算法介绍参照此文章
核心思路:
- 首选任意选取一个点,然后找到到这个点距离小于等于 eps 的所有的点。如果距起始点的距离在 eps 之内的数据点个数小于 min_samples,那么这个点被标记为噪声。如果距离在 eps 之内的数据点个数大于 min_samples,则这个点被标记为核心样本,并被分配一个新的簇标签。
- 然后访问该点的所有邻居(在距离 eps 以内)。如果它们还没有被分配一个簇,那么就将刚刚创建的新的簇标签分配给它们。如果它们是核心样本,那么就依次访问其邻居,以此类推。簇逐渐增大,直到在簇的 eps 距离内没有更多的核心样本为止。
- 选取另一个尚未被访问过的点,并重复相同的过程。
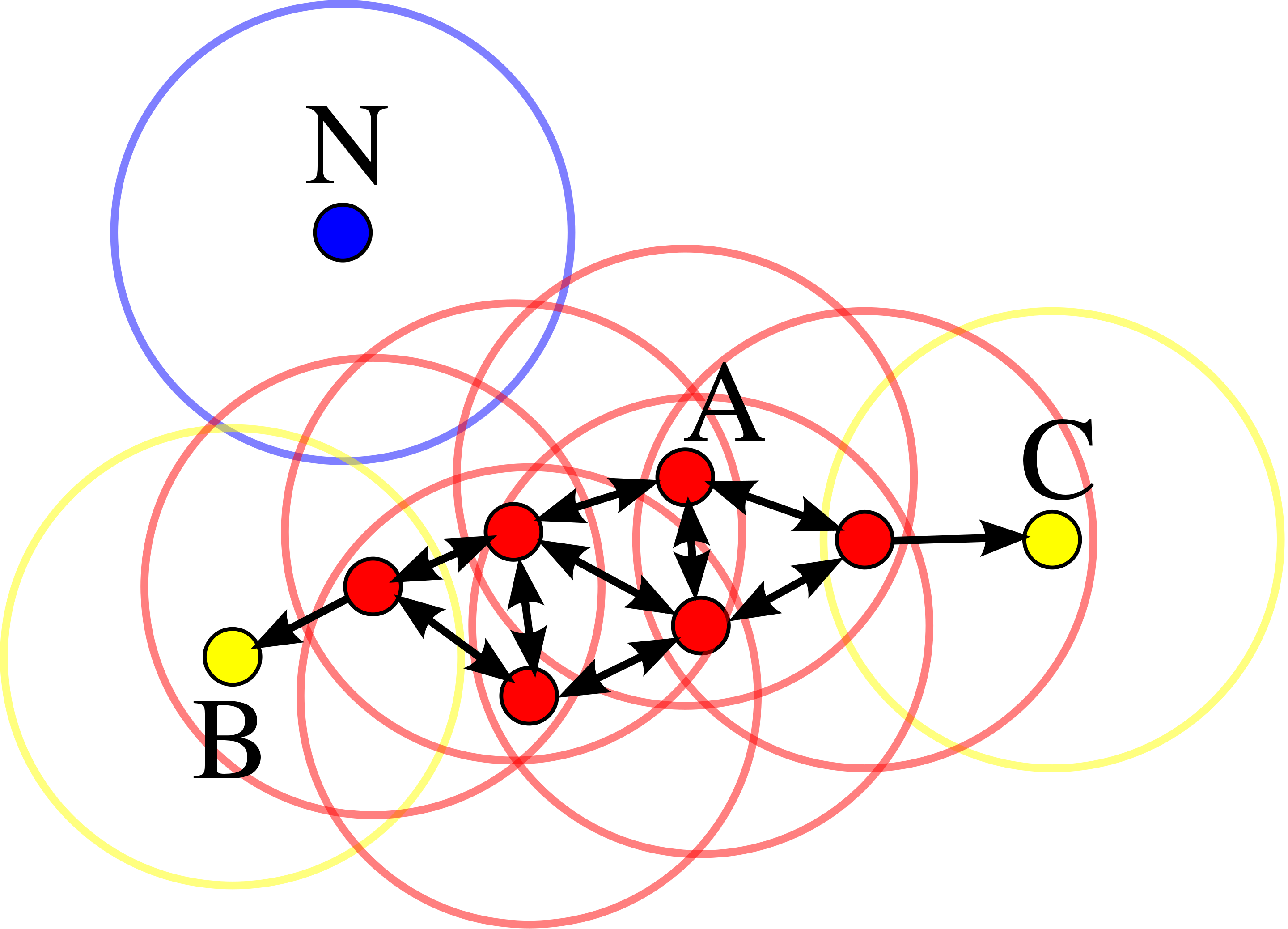
算法实现
"""
AUTHOR: chenyi
DATE: 2021-11-13
Density-Based Spatial Clustering of Applications with Noise
In order to visualize the result in a 2d dimension,
let's assume that the dimension af the points would only be 2.
Core Params:
- eps: the radius of the cluster.
- minDots: the min number of the points the cluster should have to be a cluster.
Point {
visited -> bool: indicate whether a point is visited.
coords -> (float, float): describe a point's coordination.
cluster -> int: indicate to which cluster the point belongs.
}
"""
import random
from math import sqrt
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
class Point:
"""DEFINITION"""
def __init__(self):
self.visited = False
self.coords = (random.random() * 10, random.random() * 10)
self.cluster = None
def __int__(self, coords):
self.visited = False
self.coords = coords
self.cluster = None
def cal_distance(self, other):
d = sqrt((other.coords[0] - self.coords[0]) ** 2 + (other.coords[1] - self.coords[




 本文介绍了DBSCAN聚类算法的核心思想和实现过程,包括选择核心点、寻找邻域点并进行深度优先搜索来构建簇。通过Python代码展示了DBSCAN如何在二维空间中对数据进行聚类,并提供了结果的可视化展示。算法参数包括ε(邻域半径)和min_samples(最小样本数),用于控制簇的大小和形状。
本文介绍了DBSCAN聚类算法的核心思想和实现过程,包括选择核心点、寻找邻域点并进行深度优先搜索来构建簇。通过Python代码展示了DBSCAN如何在二维空间中对数据进行聚类,并提供了结果的可视化展示。算法参数包括ε(邻域半径)和min_samples(最小样本数),用于控制簇的大小和形状。
 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章


















 111
111












