LearnOpenGL学习笔记1-Hello Triangle
原网站链接: https://learnopengl.com/Getting-started/Hello-Triangle
源码链接:https://github.com/JoeyDeVries/LearnOpenGL
这一节主要内容就是VBO、VAO、EBO三个对象的使用,跟平时编程习惯不太一样,OpenGL使用对象都是先绑定然后进行操作或者使用。这是OpenGL最基础的内容,一定要吃透。
VBO
VBO: vertex buffer object 顶点缓存对象,用来管理内存,可以在GPU中储存大量的顶点数据。优势是可以一次性发送大量数据给显卡,并在显卡中缓存。为了提升效率尽量把数据一次性发送给显卡。
unsigned int VBO;
glGenBuffers(1, &VBO); //生成数量为1的缓存对象
glBindBuffer(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, VBO); // 将VBO绑定到GL_ARRAY_BUFFER类型上,对于每种缓存类型,只能绑定一个缓存对象,绑定之后对于GL_ARRAY_BUFFER的所有操作都会修改VBO对象指向的缓存
glBufferData(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, sizeof(vertices), vertices, GL_STATIC_DRAW); // 使用这个命令将vertices中的数据拷贝到VBO中
// 完成这些操作之后我们已经将顶点数据储存到了显卡中,并用VBO进行管理
glBufferData的最后一个参数含义是指定显卡处理给定数据的方式,有三种方式
- GL_STREAM_DRAW:数据不变,GPU调用不频繁
- GL_STATIC_DRAW:数据不变,GPU调用频繁
- GL_DYNAMIC_DRAW:数据经常改变,并且调用频繁
VAO
VAO: vertex array object 顶点数组对象,用于解析顶点数据,创建方式与VBO类似,绑定后直到下一次绑定之前的顶点属性都会保存在VAO中。
unsigned int VAO;
glGenVertexArrays(1, &VAO); // 生成数量为1的数组对象
glBindVertexArrays(VAO); // 绑定数组对象,绑定之后,所有相关修改会作用于VAO
glVertexAttribPointer(0, 3, GL_FLOAT, GL_FALSE, 3 * sizeof(float), (void*)0); // 告诉OpenGL如何解析顶点数据,配置(location=0)的顶点属性
glEnableVertexAttribArray(0); // 顶点属性开启可用,默认是不可用的
[...]
glUseProgram(shaderProgram);
glBindVertexArray(VAO);
glDrawArrays(GL_TRIANGLES, 0, 3); // 使用VAO对象绘制三角形
glVertexAttribPointer函数原型:glVertexAttribPointer(GLuint index, GLint size, GLenum type, GLboolean normalized, GLsizei stride, const void *pointer);
- index:表示vertex属性的编号,在shader中对应的是location
- size:表示一组顶点属性的个数,注意不是总数,如果是vec3的属性那就填3
- type:数据类型比如GL_FLOAT
- normalized:是否要把数据正规化,不是归一化的意思,而是把整型数据统一转换为(1,0,-1)
- stride:跨距
- pointer:目标位置距离起始位置的偏移
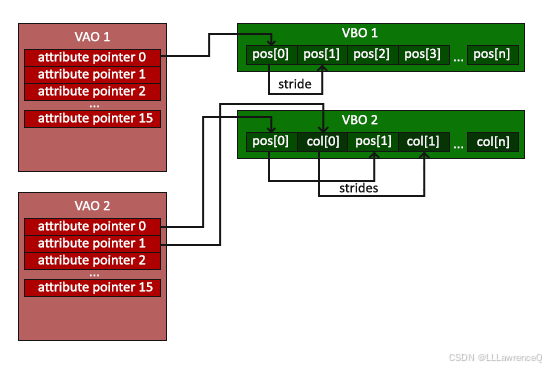
经过测试:一个VBO可以有多个VAO属性,一个VAO也可以绑定多个VBO,甚至可以用多个VAO同时绑定同一块VBO数据。
EBO
EBO:element buffer objects 元素缓存对象,用来指导OpenGL如何绘制面元。存储的是面片使用的顶点序号,使用时根据索引找到对应顶点进行渲染。
float vertices[] = {
0.5f, 0.5f, 0.0f, // top right
0.5f, -0.5f, 0.0f, // bottom right
-0.5f, -0.5f, 0.0f, // bottom left
-0.5f, 0.5f, 0.0f // top left
};
unsigned int indices[] = { // note that we start from 0!
0, 1, 3, // first triangle
1, 2, 3 // second triangle
};
unsigned int EBO;
glGenBuffers(1, &EBO);
glBindBuffer(GL_ELEMENT_ARRAY_BUFFER, EBO);
glBufferData(GL_ELEMENT_ARRAY_BUFFER, sizeof(indices), indices, GL_STATIC_DRAW); // EBO使用方法与VBO类似,区别在于EBO绑定的缓存类型是GL_ELEMENT_ARRAY_BUFFER
[...]
//绘制三角形
glUseProgram(shaderProgram);
glBindVertexArray(VAO);
glDrawElements(GL_TRIANGLES, 6, GL_UNSIGNED_INT, 0); // 改用glDrawElements绘制三角形
完整源码:
#include <glad/glad.h>
#include <GLFW/glfw3.h>
#include <iostream>
void framebuffer_size_callback(GLFWwindow* window, int width, int height);
void processInput(GLFWwindow *window);
// settings
const unsigned int SCR_WIDTH = 800;
const unsigned int SCR_HEIGHT = 600;
const char *vertexShaderSource = "#version 330 core\n"
"layout (location = 0) in vec3 aPos;\n"
"void main()\n"
"{\n"
" gl_Position = vec4(aPos.x, aPos.y, aPos.z, 1.0);\n"
"}\0";
const char *fragmentShaderSource = "#version 330 core\n"
"out vec4 FragColor;\n"
"void main()\n"
"{\n"
" FragColor = vec4(1.0f, 0.5f, 0.2f, 1.0f);\n"
"}\n\0";
int main()
{
// glfw: initialize and configure
// ------------------------------
glfwInit();
glfwWindowHint(GLFW_CONTEXT_VERSION_MAJOR, 3);
glfwWindowHint(GLFW_CONTEXT_VERSION_MINOR, 3);
glfwWindowHint(GLFW_OPENGL_PROFILE, GLFW_OPENGL_CORE_PROFILE);
#ifdef __APPLE__
glfwWindowHint(GLFW_OPENGL_FORWARD_COMPAT, GL_TRUE);
#endif
// glfw window creation
// --------------------
GLFWwindow* window = glfwCreateWindow(SCR_WIDTH, SCR_HEIGHT, "LearnOpenGL", NULL, NULL);
if (window == NULL)
{
std::cout << "Failed to create GLFW window" << std::endl;
glfwTerminate();
return -1;
}
glfwMakeContextCurrent(window);
glfwSetFramebufferSizeCallback(window, framebuffer_size_callback);
// glad: load all OpenGL function pointers
// ---------------------------------------
if (!gladLoadGLLoader((GLADloadproc)glfwGetProcAddress))
{
std::cout << "Failed to initialize GLAD" << std::endl;
return -1;
}
// build and compile our shader program
// ------------------------------------
// vertex shader
unsigned int vertexShader = glCreateShader(GL_VERTEX_SHADER);
glShaderSource(vertexShader, 1, &vertexShaderSource, NULL);
glCompileShader(vertexShader);
// check for shader compile errors
int success;
char infoLog[512];
glGetShaderiv(vertexShader, GL_COMPILE_STATUS, &success);
if (!success)
{
glGetShaderInfoLog(vertexShader, 512, NULL, infoLog);
std::cout << "ERROR::SHADER::VERTEX::COMPILATION_FAILED\n" << infoLog << std::endl;
}
// fragment shader
unsigned int fragmentShader = glCreateShader(GL_FRAGMENT_SHADER);
glShaderSource(fragmentShader, 1, &fragmentShaderSource, NULL);
glCompileShader(fragmentShader);
// check for shader compile errors
glGetShaderiv(fragmentShader, GL_COMPILE_STATUS, &success);
if (!success)
{
glGetShaderInfoLog(fragmentShader, 512, NULL, infoLog);
std::cout << "ERROR::SHADER::FRAGMENT::COMPILATION_FAILED\n" << infoLog << std::endl;
}
// link shaders
unsigned int shaderProgram = glCreateProgram();
glAttachShader(shaderProgram, vertexShader);
glAttachShader(shaderProgram, fragmentShader);
glLinkProgram(shaderProgram);
// check for linking errors
glGetProgramiv(shaderProgram, GL_LINK_STATUS, &success);
if (!success) {
glGetProgramInfoLog(shaderProgram, 512, NULL, infoLog);
std::cout << "ERROR::SHADER::PROGRAM::LINKING_FAILED\n" << infoLog << std::endl;
}
glDeleteShader(vertexShader);
glDeleteShader(fragmentShader);
// set up vertex data (and buffer(s)) and configure vertex attributes
// ------------------------------------------------------------------
float vertices[] = {
0.5f, 0.5f, 0.0f, // top right
0.5f, -0.5f, 0.0f, // bottom right
-0.5f, -0.5f, 0.0f, // bottom left
-0.5f, 0.5f, 0.0f // top left
};
unsigned int indices[] = { // note that we start from 0!
0, 1, 3, // first Triangle
1, 2, 3 // second Triangle
};
unsigned int VBO, VAO, EBO;
glGenVertexArrays(1, &VAO);
glGenBuffers(1, &VBO);
glGenBuffers(1, &EBO);
// bind the Vertex Array Object first, then bind and set vertex buffer(s), and then configure vertex attributes(s).
glBindVertexArray(VAO);
glBindBuffer(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, VBO);
glBufferData(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, sizeof(vertices), vertices, GL_STATIC_DRAW);
glBindBuffer(GL_ELEMENT_ARRAY_BUFFER, EBO);
glBufferData(GL_ELEMENT_ARRAY_BUFFER, sizeof(indices), indices, GL_STATIC_DRAW);
glVertexAttribPointer(0, 3, GL_FLOAT, GL_FALSE, 3 * sizeof(float), (void*)0);
glEnableVertexAttribArray(0);
// note that this is allowed, the call to glVertexAttribPointer registered VBO as the vertex attribute's bound vertex buffer object so afterwards we can safely unbind
glBindBuffer(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, 0);
// remember: do NOT unbind the EBO while a VAO is active as the bound element buffer object IS stored in the VAO; keep the EBO bound.
//glBindBuffer(GL_ELEMENT_ARRAY_BUFFER, 0);
// You can unbind the VAO afterwards so other VAO calls won't accidentally modify this VAO, but this rarely happens. Modifying other
// VAOs requires a call to glBindVertexArray anyways so we generally don't unbind VAOs (nor VBOs) when it's not directly necessary.
glBindVertexArray(0);
// uncomment this call to draw in wireframe polygons.
glPolygonMode(GL_FRONT_AND_BACK, GL_LINE);
// render loop
// -----------
while (!glfwWindowShouldClose(window))
{
// input
// -----
processInput(window);
// render
// ------
glClearColor(0.2f, 0.3f, 0.3f, 1.0f);
glClear(GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT);
// draw our first triangle
glUseProgram(shaderProgram);
glBindVertexArray(VAO); // seeing as we only have a single VAO there's no need to bind it every time, but we'll do so to keep things a bit more organized
//glDrawArrays(GL_TRIANGLES, 0, 6);
glDrawElements(GL_TRIANGLES, 6, GL_UNSIGNED_INT, 0);
// glBindVertexArray(0); // no need to unbind it every time
// glfw: swap buffers and poll IO events (keys pressed/released, mouse moved etc.)
// -------------------------------------------------------------------------------
glfwSwapBuffers(window);
glfwPollEvents();
}
// optional: de-allocate all resources once they've outlived their purpose:
// ------------------------------------------------------------------------
glDeleteVertexArrays(1, &VAO);
glDeleteBuffers(1, &VBO);
glDeleteBuffers(1, &EBO);
glDeleteProgram(shaderProgram);
// glfw: terminate, clearing all previously allocated GLFW resources.
// ------------------------------------------------------------------
glfwTerminate();
return 0;
}
// process all input: query GLFW whether relevant keys are pressed/released this frame and react accordingly
// ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
void processInput(GLFWwindow *window)
{
if (glfwGetKey(window, GLFW_KEY_ESCAPE) == GLFW_PRESS)
glfwSetWindowShouldClose(window, true);
}
// glfw: whenever the window size changed (by OS or user resize) this callback function executes
// ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
void framebuffer_size_callback(GLFWwindow* window, int width, int height)
{
// make sure the viewport matches the new window dimensions; note that width and
// height will be significantly larger than specified on retina displays.
glViewport(0, 0, width, height);
}























 111
111

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








