题目链接: 整数替换
有关题目
给定一个正整数 n ,你可以做如下操作:
如果 n 是偶数,则用 n / 2替换 n 。
如果 n 是奇数,则可以用 n + 1或n - 1替换 n 。
n 变为 1 所需的最小替换次数是多少?
示例 1:
输入:n = 8
输出:3
解释:8 -> 4 -> 2 -> 1
示例 2:
输入:n = 7
输出:4
解释:7 -> 8 -> 4 -> 2 -> 1
或 7 -> 6 -> 3 -> 2 -> 1
示例 3:
输入:n = 4
输出:2
提示:
1 <= n <= 2^31 - 1
题解
法一:递归 + 枚举
参考官方题解

class Solution {
public:
int integerReplacement(int n) {
if (n == 1)
return 0;
if (n % 2 == 0)//偶数替换规则
return 1 + integerReplacement(n / 2);
//奇数替换规则,n为奇数时 第一步无论加1 或 减1,第二步都为偶数
//此时最小替换次数则在第二步中选择最加1 或 减1对应的数字变为1 操作次数最少的那一个
return 2 + min(integerReplacement(n / 2), integerReplacement(n / 2 + 1));
}
};
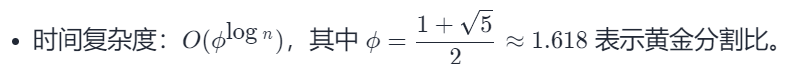

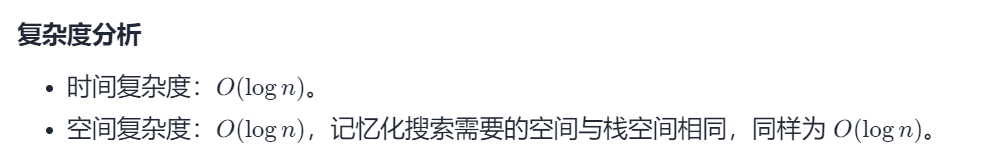
法二:记忆化搜索
参考官方题解
class Solution {
public:
unordered_map<int, int> mp;//防止重复计算某些数值,使用哈希表进行记忆化存储
int integerReplacement(int n) {
if (n == 1)
return mp[n] = 0;
if (n % 2 == 0)//偶数替换规则,并存储
return mp[n] = 1 + integerReplacement(n / 2);
//奇数替换规则,n为奇数时 第一步无论加1 或 减1,第二步都为偶数
//此时最小替换次数则在第二步中选择最加1 或 减1对应的数字变为1 操作次数最少的那一个
return mp[n] = 2 + min(integerReplacement(n / 2), integerReplacement(n / 2 + 1));
}
};
法三:贪心
参考官方题解


class Solution {
public:
unordered_map<int, int> mp;
int integerReplacement(int n) {
int ans = 0;
while(n != 1)
{
if (n % 2 == 0)
{
ans += 1;
n /= 2;
}
else if (n % 4 == 1)
{
ans += 2;
n /= 2;//n = (n - 1) / 2,注意计算机的整除
}
else //n % 4 == 3
{
if (n == 3)
{
ans += 2;
n /= 2;//n 为 三时的特殊情况,此时先n - 1,再除以 2最优
}
else
{
ans += 2;
n = n / 2 + 1;//n = (n + 1) / 2这样写 n = 2^31 - 1时会溢出
}
}
}
//奇数替换规则,n为奇数时 第一步无论加1 或 减1,第二步都为偶数
//此时最小替换次数则在第二步中选择最加1 或 减1对应的数字变为1 操作次数最少的那一个
return ans;
}
};






















 1430
1430

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








