-
算法实现:
- 模拟退火算法:基于概率接受较差解,逐步降温以收敛到最优解
- 粒子群算法:通过粒子间的协作与信息共享寻找最优解
- 遗传算法:模拟生物进化过程,通过选择、交叉和变异操作优化解
- 蚁群算法:模拟蚂蚁寻找食物的行为,利用信息素轨迹发现路径
-
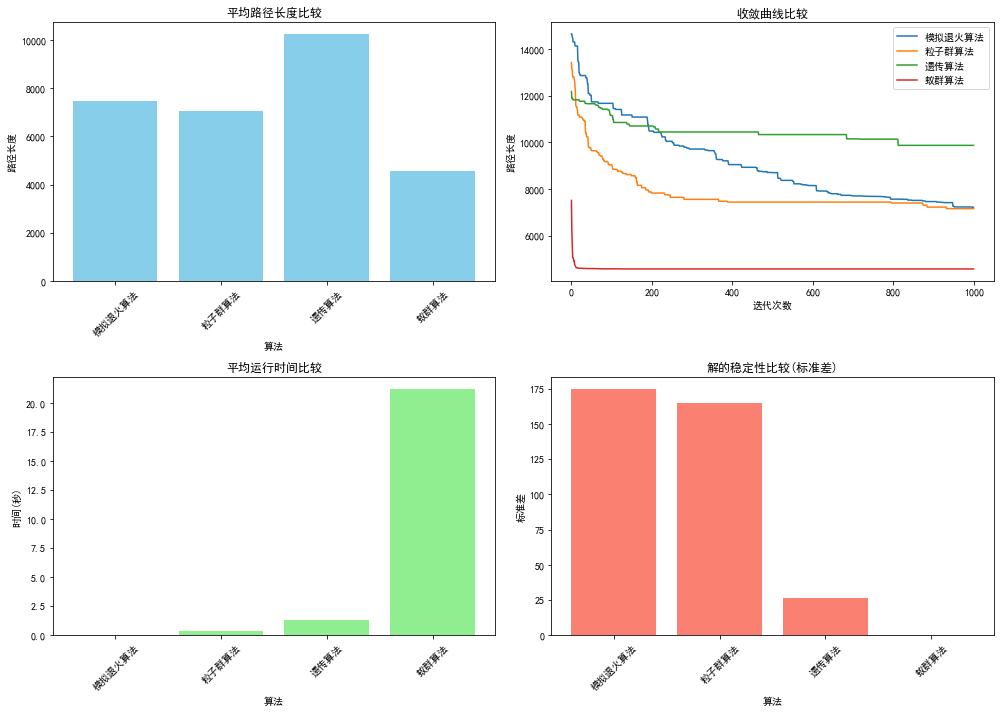
性能比较:
- 统计各算法的平均路径长度、最小路径长度、最大路径长度、标准差和运行时间
- 绘制收敛曲线比较算法的收敛速度
- 可视化各算法找到的最优路径
-
优缺点分析:
- 基于实验结果,分析每种算法在解质量、收敛速度、稳定性和计算复杂度方面的表现
- 讨论各算法的适用场景和局限性
import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import random import math import time from typing import List, Tuple, Dict, Callable # 设置随机种子以便结果可复现 np.random.seed(42) random.seed(42) class TSP: def __init__(self, num_cities: int = 20, width: int = 1000, height: int = 1000): """初始化TSP问题,随机生成城市坐标""" self.num_cities = num_cities self.cities = np.random.randint(0, width, size=(num_cities, 2)) self.distance_matrix = self._calculate_distance_matrix() def _calculate_distance_matrix(self) -> np.ndarray: """计算城市间的距离矩阵""" matrix = np.zeros((self.num_cities, self.num_cities)) for i in range(self.num_cities): for j in range(i+1, self.num_cities): dist = np.sqrt(np.sum((self.cities[i] - self.cities[j])**2)) matrix[i, j] = dist matrix[j, i] = dist return matrix def get_tour_length(self, tour: List[int]) -> float: """计算路径长度""" total_distance = 0 for i in range(len(tour) - 1): total_distance += self.distance_matrix[tour[i], tour[i+1]] # 回到起点 total_distance += self.distance_matrix[tour[-1], tour[0]] return total_distance def plot_cities(self) -> None: """绘制城市分布""" plt.figure(figsize=(10, 8)) plt.scatter(self.cities[:, 0], self.cities[:, 1], c='blue', s=50) for i, (x, y) in enumerate(self.cities): plt.annotate(str(i), (x, y), xytext=(5, 5), textcoords='offset points') plt.title('城市分布') plt.xlabel('X坐标') plt.ylabel('Y坐标') plt.grid(True) def plot_tour(self, tour: List[int], title: str = "旅行商路径") -> None: """绘制旅行路径""" plt.figure(figsize=(10, 8)) # 绘制城市 plt.scatter(self.cities[:, 0], self.cities[:, 1], c='blue', s=50) for i, (x, y) in enumerate(self.cities): plt.annotate(str(i), (x, y), xytext=(5, 5), textcoords='offset points') # 绘制路径 tour_coords = self.cities[tour] plt.plot(np.append(tour_coords[:, 0], tour_coords[0, 0]), np.append(tour_coords[:, 1], tour_coords[0, 1]), 'r-', linewidth=1.5) plt.title(title) plt.xlabel('X坐标') plt.ylabel('Y坐标') plt.grid(True) # 模拟退火算法 def simulated_annealing(tsp: TSP, initial_temperature: float = 1000, cooling_rate: float = 0.995, stopping_temperature: float = 1e-8, max_iterations: int = 10000) -> Tuple[List[int], float, List[float]]: """使用模拟退火算法求解TSP""" # 初始化当前路径为随机路径 current_tour = list(range(tsp.num_cities)) random.shuffle(current_tour) current_length = tsp.get_tour_length(current_tour) # 记录最优路径 best_tour = current_tour.copy() best_length = current_length # 温度和迭代记录 temperature = initial_temperature iteration = 0 history = [] while temperature > stopping_temperature and iteration < max_iterations: # 生成相邻解 neighbor_tour = generate_neighbor(current_tour) neighbor_length = tsp.get_tour_length(neighbor_tour) # 计算能量差 delta = neighbor_length - current_length # 判断是否接受新解 if delta < 0 or random.random() < math.exp(-delta / temperature): current_tour = neighbor_tour current_length = neighbor_length # 更新最优解 if current_length < best_length: best_tour = current_tour.copy() best_length = current_length # 记录当前最优路径长度 history.append(best_length) # 降温 temperature *= cooling_rate iteration += 1 return best_tour, best_length, history def generate_neighbor(tour: List[int]) -> List[int]: """生成相邻解:随机交换路径中的两个城市""" neighbor = tour.copy() idx1, idx2 = random.sample(range(len(tour)), 2) neighbor[idx1], neighbor[idx2] = neighbor[idx2], neighbor[idx1] return neighbor # 粒子群算法 class Particle: def __init__(self, num_cities: int): """初始化粒子""" self.position = list(range(num_cities)) random.shuffle(self.position) self.velocity = [] # 交换序列 self.pbest_position = self.position.copy() self.pbest_value = float('inf') def particle_swarm_optimization(tsp: TSP, num_particles: int = 30, max_iterations: int = 1000, w: float = 0.7, c1: float = 1.5, c2: float = 1.5) -> Tuple[List[int], float, List[float]]: """使用粒子群算法求解TSP""" num_cities = tsp.num_cities particles = [Particle(num_cities) for _ in range(num_particles)] # 初始化全局最优 gbest_position = None gbest_value = float('inf') # 历史记录 history = [] for iteration in range(max_iterations): # 评估每个粒子 for particle in particles: fitness = tsp.get_tour_length(particle.position) # 更新个体最优 if fitness < particle.pbest_value: particle.pbest_value = fitness particle.pbest_position = particle.position.copy() # 更新全局最优 if fitness < gbest_value: gbest_value = fitness gbest_position = particle.position.copy() # 记录当前全局最优 history.append(gbest_value) # 更新粒子速度和位置 for particle in particles: # 生成与个体最优的交换序列 swap_sequence_pbest = generate_swap_sequence(particle.position, particle.pbest_position) # 生成与全局最优的交换序列 swap_sequence_gbest = generate_swap_sequence(particle.position, gbest_position) # 计算新的速度(交换序列) particle.velocity = [] # 继承部分旧速度 if particle.velocity and random.random() < w: particle.velocity.append(random.choice(particle.velocity)) # 添加与个体最优相关的交换 if swap_sequence_pbest and random.random() < c1: particle.velocity.append(random.choice(swap_sequence_pbest)) # 添加与全局最优相关的交换 if swap_sequence_gbest and random.random() < c2: particle.velocity.append(random.choice(swap_sequence_gbest)) # 应用速度(执行交换) for swap in particle.velocity: i, j = swap particle.position[i], particle.position[j] = particle.position[j], particle.position[i] return gbest_position, gbest_value, history def generate_swap_sequence(tour1: List[int], tour2: List[int]) -> List[Tuple[int, int]]: """生成从tour1转换到tour2所需的交换序列""" swap_sequence = [] tour = tour1.copy() pos = {city: idx for idx, city in enumerate(tour)} for i in range(len(tour)): if tour[i] != tour2[i]: # 找到tour2[i]在tour中的位置 j = pos[tour2[i]] # 交换i和j位置的城市 tour[i], tour[j] = tour[j], tour[i] # 更新位置字典 pos[tour[i]] = i pos[tour[j]] = j # 记录交换 swap_sequence.append((i, j)) return swap_sequence # 遗传算法 def genetic_algorithm(tsp: TSP, population_size: int = 100, generations: int = 500, crossover_rate: float = 0.8, mutation_rate: float = 0.2) -> Tuple[List[int], float, List[float]]: """使用遗传算法求解TSP""" num_cities = tsp.num_cities # 初始化种群 population = [list(range(num_cities)) for _ in range(population_size)] for individual in population: random.shuffle(individual) best_fitness = float('inf') best_individual = None history = [] for generation in range(generations): # 评估适应度 fitness_values = [1 / tsp.get_tour_length(individual) for individual in population] total_fitness = sum(fitness_values) # 记录最优解 max_fitness_idx = fitness_values.index(max(fitness_values)) current_best_fitness = 1 / fitness_values[max_fitness_idx] current_best_individual = population[max_fitness_idx] if current_best_fitness < best_fitness: best_fitness = current_best_fitness best_individual = current_best_individual.copy() history.append(best_fitness) # 选择操作 - 轮盘赌 new_population = [] for _ in range(population_size): r = random.uniform(0, total_fitness) cumulative_fitness = 0 for i, fitness in enumerate(fitness_values): cumulative_fitness += fitness if cumulative_fitness >= r: new_population.append(population[i].copy()) break # 交叉操作 crossover_population = [] while len(crossover_population) < population_size: parent1, parent2 = random.sample(new_population, 2) if random.random() < crossover_rate: child1, child2 = ordered_crossover(parent1, parent2) crossover_population.extend([child1, child2]) else: crossover_population.extend([parent1.copy(), parent2.copy()]) # 确保种群大小正确 population = crossover_population[:population_size] # 变异操作 for i in range(population_size): if random.random() < mutation_rate: population[i] = swap_mutation(population[i]) return best_individual, best_fitness, history def ordered_crossover(parent1: List[int], parent2: List[int]) -> Tuple[List[int], List[int]]: """有序交叉操作""" size = len(parent1) start, end = sorted(random.sample(range(size), 2)) # 初始化子代 child1 = [-1] * size child2 = [-1] * size # 复制交叉段 child1[start:end] = parent1[start:end] child2[start:end] = parent2[start:end] # 填充剩余城市 child1_remaining = [city for city in parent2 if city not in child1[start:end]] child2_remaining = [city for city in parent1 if city not in child2[start:end]] # 填充剩余位置 index = 0 for i in range(size): if i < start or i >= end: child1[i] = child1_remaining[index] child2[i] = child2_remaining[index] index += 1 return child1, child2 def swap_mutation(individual: List[int]) -> List[int]: """交换变异操作""" if len(individual) > 1: i, j = random.sample(range(len(individual)), 2) individual[i], individual[j] = individual[j], individual[i] return individual # 蚁群算法 def ant_colony_optimization(tsp: TSP, num_ants: int = 30, max_iterations: int = 100, alpha: float = 1.0, beta: float = 2.0, rho: float = 0.5, q: float = 100.0) -> Tuple[List[int], float, List[float]]: """使用蚁群算法求解TSP""" num_cities = tsp.num_cities distance_matrix = tsp.distance_matrix # 初始化信息素矩阵 pheromone_matrix = np.ones((num_cities, num_cities)) * 0.1 np.fill_diagonal(pheromone_matrix, 0) # 对角线为0,因为城市到自身的距离为0 best_tour = None best_length = float('inf') history = [] for iteration in range(max_iterations): # 每只蚂蚁构建路径 all_tours = [] all_lengths = [] for ant in range(num_ants): # 初始化 current_city = random.randint(0, num_cities - 1) unvisited = list(range(num_cities)) unvisited.remove(current_city) tour = [current_city] # 构建路径 while unvisited: # 计算转移概率 probabilities = [] for city in unvisited: pheromone = pheromone_matrix[current_city, city] distance = distance_matrix[current_city, city] if distance == 0: # 避免除零错误 probability = 0 else: probability = (pheromone ** alpha) * ((1.0 / distance) ** beta) probabilities.append(probability) # 归一化概率 if sum(probabilities) == 0: next_city = random.choice(unvisited) else: probabilities = [p / sum(probabilities) for p in probabilities] # 轮盘赌选择下一个城市 next_city_idx = np.random.choice(len(unvisited), p=probabilities) next_city = unvisited[next_city_idx] # 更新路径和未访问城市 tour.append(next_city) unvisited.remove(next_city) current_city = next_city # 计算路径长度 tour_length = tsp.get_tour_length(tour) all_tours.append(tour) all_lengths.append(tour_length) # 更新全局最优 if tour_length < best_length: best_length = tour_length best_tour = tour.copy() # 记录当前迭代的最优路径长度 history.append(best_length) # 更新信息素 # 信息素挥发 pheromone_matrix *= (1 - rho) # 信息素沉积 for tour, length in zip(all_tours, all_lengths): if length == 0: # 避免除零错误 continue pheromone_deposit = q / length for i in range(len(tour) - 1): city1, city2 = tour[i], tour[i+1] pheromone_matrix[city1, city2] += pheromone_deposit pheromone_matrix[city2, city1] += pheromone_deposit # 回到起点 city1, city2 = tour[-1], tour[0] pheromone_matrix[city1, city2] += pheromone_deposit pheromone_matrix[city2, city1] += pheromone_deposit return best_tour, best_length, history # 比较算法 def compare_algorithms(tsp: TSP, algorithms: Dict[str, Callable], runs_per_algorithm: int = 5) -> None: """比较不同算法的性能""" results = {} # 运行每种算法多次并记录结果 for alg_name, algorithm in algorithms.items(): print(f"\n运行 {alg_name} 算法...") alg_results = [] alg_times = [] for run in range(runs_per_algorithm): print(f"第 {run+1}/{runs_per_algorithm} 次运行") start_time = time.time() best_tour, best_length, history = algorithm(tsp) end_time = time.time() alg_results.append(best_length) alg_times.append(end_time - start_time) # 只在第一次运行时绘制路径 if run == 0: tsp.plot_tour(best_tour, f"{alg_name} 算法最优路径 (长度: {best_length:.2f})") # 计算统计数据 avg_length = sum(alg_results) / runs_per_algorithm min_length = min(alg_results) max_length = max(alg_results) std_dev = np.std(alg_results) avg_time = sum(alg_times) / runs_per_algorithm results[alg_name] = { 'avg_length': avg_length, 'min_length': min_length, 'max_length': max_length, 'std_dev': std_dev, 'avg_time': avg_time, 'histories': [history for _, _, history in [algorithm(tsp) for _ in range(3)]] # 保存几次运行的历史 } # 绘制性能比较图 plot_performance_comparison(results) # 输出统计结果 print("\n算法性能比较:") print("{:<20} {:<15} {:<15} {:<15} {:<15} {:<15}".format( "算法", "平均路径长度", "最小路径长度", "最大路径长度", "标准差", "平均运行时间(秒)")) print("-" * 90) for alg_name, stats in results.items(): print("{:<20} {:<15.2f} {:<15.2f} {:<15.2f} {:<15.2f} {:<15.2f}".format( alg_name, stats['avg_length'], stats['min_length'], stats['max_length'], stats['std_dev'], stats['avg_time'])) # 算法优缺点分析 analyze_algorithms(results) def plot_performance_comparison(results: Dict[str, Dict]) -> None: """绘制算法性能比较图""" plt.figure(figsize=(14, 10)) # 绘制平均路径长度比较 plt.subplot(2, 2, 1) alg_names = list(results.keys()) avg_lengths = [results[alg]['avg_length'] for alg in alg_names] plt.bar(alg_names, avg_lengths, color='skyblue') plt.title('平均路径长度比较') plt.xlabel('算法') plt.ylabel('路径长度') plt.xticks(rotation=45) plt.tight_layout() # 绘制收敛曲线比较 plt.subplot(2, 2, 2) for alg_name, stats in results.items(): # 取多次运行的平均收敛曲线 histories = stats['histories'] min_len = min(len(h) for h in histories) avg_history = np.mean([h[:min_len] for h in histories], axis=0) plt.plot(avg_history, label=alg_name) plt.title('收敛曲线比较') plt.xlabel('迭代次数') plt.ylabel('路径长度') plt.legend() plt.tight_layout() # 绘制运行时间比较 plt.subplot(2, 2, 3) avg_times = [results[alg]['avg_time'] for alg in alg_names] plt.bar(alg_names, avg_times, color='lightgreen') plt.title('平均运行时间比较') plt.xlabel('算法') plt.ylabel('时间(秒)') plt.xticks(rotation=45) plt.tight_layout() # 绘制标准差比较 plt.subplot(2, 2, 4) std_devs = [results[alg]['std_dev'] for alg in alg_names] plt.bar(alg_names, std_devs, color='salmon') plt.title('解的稳定性比较(标准差)') plt.xlabel('算法') plt.ylabel('标准差') plt.xticks(rotation=45) plt.tight_layout() plt.show() def analyze_algorithms(results: Dict[str, Dict]) -> None: """分析各算法的优缺点""" print("\n\n算法优缺点分析:") # 找出最优算法(基于平均路径长度) best_alg = min(results, key=lambda x: results[x]['avg_length']) for alg_name in results: print(f"\n{alg_name}:") # 优点 print(" 优点:") if alg_name == best_alg: print(" - 找到的解质量最高,平均路径长度最短") if alg_name == "模拟退火算法": print(" - 实现简单,易于理解和调整") print(" - 能够跳出局部最优,找到全局最优解的概率较高") print(" - 对问题的适应性强,不需要特殊的问题结构知识") elif alg_name == "粒子群算法": print(" - 收敛速度较快,尤其在早期迭代") print(" - 保留了群体搜索的特性,能在全局和局部搜索之间取得平衡") print(" - 参数较少,易于实现") elif alg_name == "遗传算法": print(" - 并行搜索能力强,能同时探索多个解空间区域") print(" - 鲁棒性好,对初始解的依赖性较低") print(" - 适合大规模问题,可扩展性强") elif alg_name == "蚁群算法": print(" - 天然具有并行性,适合分布式计算") print(" - 能够利用信息素轨迹自适应地发现高质量路径") print(" - 具有正反馈机制,有助于快速收敛到较好的解") # 缺点 print(" 缺点:") if alg_name == "模拟退火算法": print(" - 收敛速度较慢,尤其在后期迭代") print(" - 参数调整对性能影响较大,需要谨慎选择初始温度和降温速率") print(" - 对于大规模问题,计算时间可能过长") elif alg_name == "粒子群算法": print(" - 在处理离散优化问题(如TSP)时,需要特殊的编码和解码策略") print(" - 容易陷入局部最优,尤其是在后期迭代") print(" - 对参数设置敏感,如惯性权重和学习因子") elif alg_name == "遗传算法": print(" - 编码复杂,需要设计合适的交叉和变异操作") print(" - 收敛速度可能较慢,尤其是当种群规模较大时") print(" - 参数调整(如交叉率、变异率)需要经验") elif alg_name == "蚁群算法": print(" - 初始阶段收敛速度较慢,需要一定迭代次数积累信息素") print(" - 参数众多(如信息素重要性、启发式因子、挥发率),调整困难") print(" - 容易出现停滞现象,所有蚂蚁可能集中在同一条路径上") # 适用场景 print(" 适用场景:") if alg_name == "模拟退火算法": print(" - 问题规模较小,需要高质量解") print(" - 问题结构复杂,没有明显的启发式信息") print(" - 对算法实现的简易性有较高要求") elif alg_name == "粒子群算法": print(" - 问题具有一定的连续性或可微性") print(" - 需要快速找到一个较好的解,对最优解的要求不是极高") print(" - 可以容忍一定的局部最优解") elif alg_name == "遗传算法": print(" - 问题规模较大,解空间复杂") print(" - 需要并行搜索能力") print(" - 解的多样性很重要") elif alg_name == "蚁群算法": print(" - 问题具有图结构,如路径规划、网络优化") print(" - 需要利用历史信息指导搜索") print(" - 可以接受较长的计算时间以换取高质量解") if __name__ == "__main__": # 创建TSP问题实例 tsp = TSP(num_cities=30) # 绘制城市分布 tsp.plot_cities() # 定义要比较的算法及其参数 algorithms = { "模拟退火算法": lambda tsp: simulated_annealing( tsp, initial_temperature=1000, cooling_rate=0.995, stopping_temperature=1e-8, max_iterations=1000 ), "粒子群算法": lambda tsp: particle_swarm_optimization( tsp, num_particles=30, max_iterations=1000, w=0.7, c1=1.5, c2=1.5 ), "遗传算法": lambda tsp: genetic_algorithm( tsp, population_size=100, generations=1000, crossover_rate=0.8, mutation_rate=0.2 ), "蚁群算法": lambda tsp: ant_colony_optimization( tsp, num_ants=30, max_iterations=1000, alpha=1.0, beta=2.0, rho=0.5, q=100.0 ) } # 比较算法性能 compare_algorithms(tsp, algorithms, runs_per_algorithm=3)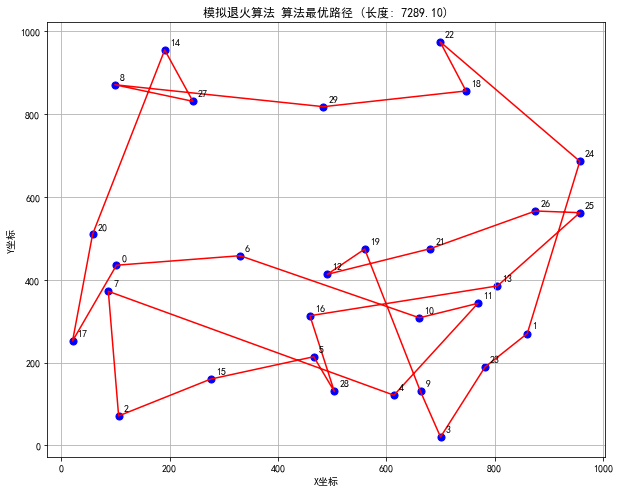
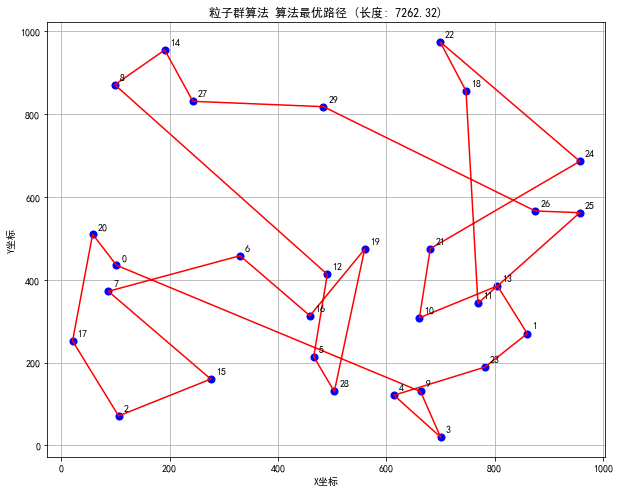
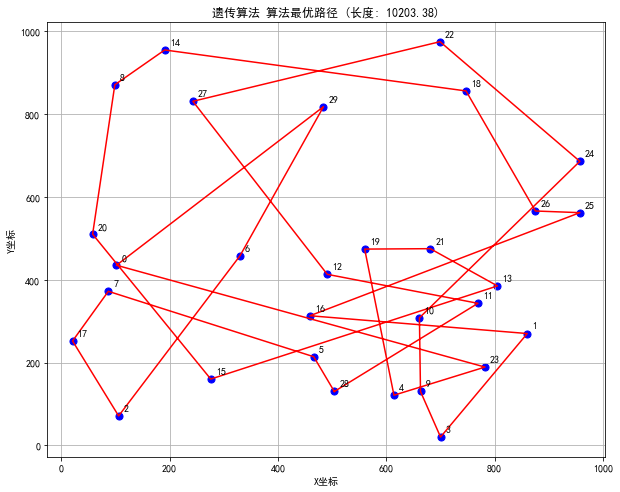
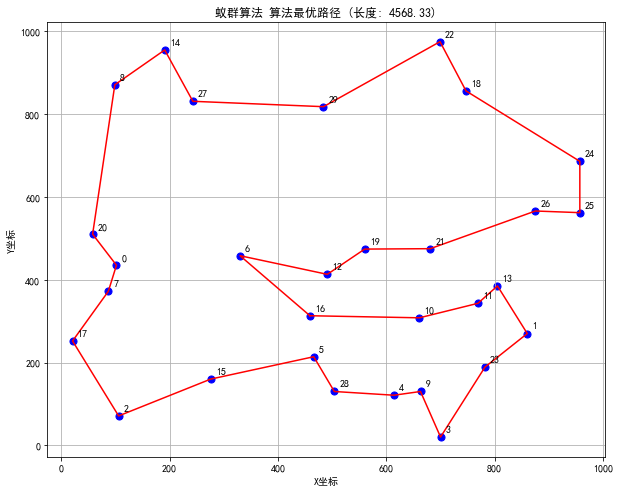
模拟退火算法、粒子群算法、遗传算法、蚁群算法TSP问题
于 2025-07-12 22:24:07 首次发布




















 269
269

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








