✅作者简介:热爱科研的Matlab仿真开发者,擅长数据处理、建模仿真、程序设计、完整代码获取、论文复现及科研仿真。
🍎 往期回顾关注个人主页:Matlab科研工作室
🍊个人信条:格物致知,完整Matlab代码及仿真咨询内容私信。
🔥 内容介绍
一、技术背景与核心需求
在无人机单机作业场景(如电力巡检单点排查、灾后定点救援、城市快递配送)中,环境常包含大量静态障碍(如建筑、树木、输电塔)与少量动态障碍(如临时施工区域),核心需求是:
- 障碍安全规避:路径需与所有障碍保持安全距离(如多旋翼无人机安全距离≥5m),避免碰撞风险;
- 路径最优性:在无碰撞前提下,最小化路径长度(降低能耗)、路径平滑度(减少姿态调整次数)、飞行时间(提升作业效率);
- 多约束适配:满足无人机物理运动约束(最大转弯半径
Rmin
、最大爬升率vzmax
,若为三维场景);
- 鲁棒性:面对不规则障碍(如不规则建筑群、密集树林),算法需稳定生成可行路径,避免陷入局部最优(如绕障后无法返回目标方向)。
传统路径规划算法(如 A*、RRT)在多障碍环境中存在局限:A * 依赖栅格地图,障碍密集时栅格数量激增导致计算量暴增;RRT 随机采样效率低,易生成冗余绕障路径。遗传算法(Genetic Algorithm, GA)作为全局优化算法,通过 “种群迭代进化” 模拟生物自然选择,无需栅格建模,可直接在连续空间中搜索最优路径,且能通过多目标适应度函数平衡路径 “安全性 - 最优性 - 约束满足”,成为多障碍环境下无人机路径规划的优选方案。

⛳️ 运行结果
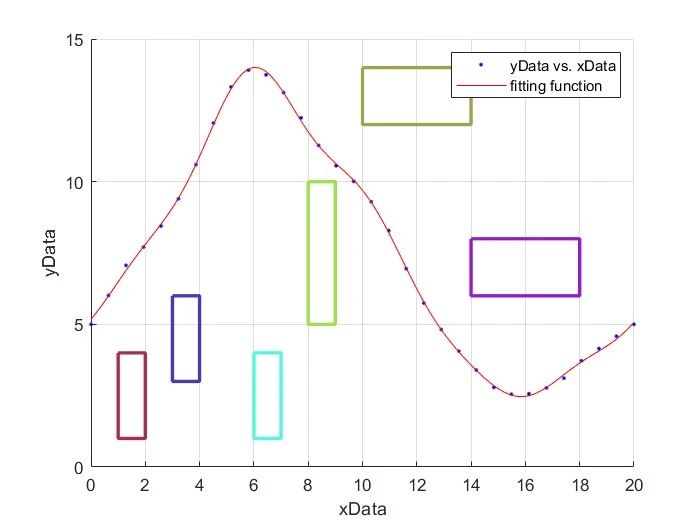
📣 部分代码
#####
##plot through working window
>> x1=out.x; x0=x1.Data; y1=out.y; y0=y1.Data;
>> plot(x0,y0);
>> plot(x0,y0);
>> hold on
>> a0 = 7.5087;
a1=-2.1673;
b1 = 4.7392;
a2 = -0.2270 ;
b2 = -0.5158 ;
a3 = 0.1598 ;
b3 = -0.3852 ;
a4 = 0.1270 ;
b4 = 0.2219 ;
a5 = -0.2227 ;
b5 = 0.0365 ;
w = 0.3127 ;
xg=linspace(0,20,100);
yg= a0 + a1*cos(xg*w) + b1*sin(xg*w) + a2*cos(2*xg*w) + b2*sin(2*xg*w) + a3*cos(3*xg*w) + b3*sin(3*xg*w) + a4*cos(4*xg*w) + b4*sin(4*xg*w) + a5*cos(5*xg*w) + b5*sin(5*xg*w);
>> plot(xg,yg);
>> hold on
Data.Obs(1).S = [1,4; 2,4; 2,1; 1,1;1,4]; Data.Obs(2).S = [3,6; 4,6; 4,3; 3,3;3,6]; Data.Obs(3).S = [6,4; 7,4; 7,1; 6,1;6,4]; Data.Obs(4).S = [8,10; 9,10; 9,5; 8,5;8,10]; Data.Obs(5).S = [10,14; 14,14; 14,12; 10,12;10,14]; Data.Obs(6).S = [14,8; 18,8; 18,6; 14,6;14,8]; % 创建一个新的图形窗口
hold on;
for i = 1:length(Data.Obs)
xy = Data.Obs(i).S;
plot(xy(:,1), xy(:,2), 'LineWidth', 2, 'Color', rand(1,3));
end
##### GA
This readme document is intended to outline and explain the main features and implementation details of the MATLAB code. The code implements a genetic algorithm (GA) based path planning optimization algorithm to find the optimal or sub-optimal path from the starting point to the end point in an environment with multiple obstacles.
1. Code overview
The code first sets the necessary parameters and data structures through a series of initialization steps, including the location of obstacles, starting and ending coordinates, population size, chromosome length, number of iterations, mutation probability, and crossover probability. The code then continuously evolves the population through genetic algorithms to find a path that does not intersect with obstacles and is as optimized as possible.
2. Main steps
2.1 Initialization
• Use clc; clear; close all; warning off; Clear the command window, workspace, and graphics window, and turn off MATLAB warnings.
• Use addpath(genpath(pwd)); Add the current directory and its subdirectories to the path of MATLAB so that custom functions can be loaded and invoked.
• Set the Data structure Data, including boundary B, starting point and ending point S_E, population size, chromosome length, etc.
• Define obstacle Obs, with each obstacle defined by a series of vertices arranged in clockwise order.
2.2 Initial population generation
• Call intpop function to generate initial population. This function generates an initial solution set based on the data provided, such as population size and chromosome length.
2.3 Checking and Repairing Paths
• Use the check_crossing function on each individual (that is, each path) to check for an intersection with an obstacle.
If an intersection is found, a new waypoint is generated using the newpop function until the path no longer intersects with any obstacles.
2.4 Evolutionary process
• Through multiple iterations, using the ideas of genetic algorithms (selection, crossover, variation) to optimize the population.
• Calculate the fitness of an individual using the cal_Fitness function.
• Use the environmental_sele function to select the environment and keep good individuals in the external archive set Qop.
In non-final iterations, a new population is generated by tournament selection binary_tournament_selection, crosscross_mutation, and smoothing operation delete_point.
2.5 Result output and visualization
• After the last iteration, the non-dominant individual (i.e. the optimal solution set) is selected for output.
Use the plotting function to draw the optimal path and obstacles into the graph window so you can visually view the results.
3. Precautions
• The Goals function in the code is used to calculate the value of the objective function, that is, to evaluate the pros and cons of the path.
4. Conclusion
The MATLAB code implements a path planning optimization algorithm based on genetic algorithm, which can find the optimal path from the starting point to the end point in the environment with complex obstacles. By iterating and evolving the population, the algorithm can gradually optimize the path until it finds an optimal or suboptimal solution that meets the requirements
🔗 参考文献
🎈 部分理论引用网络文献,若有侵权联系博主删除
👇 关注我领取海量matlab电子书和数学建模资料
🏆团队擅长辅导定制多种科研领域MATLAB仿真,助力科研梦:
🌟 各类智能优化算法改进及应用
生产调度、经济调度、装配线调度、充电优化、车间调度、发车优化、水库调度、三维装箱、物流选址、货位优化、公交排班优化、充电桩布局优化、车间布局优化、集装箱船配载优化、水泵组合优化、解医疗资源分配优化、设施布局优化、可视域基站和无人机选址优化、背包问题、 风电场布局、时隙分配优化、 最佳分布式发电单元分配、多阶段管道维修、 工厂-中心-需求点三级选址问题、 应急生活物质配送中心选址、 基站选址、 道路灯柱布置、 枢纽节点部署、 输电线路台风监测装置、 集装箱调度、 机组优化、 投资优化组合、云服务器组合优化、 天线线性阵列分布优化、CVRP问题、VRPPD问题、多中心VRP问题、多层网络的VRP问题、多中心多车型的VRP问题、 动态VRP问题、双层车辆路径规划(2E-VRP)、充电车辆路径规划(EVRP)、油电混合车辆路径规划、混合流水车间问题、 订单拆分调度问题、 公交车的调度排班优化问题、航班摆渡车辆调度问题、选址路径规划问题、港口调度、港口岸桥调度、停机位分配、机场航班调度、泄漏源定位、冷链、时间窗、多车场等、选址优化、港口岸桥调度优化、交通阻抗、重分配、停机位分配、机场航班调度、通信上传下载分配优化
🌟 机器学习和深度学习时序、回归、分类、聚类和降维
2.1 bp时序、回归预测和分类
2.2 ENS声神经网络时序、回归预测和分类
2.3 SVM/CNN-SVM/LSSVM/RVM支持向量机系列时序、回归预测和分类
2.4 CNN|TCN|GCN卷积神经网络系列时序、回归预测和分类
2.5 ELM/KELM/RELM/DELM极限学习机系列时序、回归预测和分类
2.6 GRU/Bi-GRU/CNN-GRU/CNN-BiGRU门控神经网络时序、回归预测和分类
2.7 ELMAN递归神经网络时序、回归\预测和分类
2.8 LSTM/BiLSTM/CNN-LSTM/CNN-BiLSTM/长短记忆神经网络系列时序、回归预测和分类
2.9 RBF径向基神经网络时序、回归预测和分类
2.10 DBN深度置信网络时序、回归预测和分类
2.11 FNN模糊神经网络时序、回归预测
2.12 RF随机森林时序、回归预测和分类
2.13 BLS宽度学习时序、回归预测和分类
2.14 PNN脉冲神经网络分类
2.15 模糊小波神经网络预测和分类
2.16 时序、回归预测和分类
2.17 时序、回归预测预测和分类
2.18 XGBOOST集成学习时序、回归预测预测和分类
2.19 Transform各类组合时序、回归预测预测和分类
方向涵盖风电预测、光伏预测、电池寿命预测、辐射源识别、交通流预测、负荷预测、股价预测、PM2.5浓度预测、电池健康状态预测、用电量预测、水体光学参数反演、NLOS信号识别、地铁停车精准预测、变压器故障诊断
🌟图像处理方面
图像识别、图像分割、图像检测、图像隐藏、图像配准、图像拼接、图像融合、图像增强、图像压缩感知
🌟 路径规划方面
旅行商问题(TSP)、车辆路径问题(VRP、MVRP、CVRP、VRPTW等)、无人机三维路径规划、无人机协同、无人机编队、机器人路径规划、栅格地图路径规划、多式联运运输问题、 充电车辆路径规划(EVRP)、 双层车辆路径规划(2E-VRP)、 油电混合车辆路径规划、 船舶航迹规划、 全路径规划规划、 仓储巡逻、公交车时间调度、水库调度优化、多式联运优化
🌟 无人机应用方面
无人机路径规划、无人机控制、无人机编队、无人机协同、无人机任务分配、无人机安全通信轨迹在线优化、车辆协同无人机路径规划、
🌟 通信方面
传感器部署优化、通信协议优化、路由优化、目标定位优化、Dv-Hop定位优化、Leach协议优化、WSN覆盖优化、组播优化、RSSI定位优化、水声通信、通信上传下载分配
🌟 信号处理方面
信号识别、信号加密、信号去噪、信号增强、雷达信号处理、信号水印嵌入提取、肌电信号、脑电信号、信号配时优化、心电信号、DOA估计、编码译码、变分模态分解、管道泄漏、滤波器、数字信号处理+传输+分析+去噪、数字信号调制、误码率、信号估计、DTMF、信号检测
🌟电力系统方面
微电网优化、无功优化、配电网重构、储能配置、有序充电、MPPT优化、家庭用电、电/冷/热负荷预测、电力设备故障诊断、电池管理系统(BMS)SOC/SOH估算(粒子滤波/卡尔曼滤波)、 多目标优化在电力系统调度中的应用、光伏MPPT控制算法改进(扰动观察法/电导增量法)、电动汽车充放电优化、微电网日前日内优化、储能优化、家庭用电优化、供应链优化
🌟 元胞自动机方面
交通流 人群疏散 病毒扩散 晶体生长 金属腐蚀
🌟 雷达方面
卡尔曼滤波跟踪、航迹关联、航迹融合、SOC估计、阵列优化、NLOS识别
🌟 车间调度
零等待流水车间调度问题NWFSP 、 置换流水车间调度问题PFSP、 混合流水车间调度问题HFSP 、零空闲流水车间调度问题NIFSP、分布式置换流水车间调度问题 DPFSP、阻塞流水车间调度问题BFSP
👇




















 1204
1204

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








