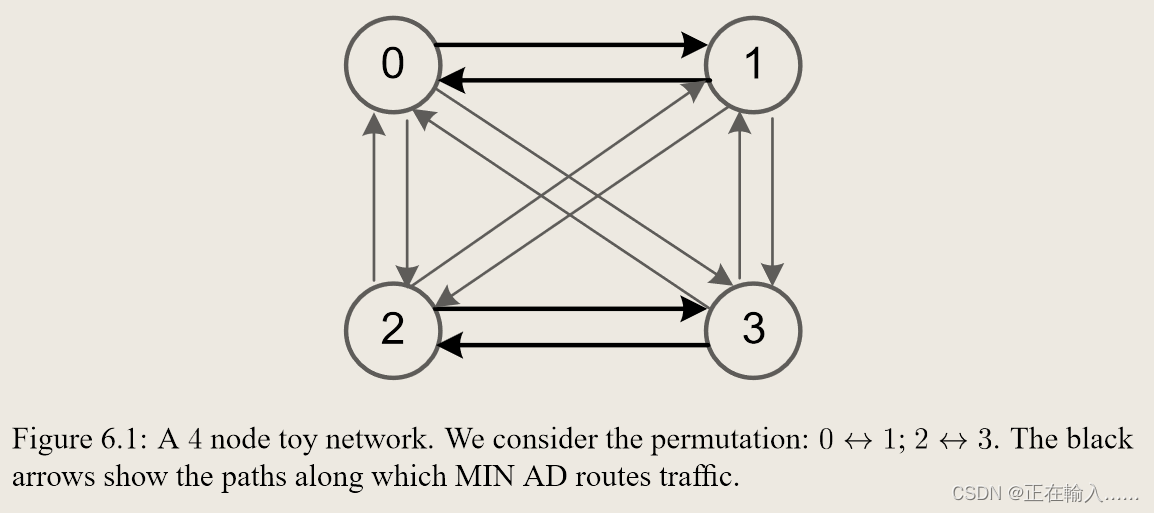











 文章介绍了一种新型的通用全局自适应负载平衡算法UGAL,它能在任意对称拓扑上提供最坏情况下的最佳性能,同时保持良性流量的性能。通过比较MINAD和VAL路由,UGAL通过动态选择最小或非最小路径来平衡负载。算法在不同拓扑结构上的性能得到验证,展示了其适应性和有效性。
文章介绍了一种新型的通用全局自适应负载平衡算法UGAL,它能在任意对称拓扑上提供最坏情况下的最佳性能,同时保持良性流量的性能。通过比较MINAD和VAL路由,UGAL通过动态选择最小或非最小路径来平衡负载。算法在不同拓扑结构上的性能得到验证,展示了其适应性和有效性。

















 2419
2419

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










