目录
堆的概念
堆是一个完全二叉树,示意图如下:
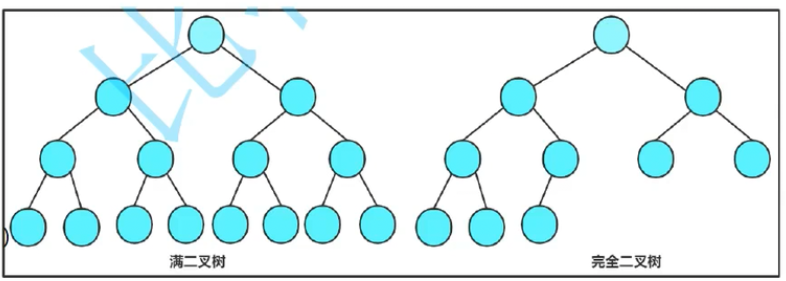
堆的表现形式有两种:
1、也是所有树通用的,如图:
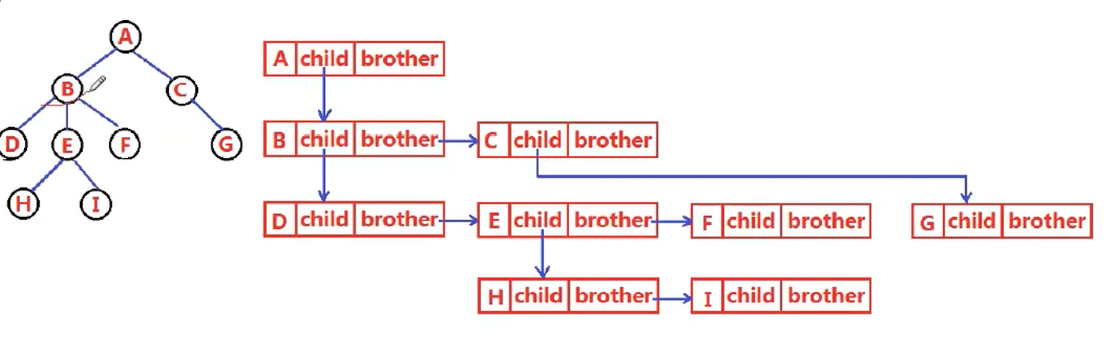
这种方法被称为leftchild,rightbrother,即存储两个指针,一个指向它的儿子,一个指向它的兄弟,(整体遵循从左到右的顺序)这是一种非常高明的方式,但是我们今天不使用它。
2、使用数组来进行储存
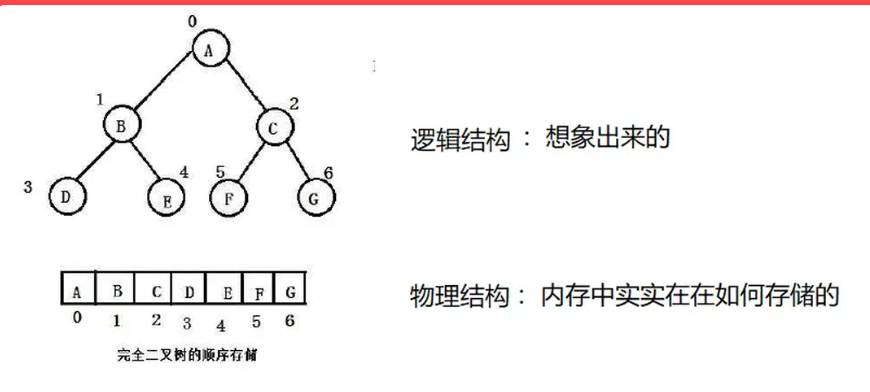
因为堆中的数据是高度有序的,所以我们可以采用数组存储的方法
在数组中,child和parent有下述关系:
1、leftchild=parent*2+1
2、rightchild=parent*2+2;
功能介绍
#pragma once
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<stdbool.h>
#include<time.h>
typedef int HpDataType;
typedef struct HP
{
HpDataType* arr;
int size;
int capacity;
}HP;
HP* HPIint();//初始化堆
void DestoryHP(HP* hp);//销毁堆
void HPPush(HP* hp,int val);//向堆中插入数据
void AdjustUp_s(HpDataType* arr, int size);//向上调整
void AdjustDown_s(HpDataType* arr, int size, int parent);//向下调整-小堆
void AdjustDown_b(HpDataType* arr, int size, int parent);//向下调整-大堆
void AdjustUp_b(HpDataType* arr, int size);//向上调整-大堆
void Swap(HpDataType* p1, HpDataType* p2);//交换两个数
HpDataType HPPop(HP* hp);//返回最顶端的数
bool HPIsEmpty(HP* hp);//判断堆是否是空的
向上&&向下调整算法
向上调整算法
向上调整算法是从下往上,从儿子到父亲
parent = (child - 1) / 2;这一步是通过child找到parent,因为child和parent都是int类型的,leftchild自不必说,rightchild减一除二也可以实现找到parent的效果。
这里的逻辑实际上是在堆里面一层一层往上推,沿途检验数据是否符合标准,不符合就交换。
void AdjustUp_s(HpDataType* arr, int size)//向上调整-小堆
{
int child = size - 1;
int parent = 0;
while (child > 0)
{
parent = (child - 1) / 2;
if (arr[parent] > arr[child])
{
Swap(&arr[parent], &arr[child]);
}
child = parent;
}
}向下调整算法
我们这里以小堆的算法做例子
向下调整算法是从上往下,从父亲到儿子
向下调整算法就比较难了
向下调整算法实际上是从堆的顶端开始,然后找到parent的child在两个child中(如果有的话)选出一个最小的
int small = child;//假设法,避免了if else 的使用
if (child + 1 < size && arr[child] > arr[child + 1])
{
small = child + 1;
}在使用这个最小的child和这个parent对比,如果parent小于最小的,那么意味着parent是符合小堆的规则的,这时就可以break了
如果small大于parent,就代表我们的paent是不符合小堆的规则,的我们就得接着遍历,接着交换
void AdjustDown_s(HpDataType* arr, int size,int parent)//向下调整-小堆
{
//这里多设置了一个接口,是为了方便以后数组建堆算法调用
int child = 0;
while (parent * 2 + 1 < size)
{
child = parent * 2 + 1;
int small = child;//假设法,避免了if else 的使用
if (child + 1 < size && arr[child] > arr[child + 1])
{
small = child + 1;
}
if (arr[small] < arr[parent])
{
Swap(&arr[small], &arr[parent]);
parent = small;//参数错了,原来是child,这里要注意
}
else//因为之前的数据都是有序地,只要在某一次验证中通过了,就不用进行接下来的验证了
{
break;
}
}
}我们在pop中使用向下调整算法时,只需要将0作为形参parent传进去(即从0开始)
堆的创建和销毁
声明
typedef struct HP
{
HpDataType* arr;
int size;
int capacity;
}HP;堆的初始化
HP* HPIint()
{
HP* hp = (HP*)malloc(sizeof(HP));
if (NULL == hp)
{
perror("malloc");
return NULL;
}
hp->capacity = 4;
hp->arr = (HpDataType*)malloc(sizeof(HpDataType) * hp->capacity);
hp->size = 0;
return hp;
}
此处的arr就是用来储存数据的数组,size是此时堆中元素的个数,同时指向下一个数据填充的位置
capacity储存了数组的大小,后面扩容时会用于判断
堆的销毁
void DestoryHP(HP* hp)
{
free(hp->arr);
free(hp);
}这没啥好说的,arr和hp的空间都是使用malloc动态开辟的,存放在堆区,是不会自动释放的,我们需要手动释放
pop函数和push函数
push函数
在push之前,我们应该先检验一下数组是不是满的,如果不满就要将数组扩容,再进行push的操作
push就是在堆的最后插入一个新的数据,并执行向上调整算法,使堆的结构不被打乱
void HPPush(HP* hp, int val)
{
if (hp->size == hp->capacity)
{
hp->capacity += 4;
HP* ret = realloc(hp->arr, hp->capacity*sizeof(HpDataType));
if (NULL != ret)
{
hp->arr = ret;
}
}
hp->arr[hp->size] = val;
hp->size++;
AdjustUp_s(hp->arr,hp->size);
}pop函数
在pop之前,我们肯定要检查一下数组是不是空的
pop时,我们pop的数据肯定是根位置的数据(其他的数据pop了是没有意义的),然后我们将pop的数据和最后一个数据交换,再执行向下调整算法。
这一步的交换是为什么呢?
如果我们直接将第一个数据踢出去的话,不仅要将剩下的数据挪动位置,还要面临剩下的数据原来的顺序被全部打乱的问题,这时再进行调整就和重新建了一个堆差不多了
所以我们这里将最后一个数据和根节点的数据交换,再将我们的hp中的size--(代表最后一个数据已经废置不用了),此时我们的堆的结构还是完好的,执行一次向下调整算法就可以将顺序重新调整好
HpDataType HPPop(HP* hp)
{
if (HPIsEmpty(hp))
{
printf("\n警告,堆现在是空的\n");
return -1;
}
else
{
HpDataType ret = hp->arr[0];
Swap(&hp->arr[0], &hp->arr[hp->size - 1]);
hp->size--;//代表被换下的数据已经是失效的了
AdjustDown_s(hp->arr, hp->size , 0);
return ret;
}
}功能实现
#include"hp.h"
HP* HPIint()
{
HP* hp = (HP*)malloc(sizeof(HP));
if (NULL == hp)
{
perror("malloc");
return NULL;
}
hp->capacity = 4;
hp->arr = (HpDataType*)malloc(sizeof(HpDataType) * hp->capacity);
hp->size = 0;
return hp;
}
void Swap(HpDataType* p1, HpDataType* p2)
{
HpDataType* temp = 0;
temp = *p1;
*p1 = *p2;
*p2 = temp;
}
void AdjustUp_s(HpDataType* arr, int size)//向上调整-小堆
{
int child = size - 1;
int parent = 0;
while (child > 0)
{
parent = (child - 1) / 2;
if (arr[parent] > arr[child])
{
Swap(&arr[parent], &arr[child]);
}
child = parent;
}
}
void AdjustDown_s(HpDataType* arr, int size,int parent)//向下调整-小堆
{
int child = 0;
while (parent * 2 + 1 < size)
{
child = parent * 2 + 1;
int small = child;
if (child + 1 < size && arr[child] > arr[child + 1])
{
small = child + 1;
}
if (arr[small] < arr[parent])
{
Swap(&arr[small], &arr[parent]);
parent = small;//参数错了,原来是child
}
else
{
break;
}
}
}
void AdjustUp_b(HpDataType* arr, int size)//向上调整-大堆
{
//这个可以改为
int child = size - 1;
int parent = 0;
while (child > 0)
{
parent = (child - 1) / 2;
if (arr[parent] < arr[child])
{
Swap(&arr[parent], &arr[child]);
}
child = parent;
}
}
void AdjustDown_b(HpDataType* arr, int size,int parent)//向下调整-大堆
{
int child = 0;
while (parent * 2 + 1 < size)
{
child = parent * 2 + 1;
int big = child;
if (child + 1 < size && arr[child] < arr[child + 1])
{
big = child + 1;
}
if (arr[big] > arr[parent])
{
Swap(&arr[big], &arr[parent]);
parent = big;
}
else
{
break;
}
}
}
void HPPush(HP* hp, int val)
{
if (hp->size == hp->capacity)
{
hp->capacity += 4;
HP* ret = realloc(hp->arr, hp->capacity*sizeof(HpDataType));
if (NULL != ret)
{
hp->arr = ret;
}
}
hp->arr[hp->size] = val;
hp->size++;
AdjustUp_s(hp->arr,hp->size);
}
HpDataType HPPop(HP* hp)
{
if (HPIsEmpty(hp))
{
printf("\n警告,堆现在是空的\n");
return -1;
}
else
{
HpDataType ret = hp->arr[0];
Swap(&hp->arr[0], &hp->arr[hp->size - 1]);
hp->size--;//代表被换下的数据已经是失效的了
AdjustDown_s(hp->arr, hp->size , 0);
return ret;
}
}
void DestoryHP(HP* hp)
{
free(hp->arr);
free(hp);
}
bool HPIsEmpty(HP* hp)
{
if (hp->size == 0)
{
return true;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}





















 6万+
6万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








