完美解决X-Anylabeling3.2.2的可视化训练的‘0x80'问题的两种思路
X-Anylabeling 3.2.2刚发布不久,咱可是按照教程一步一步操作的,无奈仍然踩坑。
暮然回首,刚抓到了一个bug,趁着记忆还没远去,先记录一下,官方若看到,记得打钱~
链接在这 :https://github.com/CVHub520/X-AnyLabeling/releases
1.环境配置过程
1.1 anaconda和CUDA
这俩毋庸置疑了,不再赘述
cuda 我配的12.1.0 cudnn配套8.9.7
大家根据自己显卡来配
我是4060 Laptop显卡,如果不用gpu训练可以略过
1.2 参照readme.md
咱可是按教程操作的乖娃子嘿
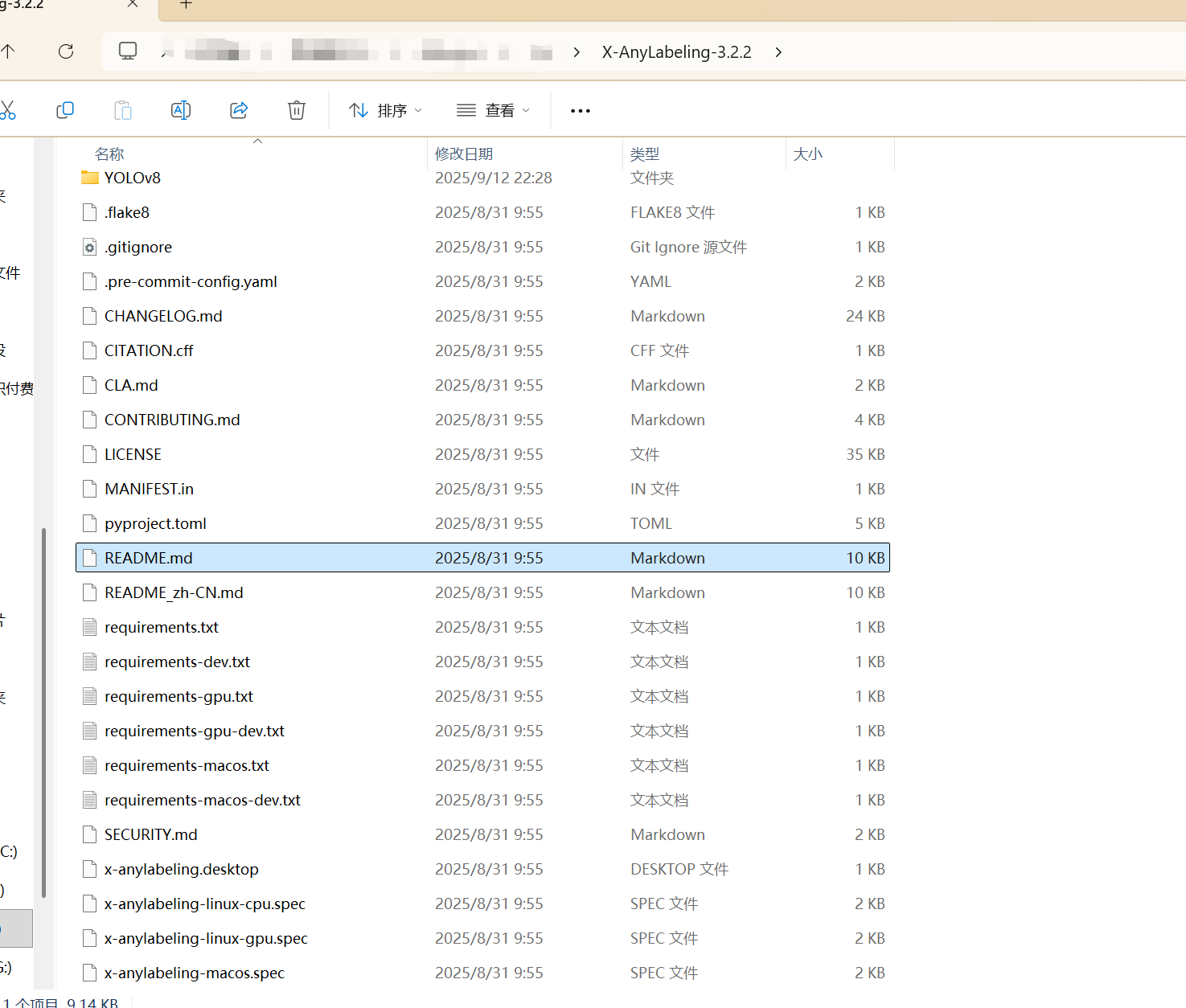
但是注意,他的文件结构比较隐蔽,真实的指令配置在下面的路径
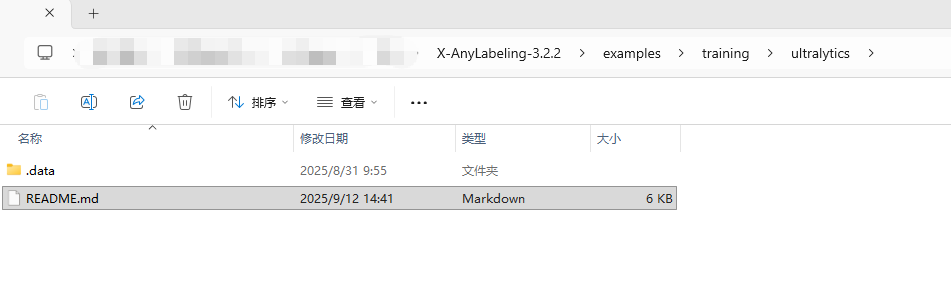
这个才是真的安装指令文件。
下面展示我的安装过程,上指令~
打开anaconda prompt,我的虚拟环境是python 3.11
conda create -n x-anylabeling-yolo python=3.11 -y
conda activate x-anylabeling-yolo
pip install --upgrade uv
#下面的cu121大家换成自己的cuda版本即可,或者只用cpu版本最后的指令可以去掉
uv pip install ultralytics --torch-backend=cu121
#开发版最全,就搞gpu开发版
pip install -r requirements-gpu-dev.txt
保障网速的情况下,三下五除二,如果你下完了,恭喜你,离大坑又近一步。
2.踩到的坑
我用的yolov8n-seg去测试训练的
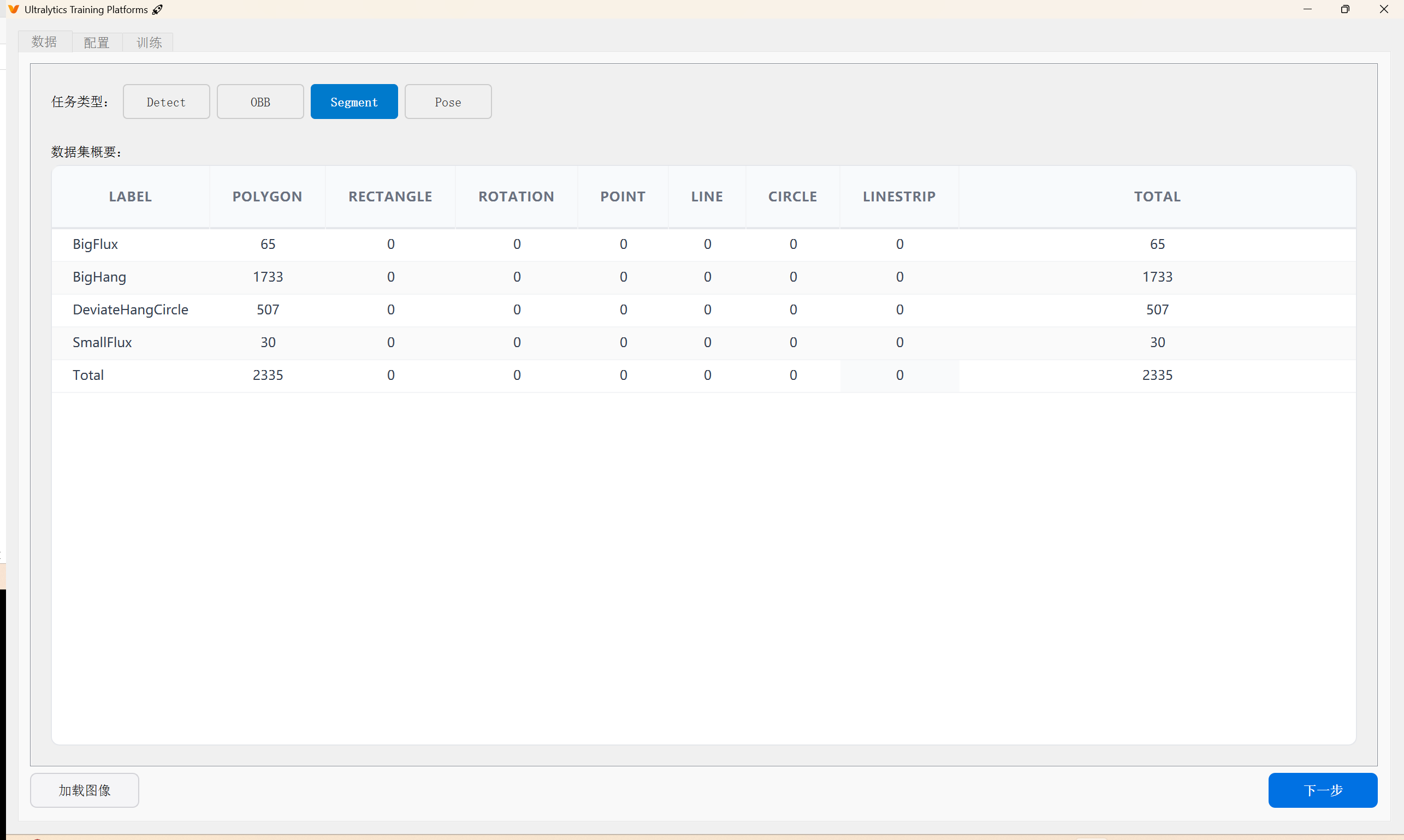
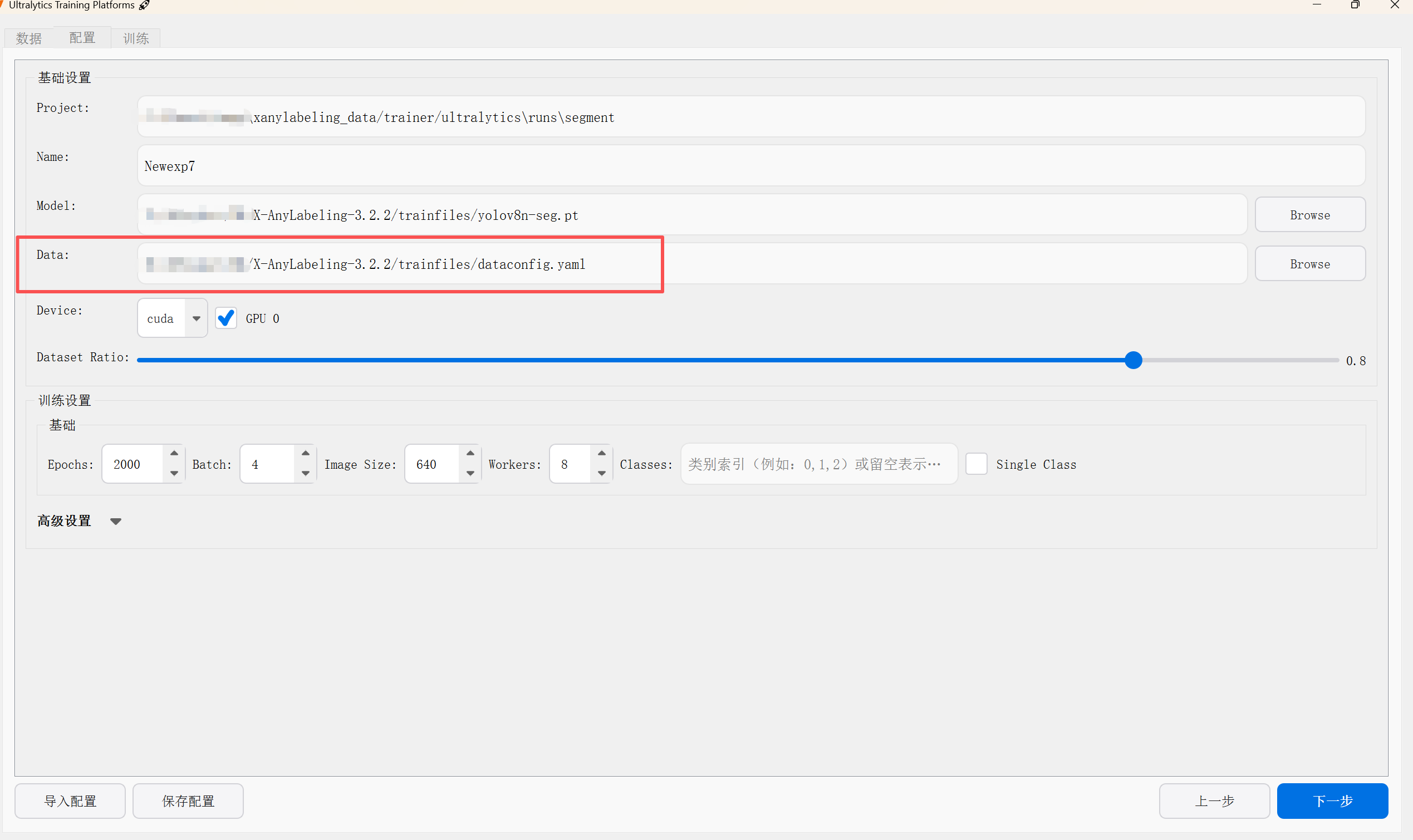
2.1 yaml问题
遇到的第一个问题是yaml,这里要注意:只要在已有的类如coco8.yaml coco128.yaml这类的配置文件,改一下模型种类和标签种类就好了,参考我的格式
# config.yaml
model:
backbone: yolov8n-seg
num_classes: 4
data:
train: images/train
val: images/val
names:
0: "BigHang"
1: "DeviateHangCircle"
2: "BigFlux"
3: "SmallFlux"
还需要一个类别的txt,训练后自动标注用
# classes.txt
BigHang
DeviateHangCircle
BigFlux
SmallFlux
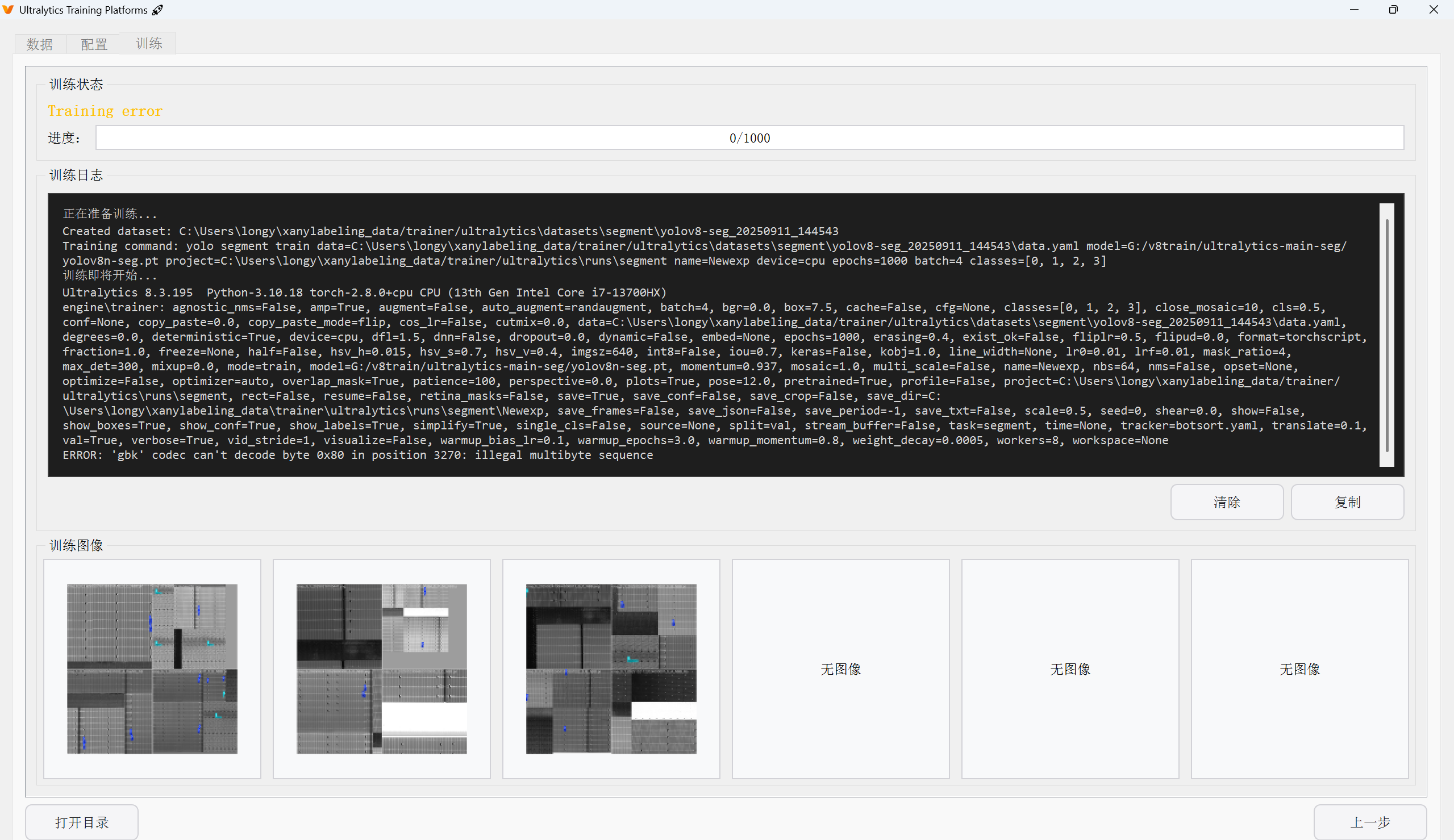
2.2 codec can’t decode byte 0x80: illegal multibyte sequence
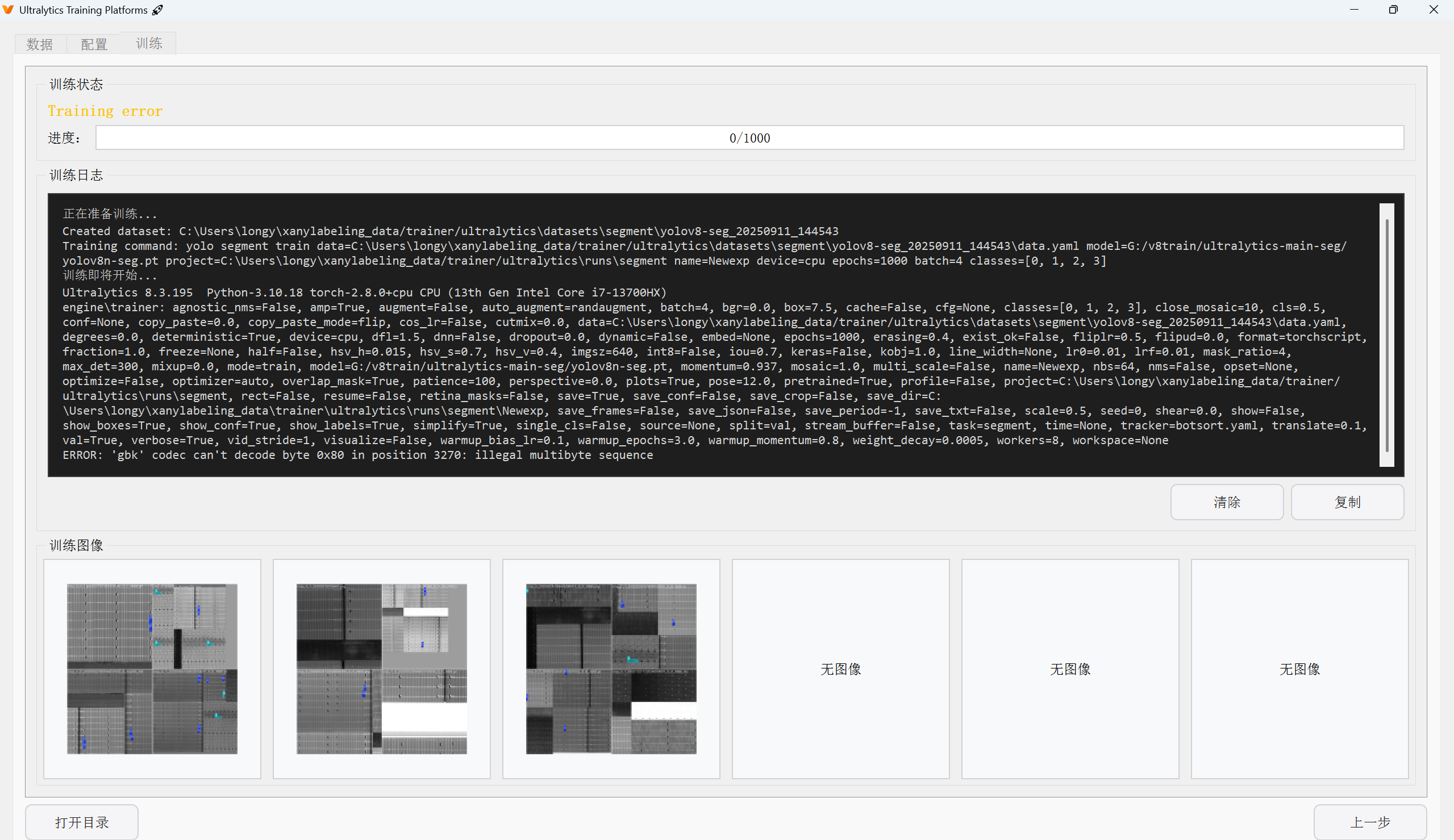
这就是文章开头的报错,这个看起来是编码问题,不难,但是这个要缩小区间简直太费劲了
因为他没直接提示这是在哪个文件里的报错,所以只能打断点缩小范围,最后到了这里
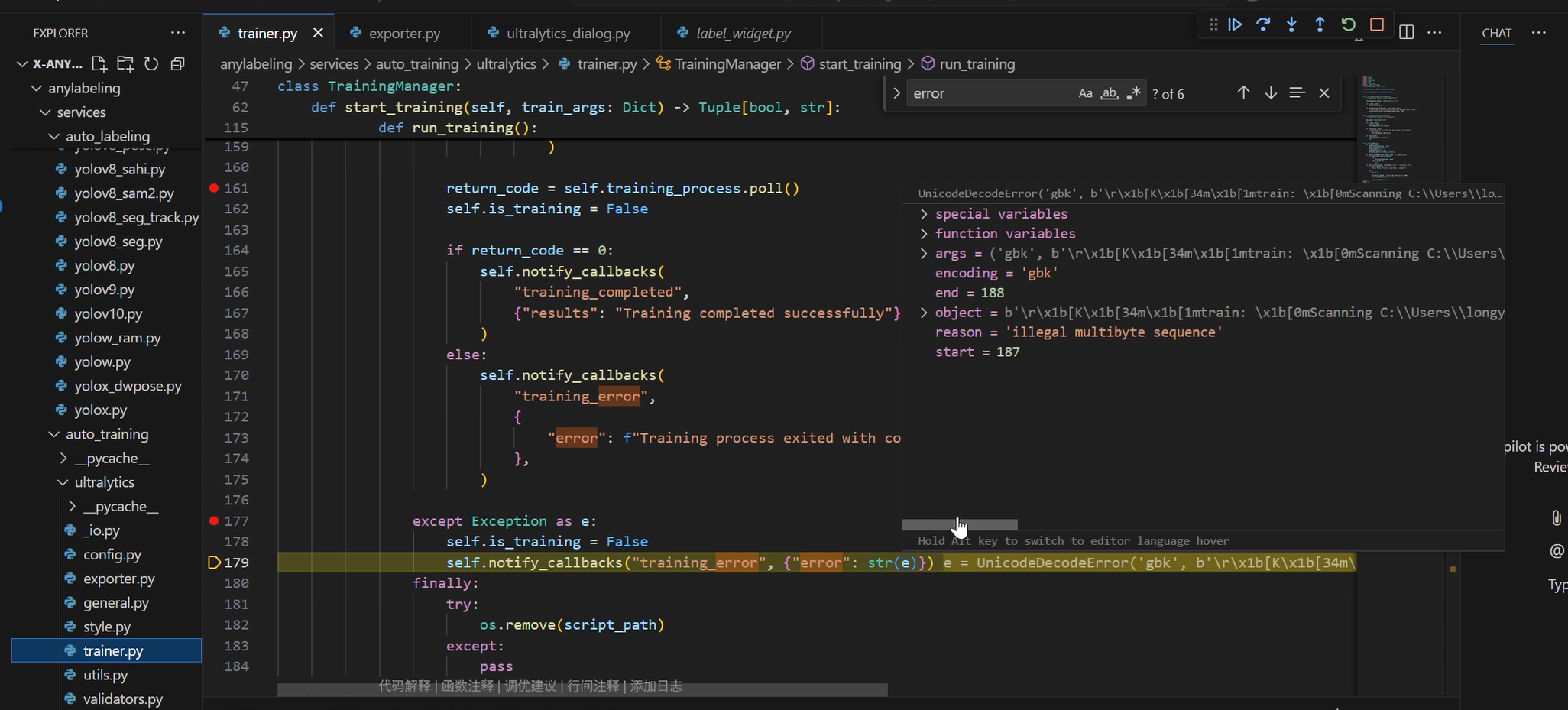
注意这个目录层级,既然找到他了,发现生成的训练指令编码错乱,那么就聚焦在这里,按下述方式来进行修改。
3.解决思路
修改run_training() 函数,这个改动可以和原函数自行比对
思路1:找到合适的编码,推测编码并自适应
这种方法需要先行安装chardet包
pip install chardet
def run_training():
try:
self.is_training = True
self.notify_callbacks(
"training_started", {"total_epochs": self.total_epochs}
)
self.training_process = subprocess.Popen(
[sys.executable, script_path],
stdout=subprocess.PIPE,
stderr=subprocess.STDOUT,
bufsize=1,
preexec_fn=os.setsid if os.name != "nt" else None
)
# 使用chardet检测实时编码
detector = chardet.UniversalDetector()
detected_encoding = None # 最终确定的编码
using_detected_encoding = False # 是否开始使用检测到的编码
while True:
if self.stop_event.is_set():
self.training_process.terminate()
try:
self.training_process.wait(timeout=5)
except subprocess.TimeoutExpired:
if os.name == "nt":
self.training_process.kill()
else:
os.killpg(
os.getpgid(self.training_process.pid),
signal.SIGKILL,
)
self.is_training = False
self.notify_callbacks("training_stopped", {})
return
# 读取原始字节输出
output = self.training_process.stdout.readline()
if output == b'' and self.training_process.poll() is not None:
break
if output:
# 如果尚未确定编码,则继续喂数据给检测器
if not using_detected_encoding:
detector.feed(output)
if detector.done:
detected_encoding = detector.result['encoding']
confidence = detector.result['confidence']
# 置信度较高或常见编码则开始使用
if detected_encoding and (confidence > 0.6 or detected_encoding.lower() in ['utf-8', 'ascii', 'iso-8859-1', 'gb2312', 'gbk']):
using_detected_encoding = True
else:
# 置信度低时尝试常用编码或默认值
detected_encoding = 'utf-8'
using_detected_encoding = True
detector.close()
# 解码行
try:
if using_detected_encoding:
cleaned_output = output.decode(detected_encoding, errors='replace').strip()
else:
# 在检测过程中,尝试使用UTF-8解码,但允许替换错误
cleaned_output = output.decode('utf-8', errors='replace').strip()
except UnicodeDecodeError:
# 如果解码失败,使用错误替换策略
cleaned_output = output.decode('utf-8', errors='replace').strip()
if cleaned_output:
self.notify_callbacks(
"training_log", {"message": cleaned_output}
)
return_code = self.training_process.poll()
self.is_training = False
if return_code == 0:
self.notify_callbacks(
"training_completed",
{"results": "Training completed successfully"},
)
else:
self.notify_callbacks(
"training_error",
{
"error": f"Training process exited with code {return_code}"
},
)
except Exception as e:
self.is_training = False
self.notify_callbacks("training_error", {"error": str(e)})
finally:
try:
os.remove(script_path)
except:
pass
思路2:直接对应编码型号改逻辑
def run_training():
try:
self.is_training = True
self.notify_callbacks(
"training_started", {"total_epochs": self.total_epochs}
)
self.training_process = subprocess.Popen(
[sys.executable, script_path],
stdout=subprocess.PIPE,
stderr=subprocess.STDOUT,
bufsize=1,
preexec_fn=os.setsid if os.name != "nt" else None,
)
# 使用本地编码猜测(例如Unix系常用UTF-8,Windows常用GBK)
# 这里根据系统默认提供一个初始编码猜测
assumed_encoding = 'utf-8' if os.name != 'nt' else 'gbk'
while True:
if self.stop_event.is_set():
self.training_process.terminate()
try:
self.training_process.wait(timeout=5)
except subprocess.TimeoutExpired:
if os.name == "nt":
self.training_process.kill()
else:
os.killpg(
os.getpgid(self.training_process.pid),
signal.SIGKILL,
)
self.is_training = False
self.notify_callbacks("training_stopped", {})
return
# 读取字节流输出
output = self.training_process.stdout.readline()
if output == b'' and self.training_process.poll() is not None:
break
if output:
try:
# 尝试使用假设的编码解码
cleaned_output = output.decode(assumed_encoding).strip()
except UnicodeDecodeError:
try:
# 如果失败,尝试UTF-8(常见的跨平台编码)
cleaned_output = output.decode('utf-8').strip()
assumed_encoding = 'utf-8' # 更新假设编码
except UnicodeDecodeError:
try:
# 如果再失败,尝试GBK(常见于Windows中文环境)
cleaned_output = output.decode('gbk').strip()
assumed_encoding = 'gbk' # 更新假设编码
except UnicodeDecodeError:
# 如果依然无法解码,使用错误忽略策略确保程序继续运行
cleaned_output = output.decode(assumed_encoding, errors='ignore').strip()
if cleaned_output:
self.notify_callbacks(
"training_log", {"message": cleaned_output}
)
return_code = self.training_process.poll()
self.is_training = False
if return_code == 0:
self.notify_callbacks(
"training_completed",
{"results": "Training completed successfully"},
)
else:
self.notify_callbacks(
"training_error",
{
"error": f"Training process exited with code {return_code}"
},
)
except Exception as e:
self.is_training = False
self.notify_callbacks("training_error", {"error": str(e)})
finally:
try:
os.remove(script_path)
except:
pass
只替换trainer.py中的run_training()函数即可。
4.附赠:打包程序为exe
软件很贴心,官方给了个打包的spec文件 我们只需几行代码打包他。
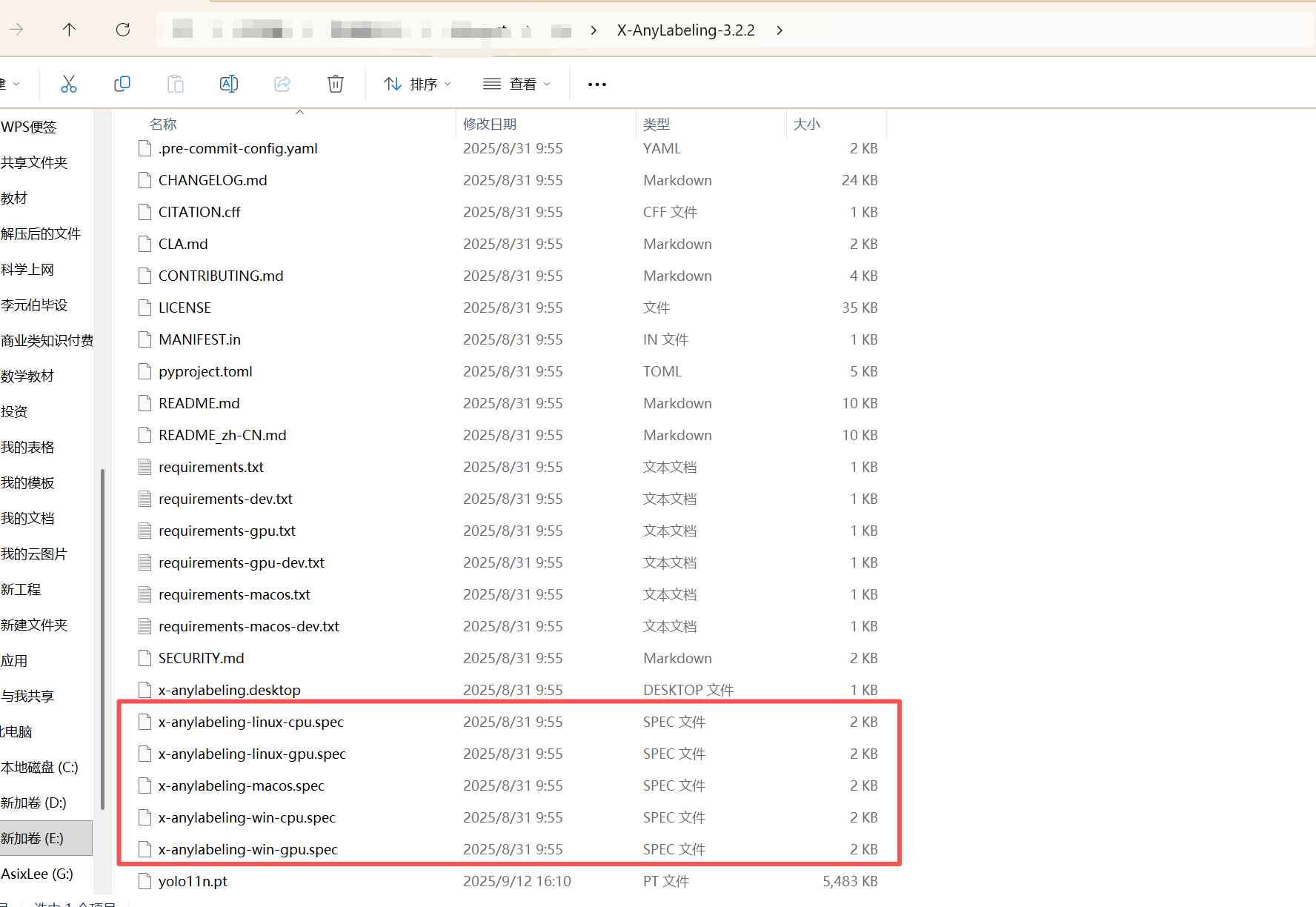
想包谁包谁,放开操作!
把大象放冰箱只需三步
spec文件中的dll路径要改成自己的
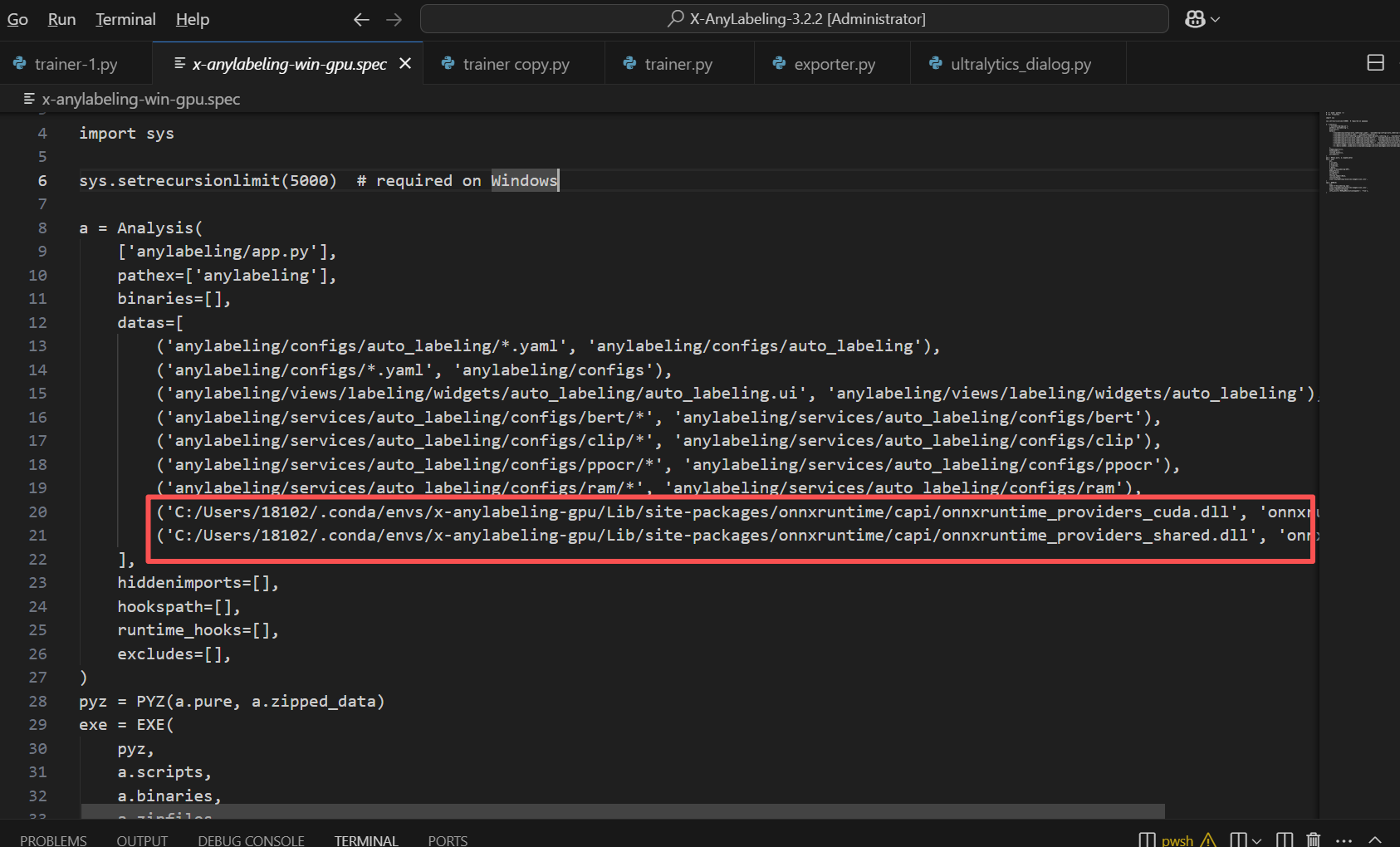
cd ../X-AnyLabeling-3.2.2 #换成自己的代码路径
pyinstaller x-anylabeling-win-gpu.spec
一顿hook,等他操作完
最后在dist目录下找到exe文件,点开验证即可
9.18更新:
今天发现,3.2.3版本已经改善了这个bug 可以直接下载新版本
https://github.com/CVHub520/X-AnyLabeling/releases
























 5万+
5万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








